[bookmark] Cheat system administrator for Linux network tools
The daily tasks of system administrators include working with networks and with equipment connected to them. Often, the role of the administrator’s workplace is played by the computer on which any Linux distribution is installed. Linux utilities and commands, which will be discussed in the material that we are translating today, include a list of tools of varying complexity - from simple to advanced, which are designed to solve a wide range of network management and network troubleshooting tasks.

In some of the examples considered here, you will come across the abbreviation
The
')
Ping, in addition, can be used to find out the IP addresses of sites based on their names. Here's what it looks like.
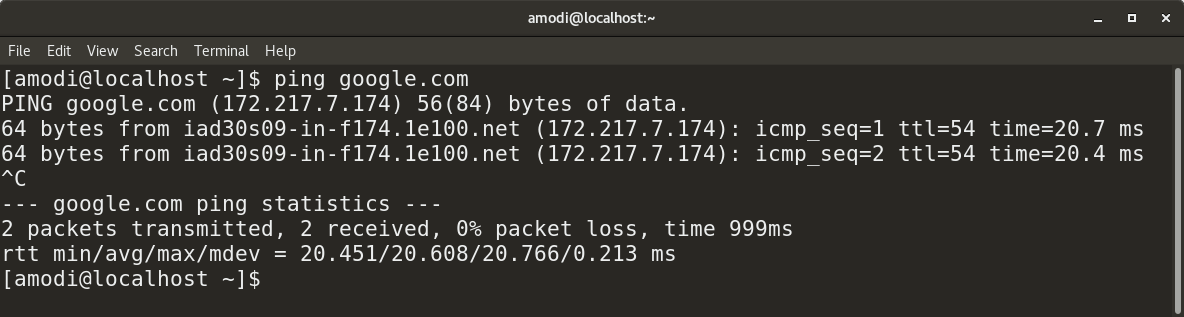
Use ping to find out the site’s IP address by its name.
The
To organize a Telnet session with another computer, use the following command:
This command allows you to collect information about the network and is used in the course of searching and correcting network problems, is used to verify data on the operation of interfaces and ports, to study the routing tables, to study information on the operation of protocols. This team must be present in the arsenal of the system administrator.
To get a list of all ports that are in listening mode, use the following command:
The following command displays information about all ports. In order to be limited to TCP ports, you need to use the
To view the routing tables, use the following command:
Here is the result of executing this command.
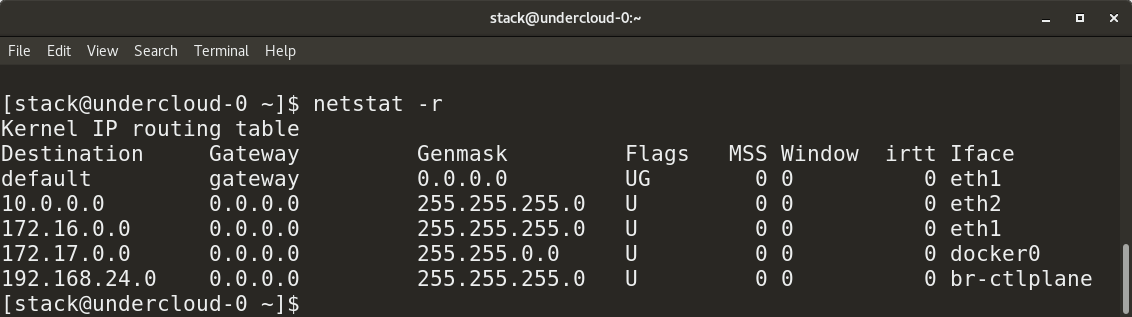
Routing Table Information
Here is a variant of this command that displays protocol statistics:
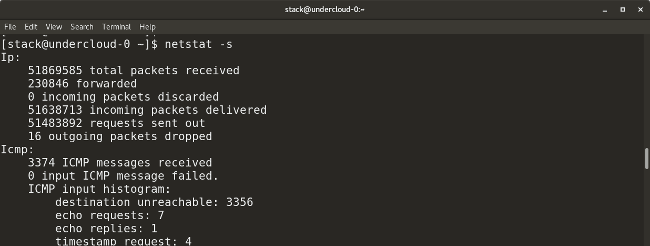
Protocol statistics
The following
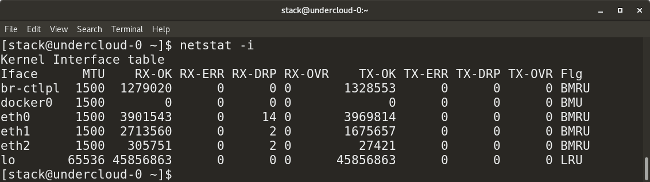
Data on sent and received packets
The
Here's how to use
So you can display information on a specific interface:
The following command call option allows you to check the device’s connection to the network:
Examples of using nmcli
This command allows you to disable the specified interface:
And this allows you to enable the interface:
Here is an example of a command that adds a VLAN interface with a given VLAN number, IP address and gateway to the specified interface:
There are many commands that can be used to check the routing rules and their settings. Consider the most useful ones.
The following command shows all the current routes configured for the corresponding interfaces:
Routes configured for interfaces
This command allows you to add a default gateway to the routing table:
The following command adds a new network route to the routing table. There are many other parameters that allow you to perform operations such as adding a route and a gateway, used by default, and so on.
With this command, you can delete an entry for a given route from the routing table:
Here are some examples of using the
Using the route command
Here is the command that is used to display the current neighbor table. In addition, it can be used to add, modify, or delete information about neighbors:
Let's look at examples of its use.
Data received using the ip neighbor command
Here is the
Ip neigh details
The
Here is an example of her call.
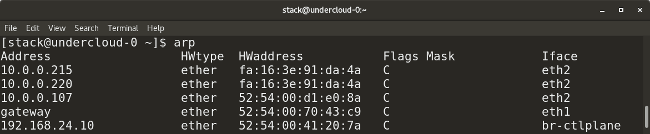
Calling the arp command
Linux gives the administrator a variety of tools for capturing and analyzing packets. Among them, for example,
This command shows, in real time, packets from a given interface:
Packages can be saved to a file using the
Here is an example of using
Using tcpdump
The following command variant is used to capture packets coming from the specified IP source system:
So you can capture the packets going to the specified address of the receiving system:
Here is an example of using
Here is how
The
The following command displays all existing
This command deletes all existing rules:
The following commands allow traffic from the specified port number to the specified interface:
The following commands allow loopback access to the system:
The
The following command displays the IP addresses of your DNS server in the Server field, and, below, gives the IP address of the desired site:
This command shows all available entries for a given website or domain:
Here is a set of commands and a list of important files used to identify network problems.
In this small cheat sheet, we talked about Linux networking tools for system administrators. We hope you find these tools useful.
Dear readers! What do you use to administer networks and to determine the causes of network problems?


In some of the examples considered here, you will come across the abbreviation
<fqdn> (fully qualified domain name). server-name.company.com him, replace him, depending on the circumstances, with the address of the site or server of interest, for example, with something like server-name.company.com .Ping
The
ping utility, as can be judged by its name, is used to test communication between network nodes, between the computer on which it is started, and another system. This utility uses the ICMP protocol, sending pings that are answered by the remote system that receives them. Using ping , in addition, is a good way to check network connectivity as the first step in troubleshooting a network. The ping command can be used with IPv4 and IPv6 addresses. Here you can read details about IP-addresses and about working with them.')
▍Examples
IPv4: ping <ip address>/<fqdn> IPv6: ping6 <ip address>/<fqdn> Ping, in addition, can be used to find out the IP addresses of sites based on their names. Here's what it looks like.

Use ping to find out the site’s IP address by its name.
Traceroute
Traceroute is a nice utility that allows you to explore data transfer routes between computers. While the ping command seeks to establish whether it is possible to establish a connection between two network nodes, traceroute gives information about the IP addresses of routers through which data passes from your system to the destination, for example, to a website or server. The traceroute command is usually applied in the second step of network diagnostics, after the ping command.▍Example
traceroute <ip address>/<fqdn> Telnet
The
telnet utility allows you to connect to a remote computer using the Telnet protocol and interact with it using the appropriate commands.▍Example
To organize a Telnet session with another computer, use the following command:
telnet <ip address>/<fqdn> Netstat
This command allows you to collect information about the network and is used in the course of searching and correcting network problems, is used to verify data on the operation of interfaces and ports, to study the routing tables, to study information on the operation of protocols. This team must be present in the arsenal of the system administrator.
▍Examples
To get a list of all ports that are in listening mode, use the following command:
netstat -l The following command displays information about all ports. In order to be limited to TCP ports, you need to use the
-at key, in order to get data about UDP ports, use the -au key. netstat -a To view the routing tables, use the following command:
netstat -r Here is the result of executing this command.

Routing Table Information
Here is a variant of this command that displays protocol statistics:
netstat -s 
Protocol statistics
The following
netstat call option allows you to find out information about packets sent and received (transmission / receive, TX / RX) on each interface:
Data on sent and received packets
Nmcli
The
nmcli utility nmcli great for managing network connections, for making settings and for solving other similar tasks. With it, you can control the program NetworkManager and modify the network parameters of various devices.▍Examples
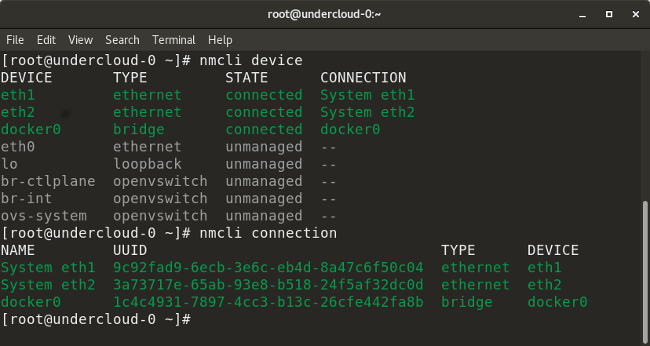
Here's how to use
nmcli to list the network interfaces: nmcli device So you can display information on a specific interface:
nmcli device show <interface> The following command call option allows you to check the device’s connection to the network:
nmcli connection 
Examples of using nmcli
This command allows you to disable the specified interface:
nmcli connection down <interface> And this allows you to enable the interface:
nmcli connection up <interface> Here is an example of a command that adds a VLAN interface with a given VLAN number, IP address and gateway to the specified interface:
nmcli con add type vlan con-name <connection-name> dev <interface> id <vlan-number> ipv4 <ip/cidr> gw4 <gateway-ip> Routing
There are many commands that can be used to check the routing rules and their settings. Consider the most useful ones.
▍Examples
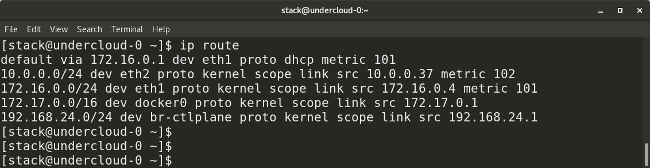
The following command shows all the current routes configured for the corresponding interfaces:
ip route 
Routes configured for interfaces
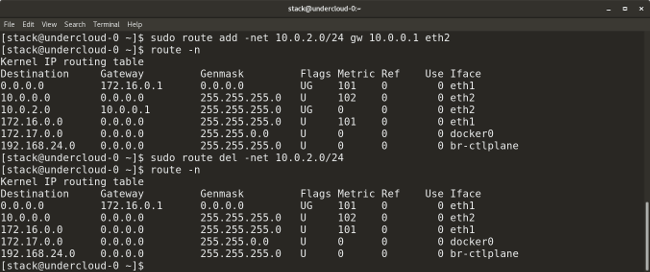
This command allows you to add a default gateway to the routing table:
route add default gw <gateway-ip> The following command adds a new network route to the routing table. There are many other parameters that allow you to perform operations such as adding a route and a gateway, used by default, and so on.
route add -net <network ip/cidr> gw <gateway ip> <interface> With this command, you can delete an entry for a given route from the routing table:
route del -net <network ip/cidr> Here are some examples of using the
route command.
Using the route command
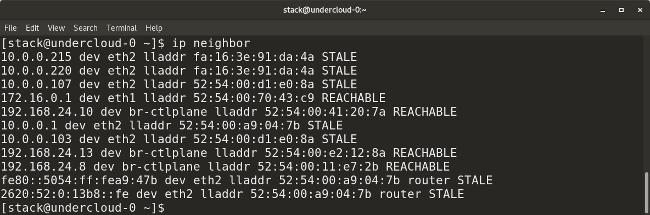
Here is the command that is used to display the current neighbor table. In addition, it can be used to add, modify, or delete information about neighbors:
ip neighbor Let's look at examples of its use.

Data received using the ip neighbor command
Here is the
ip neigh
Ip neigh details
The
arp command (ARP is an abbreviation for Address Resolution Protocol, addressing protocol) is similar to ip neighbor . The arp utility displays information about the compliance of IP addresses with MAC addresses. Here is how to use it: arp Here is an example of her call.

Calling the arp command
Tcpdump and Wireshark
Linux gives the administrator a variety of tools for capturing and analyzing packets. Among them, for example,
tcpdump , wireshark , tshark , and others. They are used to capture network traffic in packets transmitted by the system or in packets received by it. This makes them a very valuable administrator tool to help determine the causes of various network problems. Those who prefer the command line to all other ways to communicate with computers will love tcpdump . For those who love graphical interfaces, wireshark can be recommended - a great tool for capturing and analyzing packets. The tcpdump utility is a Linux tool for capturing network traffic. It can be used to capture and output traffic with filtering by ports, protocols, and other features.▍Examples
This command shows, in real time, packets from a given interface:
tcpdump -i <interface-name> Packages can be saved to a file using the
-w flag and specifying the file name: tcpdump -w <output-file.> -i <interface-name> Here is an example of using
tcpdump .
Using tcpdump
The following command variant is used to capture packets coming from the specified IP source system:
tcpdump -i <interface> src <source-ip> So you can capture the packets going to the specified address of the receiving system:
tcpdump -i <interface> dst <destination-ip> Here is an example of using
tcpdump to capture packets for a given port number, for example, it can be port 53, 80, 8080, and so on: tcpdump -i <interface> port <port-number> Here is how
tcpdump capture packets of a given protocol, such as TCP, UDP, or others: tcpdump -i <interface> <protocol> Iptables
The
iptables utility is similar to a firewall, it supports packet filtering, which allows you to manage traffic by passing or blocking it. The range of possibilities of this utility is huge. Consider a few of the most common options for its use.▍Examples
The following command displays all existing
iptables rules: iptables -L This command deletes all existing rules:
iptables -F The following commands allow traffic from the specified port number to the specified interface:
iptables -A INPUT -i <interface> -p tcp –dport <port-number> -m state –state NEW,ESTABLISHED -j ACCEPT iptables -A OUTPUT -o <interface> -p tcp -sport <port-number> -m state – state ESTABLISHED -j ACCEPT The following commands allow loopback access to the system:
iptables -A INPUT -i lo -j ACCEPT iptables -A OUTPUT -o lo -j ACCEPT Nslookup
The
nslookup tool is used to get information about assigning IP addresses to network resources. It can also be used to obtain information from DNS servers, for example, such as all DNS records for a certain web site (we will consider an example below). The nslookup is similar to the dig (Domain Information Groper) utility.▍Examples
The following command displays the IP addresses of your DNS server in the Server field, and, below, gives the IP address of the desired site:
nslookup <website-name.com> This command shows all available entries for a given website or domain:
nslookup -type=any <website-name.com> Troubleshooting
Here is a set of commands and a list of important files used to identify network problems.
▍Examples
ssis a utility for displaying statistical information about sockets.nmap <ip-address>- the name of this command is short for Network Mapper. It scans network ports, detects hosts, discovers MAC addresses and performs many other tasks.ip addr/ifconfig -a- this command provides information about IP-addresses and other data on all interfaces of the system.ssh -vvv user@<ip/domain>- this command allows you to connect via SSH to another computer using the specified IP address or computer's domain name and username. The-vvvflag allows-vvvto get detailed information about what is happening.ethtool -S <interface>- this command allows you to display statistical information on the specified interface.ifup <interface>- this command enables the specified interface.ifdown <interface>- this command disables the specified interface.systemctl restart network- with this command you can restart the system network subsystem./etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/<interface-name>—This is the interface configuration file used to specify the IP address, network, gateway, and other parameters for a given interface. Here you can set the interface to use the DHCP mode./etc/hosts- this file contains information on the correspondence of hosts or domains to IP addresses configured by the administrator./etc/resolv.conf- DNS settings are stored in this file./etc/ntp.conf- this file stores the NTP settings.
Results
In this small cheat sheet, we talked about Linux networking tools for system administrators. We hope you find these tools useful.
Dear readers! What do you use to administer networks and to determine the causes of network problems?

Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/417485/
All Articles