Gartner: Highlights on the IaaS Market in 2018

In May, the 2018 Gartner Magic Quadrant appeared for the IaaS market: Magic Quadrant for Cloud Infrastructure as a Service, Worldwide . The Mail.Ru Cloud Solutions team has done a squeeze on the most interesting topics that we share with you - maybe someone will be useful. How does business use the clouds and what does it expect? What are the trends of the year in the cloud services market? What does the “magic quadrant” look like today for IaaS? In the final part of the post, we share our vision of the situation in the domestic market.
- What is IaaS
- The effect of the introduction of IaaS
- Technological trends
- General trends in the IaaS market
- What to consider users when choosing IaaS
- What should IaaS providers take into account in their strategy?
- Magic quadrant
- On the situation in the Russian cloud market
What is IaaS
Gartner defines IaaS as a standardized service, within which the user gets access to the provider's infrastructure resources in the required amount (on-demand). This is done through automated self-service, without manual actions of the provider’s employees. The minimum set of services for IaaS are computing resources (VMs), storage, and management tools for network connections.
As part of the IaaS, the provider manages the data center, hardware, and virtualization. Everything that is above the level of the hypervisor — the OS, middleware, and applications — is managed either by the user or the additional managed service. Sometimes the managed service is provided by the same provider as IaaS, sometimes by a third party.
')
The effect of the introduction of IaaS
IaaS is a digital transformation trigger . Many companies view IaaS simply as “leased virtualization”, an opportunity to save themselves from the capital costs of a private cloud or their own data center. But the direct transfer of local virtualized infrastructure to the public cloud rarely gives the desired effect to the business. This provides savings, limited improvement in reliability and security, but the transfer itself does not reveal all the possibilities of the cloud.
Digital transformation begins when business process optimization is added to the port through virtual automation possible in the public cloud. Automation does not affect the applications themselves, ported from a private cloud, but changes the approach to managing IT-operations.
Digital transformation brings to IT operations:
- Hyper-scalability: a change in system capacity along with a change in the need for its computing resources, memory, network resources, and storages.
- Reduced time to market for new products.
- Instant connection of PaaS and other services in any volume. Thanks to automation, setting up new services does not require the involvement of expensive experts and reduces dependence on integrator services.
- Reducing the cost of ownership of infrastructure dozens of times, reducing operating costs by automating the provision of services.
IaaS does not necessarily reduce costs . Planning to implement IaaS, many initially expect to reduce costs. But in the end, most companies are implementing IaaS for the sake of greater business flexibility or access to new infrastructure opportunities offered by digital transformation.
IaaS allows you to significantly save on the provision of short-term or seasonal peak needs, batch-computing, spare capacity for disaster recovery. IaaS is also beneficial for companies that cannot invest in infrastructure, for example, startups. For large companies with their own data center, a mature virtual infrastructure, an efficient IT team and a high level of automation, implementing IaaS for already established business processes may even increase their value.
In general, the less efficient the business processes, the greater the savings that the cloud will provide. At the same time, the largest providers are constantly reducing the cost, and access to automated managed services (MSP) significantly reduces the cost of infrastructure management. The benefits of using the cloud will only grow.
Public cloud providers offer higher security than private data centers . Although using a public cloud, many security settings fall on the user's shoulders, at the platform level most major IaaS providers offer a high level of protection. Transparent encryption of LAN, WAN and storage will soon become the standard for cloud-based IaaS as protection against the latest cyber attacks. Gartner strongly recommends implementing DevSecOps approaches for managing security in an IaaS environment.
Technological trends
The advantages of serverless computing are the easiest to get in the cloud . Serverless computing solutions free developers from many routine management procedures and reduce operational costs. The spectrum of serverless solutions grows, FaaS (function as a service, or fPaaS) appeared , for example, AWS Lambda and Azure Functions. Features serverless computing contribute to the transition of flexible IT-companies in the public cloud.
IaaS-providers offer solutions for microservice infrastructure . Providers develop microservice architecture creation tools integrated into the IaaS platform: microservice execution environment, development framework, life cycle automation technology. A key aspect for the development of microservices is a managed container system. It includes container IaaS, high-level aPaaS (service of development environments and applications) and FaaS. Most microservice technologies are immature and are among the most innovative features offered by cloud providers.
General trends in the IaaS market
Blurring the boundaries of IaaS and PaaS
IaaS providers are increasingly offering software infrastructure services such as PaaS, FaaS, container orchestration (for example, Docker) and middleware services. Often, neither the user nor the provider makes a distinction between PaaS and IaaS services: users simply select a combination of services that solves their problems.
To make it easy for the user to connect new services, providers should offer a common catalog of all services, tools for managing them with common identification and access control, simple connectivity of services with low latency, common for services security management.
Multi-cloud
Most companies follow a multi-cloud strategy . Typically, companies choose one strategic IaaS provider, sometimes two. For individual applications, companies may attract additional "tactical" providers. Using multiple clouds gives a wider choice of solutions. But very few people build a true multi-cloud infrastructure in which one application or task runs on several strategic cloud providers: such architectures are extremely complex.
It's hard for companies to manage multi-cloud IaaS . With the simultaneous use of multiple clouds, it is difficult to create standardized policies and procedures, to start routine processes, organize general management, and optimize costs. Managing all cloud resources “from one console”, seamless movement between IaaS platforms, seamless adjustment of local cloud resources (cloudbursting) are unlikely to ever become possible, even when IaaS providers in multi-cloud use the same cloud infrastructure framework (CIF, for example , OpenStack or VMWare), the same open API and general application container technology. Providers' statements about the openness of their ecosystem are irrelevant to the real portability of services, and the no vendor lock-in topic is just a marketing hyip.
Third-party tools are often used to control the cloud, especially multi-cloud . Most IaaS-intensive companies lack integrated management capabilities. Additional multi-cloud management tools support integrated cost, identification and access management; monitoring security and compliance; network management.
IaaS market consolidation and local providers
Since 2015, AWS and Microsoft Azure provide most of the demand in the IaaS market . Considering PaaS, their share is even higher. Moreover, AWS is many times larger than Azure, and the market structure is even more skewed. This makes life difficult for other providers and reduces the confidence of their customers.
Chinese providers have entered the world market, but their success is limited . They often replicate the functionality of global leaders. This led to success in the home region, but they did not become leaders in the global market. Their clients are companies with a business in China and its sphere of economic influence.
The rest of the IaaS market is highly fragmented . In the shadow of the leaders - thousands of IaaS providers. Some of them are managed hosting providers or managed services of local importance, for which IaaS is just an infrastructure platform for building your business. Others offer managed services on foreign IaaS, and others provide virtual private server (VPS) hosting for small businesses. These providers serve local markets. Usually they offer limited functionality and do not have a developed partner ecosystem.
Local providers are in demand, but their capabilities are limited . Companies prefer to keep data in the region where they will be used - for reasons of network delays. In addition, companies outside the United States are forced to acquire IaaS from local providers, because this is required by the local regulator. I recall recent revelations about the access of foreign intelligence services to private data.
Unfortunately, many local providers do not have global capabilities, most of them are focused on small businesses, and not on large ones. At the same time, data storage in the home region does not guarantee protection from surveillance both from inside the region and from the outside. As a result, companies that are denied access to global providers receive only basic IaaS functionality, and this hinders the implementation of IaaS in the region. According to the observations of the Mail.Ru Cloud Solutions team, Russian providers are trying to change the situation and are expanding the range of IaaS- and PaaS-level services.
IaaS competition with private clouds
Companies prefer single-tenant public cloud IaaS, rather than hosted private cloud IaaS . IaaS-providers introduce the ability to create instances and repositories in single tenant mode. This allows many users to comply with the requirements of the regulator or software licenses that require exactly this mode of use. Public cloud IaaS (even in single tenant mode) usually offers much more features than hosted private IaaS. Many users choose the single-tenant public cloud IaaS configuration, or supplement the public cloud IaaS with colocation equipment. As a result, few hosted private cloud IaaS providers succeed in competition with the public cloud.
Private IaaS-cloud in its own data center is beneficial mainly due to additional add-ons . Most companies that have built a private IaaS cloud in their own data center have achieved only limited success. They have to go further: strengthen the virtualized infrastructure with additional automation, create the container infrastructure, deploy PaaS frameworks and buy private PaaS, and finally switch to a public cloud. It is not by chance that private IaaS providers also offer private PaaS as an add-on, and many customers acquire them.
What to consider users when choosing IaaS
IaaS offers are not equivalent . IaaS-services, similar at the level of functions, are differently implemented by different providers, provide different availability, performance and security, have different costs. Buyer should take into account the risks of vendor lock-in and portability of applications - just in case you have to move to another service in the future.
Choosing IaaS, consider what additional services are available on its base . All providers offer similar basic IaaS functionality as a service: computing, storage, and software-defined network connections. Significant functional differences begin at the level of additional services that providers offer on top of IaaS: middleware, DBaaS, various PaaS, DevOps-oriented services.
Carefully evaluate the new providers . In 2016 and 2017, new and heavily modified IaaS platforms appeared on the market, and in 2018 more are expected. Many of them are services with minimalist functionality, low reliability and no support ecosystem. New providers hunt for new users, giving generous discounts. It looks attractive, but if you decide to contact such a provider, carefully evaluate its reliability and level of support, study the customer feedback from this provider with similar requirements.
What should IaaS providers take into account in their strategy?
The main generator of IaaS values is the management and development services integrated into the IaaS platform . When a user can connect services that are integrated into the IaaS platform, it is more convenient than non-integrated solutions from different providers, which have to be integrated independently. Therefore, IaaS-providers will only expand the range of such services, including software infrastructure and PaaS.
Users are counting on a powerful partner ecosystem that grows around the IaaS platform . The partner ecosystem includes:
- third-party IaaS applications (ISVs);
- tools integrated into the IaaS platform via an API, especially IT management tools (ITOM) and DevOps;
- automated professional and expert services that support migration, application integration, IaaS-based development;
- assistance of local partners, especially at the level of professional and managed services.
The API forms the basis of the partner ecosystem . The ability to access IaaS through the API allows you to create integrated into IaaS applications and management tools, tools for integrating multi-cloud environments. Contrary to this logic, the current market is moving away from open APIs that create a partner ecosystem, such as OpenStack, in the direction of proprietary APIs. One of the side effects of the partner ecosystem is increasing the vendor lock-in risk for users, because applications are integrated with a specific middleware and IaaS environment.
Introducing new hyper-scalable integrated IaaS-PaaS to the market is difficult . Providers who have fallen into the “magic quadrant” of 2018 are either already offering or are going to bring to the market a hyper-scalable integrated IaaS-PaaS. Entering this market requires huge initial investment in development and infrastructure for the years ahead, deep technical expertise and the ability to build an ecosystem of support. At the same time, partner companies prefer to work with market leaders. When introducing a new supply to the market, the provider risks getting stuck in a narrow niche.
Companies often choose clouds from providers whose applications they already use . For example, a company that uses Microsoft’s developer and middleware tools will surely choose Microsoft Azure cloud as the medium for these applications. The reverse is also true - companies are building an application deployment strategy based on the capabilities of the cloud provider already involved.
For narrow scenarios, specialized IaaS are well suited . Providers who create solutions for narrow scenarios can thrive in their niche. They usually offer only basic IaaS functionality, but specially tailored for targeted scenarios and complemented with specific features. Such an approach can single out a provider in the market and conquer users in separate scenarios, even when these users already use another strategic provider for more general scenarios.
Magic quadrant
What new trends are reflected in the “magic quadrant” for IaaS 2018?
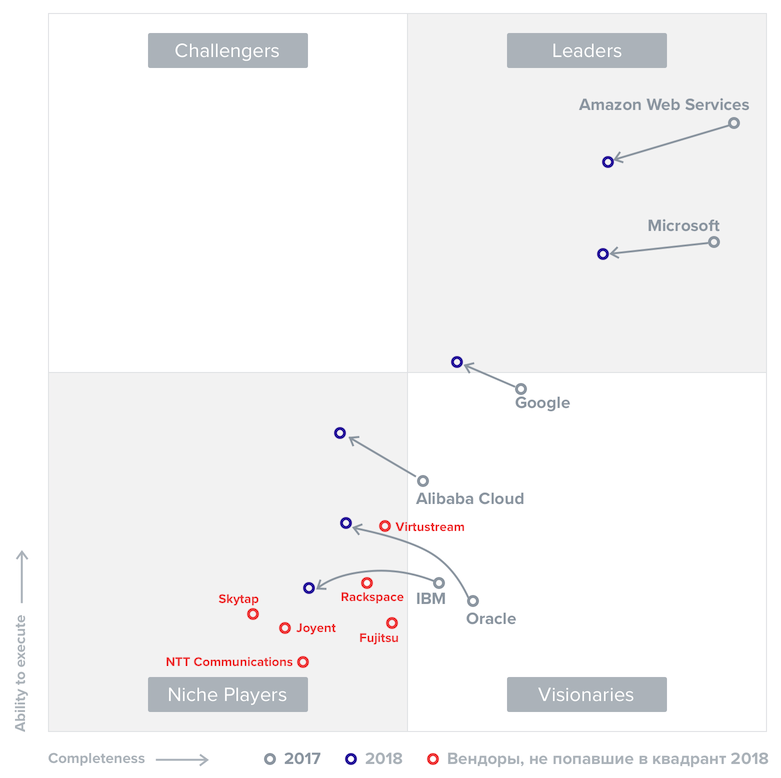
Magic quadrant: IaaS. Changes for the year (May 2018 vs June 2017)
In 2018, the “magic quadrant” included only six IaaS providers. This is eight less than last year: CenturyLink, Fujitsu, Interoute, Joyent, Rackspace, NTT Communications, Skytap, Virtustream are excluded. The reduction reflects market consolidation and rising customer expectations, which Gartner reflected in the more stringent criteria for inclusion in the "magic quadrant."
In 2018, when choosing strategic IaaS-providers, Gartner customers pay attention to the globality of service provision:
- IaaS should be available as a standalone service, without the need to purchase additional services.
- The provider must be one of the top global IaaS providers.
- IaaS should be provided globally (outside of your home region), with the possibility of cashless payments, consolidated billing, with support and documentation in English.
In addition, customers expect technical maturity of providers, support for critical processes and large-scale workloads. Technical maturity implies:
- software defined computing capacity, storage and network;
- management tools, monitoring and autoscaling;
- hyper-scalable architecture, creating instances in real time, providing Docker containers in seconds;
- VM not less than 16 vCPU and 128 GB RAM;
- SLA not less than 99.9%;
- ensuring information security when expanding the company's data center resources to the cloud;
- support of many users and API keys, role-based access model.
On the situation in the Russian cloud market
The alignment that Gartner describes is reflected in our cloud services market. At the same time, the market has its own specifics:
PaaS source of large-scale savings . Russian companies are less and less outsourcing the construction and maintenance of critical business systems and are increasingly using PaaS services. As a result, the business gets off the “needles” of service companies and reduces the cost of ownership (TCO) by 2-3 times due to the fact that human expertise (which is expensive and does not scale well) is now completely replaced by automation.
SaaS - IaaS engine and PaaS . We see a growing need for software development companies (ISVs) for the ever increasing automation that the cloud platform should provide for solving the problems of creating SaaS services. For such companies, translating their classic SaaS applications not only increases business margins, but also greatly simplifies customer support, initial installation and centralized update of software versions. The increased degree of automation provided by IaaS and PaaS reduces the time-to-market and allows you to win in a competitive race.
Big business needs hybrid clouds . Banks, manufacturing and other large companies have complex processes, monolithic systems of many years ago. For them, the advantages of the cloud are fast scaling without tenders. Hybrid clouds are ideal for such companies. Companies are testing new products, technologies, markets in the cloud, and the old ones are keeping "at home". The second positive moment of “hybrids” is manifested when using multivendor clouds, when the company is not tied to a single contractor, can move resources between vendors without final binding and choose the optimal mode of using the cloud.
Cloud and integrators: competitors or partners? Cloud vendors transform the market of partners and integrators and create new niches where partner expertise is needed.
First, we need consulting in the field of migration to the cloud. Imagine a large company with strict uptime requirements. How to make a transition for her gradual, have time to test the load, take into account all the risks? The second question - companies need support to fully realize the potential of the cloud. It’s not enough to transfer the IT system to the cloud as it is;
We see a great demand for such services and are well aware of the importance of building a partner ecosystem. For a year or two, we expect the emergence of integrators adapted to this new niche, with cases and experience working with hybrids. Connecting consultants and integrators to support cloud solutions will give a significant boost to the cloud market as a whole.
The material was prepared by the team of the cloud platform Mail.Ru Cloud Solutions .
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/416987/
All Articles