Interface List Guide in MikroTik
Interface lists have appeared in MikroTik RouterOS for quite some time, but by observation, not everyone knows about them and therefore does not use them.
What is this is clear from the name - Interfaces List, the same as address lists (address list), only with interfaces. Not to be confused with bridges (bridge) and bounding interfaces, these are three different technologies for different tasks. This functionality appeared about a year ago and is present in all current (current and bugfix) releases of RouterOS 6.
The main thing that is worth remembering: The interfaces in the lists continue to be independent, traffic will not start to go through between them (as in the case of the bridge) and will not be parallelized (as in the case of bounding), that's funny to you, and there are clever people.
[Interfaces] -> [Interfaces List] -> [Lists]
By default, there are three lists: all, none, dynamic. With the first two everything is clear, dynamic is currently filled in from certain ppp connections and Detect Internet.
')
Console option:
Create your list
[Interfaces] -> [Interfaces List] -> [Lists] -> [+]
name - name
include - include interfaces from the specified list to the new list
exclude - exclude interfaces from the specified list from the new list
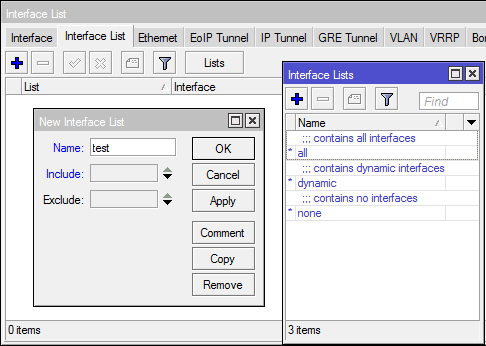
Console option:
You can add any interfaces: ethernet, wlan, bridge, vlan, vpn, vif, ... Everything is done from the main menu [Interface Lists].

Console option:
The main application is to simplify the firewall rules, let's say you have a vpn hub and you need to tweak the rules for passing traffic cleverly, but do it as clearly as possible.

Earlier:
Check in-interface, send to chain-1.
In the chain-1, check out-interface, send to the chain-2.
In the chain-2 we set up rules.

And so for each interface. 4 connections - 8 rules, 8 connections - 16 rules. Are the connections dynamic? You can get out and use all ppp, throw in the chain-1, and then from the chain-1 return extra interface.
Now:
We add all interfaces to one list and create one rule with the same in-interface-list and out-interface-list, which transfers them to chains with filtering rules. It has become noticeably shorter.
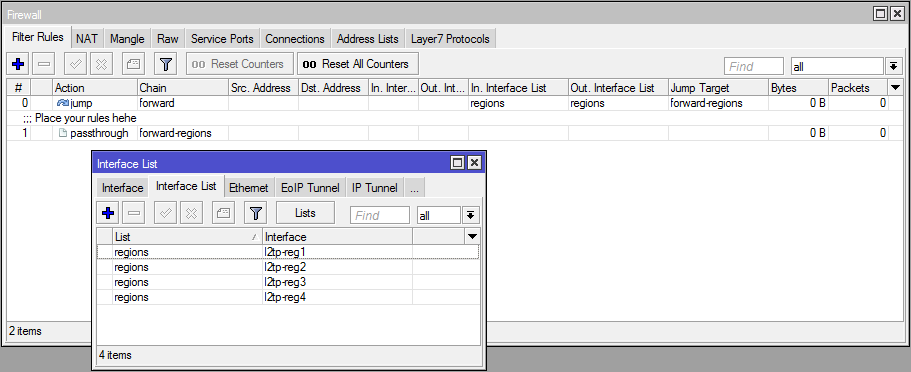
In this scheme there is also a minus, if you look at “earlier”, then for each interface the address subnets that are expected on the interface are specified, you can drive all the interfaces into the address list, but the subnet addresses will no longer be clearly tied to the interfaces.
Another example is that you have several providers and laziness for each duplicate rules:

When the interface lists just appeared, on the mikrotik forum they complained about the work of the interface lists in nat, now they seem to fix it. I decided to search
Test bench:

The diagram does not have enough addresses for the same
Results:
Chain src-nat:
* masquerade - works. Depending on the output interface, substitutes the corresponding ip.
* src-nat - works. Substitutes the specified ip only for the interface on which this ip is present.
* same - works. Similarly with src-nat.
Chain dst-nat:
* redirect - works.
* dst-nat - works. Including in combination with masquerade.
* netmap - works. If you use it instead of dst-nat. When used as intended, it also works.
Works. For example, if you need to tag all incoming traffic from interfaces for queue tree.
We recall the example of regional vpn. A fifth region has been added and you add it with your hands to the interface list, or you can do it easier and in the vpn profile specify which list the interface will be placed on when you connect, regardless of whether there is a binding for it or it is created automatically when the client disconnects the interface from the list deleted. For outgoing vpn this also works.
[PPP] -> [Profiles]

Everything is good, but there is a bug (at the time of publication, version RoS 6.42.6). If you created a binding and statically added it to the list specified in profiles, the connection will not be established. In the logs (server) will be about the following:

You can specify a list of interfaces as a bridge member, but only interfaces capable of working on Layer 2 (ethernet, wlan, bounding, eoip, ovpn-ethernet, ...) will be added, except for the other bridge.

The functionality appeared in the current firmware version and is not yet ready for use.
[Interfaces] -> [Detect Intrnet]
* Detect Interface List - a list with interfaces on which checks will be made.
* LAN Interface List - a list to which all active layer2 interfaces are added. Get the status of lan.
* WAN Interface List - a list to which all lte and vpn interfaces are added. Also, interfaces with the status of lan which do not have dhcp server and with which the address 8.8.8.8 is available. In addition to everything, mikrotik will add to the dhcp client interface in attempts to get settings automatically.
* Internet Interface List - the list of interfaces with the status of wan if cloud.mikrotik.com…0000 is accessible from them. Rechecking every minute, after 3 unsuccessful attempts, the interface returns to wan status. Change the address of the check, or intervals can not be.
[Interface Statuses] - check results.
So it should work, but in practice requests are not sent to cloud.mikrotik.com. We are waiting and we hope that: they will fix it; remove restrictions; will add the ability to run scripts when the interface state changes.
In the current MikroTik branch, it was decided that the Interface List should be used more actively and the following options are now configured via interface lists, instead of specific interfaces:
* [IP] -> [Neighbors] -> [Discovery Settings]

* [Tools] -> [MAC-Server] -> [Mac-Telnet Server] & [Mac-Winbox Server]

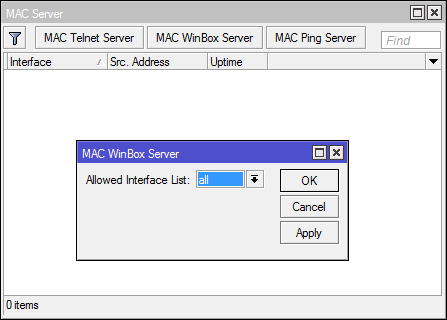
After the upgrade, do not forget to reconfigure.
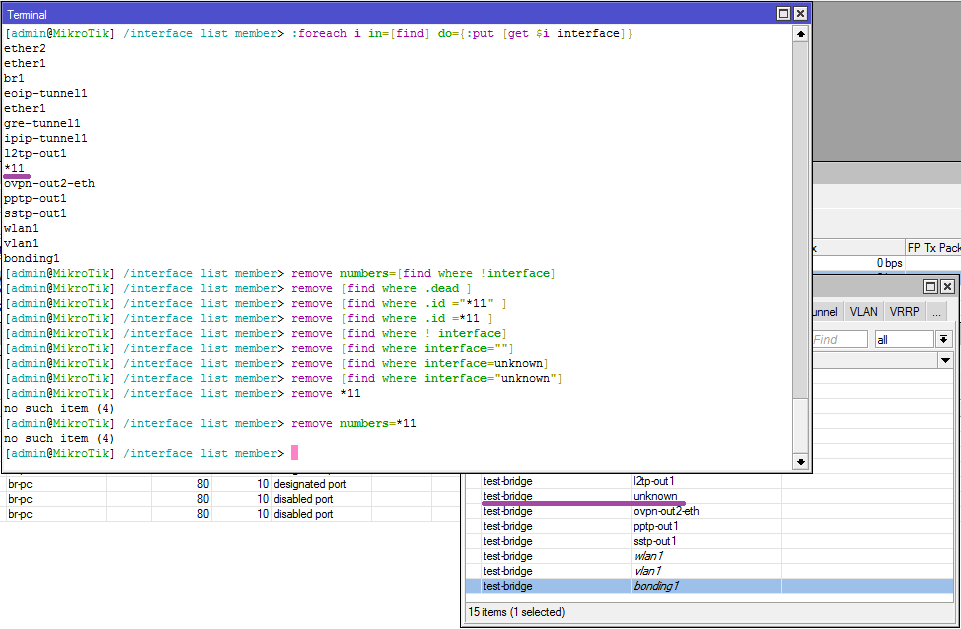
You may encounter a situation where one of the interfaces in the list becomes unknown (if you remove the interface before deleting from the list) and personally I haven’t managed to find a simple way (without clearing the entire list and refilling) deleting such an interface using cli and scripts. If anyone knows - write in the comments.
That's all. I hope the world will become less configurations with the union of interfaces in the bridge for the sake of reducing the rules in the firewall.
Description
What is this is clear from the name - Interfaces List, the same as address lists (address list), only with interfaces. Not to be confused with bridges (bridge) and bounding interfaces, these are three different technologies for different tasks. This functionality appeared about a year ago and is present in all current (current and bugfix) releases of RouterOS 6.
The main thing that is worth remembering: The interfaces in the lists continue to be independent, traffic will not start to go through between them (as in the case of the bridge) and will not be parallelized (as in the case of bounding), that's funny to you, and there are clever people.
Standard listings
[Interfaces] -> [Interfaces List] -> [Lists]
By default, there are three lists: all, none, dynamic. With the first two everything is clear, dynamic is currently filled in from certain ppp connections and Detect Internet.
')
Console option:
/interface list print Create your list
[Interfaces] -> [Interfaces List] -> [Lists] -> [+]
name - name
include - include interfaces from the specified list to the new list
exclude - exclude interfaces from the specified list from the new list

Console option:
/interface list add name=test Use example include
There are the following interfaces for Internet access:
ether1-wan (real ip)
ether2-wan (real ip)
l2tp-vpn1 (gray ip)
l2tp-vpn2 (gray ip)
From the first two, we expect incoming connections from the outside, from the second if they are, then we are not interested.
The ether1-wan and ether2-wan interfaces are combined into a wan list. Green lines.
The l2tp-vpn1 and l2tp-vpn2 interfaces are combined into a vpn list. Red lines.
The inet list contains (in) wan and vpn. Black lines.

Now, in the firewall, you can split incoming (and passing from wan / vpn) traffic from wan and vpn and write separate rules, and send outgoing (and passing to wan / vpn) together (there most likely will be a common established, new) through inet .
The example is clumsy, but I have no other.
ether1-wan (real ip)
ether2-wan (real ip)
l2tp-vpn1 (gray ip)
l2tp-vpn2 (gray ip)
From the first two, we expect incoming connections from the outside, from the second if they are, then we are not interested.
The ether1-wan and ether2-wan interfaces are combined into a wan list. Green lines.
The l2tp-vpn1 and l2tp-vpn2 interfaces are combined into a vpn list. Red lines.
The inet list contains (in) wan and vpn. Black lines.

Now, in the firewall, you can split incoming (and passing from wan / vpn) traffic from wan and vpn and write separate rules, and send outgoing (and passing to wan / vpn) together (there most likely will be a common established, new) through inet .
The example is clumsy, but I have no other.
Adding Interfaces
You can add any interfaces: ethernet, wlan, bridge, vlan, vpn, vif, ... Everything is done from the main menu [Interface Lists].

Console option:
/interface list member add interface=ether1 list=test Use in firewall filter
The main application is to simplify the firewall rules, let's say you have a vpn hub and you need to tweak the rules for passing traffic cleverly, but do it as clearly as possible.

Earlier:
Check in-interface, send to chain-1.
In the chain-1, check out-interface, send to the chain-2.
In the chain-2 we set up rules.

And so for each interface. 4 connections - 8 rules, 8 connections - 16 rules. Are the connections dynamic? You can get out and use all ppp, throw in the chain-1, and then from the chain-1 return extra interface.
Now:
We add all interfaces to one list and create one rule with the same in-interface-list and out-interface-list, which transfers them to chains with filtering rules. It has become noticeably shorter.

In this scheme there is also a minus, if you look at “earlier”, then for each interface the address subnets that are expected on the interface are specified, you can drive all the interfaces into the address list, but the subnet addresses will no longer be clearly tied to the interfaces.
Another example is that you have several providers and laziness for each duplicate rules:

Use in firewall nat
When the interface lists just appeared, on the mikrotik forum they complained about the work of the interface lists in nat, now they seem to fix it. I decided to search
Test bench:

The diagram does not have enough addresses for the same
Results:
Chain src-nat:
* masquerade - works. Depending on the output interface, substitutes the corresponding ip.
* src-nat - works. Substitutes the specified ip only for the interface on which this ip is present.
* same - works. Similarly with src-nat.
Chain dst-nat:
* redirect - works.
* dst-nat - works. Including in combination with masquerade.
* netmap - works. If you use it instead of dst-nat. When used as intended, it also works.
Use in firewall mangle
Works. For example, if you need to tag all incoming traffic from interfaces for queue tree.
Use in vpn profiles
We recall the example of regional vpn. A fifth region has been added and you add it with your hands to the interface list, or you can do it easier and in the vpn profile specify which list the interface will be placed on when you connect, regardless of whether there is a binding for it or it is created automatically when the client disconnects the interface from the list deleted. For outgoing vpn this also works.
[PPP] -> [Profiles]

Everything is good, but there is a bug (at the time of publication, version RoS 6.42.6). If you created a binding and statically added it to the list specified in profiles, the connection will not be established. In the logs (server) will be about the following:

Use in bridge
You can specify a list of interfaces as a bridge member, but only interfaces capable of working on Layer 2 (ethernet, wlan, bounding, eoip, ovpn-ethernet, ...) will be added, except for the other bridge.

Detect internet
The functionality appeared in the current firmware version and is not yet ready for use.
[Interfaces] -> [Detect Intrnet]
* Detect Interface List - a list with interfaces on which checks will be made.
* LAN Interface List - a list to which all active layer2 interfaces are added. Get the status of lan.
* WAN Interface List - a list to which all lte and vpn interfaces are added. Also, interfaces with the status of lan which do not have dhcp server and with which the address 8.8.8.8 is available. In addition to everything, mikrotik will add to the dhcp client interface in attempts to get settings automatically.
* Internet Interface List - the list of interfaces with the status of wan if cloud.mikrotik.com…0000 is accessible from them. Rechecking every minute, after 3 unsuccessful attempts, the interface returns to wan status. Change the address of the check, or intervals can not be.
[Interface Statuses] - check results.
So it should work, but in practice requests are not sent to cloud.mikrotik.com. We are waiting and we hope that: they will fix it; remove restrictions; will add the ability to run scripts when the interface state changes.
Spoiler header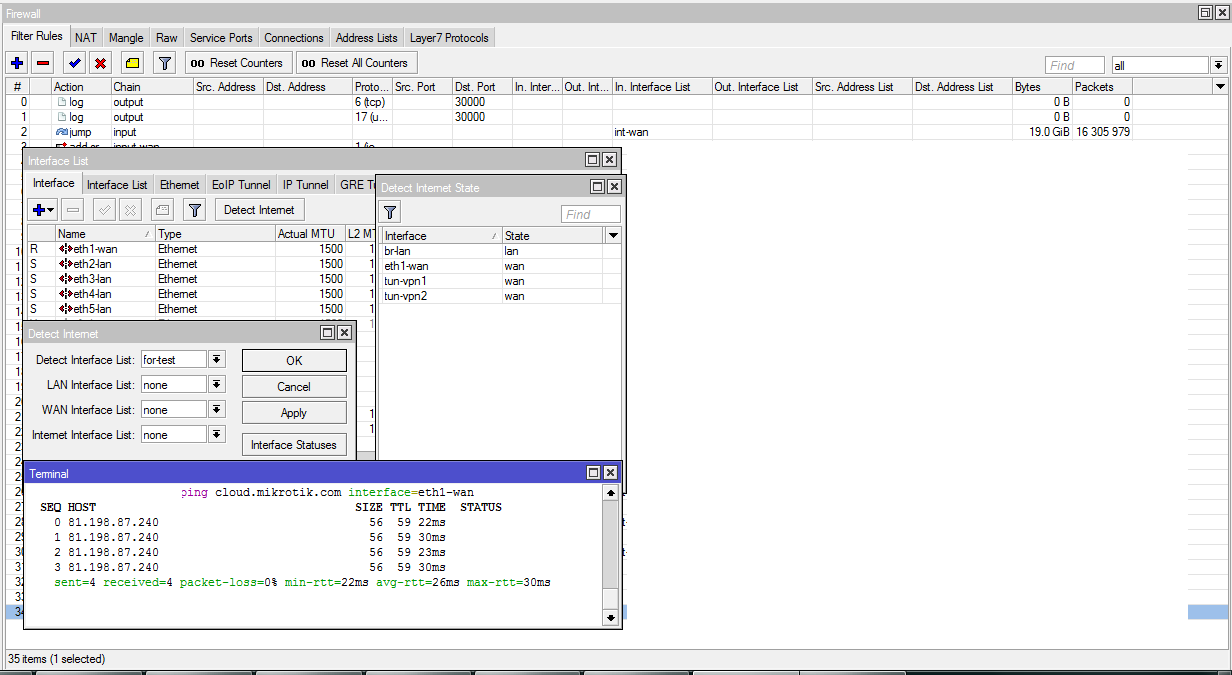

Other
In the current MikroTik branch, it was decided that the Interface List should be used more actively and the following options are now configured via interface lists, instead of specific interfaces:
* [IP] -> [Neighbors] -> [Discovery Settings]

* [Tools] -> [MAC-Server] -> [Mac-Telnet Server] & [Mac-Winbox Server]


After the upgrade, do not forget to reconfigure.
Scripts and cli
You may encounter a situation where one of the interfaces in the list becomes unknown (if you remove the interface before deleting from the list) and personally I haven’t managed to find a simple way (without clearing the entire list and refilling) deleting such an interface using cli and scripts. If anyone knows - write in the comments.

That's all. I hope the world will become less configurations with the union of interfaces in the bridge for the sake of reducing the rules in the firewall.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/419327/
All Articles