Numerical solution of mathematical models of objects given by systems of differential equations
Introduction:
In mathematical modeling of a number of technical devices, systems of differential nonlinear equations are used. Such models are used not only in technology, they are used in economics, chemistry, biology, medicine, management.
The study of the functioning of such devices requires the solution of these systems of equations. Since the main part of such equations are nonlinear and non-stationary, it is often impossible to obtain their analytical solution.
There is a need to use numerical methods, the most famous of which is the Runge – Kutta method [1]. As for Python, in publications on numerical methods, for example [2,3], there are very few data on the use of Runge - Kutta, and on its modification - in general there is no Runge-Kutta-Fellberg method.
')
Currently, thanks to a simple interface, the most popular in Python is the odeint function from the scipy.integrate module. The second ode function from this module implements several methods, including the mentioned five-rank Runge-Kutta-Fellberg method, but due to its universality, it has limited speed.
The purpose of this publication is a comparative analysis of the listed tools for the numerical solution of systems of differential equations with a modified author under the Python method of Runge-Kutta-Fellberg. The publication also provides solutions for boundary value problems for systems of differential equations (SDEs).
Brief theoretical and actual data on the considered methods and software for the numerical solution of the CDS
Cauchy problem
For a single differential equation of the nth order, the Cauchy problem is to find a function that satisfies the equality:
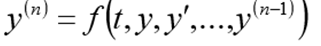
and initial conditions
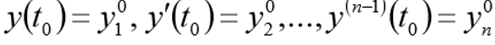
Before solving this problem should be rewritten in the form of the next CDS
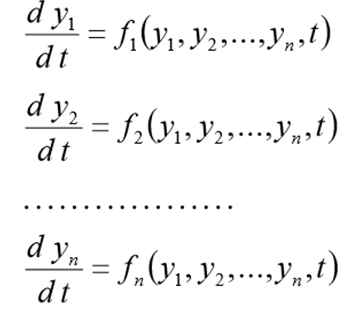 (one)
(one)with initial conditions
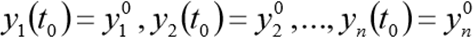
Module scipy.integrate
The module has two functions ode () and odeint (), designed to solve systems of ordinary differential equations (ODE) of the first order with initial conditions at one point (the Cauchy problem). The ode () function is more versatile, and the odeint () function (ODE integrator) has a simpler interface and solves most problems well.
Odeint () function
The odeint () function has three required arguments and many options. It has the following format: odeint (func, y0, t [, args = (), ...]) The argument func is the name of the Python function of two variables, the first of which is the list y = [y1, y2, ..., yn ], and the second is the name of the independent variable.
The func function should return a list of n function values.
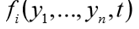 for a given value of the independent argument t. In fact, the function func (y, t) implements the calculation of the right-hand sides of the system (1).
for a given value of the independent argument t. In fact, the function func (y, t) implements the calculation of the right-hand sides of the system (1).The second argument y0 of the odeint () function is an array (or list) of initial values.
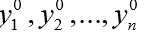 at t = t0.
at t = t0.The third argument is an array of points in time at which you want a solution to the problem. In this case, the first element of this array is considered as t0.
The odeint () function returns an array of size len (t) x len (y0). The odeint () function has many options that control its operation. The options rtol (relative error) and atol (absolute error) determine the calculation error ei for each value of yi using the formula
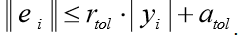
They can be vectors or scalars. Default
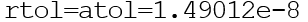
Ode () function
The second function of the scipy.integrate module, which is designed to solve differential equations and systems, is called ode (). It creates an ODU object (type scipy.integrate._ode.ode). Having reference to such an object, its methods should be used to solve differential equations. Similar to the odeint () function, the ode (func) function assumes the reduction of a problem to a system of differential equations of the form (1) and the use of its function on the right-hand sides.
The only difference is that the function of the right-hand sides func (t, y) takes the independent variable as the first argument, and the second as the list of values of the desired functions. For example, the following sequence of instructions creates an ODE object representing the Cauchy task.
Runge — Kutta Method
When constructing numerical algorithms, we assume that the solution to this differential problem exists, it is unique and has the necessary smoothness properties.
In the numerical solution of the Cauchy problem
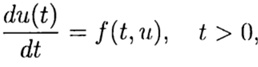 (2)
(2)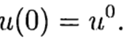 (3)
(3)According to the well-known solution at the point t = 0, it is necessary to find a solution from equation (3) for other t. In the numerical solution of problem (2), (3), we will use a uniform, for simplicity, grid in the variable t with step m> 0.
Approximate solution of problem (2), (3) at point
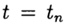 denote
denote 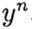 . The method converges at
. The method converges at 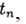 if a
if a 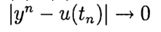 at
at  . The method has the pth order of accuracy if
. The method has the pth order of accuracy if 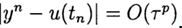 , p> 0 when
, p> 0 when  . The simplest difference scheme for the approximate solution of problem (2), (3) is
. The simplest difference scheme for the approximate solution of problem (2), (3) is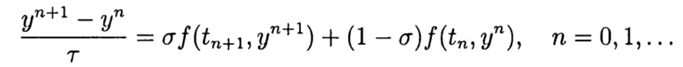 (four)
(four)With
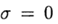 we have an explicit method and in this case the difference scheme approximates equation (2) with the first order. Symmetric scheme
we have an explicit method and in this case the difference scheme approximates equation (2) with the first order. Symmetric scheme 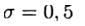 in (4) has the second order of approximation. This scheme belongs to the class of implicit ones — to determine an approximate solution on a new layer, it is necessary to solve a nonlinear problem.
in (4) has the second order of approximation. This scheme belongs to the class of implicit ones — to determine an approximate solution on a new layer, it is necessary to solve a nonlinear problem.Explicit schemes of the second and higher order approximations can be conveniently constructed based on the predictor-corrector method. At the stage of predictor (prediction), an explicit scheme is used.
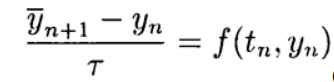 (five)
(five)and at the stage of the corrector (clarification) - the scheme
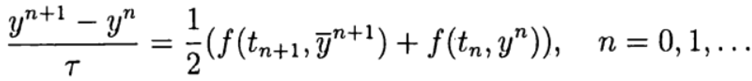
In the one-step Runge – Kutta methods, the ideas of the predictor-corrector are implemented most fully. This method is written in general:
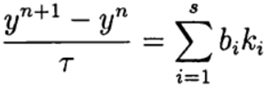 (6),
(6),Where
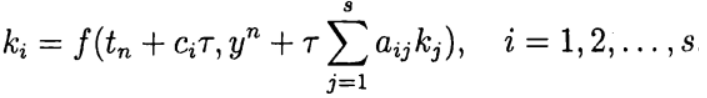
Formula (6) is based on s calculations of the function f and is called s-stage. If a
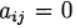 at
at 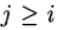 we have an explicit Runge – Kutta method. If a
we have an explicit Runge – Kutta method. If a 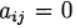 with j> 1 and
with j> 1 and 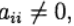 that
that 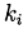 determined implicitly from the equation:
determined implicitly from the equation: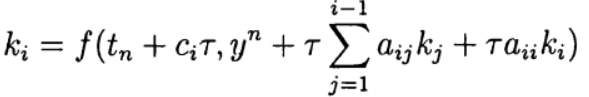 (7)
(7)This Runge – Kutta method is referred to as being diagonally implicit. Options
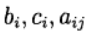 determine the variant of the Runge – Kutta method. The following method representation is used (Butcher table)
determine the variant of the Runge – Kutta method. The following method representation is used (Butcher table)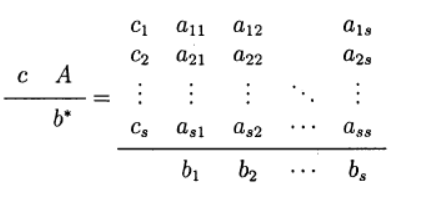
One of the most common is the explicit fourth-order Runge – Kutta method.
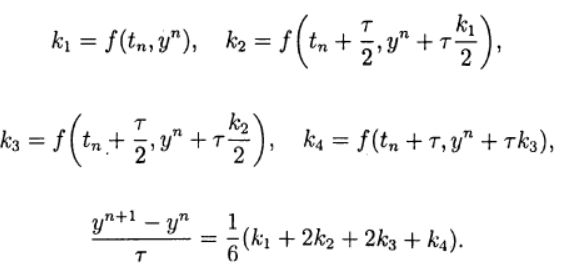 (eight)
(eight)Runge – Kutta – Felberg method
I give the value of the calculated coefficients
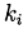 method
method (9)
(9)In view of (9), the general solution is:
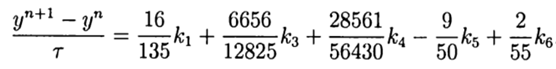 (ten)
(ten)This solution provides the fifth order of accuracy, it remains to adapt it to Python.
Computational experiment to determine the absolute error of the numerical solution of a nonlinear differential equation 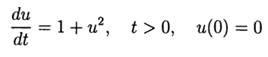 using both the def odein (), def oden () functions of the scipy.integrate module and the Pyunge-adapted Runge — Kutta and Runge — Kutta — Fellberg methods
using both the def odein (), def oden () functions of the scipy.integrate module and the Pyunge-adapted Runge — Kutta and Runge — Kutta — Fellberg methods
Program listing
from numpy import* import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from scipy.integrate import * def odein(): #dy1/dt=y2 #dy2/dt=y1**2+1: def f(y,t): return y**2+1 t =arange(0,1,0.01) y0 =0.0 y=odeint(f, y0,t) y = array(y).flatten() return y,t def oden(): f = lambda t, y: y**2+1 ODE=ode(f) ODE.set_integrator('dopri5') ODE.set_initial_value(0, 0) t=arange(0,1,0.01) z=[] t=arange(0,1,0.01) for i in arange(0,1,0.01): ODE.integrate(i) q=ODE.y z.append(q[0]) return z,t def rungeKutta(f, to, yo, tEnd, tau): def increment(f, t, y, tau): if z==1: k0 =tau* f(t,y) k1 =tau* f(t+tau/2.,y+k0/2.) k2 =tau* f(t+tau/2.,y+k1/2.) k3 =tau* f(t+tau, y + k2) return (k0 + 2.*k1 + 2.*k2 + k3) / 6. elif z==0: k1=tau*f(t,y) k2=tau*f(t+(1/4)*tau,y+(1/4)*k1) k3 =tau *f(t+(3/8)*tau,y+(3/32)*k1+(9/32)*k2) k4=tau*f(t+(12/13)*tau,y+(1932/2197)*k1-(7200/2197)*k2+(7296/2197)*k3) k5=tau*f(t+tau,y+(439/216)*k1-8*k2+(3680/513)*k3 -(845/4104)*k4) k6=tau*f(t+(1/2)*tau,y-(8/27)*k1+2*k2-(3544/2565)*k3 +(1859/4104)*k4-(11/40)*k5) return (16/135)*k1+(6656/12825)*k3+(28561/56430)*k4-(9/50)*k5+(2/55)*k6 t = [] y= [] t.append(to) y.append(yo) while to < tEnd: tau = min(tau, tEnd - to) yo = yo + increment(f, to, yo, tau) to = to + tau t.append(to) y.append(yo) return array(t), array(y) def f(t, y): f = zeros([1]) f[0] = y[0]**2+1 return f to = 0. tEnd = 1 yo = array([0.]) tau = 0.01 z=1 t, yn = rungeKutta(f, to, yo, tEnd, tau) y1n=[i[0] for i in yn] plt.figure() plt.title(" (..- u(t)=tan(t)) \n\ du/dt=u**2+1 cu(0)=0 t>0") plt.plot(t,abs(array(y1n)-array(tan(t))),label=' — \n\ - ') plt.xlabel('') plt.ylabel(' .') plt.legend(loc='best') plt.grid(True) z=0 t, ym = rungeKutta(f, to, yo, tEnd, tau) y1m=[i[0] for i in ym] plt.figure() plt.title(" (..- u(t)=tan(t)) \n\ du/dt=u**2+1 cu(0)=0 t>0") plt.plot(t,abs(array(y1m)-array(tan(t))),label=' —— \n\ - ') plt.xlabel('') plt.ylabel(' .') plt.legend(loc='best') plt.grid(True) plt.figure() plt.title(" (..- u(t)=tan(t)) \n\ du/dt=u**2+1 cu(0)=0 t>0") y,t=odein() plt.plot(t,abs(array(tan(t))-array(y)),label=' odein') plt.xlabel('') plt.ylabel(' .') plt.legend(loc='best') plt.grid(True) plt.figure() plt.title(" (..- u(t)=tan(t)) \n\ du/dt=u**2+1 cu(0)=0 t>0") z,t=oden() plt.plot(t,abs(tan(t)-z),label=' ode —— \n\ ') plt.xlabel('') plt.ylabel(' .') plt.legend(loc='best') plt.grid(True) plt.show() We get:
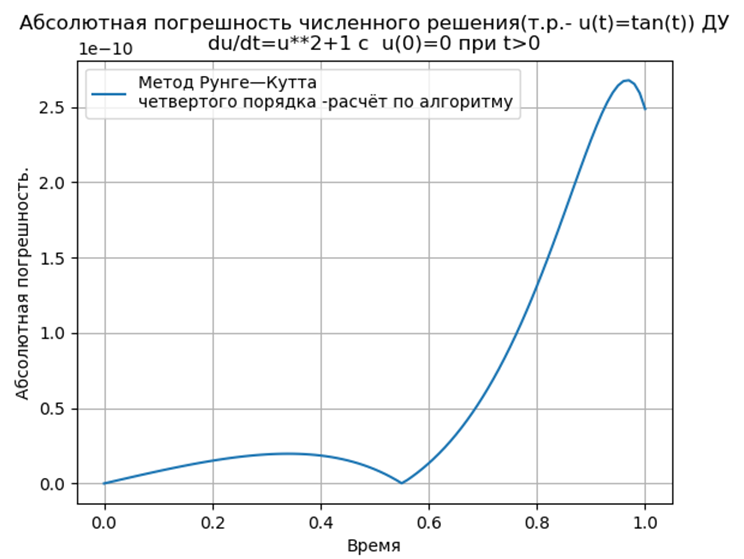
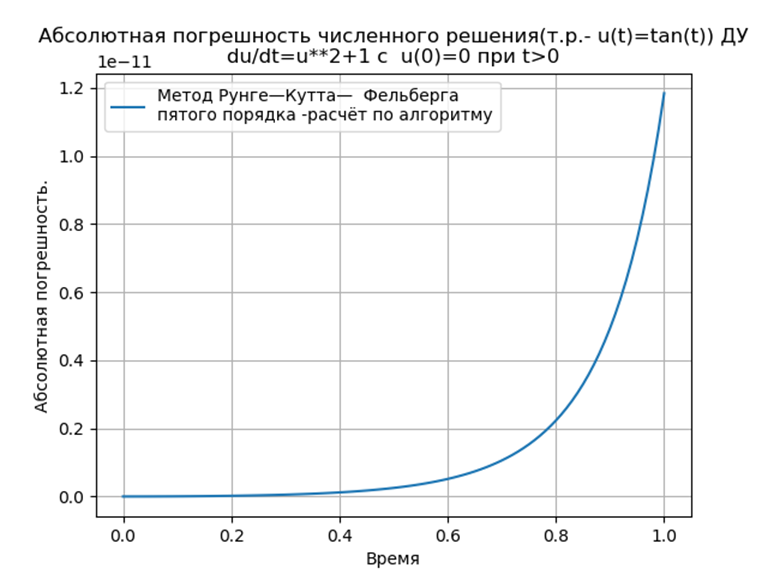
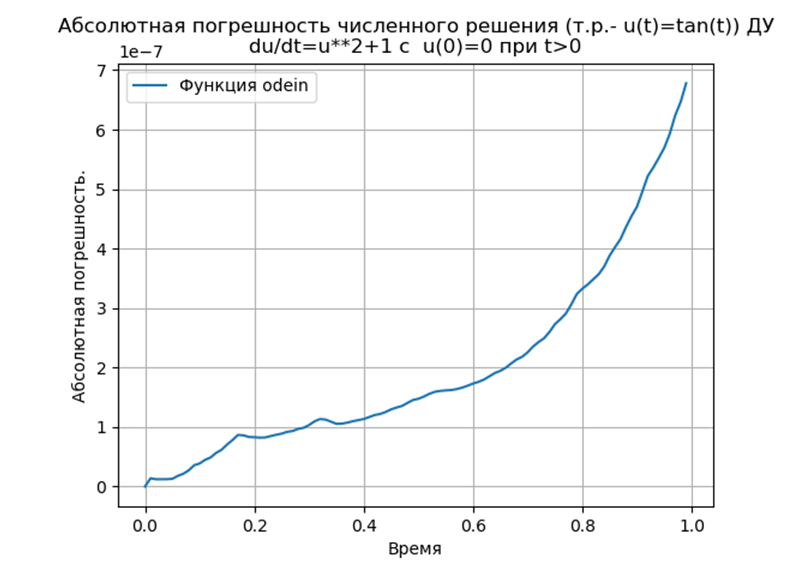
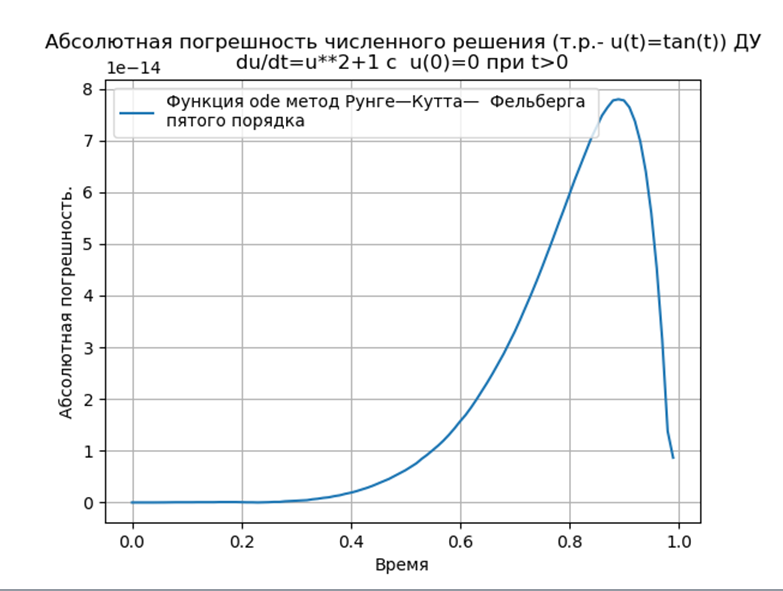
Conclusion:
Python-adapted Runge — Kutta and Runge — Kutta — Feelberg methods have a smaller absolute solution than using the odeint function, but more than using the edu function. It is necessary to conduct a performance study.
A numerical experiment comparing the speed of a CDS numerical solution using the ode function with the dopri5 attribute (Runge – Kutta method of the 5th order) and using the Runge — Kutta – Felberg method adapted to Python
Comparative analysis will be conducted on the example of the model problem given in [2]. In order not to repeat the source, I will give the formulation and solution of the model problem from [2].
We solve the Cauchy problem, which describes the motion of a body thrown with an initial velocity v0 at an angle α to the horizon under the assumption that air resistance is proportional to the square of the velocity. In the vector form, the equation of motion is
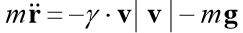
Where
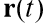 - the radius of the vector of the moving body,
- the radius of the vector of the moving body, 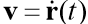 - the velocity vector of the body,
- the velocity vector of the body, 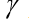 - resistance coefficient, vector
- resistance coefficient, vector 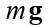 force of body weight of mass m, g - acceleration of free fall.
force of body weight of mass m, g - acceleration of free fall.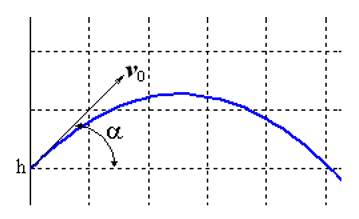
The peculiarity of this task is that the movement ends at an unknown moment of time when the body falls to the ground. If to designate
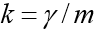 then in the coordinate form we have the system of equations:
then in the coordinate form we have the system of equations: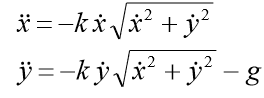
Initial conditions should be added to the system:
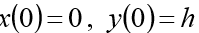 (h initial height),
(h initial height), 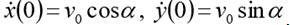 . Set
. Set 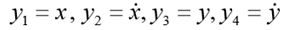 . Then the corresponding first order ODE system will take the form:
. Then the corresponding first order ODE system will take the form: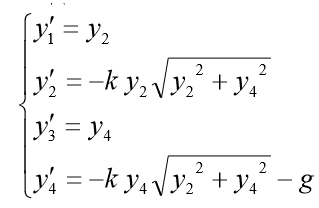
For the model problem we set
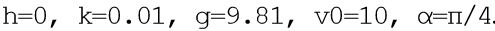 . Omitting a rather extensive description of the program, I will give only a listing from the comments to which, I think, the principle of its operation will be clear. The program added countdown time for comparative analysis.
. Omitting a rather extensive description of the program, I will give only a listing from the comments to which, I think, the principle of its operation will be clear. The program added countdown time for comparative analysis.Program listing
import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import time start = time.time() from scipy.integrate import ode ts = [ ] ys = [ ] FlightTime, Distance, Height =0,0,0 y4old=0 def fout(t, y):# global FlightTime, Distance, Height,y4old ts.append(t) ys.append(list(y.copy())) y1, y2, y3, y4 = y if y4*y4old<=0: # Height=y3 if y4<0 and y3<=0.0: # FlightTime=t Distance=y1 return -1 y4old=y4 # def f(t, y, k): # k g=9.81 y1, y2, y3, y4 = y return [y2,-k*y2*np.sqrt(y2**2+y4**2), y4,-k*y4*np.sqrt(y2**2+y4**2)-g] tmax=1.41 # alph=np.pi/4 # v0=10.0 # K=[0.1,0.2,0.3,0.5] # y0,t0=[0, v0*np.cos(alph), 0, v0*np.sin(alph)], 0 # ODE=ode(f) ODE.set_integrator('dopri5', max_step=0.01) ODE.set_solout(fout) fig, ax = plt.subplots() fig.set_facecolor('white') for k in K: # ts, ys = [ ],[ ] ODE.set_initial_value(y0, t0) # ODE.set_f_params(k) # k # f(t,y,k) ODE.integrate(tmax) # print('Flight time = %.4f Distance = %.4f Height =%.4f '% (FlightTime,Distance,Height)) Y=np.array(ys) plt.plot(Y[:,0],Y[:,2],linewidth=3,label='k=%.1f'% k) stop = time.time() plt.title(" \n ode dopri5 ") print (" : %f"%(stop-start)) plt.grid(True) plt.xlim(0,8) plt.ylim(-0.1,2) plt.legend(loc='best') plt.show() We get:
Flight time = 1.2316 Distance = 5.9829 Height = 1.8542
Flight time = 1.1016 Distance = 4.3830 Height = 1.5088
Flight time = 1.0197 Distance = 3.5265 Height = 1.2912
Flight time = 0.9068 Distance = 2.5842 Height = 1.0240
Time to model problem: 0.454787
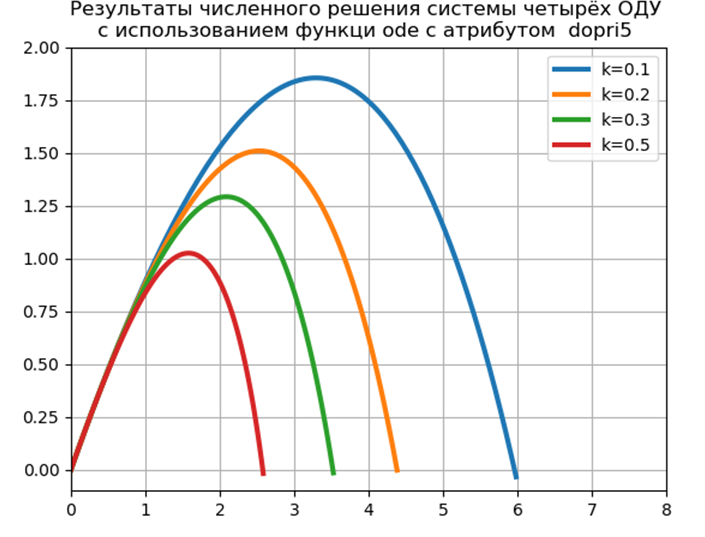
To implement the Python tools using the numerical solution of the CDS without using special modules, I have proposed and investigated the following function:
def increment(f, t, y, tau
k1=tau*f(t,y)
k2=tau*f(t+(1/4)*tau,y+(1/4)*k1)
k3 =tau *f(t+(3/8)*tau,y+(3/32)*k1+(9/32)*k2)
k4=tau*f(t+(12/13)*tau,y+(1932/2197)*k1-(7200/2197)*k2+(7296/2197)*k3)
k5=tau*f(t+tau,y+(439/216)*k1-8*k2+(3680/513)*k3 -(845/4104)*k4)
k6=tau*f(t+(1/2)*tau,y-(8/27)*k1+2*k2-(3544/2565)*k3 +(1859/4104)*k4-(11/40)*k5)
return (16/135)*k1+(6656/12825)*k3+(28561/56430)*k4-(9/50)*k5+(2/55)*k6The increment function (f, t, y, tau) provides the fifth order of the numerical solution method. The remaining features of the program can be found in the following listing:
Program listing
from numpy import* import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import time start = time.time() def rungeKutta(f, to, yo, tEnd, tau): def increment(f, t, y, tau):# ——. k1=tau*f(t,y) k2=tau*f(t+(1/4)*tau,y+(1/4)*k1) k3 =tau *f(t+(3/8)*tau,y+(3/32)*k1+(9/32)*k2) k4=tau*f(t+(12/13)*tau,y+(1932/2197)*k1-(7200/2197)*k2+(7296/2197)*k3) k5=tau*f(t+tau,y+(439/216)*k1-8*k2+(3680/513)*k3 -(845/4104)*k4) k6=tau*f(t+(1/2)*tau,y-(8/27)*k1+2*k2-(3544/2565)*k3 +(1859/4104)*k4-(11/40)*k5) return (16/135)*k1+(6656/12825)*k3+(28561/56430)*k4-(9/50)*k5+(2/55)*k6 t = []# t y= []# y t.append(to)# t to y.append(yo)# y yo while to < tEnd:# t,y tau = min(tau, tEnd - to)# tau yo = yo + increment(f, to, yo, tau) # t0,y0 to = to + tau # t.append(to) # t y.append(yo) # y return array(t), array(y) def f(t, y): # f = zeros([4]) f[0]=y[1] f[1]=-k*y[1]*sqrt(y[1]**2+y[3]**2) f[2]=y[3] f[3]=-k*y[3]*sqrt(y[1]**2+y[3]**2) -g if y[3]<0 and y[2]<=0.0: # return -1 return f to = 0# tEnd = 1.41# alph=pi/4# v0=10.0 # K=[0.1,0.2,0.3,0.5]# g=9.81 yo = array([0.,v0*cos(alph),0.,v0*sin(alph)]) # tau =0.01# for i in K: # k=i t, y = rungeKutta(f, to, yo, tEnd, tau) y1=array([i[0] for i in y]) # y y3=array([i[2] for i in y]) # "" s,h,t plt.plot(y1,y3,linewidth=2,label='k=%.1f h=%.3f s=%.2f t=%s' % (k,max(y3),max(y1),round(t[list(y1).index(max(y1))],3))) stop = time.time() plt.title(" \n Python\n —— ") print (" : %f"%(stop-start)) plt.xlabel(' h') plt.ylabel(' s') plt.legend(loc='best') plt.xlim(0,8) plt.ylim(-0.1,2) plt.grid(True) plt.show() We get:
Time to model problem: 0.259927
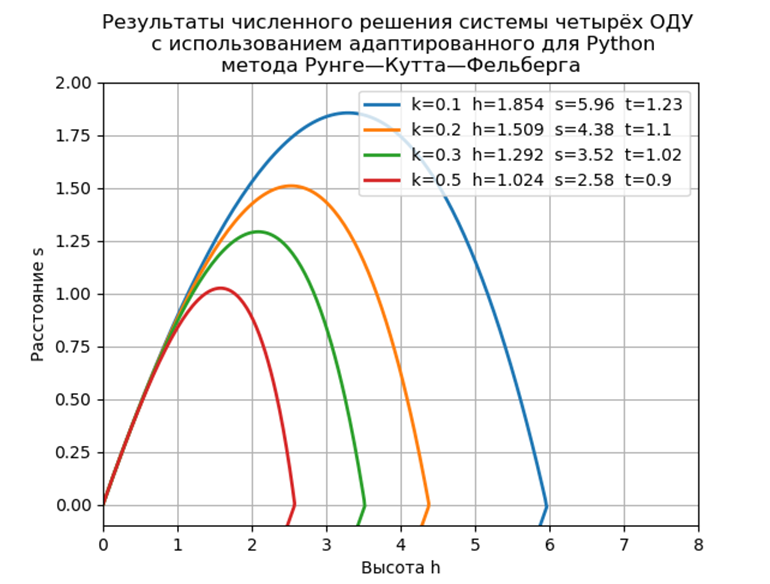
Conclusion
The proposed software implementation of the model problem without the use of special modules is almost twice as fast as with the ode function, but we must not forget that ode has a higher accuracy of the numerical solution and the possibility of choosing a solution method.
Solution of a boundary value problem with continuously separated boundary conditions
Let us give an example of some concrete boundary value problem with streamlined separated boundary conditions:
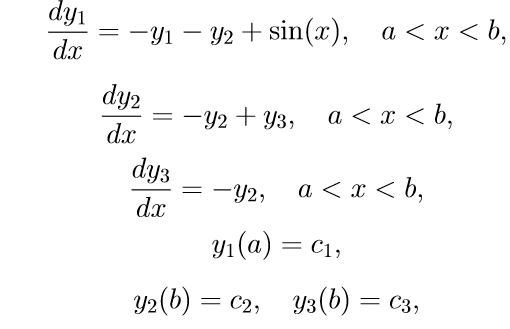 (eleven)
(eleven)To solve problem (11), we use the following algorithm:
1. Solve the first three inhomogeneous equations of system (11) with initial conditions

We introduce the notation for solving the Cauchy problem:
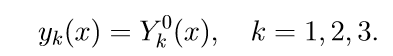
2. Solve the first three homogeneous equations of system (11) with initial conditions
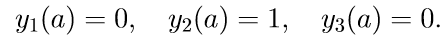
We introduce the notation for solving the Cauchy problem:
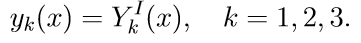
3. Solve the first three homogeneous equations of system (11) with initial conditions
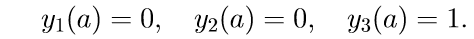
We introduce the notation for solving the Cauchy problem:

4. The general solution of the boundary value problem (11) with the help of solutions of Cauchy problems is written in the form of a linear combination of solutions:
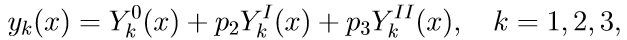
where p2, p3 are some unknown parameters.
5. To determine the parameters p2 and p3, we use the boundary conditions of the last two equations (11), that is, the conditions for x = b. Substituting, we obtain a system of linear equations for the unknowns p2, p3:
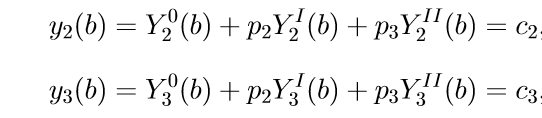 (12)
(12)Solving (12), we obtain the relations for p2, p3.
Using the above algorithm, using the Runge – Kutt – Felberg method, we obtain the following program:
Program listing
# from numpy import* import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import matplotlib.font_manager as fm,os import matplotlib.patches as mpatches import matplotlib.lines as mlines from scipy.integrate import odeint from scipy import linalg import time start = time.time() c1 = 1.0 c2 = 0.8 c3 = 0.5 a =0.0 b = 1.0 nn =100 initial_state_0 =array( [a, c1, 0.0, 0.0]) initial_state_I =array( [a, 0.0, 1.0, 0.0]) initial_state_II =array( [a, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0]) to = a tEnd =b N = int(nn) tau=(ba)/N def rungeKutta(f, to, yo, tEnd, tau): def increment(f, t, y, tau): k1=tau*f(t,y) k2=tau*f(t+(1/4)*tau,y+(1/4)*k1) k3 =tau *f(t+(3/8)*tau,y+(3/32)*k1+(9/32)*k2) k4=tau*f(t+(12/13)*tau,y+(1932/2197)*k1-(7200/2197)*k2+(7296/2197)*k3) k5=tau*f(t+tau,y+(439/216)*k1-8*k2+(3680/513)*k3 -(845/4104)*k4) k6=tau*f(t+(1/2)*tau,y-(8/27)*k1+2*k2-(3544/2565)*k3 +(1859/4104)*k4-(11/40)*k5) return (16/135)*k1+(6656/12825)*k3+(28561/56430)*k4-(9/50)*k5+(2/55)*k6 t = [] y= [] t.append(to) y.append(yo) while to < tEnd: tau = min(tau, tEnd - to) yo = yo + increment(f, to, yo, tau) to = to + tau t.append(to) y.append(yo) return array(t), array(y) def f(t, y): global theta f = zeros([4]) f[0] = 1 f[1] = -y [1]-y[2] +theta* sin(y[0]) f[2] = -y[2]+y[3] f[3] = -y[2] return f # -- theta = 1 theta = 1.0 yo =initial_state_0 t, y = rungeKutta(f, to, yo, tEnd, tau) y2=[i[2] for i in y] y3=[i[3] for i in y] # # Y20 = Y2(b), Y30 = Y3(b) Y20 = y2[N-1] Y30 = y3[N-1] # -- theta = 0, I theta = 0.0 yo= initial_state_I t, y = rungeKutta(f, to, yo, tEnd, tau) y2=[i[2] for i in y] y3=[i[3] for i in y] # # Y21= Y2(b), Y31 = Y3(b) Y21= y2[N-1] Y31 = y3[N-1] # -- theta = 0, II theta = 0.0 yo =initial_state_II t, y = rungeKutta(f, to, yo, tEnd, tau) y2=[i[2] for i in y] y3=[i[3] for i in y] # # Y211= Y2(b), Y311 = Y3(b) Y211= y2[N-1] Y311 = y3[N-1] # # p2, p3 b1 = c2 - Y20 b2 = c3 - Y30 A = array([[Y21, Y211], [Y31, Y311]]) bb = array([[b1], [b2]]) # p2, p3 = linalg.solve(A, bb) # # , theta = 1 theta = 1.0 yo = array([a, c1, p2, p3]) t, y = rungeKutta(f, to, yo, tEnd, tau) y0=[i[0] for i in y] y1=[i[1] for i in y] y2=[i[2] for i in y] y3=[i[3] for i in y] # print('y0[0]=', y0[0]) print('y1[0]=', y1[0]) print('y2[0]=', y2[0]) print('y3[0]=', y3[0]) print('y0[N-1]=', y0[N-1]) print('y1[N-1]=', y1[N-1]) print('y2[N-1]=', y2[N-1]) print('y3[N-1]=', y3[N-1]) j = N xx = y0[:j] yy1 = y1[:j] yy2 = y2[:j] yy3 = y3[:j] stop = time.time() print (" : %f"%(stop-start)) plt.subplot(2, 1, 1) plt.plot([a], [c1], 'ro') plt.plot([b], [c2], 'go') plt.plot([b], [c3], 'bo') plt.plot(xx, yy1, color='r') # plt.plot(xx, yy2, color='g') # plt.plot(xx, yy3, color='b') # plt.xlabel(r'$x$') # x TeX plt.ylabel(r'$y_k(x)$') # y TeX plt.title(r' ', color='blue') plt.grid(True) # patch_y1 = mpatches.Patch(color='red', label='$y_1$') patch_y2 = mpatches.Patch(color='green', label='$y_2$') patch_y3 = mpatches.Patch(color='blue', label='$y_3$') plt.legend(handles=[patch_y1, patch_y2, patch_y3]) ymin, ymax = plt.ylim() xmin, xmax = plt.xlim() plt.subplot(2, 1, 2) font = {'family': 'serif', 'color': 'blue', 'weight': 'normal', 'size': 12, } plt.text(0.2, 0.8, r'$\frac{dy_1}{dx}= - y_1 - y_2 + \sin(x),$', fontdict=font) plt.text(0.2, 0.6,r'$\frac{dy_2}{dx}= - y_1 + y_3,$', fontdict=font) plt.text(0.2, 0.4, r'$\frac{dy_3}{dx}= - y_2 - y_2,$', fontdict=font) plt.text(0.2, 0.2, r'$y_1(a)=c_1, ' r'\quad y_2(b)=c_2, \quad y_3(b)=c_3.$', fontdict=font) plt.subplots_adjust(left=0.15) plt.show() We get:
y0 [0] = 0.0
y1 [0] = 1.0
y2 [0] = 0.7156448588231397
y3 [0] = 1.324566562303714
y0 [N-1] = 0.9900000000000007
y1 [N-1] = 0.1747719838716767
y2 [N-1] = 0.8
y3 [N-1] = 0.50000000000001
Time to model problem: 0.070878
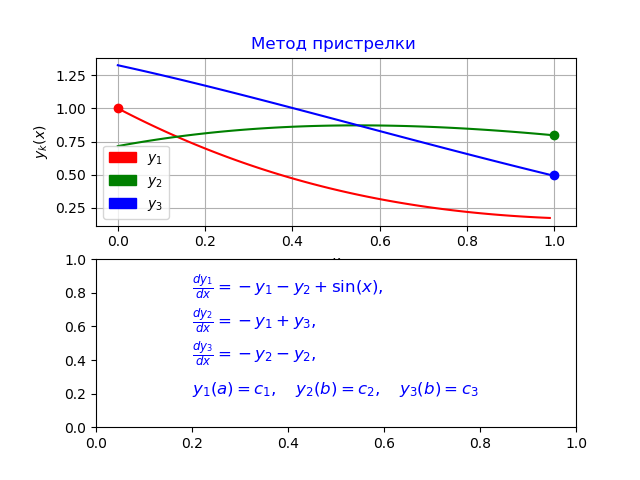
Conclusion
The program I developed differs from the smaller error given in [3], which confirms the comparative analysis of the odeint function given at the beginning of the article with the Runge – Kutt – Feelberg method implemented in Python.
References:
1. Numerical solution of mathematical models of objects defined by composite systems of differential equations.
2. Introduction to Scientific Python.
3. N.M. Polyakova, E.V. Shiryaeva Python 3. Creating a graphical user interface (by the example of solving the boundary-value problem for linear ordinary differential equations using the method of adjustment). Rostov-on-Don 2017.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/418139/
All Articles