Laser ablation, tellurite glass and Er2O3 dopant

In any system, no matter how complex it may be, from how many working elements would not consist, it is almost always possible to single out one fundamentally important detail. Similarly, in modern communication systems, the basis of the foundations is often optical fibers, which allow data to be transmitted over long distances and at high speeds. And all would be nothing if it were not for the slogan of some scientists - "the world in a thimble." There is nothing wrong with the desire to minimize the size of a device, but the mini version should not be inferior to the original in performance, and may even exceed it.
In order to transmit signals inside the device, the maximum amount of fiber is required. You can't just trim it and everything will work just as well. It is for this reason that scientists began to study alternative methods and materials for signal transmission, which would reduce the various devices in size. Flat waveguide amplifiers based on unusual glass became one of the discoveries in such studies. However, any technology must go through a long stage of improvement. Today we will get acquainted with studies of ablation of a tellurite glass surface with an admixture of Er 2 O 3 by a femtosecond laser. What features have "participants" of experiments and what results have scientists achieved? We will look for answers in the research report. Go.
')
The essence of the study
Researchers from the University of Leeds (UK) conducted a laser study of an unusual type of glass, which can be an excellent material for broadband flat waveguide amplifiers. The material was obtained by doping * erbium * substances from zinc, sodium and tellurium.
Doping * - adding a small amount of impurities (in this case, erbium) to change the chemical and / or physical properties of the material. Adding impurities to a semiconductor helps change its electrical properties.
Erbium * is a rare-earth element, in network technologies it is used as an impurity when creating optical fibers to achieve signal regeneration during its transmission over long distances, when the use of transforming stations is impossible (for example, when laying the route under water).
Dopant * - an impurity that increases the electrical or optical conductivity of the material. In this case, it is erbium.Erbium-doped waveguide amplifiers are not new to the last couple of years. Already in the 90s, the development and research of this technology was carried out around the world. According to the researchers, they used this type of amplifiers, since the electronic transition * for erbium occurs at the same wavelength (1.5 μm) as in modern network technologies.
Electronic transition * - transition of an electron inside a molecule from one energy level to a higher one.Among other things, the researchers used ultra-fast laser plasma ablation: a high-intensity laser is directed to the surface of glass doped with erbium; The laser beam pierces small funnels (hollows) on the glass surface, which leads to the formation of a thin film of the material produced during the formation of the funnels. A primitive, but still an example: after a projectile hits the ground, a funnel forms, and the earth falls asleep all around the point of impact.
At the time of the formation of the craters, the researchers focused their attention on the ablation threshold * of glass. Links between the ablation threshold and the diameter of the laser beam, the number of pulses, and erbium concentration in the laser “impact” region were also detected.
Ablation * is a method of removing a substance from the surface by a laser pulse.Educated funnels were also studied in detail, since their morphology can tell researchers how best to control the porosity of a material and its ability to absorb and diffuse light.
Visualization of the process of laser ablation. We also see funnel formation
Preparation of the prototype
Glass prototypes consist of (80-x) TeO 2 –10ZnO – 10Na 2 O – xEr 2 O 3 , where:
- x is equal in different samples 0.00, 0.25, 0.50 0.75, 1.00, 1.25, 1.50 mole-percent * ;
- TeO 2 - tellurium dioxide;
- ZnO - zinc oxide;
- Na 2 O is sodium oxide;
- Er 2 O 3 - erbium oxide.
The mole percent * is equal to the mole fraction multiplied by 100, thus showing how many mole of the substance is contained in 100 mole of the solution.These chemical reagents are analytical reagents and have a purity of more than 99.99%. Glass was synthesized by standard melting and tempering. In other words, the basis of this substance is tellurite glass (hereinafter simply TZN ), which must contain tellurium dioxide in its composition, which we see from the formula above.
After determining the molar mass of each of the involved chemical compounds, the substances were ground into a fine powder using a marble mortar and pestle.
Then a gold crucible * with a prototype glass was placed in an oven at a temperature of 875 ° for 3 hours.
A crucible * is a container for firing, melting, drying or heating various materials. In making the crucible, refractoriness and resistance to various kinds of effects are important. In this case, a gold crucible is used, since it is excellent for particularly precise chemical work.At the same time, the oxygen supply was reduced to 1-2 l / min in order to remove steam from the furnace chamber and to keep the OH level low.
Then the melt was poured into a pre-heated form of brass and transferred to a kiln, where it was kept for 4 hours at a temperature of 295 ° C. This stage was necessary to remove thermal and mechanical deformations. The finished sample was cooled to room temperature at a rate of 0.5 ° C / min.
The final stage of production: the samples were cut into pieces of size 30x30x3 nm 3 and polished to achieve optical quality.
The whole process of making the tested glass, as you can see, was very laborious and was associated with very accurate measurements of both the molar mass of the composite substances and the temperatures at which the operations were performed. We now turn to the search for an answer to the question: is the game worth the candle? In other words - what results shows the substance so difficult to manufacture.
Optical properties of samples
Radiographs showed that the samples were amorphous. The introduction of 1.5 mole percent Er 2 O 3 into the sample composition increased its density from 5.18 to 5.27 g / cm 3 . This increase is justified by replacing TeO 2 with Er 2 O 3 , which has a higher molecular weight. The refractive index of tellurite glass is 2.048. And the increase in the number of Er 3+ ions led to the fact that the sample became dark pink in color (it was transparent before), which is associated with the transition of electrons to the excited state.

Schedule number 1
The graph above shows the indicators of the absorption spectrum of the samples, calculated by the formula:
α (ν) = A / L , where
L is the sample thickness;
And - the absorbing ability measured by a spectrometer.
TZN exhibits a striking absorption of about 0.11 cm -1 after the absorption band edge * of the UV light at 387 nm.
The edge of the absorption band * is a measure of the energy of radiation, exceeding which dramatically increases the absorption of this radiation by matter.If we add a dopant in the form of Er 3+ ions, then there are 11 noticeable transitions from the ground state ( 4 I 15/2 ) to various excited states:
4 I 13/2 , 4 I 11/2 , 4 I 9/2 , 4 F 9/2 , 4 S 3/2 , 2 H 11/2 , 4 F 7/2 , 4 F 5/2 , 4 F 3/2 , 2 H 9/2 , 4 G 11/2
each of which corresponded to the wavelength:
1531 (with a small jump of 1497), 976, 800, 653, 545, 522, 489, 452, 444, 407 and 380 nm.
The energy levels of the Er 3+ ion inside the sample are separated due to the Stark effect * .
The Stark effect * is the displacement and splitting of the state of the electronic subsystem of the ion, which determines the energy level, in an external electric field.At another dopant concentration, the samples showed similar results when the peaks increased with increasing concentration of Er 3+ ions in the glass.
Funnel morphology
In order to understand all the properties of the sample, it is necessary to pay attention to the funnels formed on it.
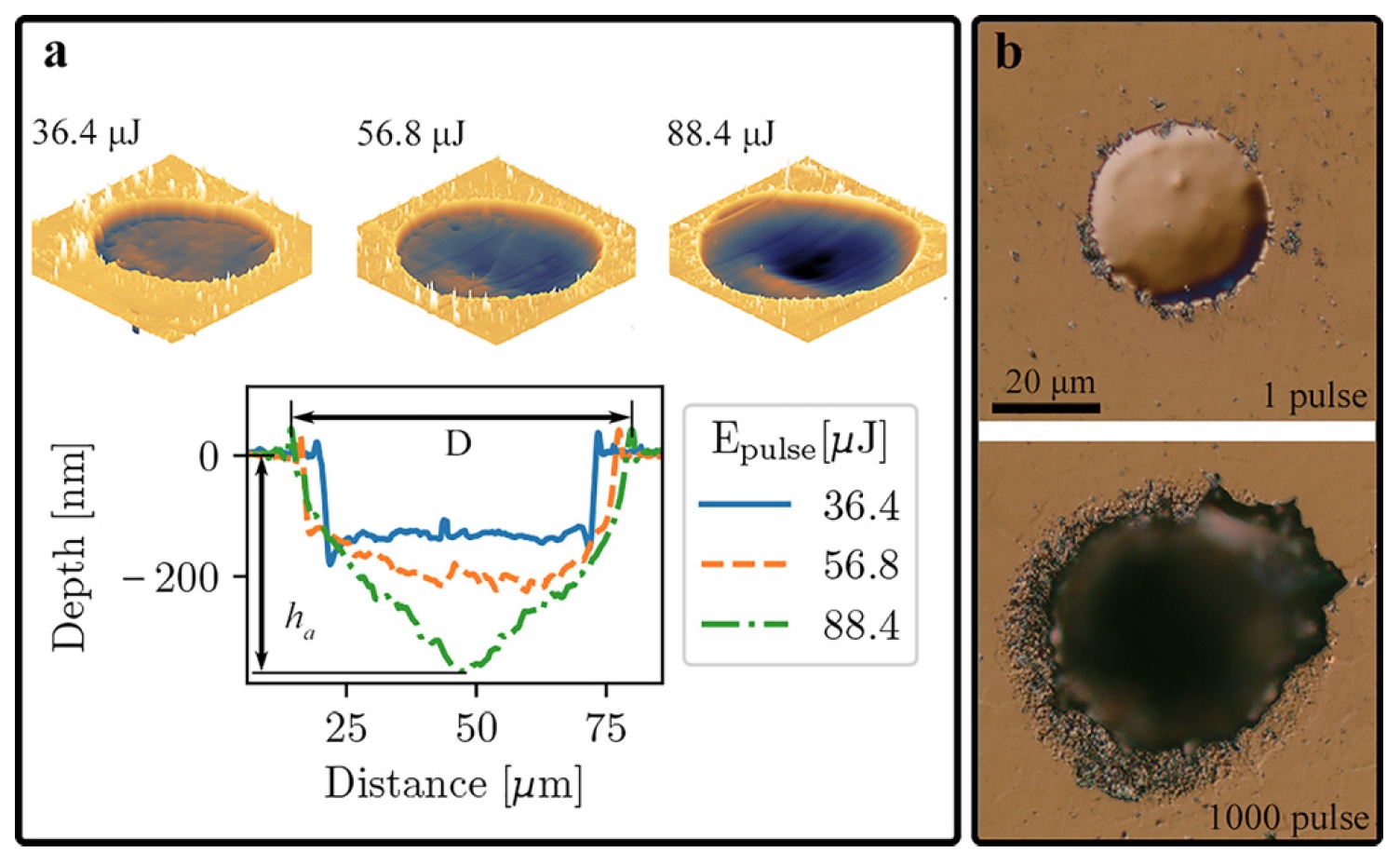
Image number 2: funnels and their characteristics
Image 2a shows images of funnels taken with an atomic force microscope. Each funnel was formed by a single laser pulse with a power of 36.4, 56.8, and 88.4 μJ (microjoule, 1 μJ = 10 −6 J). The size of the point of impact of the pulse was 32.0 microns.
As can be seen from the comparative graph below the images, the profile of each of the funnels is rather small. At a low pulse power level, when the fluence * is 2 J / cm 2 , the funnels take a cylindrical shape. With a further increase in fluence, the funnels change into a Gaussian profile.

A snapshot of the sample, which shows the funnels
Fluence * is the time integral of the particle flux or energy density.Protruding edges are observed around the funnels, from 20 to 50 nm in height. With increasing laser fluence, the height of the edges also increases. Among other things, radial surges were observed. Such features are due to the formation of a thin molten region under the ablation zone and the flow generated by the plasma. That is, with a low laser fluence, the plasma pressure may be too small for the release of molten material from the funnel to occur. As a result of such factors, re-solidification occurs, leading to the formation of a flat bottom of the funnel.
A similar effect will be stronger in tellurite glass due to its low glass transition temperature * in comparison with other types of glass.
The glass transition temperature * is the temperature at which the crystallizing substance passes into the glassy state.2b are snapshots of a differential interference-contrast microscope, in which we see the funnels formed at a laser pulse power of 45.8 mJ, the size of the impact point is 13.9 μm and a different number of pulses.
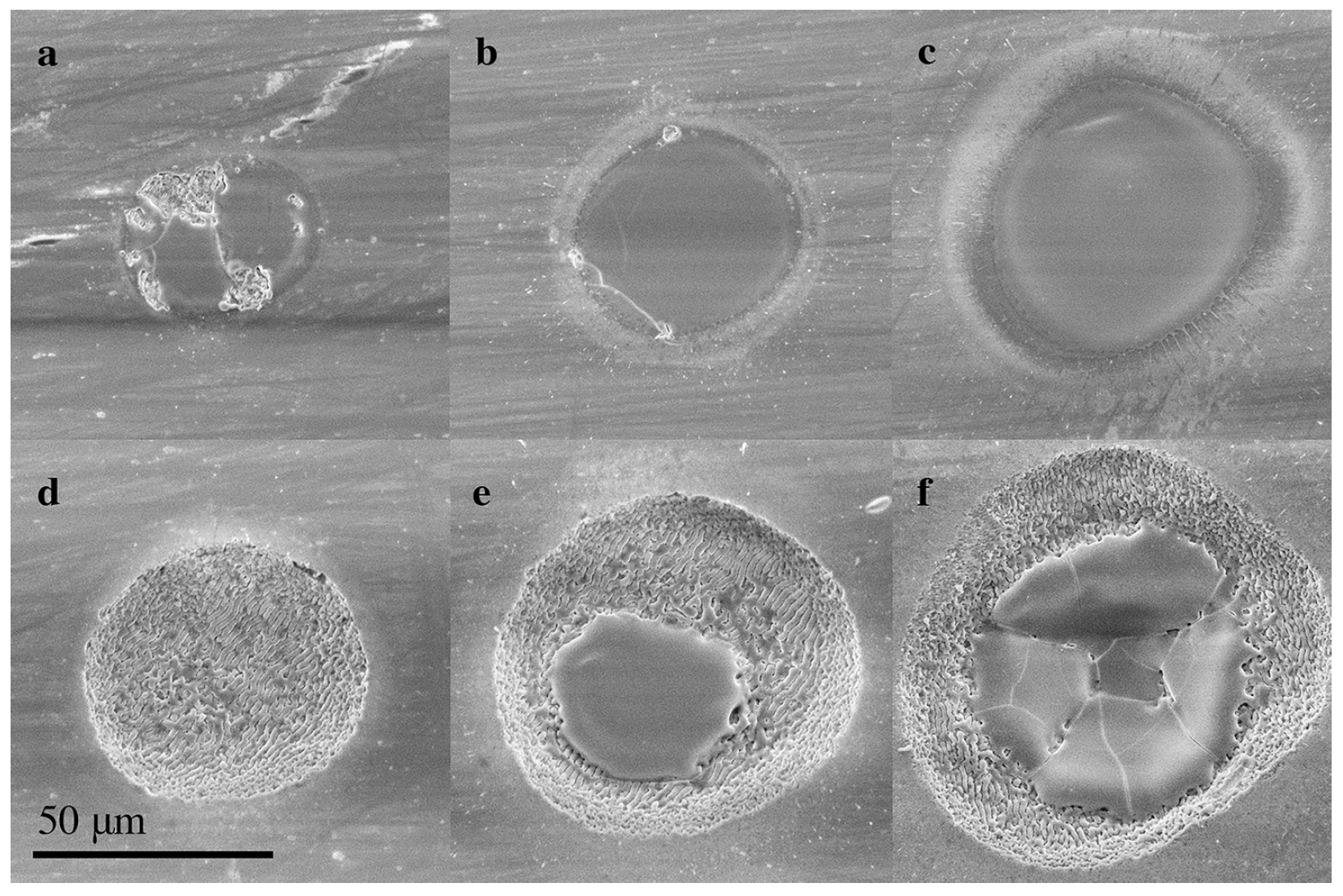
Image number 3
The image above shows images of funnels with different laser fluence and the number of laser pulses from 10 to 32.
Irradiation of 32 pulses, being close enough to the ablation threshold, leads to the formation of a wavy surface of the funnel ( 3d ), which is not on the sample at 10 pulses ( 3a ).
Such “waves” were most distinct and homogeneous when the fluence was less than 5 times higher than the threshold of pulsed ablation (0.85 J / cm 2 ). The periodicity of the waves was 1.4 µm, which is greater than the length of the incident wave.
On 3e and 3f, you can see the irregularities of the circle and smoothness in the middle of the funnel, where the Gaussian beam had a smaller fluence. If the fluence is even larger, then a columnar region ( 3f ) is formed.
Dopant Er 3+ ion
Measurements of the ablation threshold of the sample with Er 3+ added ion and the size of the laser irradiation area of 13.9 μm did not show significant changes when the concentration of the dopant was changed.
In order to correspond to the derived ablation formula, which remains unchanged with a different number of pulses, the mean and standard deviation of parameters for all samples were as follows:
F th (1) = 0.51 ± 0.03 J / cm 2 ;
F th (∞) = 0.18 ± 0.01 J / cm 2 ;
k = 0.053 ± 0.009.
F th (N) = F th (∞) + [F th (1) - F th (∞)] e -k (N-1) , whereSimilar indicators are expected if the dopant concentration is low due to the following reasons:
F th - ablation threshold;
N is the number of pulses per exposure point;
k is a parameter that determines the speed at which the fluence threshold approaches an infinite pulse value;
- femtosecond laser ablation is a non-linear process due to a very intense laser field of short pulse duration. Because of what the size of the forbidden zone * is one of the main parameters describing this process. And it did not change in any way with increasing concentration of Er 3+ ions;
- at the maximum concentration of dopant (1.5 mol-percent), the linear absorption of the sample increased from 0.11 cm -1 to 0.85 cm -1 . The absorption coefficient for a nonlinear process is 5.4104 cm -1 , which is 5 orders of magnitude greater if the process is linear, which indicates the absence of it in the sample.
- Physical changes in glass parameters (density, refractive index, and melting point) are insignificant at low dopant concentrations. As a result, a change in the ablation threshold does not occur.
The forbidden zone * is the range of energy values that an electron cannot have in an ideal crystalline body.Summarizing
The researchers were able to analyze the characteristics of tellurite glass with an Er 2 O 3 admixture under the influence of femtosecond laser radiation. The forbidden zone of the sample was 3.276 eV (electron-volt), which is twice the photon energy of the laser (1.55 eV or 800 nm). The profile of the funnels created by laser pulses directly depends on the applied fluence and the number of pulses. When the fluence is below average (2 J / cm 2 ), the funnels have a cylindrical shape. If the fluence is above average, then the funnels acquire the features of a Gaussian profile. The fluence and the number of pulses determine whether the sample should be nanomicro- or macro-structuring. The frequency of the “waves” on the sample surface was 1.4 μm, when several pulses were applied close to the ablation threshold.
Measurements of the diameters of funnels with different fluence showed a single pulse impulse ablation threshold of 0.51 J / cm 2 with a diameter of 13.9 μm and 0.32 J / cm 2 with a diameter of 32.0 μm. The ablation threshold for several pulses was detected after applying about 50 pulses and was equal to 40% of the threshold with a single pulse.
It was also found that the ablation threshold decreases with increasing diameter of the point of exposure to laser radiation, due to the increased likelihood that the laser beam can damage the sample.
With an increase in the Er 2 O 3 impurity concentration to 1.5 mol-percent, the ablation threshold did not change. The amount of material removed at a unit of applied energy was 6.8 μm 3 / μJ with a fluence of 2 J / cm 2 . This indicator decreased linearly.
A decrease in the ablation efficiency with increasing fluence may be associated with an increase in the reflectivity of the sample surface.
To learn more about the details of the study I strongly recommend that you read the report of scientists.
Epilogue
Such studies are necessary in modern realities, when any device is becoming less and less. In order to preserve, and sometimes even improve, its performance, it is necessary to study the characteristics of new materials, rediscover the already known, and even combine the new with the long forgotten old. Of course, everything has its limit due to physical characteristics. However, scientists from time to time show us that this limit has not yet been reached.
Thank you for staying with us. Do you like our articles? Want to see more interesting materials? Support us by placing an order or recommending to friends, 30% discount for Habr users on a unique analogue of the entry-level servers that we invented for you: The whole truth about VPS (KVM) E5-2650 v4 (6 Cores) 10GB DDR4 240GB SSD 1Gbps from $ 20 or how to share the server? (Options are available with RAID1 and RAID10, up to 24 cores and up to 40GB DDR4).
Dell R730xd 2 times cheaper? Only we have 2 x Intel Dodeca-Core Xeon E5-2650v4 128GB DDR4 6x480GB SSD 1Gbps 100 TV from $ 249 in the Netherlands and the USA! Read about How to build an infrastructure building. class c using servers Dell R730xd E5-2650 v4 worth 9000 euros for a penny?
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/418737/
All Articles

