Accident Response: Stretched Cluster vs. DR Site

We have two approaches to Disaster Recovery: a “stretched” cluster (active-active installation) and a platform with virtual machines turned off (replicas). They have several snapshot save points.
There is a request for disaster recovery, and many of our clients really need it. Therefore, we began to work out both schemes in the framework of our production.
')
The methods have pros and cons, now I'll tell you about them.
"Stretched" cluster
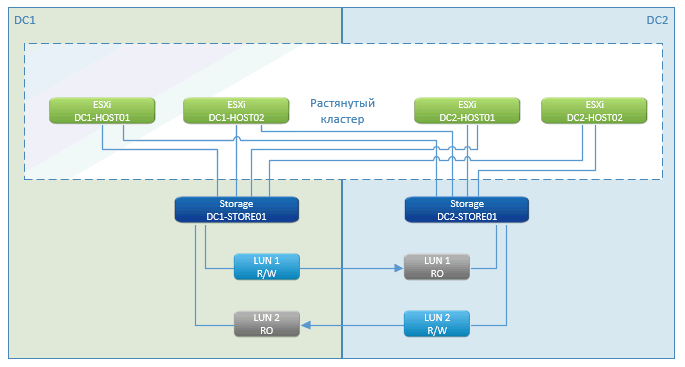
As you can see, this is the standard history of the metrocluster. In the pros - almost zero idle, a pause only for the time of launching virtual machines. Handles this feature - VMware High Availability (HA). She sees that the hosts are lost, and immediately restarts the VM on the remote site.
The launch is done immediately with the storage system that is in the cluster.
A geo-distributed cluster storage system is a marketing feature of NetApp. Other manufacturers have something with a similar name. In fact, this is a well-thought-out asynchronous replication from one side to the other. We write to one node in the local network and synchronize it through specialized communication channels with another.
In the event of a failure of one of the storage systems, the remaining (on the other site) presents the paths to the disks to the remaining hosts. VMs that have died are restarted on them. Everything happens automatically - the data center crashed, everything rebooted, the storage system worked, VMware worked. The client saw that everything blinked and restarted.
The only cache from the VM's RAM may be lost. But if the database dropped it, then the loss is zero in time.
If we lose the connection between the sites, then everything continues to work in its place and, as soon as the connection is restored, it begins to synchronize.
Minus - high price. Because what is actually needed is a double storage system (moreover, it is similar in type, speed and volume of disks of the first storage system on the main site), which cannot be used except as a reserve. Plus strapping to the storage for the metrocluster, it is FC-bridges, FC-network and so on.
We have two data centers, between them FC-bundle on two rays (four lines of dark optics and DWDM). These are two pieces of iron, each provides 200 Gbps of bandwidth for FC and Ethernet.
Alternative with DR

There is software with an intuitively memorable name - VMware vCloud Availability for Cloud-to-Cloud DR.
This is a system for creating an identical VM on a remote site once, relatively speaking, in 15 minutes. To her, on an insulating tape, the presentation system of all of this is correctly attached to the mechanisms for managing the cloud.
That is, VMware Replication technology is in the backend. In case of a failure, we manually launch the DR plan on the second site, it automatically stops attempts to replicate, then registers the VM with vCloud Director, customizes the IP addresses (so that they do not have to be changed on the VM) and starts the VM in the right order. In our decision to change the addressing is not necessary, we stretch the network to both data centers.
Machines are replicated constantly, but not the entire data center, but only the selected ones - critical processes. It is replicated once in a while, the minimum interval is 15 minutes (this is an ideal case when everything flies and there is a dedicated replication server and a minimum of changes on the VM). In practice, you have a copy for half an hour or an hour ago. If something went wrong, then the data that fell into the interval are lost. 15 minutes is a question for the agent who is collecting the new replication. Veeam say it can take less than 15 minutes, but in fact it is also longer in practice if you do not use the DSS features. I have not seen on the industrial machine (not on the test), so it was different.
For a long time, NetApp, like many other storage vendors, has SnapMirror technology, which allows you to shift replication work from hypervisors to storage systems, and VMware Replication is able to use it.
While the replication service runs, the train goes far. But it is cheap.
Why else is cheap - because you can use any storage system from any side (from different manufacturers, different classes), you do not need to allocate in advance a large amount of disks.
It is not necessary to allocate a large disk group, within which the moons are cut. It just takes a place on the local storage system and is applied upon the fact of recording from the virtual machine. Due to this, the storage space is optimally managed if it is used for other tasks. And it is used, since we do not provide this service to all customers.
Minus - you need to configure replication at the VM level, that is, to control that everything is correctly configured, that this is the machine, to ensure that the replication passes, that there are no errors. Create DR-plans for each client, conduct their tests.
In the first case, the storage system is taken, conditionally, infrastructurally, almost by sector (more precisely, by facilities). And here one machine may fall off due to the task falling off due to some software reasons related to the bug at high levels or due to accessibility problems. This happens a little more often than if you take low levels.
In the black - DR stores several points. You can roll back a few snapshots.
Outside of the guest OS you need additional software.
In order to prokinit all the necessary networks before Vcloud Director, we need the work of our administrator. In general, all network connectivity in this variant remains on our administrator. For a cloud client, this means an application that also takes time.
Replication is also configured through the application. Added VM - you need to send a request that you need to replicate it. Automatically, it will not get into replication tasks. Need to pay attention to the admin.
Difference
As a result, the price may differ by more than twice. Replication will multiply the cost of disk space by two or more (two full copies + change history), plus something for the service and reservation of computing resources. In the case of a metrocluster, the cost of space will be multiplied by two, but the space itself will cost significantly more, plus you need to strictly reserve nodes at a remote site. That is, computing resources should be multiplied by two, we can not dispose of them for something else.
In the case of a metro cluster, we can use only the same types of disks, so that there is a complete mirror. If part of the disks on the main data center are fast, some are slow at 10 thousand revolutions per minute, then an identical configuration is needed. In the case of replicas, slower disks are possible on the backup site, and this is cheaper due to storage. But when switching to a reserve, it will be lower in performance. That is, if it stores something on the SSD in the main cluster and replicates to regular disks, then storage will be much cheaper at the cost of slowing the infrastructure of the reserve.
Right now we are choosing what will be included in an earlier release, so we want to consult: can you briefly tell how you organize your DR platforms and what would you like from them in general as a whole?
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/420971/
All Articles