MIT course "Computer Systems Security". Lecture 5: "Where Security Errors Come From", Part 2
Massachusetts Institute of Technology. Lecture course # 6.858. "Security of computer systems". Nikolai Zeldovich, James Mykens. year 2014
Computer Systems Security is a course on the development and implementation of secure computer systems. Lectures cover threat models, attacks that compromise security, and security methods based on the latest scientific work. Topics include operating system (OS) security, capabilities, information flow control, language security, network protocols, hardware protection and security in web applications.
Lecture 1: "Introduction: threat models" Part 1 / Part 2 / Part 3
Lecture 2: "Control of hacker attacks" Part 1 / Part 2 / Part 3
Lecture 3: "Buffer overflow: exploits and protection" Part 1 / Part 2 / Part 3
Lecture 4: "Separation of privileges" Part 1 / Part 2 / Part 3
Lecture 5: "Where Security Errors Come From" Part 1 / Part 2
Filling in the credentials in iframes significantly increases the scale of the attack, and visiting a malicious page can very quickly compromise large sets of credentials.
')

Security researchers have discovered the vulnerability of unverified password managers, such as Chrome extensions for Windows , and later research by researchers, including those from MIT , revealed the vulnerability of the LastPass extension for the Safari browser.
Consider cross-domain queries. Do you think it is possible that the authorization form https: // example.com filled in by the password manager would be submitted to login https: // www.isecpartners.com , can the password manager transfer data to a third party? Yes, it can, and this makes it possible to find a vulnerability or function that allows an attacker to create a domain login form, after which the malicious login form is sent to the authentic site https: // www.isecpartners.com .
Keep in mind that all verified password managers safely send passwords to different domains.
What is true for domains is also true for subdomains. A feature of subdomains is that their “sensitivity” to security can be very different from the security checks performed by domains. Subdomains such as blog. * , Forum. * Or mail. * May have completely different security requirements. Processing subdomains as domain equivalent increases the attack surface. It should be borne in mind that all verified password managers considered subdomains to be equivalent to the domain page.
It is necessary to carefully approach the identification of login pages. Internet applications change, and this causes the login pages to move. Therefore, their authenticity should be checked even more carefully than the authenticity of subdomains.
It should be borne in mind that most web applications have a small set of login pages. You can link them together so that the appearance of the login page triggers auto-completion or form auto-submission to the same primary domain. In this case, the password manager will fill in any authorization form for any meeting subdomain.
The attack vector in this case can be HTML email . For example, Google , Yahoo and Outlook use such a thing as filling out a form online. The slide shows an example with the following text: “if you have difficulty filling or sending this form, you can fill it in online at this link” and a link to the form is sent that directs the user to the domain docs.google.com . And further on the page it says: “Never send passwords using Google Forms!”

Since people often use mail to send forms, attackers have focused on the users of these three services. You fill out a form, for example, answering questions from various surveys, and use your inbox to send it. How do these services resist attacks?
It is best opposed to Outlook hackers ( live.com ). It prevents the possibility of an attack by prohibiting the provision of any original material to a third party, including forms and personal information of users.
In second place is Google , which simply warns users against committing such actions, which does not exclude the possibility of password theft.
Yahoo allows you to steal passwords without warning.
The danger of the built-in autofill mechanism and creation of authentication forms is that services do not always warn about the danger of sending them to a third party or the danger of using these functions on the pages of other Internet resources. For example, when passing the above survey, there is a suspicious function Submit . Answering the question, who is better, a dog or cat, and clicking on the Submit button, you not only confirm the answer you have chosen, but at the same time you confirm the sending of your login and password to the attacker.
Yahoo is the worst security service, especially if you use LastPass Password Manager.
Mobile versions of browsers are protected even worse. There are no extensions here, but security researchers have discovered a plugin for the Chrome mobile browser called Javascript Bookmarklets . It runs a fake security code on hostile sites you visit. In fact, it masks their danger, creating a sense of false security that can cause you great damage.
You can familiarize yourself with other browser extensions and find out the results of research into attacks and password protection at the links of organizations in the field of security research of Berkeley and Joint Stanford .
I want you to understand: having familiarized yourself with the basics of the work of password managers, you yourself can find almost all the security errors of these applications.
You need to understand what kind of functionality the developer laid out in the application and how it works in practice. If you do this, it will be much easier for you to find vulnerabilities.
Consider a TLS attack called CRIME , which is short for Compression Ratio Info-leak Made Easy . This is a security exploit that allows you to decode HTTPS sessions, including custom cookies, by intercepting encrypted traffic between the server and the browser. All versions of TLS , including TLS 1.2 , are vulnerable.
During this attack, the hacker intercepts user traffic, adds its data to it and sends requests to the server. The compression algorithm when repeating part of the text compresses it. After sending data to the server, the hacker looks for the length of the message and if it has decreased, then the correct sequence is selected. Thus, it is possible to select individual lines and parameters in the request, for example, cookie values.

This attack is based on the fact that your browser interacts with the site using an internal interface - the HTTP protocol. At the same time, if I go to the site example.com , the browser sends it my cookies with all the information available in the previously completed authorization form, including the username and password. In HTTP form, it looks like this:
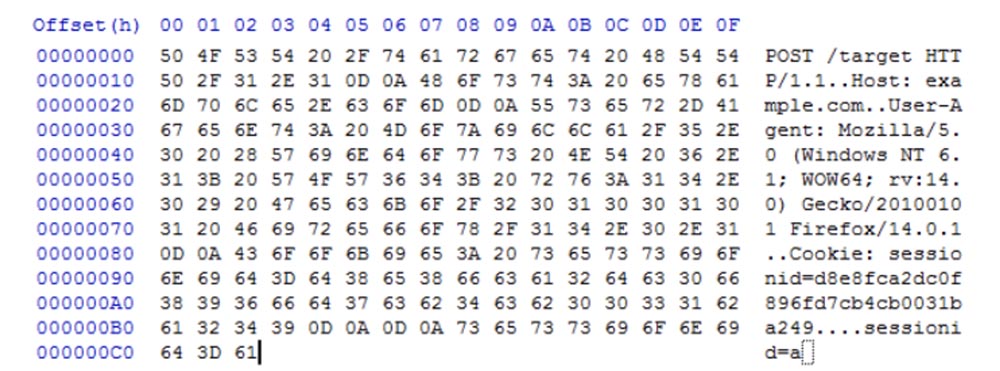
Even if the data is protected by an SSL / TLS connection , I can still get some of the information if I own the network. Here's what the SSL information looks like:

Here I see the following information: the transmission time, from whom the message is sent, that is, the user's IP, to whom the message is sent, that is, the recipient's IP, and message length.
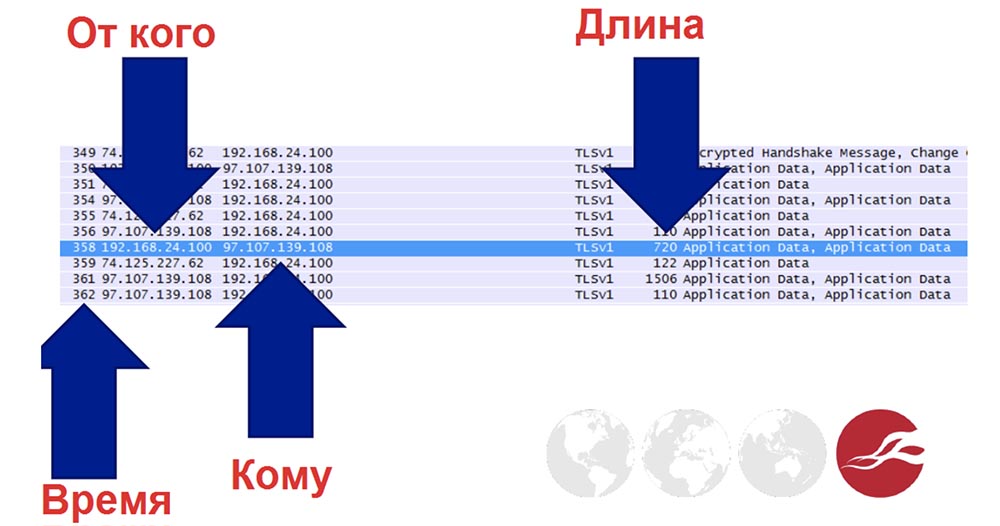
Such is the design of the cryptographic protocol of SSL protected sockets level. If you have the ability to analyze traffic, this data provides a huge field for malicious activity.
Consider the message that the browser sends.
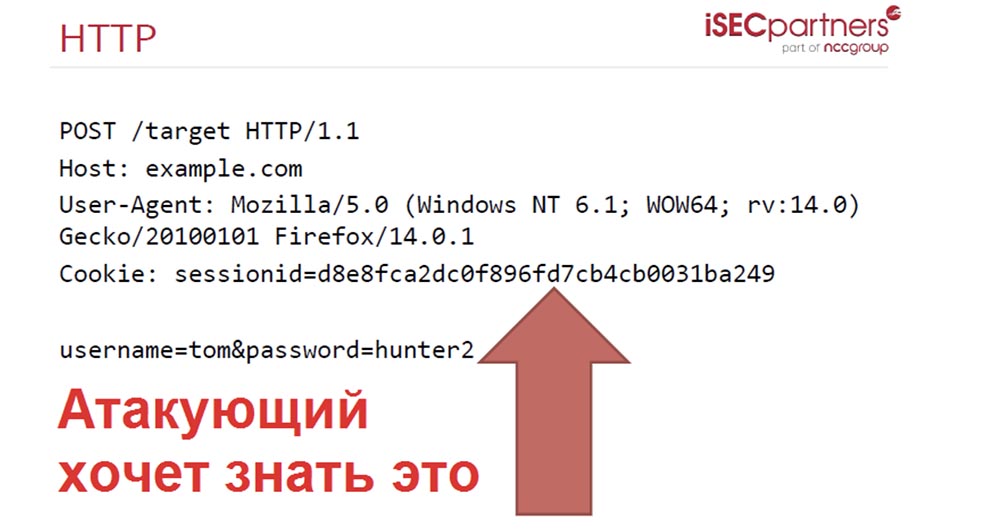
If the browser allows you to make cross-domain requests, then it will send the request with a cookie containing the form data to any site that will be redirected to by an attacker, for example, example.com. If an attacker seizes these cookies, he can control the following parameters:

In order to guess the user's password, I begin to select the parameter for the string username = tom & password and instead of hunter2 I enter the letter a .
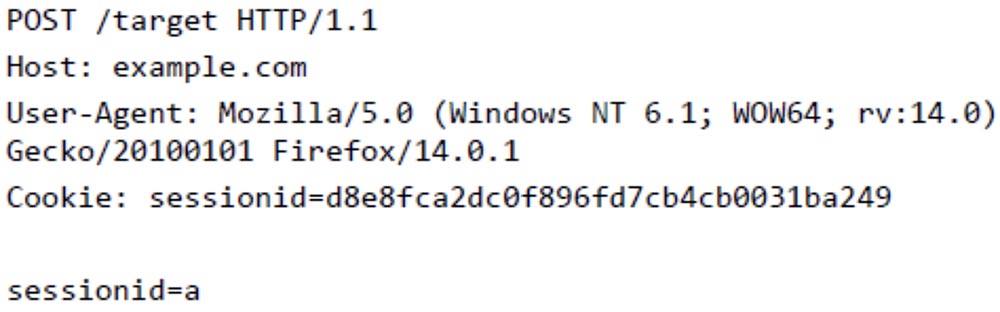
Then I look at HTTP decryption and I see that this parameter takes 195 bytes.
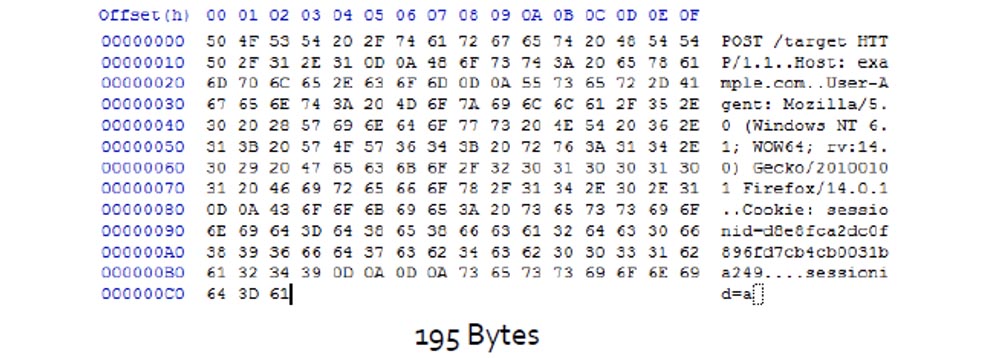
To facilitate his work, the hacker uses TLS compression. The compression algorithm, when repeating a part of the text, compresses it, and compression creates markers for these parts and places them in the form of an HTTP message.
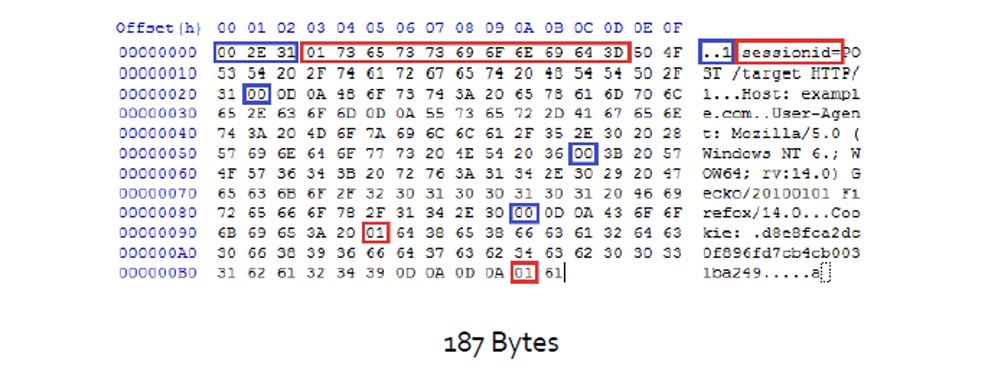
In this case, the session ID is equivalent to the parts of the code marked with the corresponding marker, and the size of the compressed message is 187 bytes.
What happens if I equate session ID = d ?
The message size is reduced because it needs to compress more bytes. This can be seen if we compare the number of arguments surrounded by a red frame in the 2nd line above.
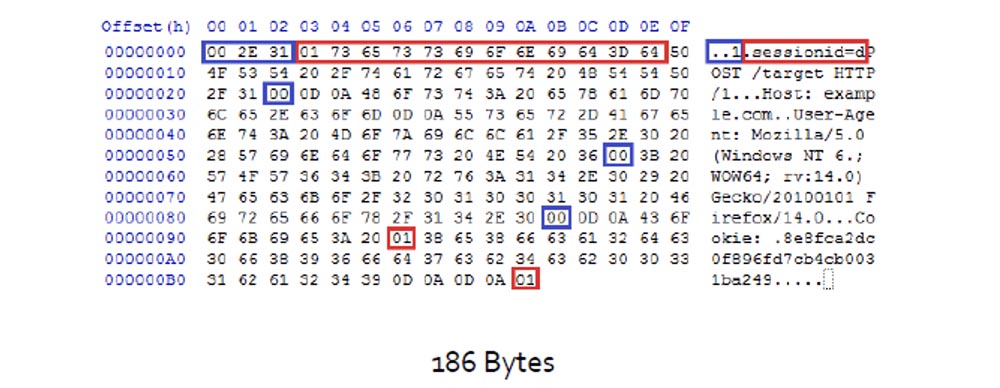
This is what the attacker sees. He sees that the message is compressed, and because of this he finds out that he guessed the first letter in the session ID . Then it replaces session ID = da and gets the message size 188 bytes.
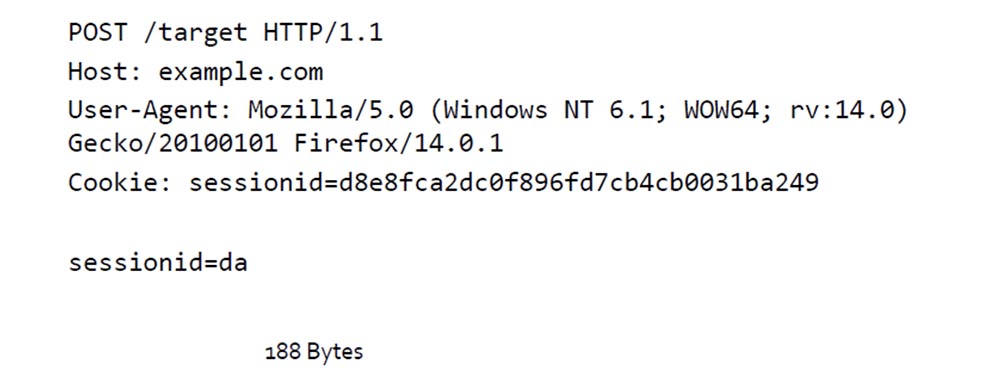
So, successively substituting letters and numbers and analyzing changes in message size, he guesses the entire session ID . That is, it selects not the encryption key, but the content of the encrypted message itself.

In order to deal with CRIME , it is necessary to prohibit the browser to perform TLS compression. You also need to change the SPDY protocol so that when you request secret data, they are compressed in a separate context.
Consider HTTP violation cases. HTTP responses that come to the user after accessing the server may contain such secret data as CSRF tokens or other confidential information. Attacks like CRIME require the knowledge of at least one secret session prefix and the ability to enter their data in the response message.
You can prevent an attack by banning the compression of responses or drowning out a CRIME attack, since this attack uses the MiTM principle (the person is in the middle) and can "bring down" actual requests. This is a content “noisy” attack that can be detected, since the attacker usually does not communicate directly with the server, but uses access to the router, and the server may even “not know” about the attack.
You can also protect yourself by placing various secret information in various files, such as javascript , but this is difficult to implement in practice and also difficult to modify to existing applications.
You can try to randomize secret information in requests, mainly for CSRF tokens, but this method will lead to a dramatic drop in performance.
Knowing the principles of the application and vulnerabilities, you can "bring down" the entire Internet: SSL / TLS , DNS , DNSSEC / DNSEC , IPv6 , it is quite feasible.

And now I want to talk about a very big player in the field of security - the NSA , the National Security Agency, or the NSA. These are people who often create security problems and solve them themselves.
For some things I’m ready to hate them. However, NSA employees are not able to change the current policy. They contribute to the intellectual development of everything related to security, and I hope they believe that the result of their work will be used for good purposes.
In their work there are two sides of the medal, but this is only my opinion and it may not coincide with the opinion of my employers. And I think that not all the research data that I will tell you about is officially declassified.
Snowden said that some statements can be proved as true, and some as false. An example of a false statement is the NSA 's statement that “there is direct access to Google networks”, because the true state of affairs with access to these networks is shown in the following figure, which the NSA itself made.
Google currently encrypts all of its traffic because it’s worrying that someone can break their network. In addition, all news is filtered through the media, and we see only excerpts from the documents.
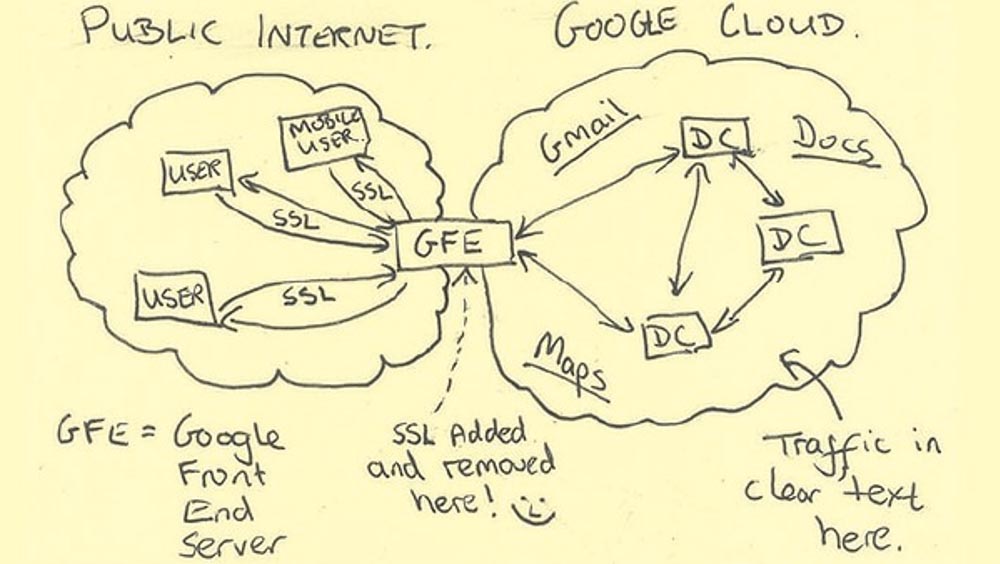
You see a smiley next to the phrase “ SSL is being added and removed here on the head server of Google, ” because it is from here that the NSA can extract data. Google , which has data centers around the world, makes extensive use of dedicated fiber optic lines for its networks. Due to this traffic is transmitted at high speed and it is very difficult to get to it.
The government has not only great technical capabilities, but also leverage. Some companies find it very difficult to resist coercion to cooperate with the government. An example of opposition to the state is the free email service Lavabit , created as an alternative to Gmail , because the latter violated the privacy of users ’correspondence requested by government services.
The state may also force companies not to publicly acknowledge that they cooperate with government services.
Consider the tools that the state has to implement security policies.
First of all, it is SIGINT - the Worldwide Cryptographic Security Platform. It is based on fiber-optic networks. The following site shows the outline of a highly classified document published by Snowden. You see on it a multitude of yellow dots, denoted as CNE. Snowden assumes that equipment for breaking networks is located in these places. Their number is over 50,000 worldwide.
Networks can be hacked in a variety of ways. The government uses a supply chain attack for this — cyber attacks that target the least protected elements in the networks of various organizations. In order to protect themselves from such attacks, the government avoids cooperation of any kind, providing only direct access to its own networks, without any intermediaries and third parties.
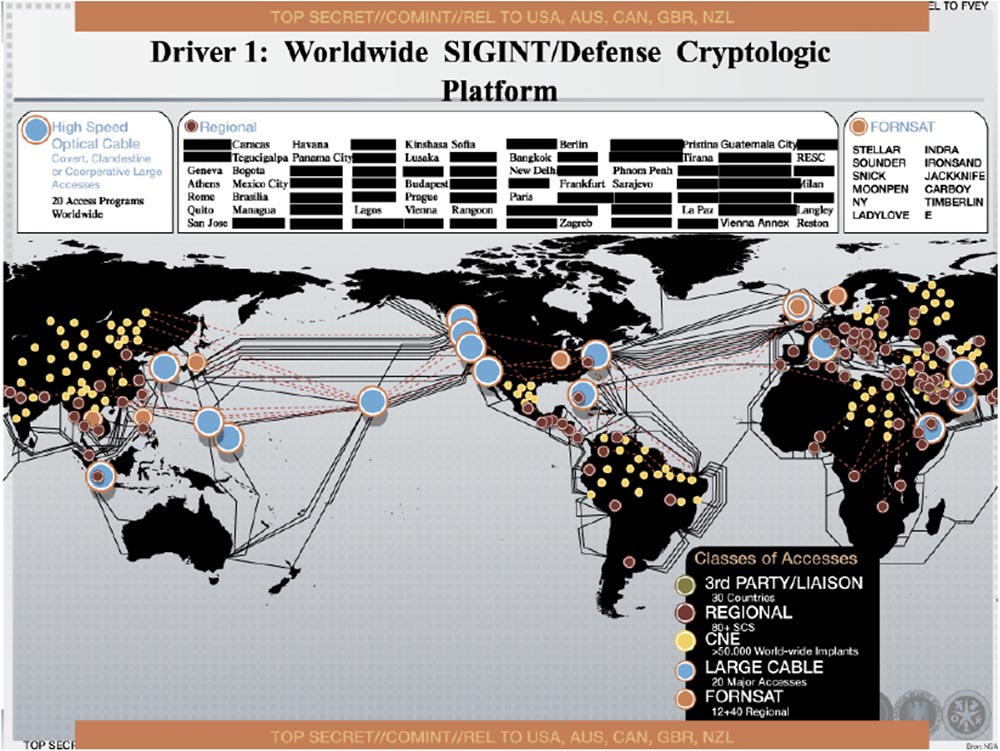
According to the non-governmental organization EFF (Electronic Frontier Foundation) and the trials initiated by it, the NSA likes to use the so-called “optical switches”, which allow intercepting telephone conversations, including from MPLS and interfering with the leakage of target information to intermediaries. The majority of intermediaries involved in the transfer of information between users not only in the United States, but throughout the world are involved in this.
Hope TLS can counter such an intervention.
The government is able to compromise even the internal network infrastructure using Pokemon’s private end- point encryption keys. This allows you to organize heartbleed attacks and standard network attacks. The government often uses the DOD networking model developed by the US Department of Defense. Such a system is used in google.com networks.
It is possible to use crypto attacks against TLS . It is assumed that the Stuxnet computer worm, which infects computers running Windows , was developed at the initiative of the US government. It uses a conflict within the MD5 encryption algorithm that has a valid certificate. This worm intercepts data between controllers and logical stations and can interfere with the process of automated control of various industrial complexes. This is the only virus that can destroy the physical infrastructure of networks.
There is an NIST organization that develops encryption standards for virtually everything. She recommends using a DUAL_EC_PRNG cryptographically strong pseudo-random number generator to create encryption keys. However, it still has vulnerabilities. If you use the elliptic curve points specified in its encryption standard, then because of the large number of output bits per generation round, it is possible to penetrate the generator code and crack it with the brute force method. The creators of the algorithm were aware of this vulnerability from the very beginning. This does not mean that a backdoor was originally provided for in this generator, but it means that a backdoor can be created there at any time.
Note that NSA most often uses attacks based on contradictions within the latest MD5 encryption algorithms .

The state has a global impact on the Internet around the world. Most of the world's communications are through the USA. Telephone conversations, e-mail and chat rooms are carried out on the cheapest ways, not physically always direct, and you can always follow this path. Most of the global Internet traffic passes through the United States. In any case, the path by which communication is made with the ultimate goal of your contact can easily be redirected to the United States, that is, the state can control any telecommunications flows around the world.
I will give an example of "return" from such activity. The state intervenes not only in the communication of private persons, but also in the work of companies. In November 2013, the Washington Post published information that the NSA intercepts traffic between Google data centers through a fiber-optic cable before it is encrypted between end servers and users' computers. Were published additional data on the government program MUSCULAR and fragments of packages stolen from the internal network of Google .

Employees of Google confirmed the fact of hacking into their network by the NSA, not being embarrassed in expressions - Google security specialist Brandon Downey directly wrote: “Fuck these guys!”, Meaning the unprecedented impudence of the NSA .
Therefore, it is difficult for people to trust US network equipment and services provided by US network providers. I will quote Cardinal Richelieu's words: “Give me six lines, written by the hand of the most honest person, and I will find in them something for which you can hang it.”
I do not want you to become paranoid in the sense of distrust of the government and have seen total espionage and breach of confidentiality of information and privacy. But as future software developers, you need to know how an attacker can act. If you work in a large company, a hacker can use government tools and techniques to organize an attack. Therefore, you need to do such useful things as Google does by encrypting all your internal traffic and using penetration testing certificates.
I want to introduce you to several other types of malicious software. One of them is called Flame , or Flame.

, Stuxnet . , :
- GPS ;
- , Bluetooth;
- , .
Flame MD5 , , . - 2008 , CA -, RapidSSL . Internet Public Key Infrastructure (PKI) , .
4 RapidSSL . 3- , 215 Sony PlayStation 3 . , , MD5 .
, Microsoft Microsoft Terminal Server , MD5 . MD5 , , 1 . Microsoft , , Windows . , MS , Flame , . , , .
– , ? -, , .
, « »? « ?», .

, , . , .
, , , . , .
:
- « » , ;
- jailbreakme.com , iOS root- . , , , ;
- – , , , ;
- , ;
- , , .
.
, . , . , . , . , , .
. , , . , , . , , .
, , , . , , , .
, .
— .
, iSEC Partners:
- 2 -3 20-30 . , , MIT;
- , ;
- , ;
- , ;
- , !
paul@isecpartners.com . , .

. , , «». , , . , . «» IBM .
, , , . . , , , Facebook , Google Yahoo . , , , .
!
Full version of the course is available here .
Thank you for staying with us. Do you like our articles? Want to see more interesting materials? Support us by placing an order or recommending to friends, 30% discount for Habr users on a unique analogue of the entry-level servers that we invented for you: The whole truth about VPS (KVM) E5-2650 v4 (6 Cores) 10GB DDR4 240GB SSD 1Gbps from $ 20 or how to share the server? (Options are available with RAID1 and RAID10, up to 24 cores and up to 40GB DDR4).
Dell R730xd 2 times cheaper? Only we have 2 x Intel Dodeca-Core Xeon E5-2650v4 128GB DDR4 6x480GB SSD 1Gbps 100 TV from $ 249 in the Netherlands and the USA! Read about How to build an infrastructure building. class c using servers Dell R730xd E5-2650 v4 worth 9000 euros for a penny?
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/418215/
All Articles