Heating system of an apartment building. Likbez with examples
Hello! My name is Victor and this is my first post on Giktayms, please do not judge strictly. I myself am a web programmer in my life, but among other things, I am also a member of the board of housing cooperatives, and therefore I am actively engaged in housing and utilities issues. Housing and communal services in Russia got stuck in the 80s of the last century, although the utilities technologies had long gone ahead. If the community will not mind, I will periodically share with you practical ideas and information on the topic of housing and communal services, and what can be done to get the situation off the ground at least within your house.
In most of the homes of our vast Motherland, which, by the way, consists of permafrost by 2/3, heat comes from CHP plants to the apartments, and this is called the proud word “central heating”. We will talk about this today. The CHP heats the heat carrier through pipes, like through blood vessels, the whole city receives heat to your house: first, to the thermal node, which is usually located in the basement, and then to the batteries of your apartment. Giving up heat, the coolant cools down and through the so-called return flow, goes back to the CHP. By the way, as a rule, the coolant is ordinary water with the addition of additives that prevent deposits in the radiators and pipes.
Here, by the way, there is a very important nuance, which, as my practice has shown, even many plumbers do not suspect. In the thermal node there is an elevator unit, an invention of the 19th century, but alas, it is still widely used.
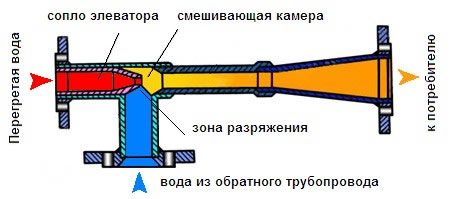
In the elevator assembly, there is a so-called nozzle, also known as a cone. Many plumbers believe that its task is simply to narrow the section so that less heat enters the house. Not really. Its task is to create a vacuum in which hot water from the supply pipeline at high speed, but with less pressure, begins to mix with the cooled return flow (with that water that has already passed through the radiators of your house) and due to this, the heating temperature is controlled at entering the house. Unfortunately, the nozzle is a primitive device, invented in the 19th century, and therefore mixing is always the same, regardless of what the temperature is +5 or -40 outside.
')
Many plumbers, when they receive complaints from residents, who have become cold bore the elevator nozzle above the standard section or even remove it completely. It is categorically not recommended to do this, since according to the schedule, the heat and power plant supplies the heat carrier in extreme cold under extremely high pressure with temperatures up to 130 degrees! If you run such heat into the apartment, and God forbid, it will burst a heating battery - the victims are guaranteed. By the way, it is for this reason that manufacturers of polypropylene pipes, so widely loved by Russian plumbers, are prohibited or not recommended to use them for central heating . Most polypropylene pipes hold a maximum of 90 degrees and something relatively long term. Look now at the pipes in your apartment and think.
Practically in each house there is already a special device called a thermal computer. Its task is to calculate how much heat your house has taken. Unfortunately, for historical reasons, when we had everything in common, and therefore no one’s, we are not accustomed to counting the cost of heating. In the meantime, today heating is the most expensive expense graph in bills. And due to the fact that historically, heating in our country, no one considered - this area is now the most bribe-intensive and extremely inefficient. And in order to somehow remedy the situation, everyone who is interested in what kind of numbers they are put in utility bills must remember and understand the main formula in the housing and utilities sector:
It is according to this school formula that the heat meter calculates the cost of heating for you: m is the mass of heat carrier that passed through your house in 1 hour, dT is the temperature difference between the flow and return. Those. at the entrance, for example, 80 degrees, the coolant passing through the radiators at home cools down to 50 degrees - dT is equal to 30 degrees. Multiplying the mass of the coolant by the temperature difference, we get the very Gigakaloriya. Each region has its own price for 1 Gigakaloriya, for example, in my Vladimir it is equal to 1987 rubles 40 kopecks. The Q received for the month is multiplied by the tariff, further divided by the total living area of the house, and we get the cost of heating per 1 square meter. Well, how many square meters you own, as much as you actually have to pay. This is such a fairly simple scheme, which many in our country do not even suspect, including to everyone's surprise, even those who deal with this housing and utilities infrastructure (as shown by my experience).
Only by understanding how the heat meter works and what the price for heating is formed from, can one deal with energy saving issues. And as the formula shows, you can save either on the temperature difference, or on the mass of coolant flowing through the house. Here it is necessary to make a reservation, just like that, it is impossible to take and start the supply to the return, if the house does not take heat at all, and the temperature difference between the supply and return temperatures is less than 3 degrees, such a heat meter is removed from the register and the house is charged according to the standard. This feature of the city’s heat network, which we will not discuss now.
Well, now we come to the most interesting. Most modern thermal calculators are very modern devices, the capabilities of which are completely unused, since Vasya’s sanitary ware from the distant past and grandmother from the HOA are in charge of the houses. I urge all IT professionals not to be lazy and go down to the basement of your house, and look at this very interesting computing device. For example, in my house there was a heat meter Thermotronic TV7 :

This device has quite large capabilities, such as connection via Ethernet, USB, RS-232, but most importantly it has an SD card reader. Simply insert the SD card into it, and it automatically records the entire history of the readings — pressure, temperature, coolant volume, and other characteristics necessary to calculate the cost of heating. By the way, in my case, it also turned out that if native flow meters were used (a sensor that calculates the mass of the coolant), then it would be possible to automatically fix leaks in the house and send sms to the plumber - you have a flood, run to the house!
And so we downloaded the data from the heat calculator, and now with the help of the Archiver program we can process the data from the meter:
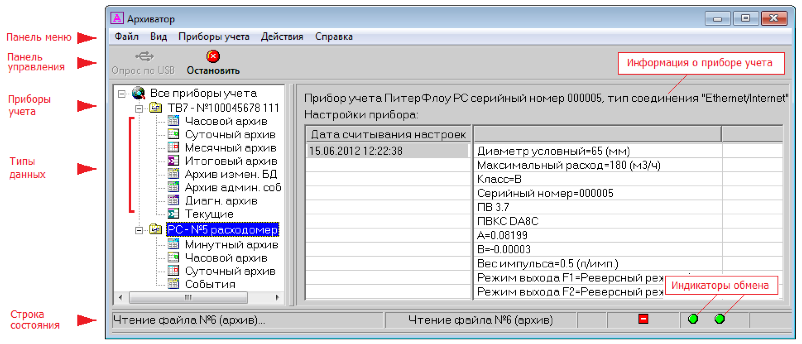
The program itself is quite primitive, and does not even know how to build graphs, and does not even export to Excel. But the good old ctrl-c ctrl-v make it easy to deal with the problem!
Now that we have data in Excel, we can draw graphs and draw some conclusions. Oh, how much you can see on the charts! For example, in the first graph, two subsidences in the heat carrier volume (upper dark blue and gray lines) passing through the house are most likely pipe failures in the area. Just coincides with the increase in feed temperature (frost!)
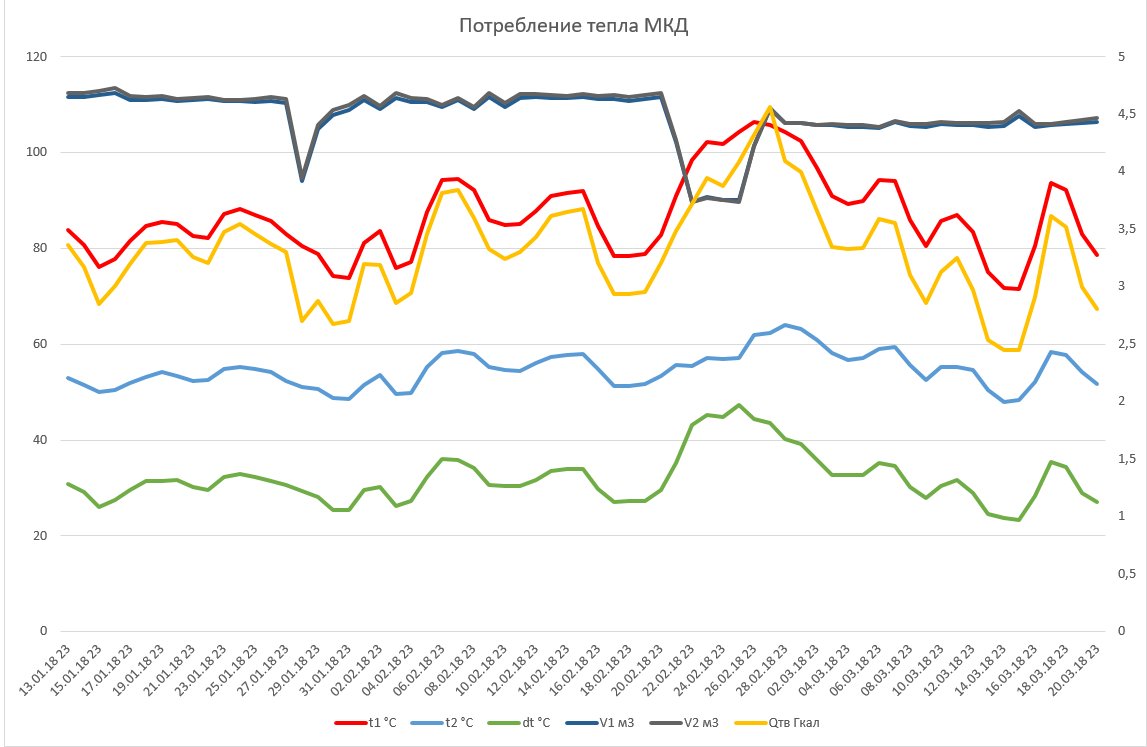
The right axis is Q, showing heat in daily gigcalories. As I said at the rate of 1, the Gigakaloriya in Vladimir costs 1987.40 rub. On the graph Gigacalorie marked with a yellow line. That's how much a month the gigacalories house accumulates, this amount is multiplied by 1987.40 rubles, then it is broken into apartments and you pay it in your receipts for communal.
The red and blue lines are the flow temperature and the return temperature. Values on the left scale. The green line is the delta, i.e. that temperature, how much your house took for heating. As you can see the temperature of the feed in the cold above 100 degrees And if it does, it is life threatening!
It can be noted that despite the jump in flow temperature, the return temperature is always about the same. This is an interesting phenomenon. Does anyone know why? I have a version, but for now I'll leave it with me, go in the comments! :) It's a shame actually, it’s not possible to save on the obvious, on the temperature difference.
The dark blue and gray lines are the volume of coolant passing per hour through the inlet and outlet, respectively. For some reason, it takes us a little more than it comes. Either the measurement error, or something flows somewhere ... I will understand this issue.
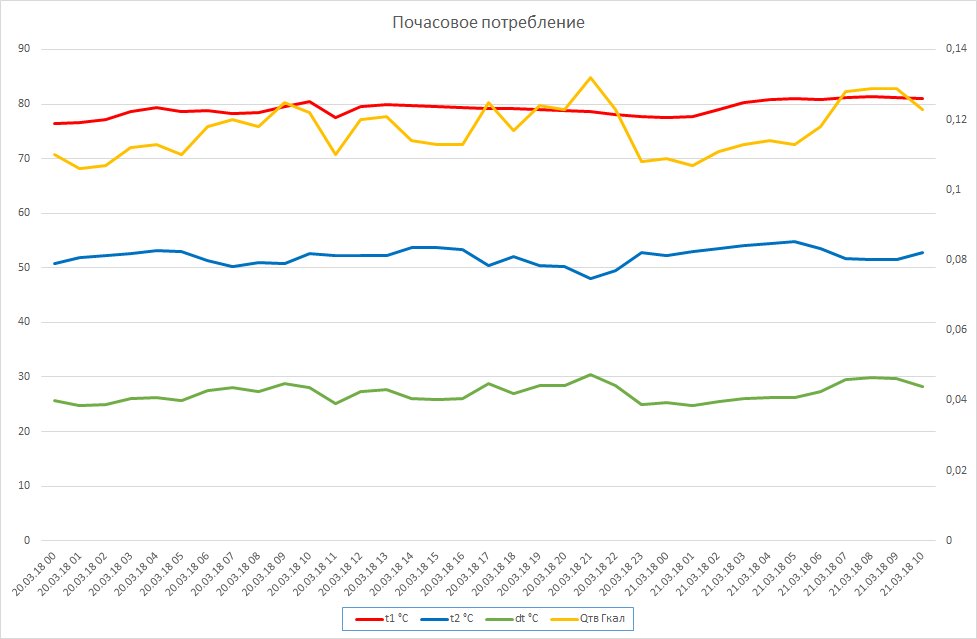
And the second figure is the hourly consumption for the last 24 hours. Here, basically all the peaks in gigacalories (orange line) are connected with the life of the house. At 7 in the morning they get up, at 12 o'clock, at 17 at dinner, and around 9-10 in the evening, everyone takes a shower and actively pours hot water. What disciplined neighbors I have! :)
Well, now, when it is possible to track the heat consumption of an apartment building, you can raise the issue of energy efficiency. First of all, I plan to wrap all the pipes in the house into an energy-flex, as well as install weather-dependent automation, remove the prehistoric elevator assembly from the scheme, install a modern three-way valve that can be controlled automatically or via the Internet. I spend this whole thing with thermal imaging control. About the thermal imager, I think I will also publish several posts if the audience accepts this topic. Well, in general, I plan to tackle the issue of energy saving in a dense way, as at the moment the readings of energy consumption at home are extremely high, which we clearly see on the chart.
How the central heating system works
In most of the homes of our vast Motherland, which, by the way, consists of permafrost by 2/3, heat comes from CHP plants to the apartments, and this is called the proud word “central heating”. We will talk about this today. The CHP heats the heat carrier through pipes, like through blood vessels, the whole city receives heat to your house: first, to the thermal node, which is usually located in the basement, and then to the batteries of your apartment. Giving up heat, the coolant cools down and through the so-called return flow, goes back to the CHP. By the way, as a rule, the coolant is ordinary water with the addition of additives that prevent deposits in the radiators and pipes.
Here, by the way, there is a very important nuance, which, as my practice has shown, even many plumbers do not suspect. In the thermal node there is an elevator unit, an invention of the 19th century, but alas, it is still widely used.

In the elevator assembly, there is a so-called nozzle, also known as a cone. Many plumbers believe that its task is simply to narrow the section so that less heat enters the house. Not really. Its task is to create a vacuum in which hot water from the supply pipeline at high speed, but with less pressure, begins to mix with the cooled return flow (with that water that has already passed through the radiators of your house) and due to this, the heating temperature is controlled at entering the house. Unfortunately, the nozzle is a primitive device, invented in the 19th century, and therefore mixing is always the same, regardless of what the temperature is +5 or -40 outside.
')
Many plumbers, when they receive complaints from residents, who have become cold bore the elevator nozzle above the standard section or even remove it completely. It is categorically not recommended to do this, since according to the schedule, the heat and power plant supplies the heat carrier in extreme cold under extremely high pressure with temperatures up to 130 degrees! If you run such heat into the apartment, and God forbid, it will burst a heating battery - the victims are guaranteed. By the way, it is for this reason that manufacturers of polypropylene pipes, so widely loved by Russian plumbers, are prohibited or not recommended to use them for central heating . Most polypropylene pipes hold a maximum of 90 degrees and something relatively long term. Look now at the pipes in your apartment and think.
Heat calculator
Practically in each house there is already a special device called a thermal computer. Its task is to calculate how much heat your house has taken. Unfortunately, for historical reasons, when we had everything in common, and therefore no one’s, we are not accustomed to counting the cost of heating. In the meantime, today heating is the most expensive expense graph in bills. And due to the fact that historically, heating in our country, no one considered - this area is now the most bribe-intensive and extremely inefficient. And in order to somehow remedy the situation, everyone who is interested in what kind of numbers they are put in utility bills must remember and understand the main formula in the housing and utilities sector:
It is according to this school formula that the heat meter calculates the cost of heating for you: m is the mass of heat carrier that passed through your house in 1 hour, dT is the temperature difference between the flow and return. Those. at the entrance, for example, 80 degrees, the coolant passing through the radiators at home cools down to 50 degrees - dT is equal to 30 degrees. Multiplying the mass of the coolant by the temperature difference, we get the very Gigakaloriya. Each region has its own price for 1 Gigakaloriya, for example, in my Vladimir it is equal to 1987 rubles 40 kopecks. The Q received for the month is multiplied by the tariff, further divided by the total living area of the house, and we get the cost of heating per 1 square meter. Well, how many square meters you own, as much as you actually have to pay. This is such a fairly simple scheme, which many in our country do not even suspect, including to everyone's surprise, even those who deal with this housing and utilities infrastructure (as shown by my experience).
Only by understanding how the heat meter works and what the price for heating is formed from, can one deal with energy saving issues. And as the formula shows, you can save either on the temperature difference, or on the mass of coolant flowing through the house. Here it is necessary to make a reservation, just like that, it is impossible to take and start the supply to the return, if the house does not take heat at all, and the temperature difference between the supply and return temperatures is less than 3 degrees, such a heat meter is removed from the register and the house is charged according to the standard. This feature of the city’s heat network, which we will not discuss now.
Get down to the basement
Well, now we come to the most interesting. Most modern thermal calculators are very modern devices, the capabilities of which are completely unused, since Vasya’s sanitary ware from the distant past and grandmother from the HOA are in charge of the houses. I urge all IT professionals not to be lazy and go down to the basement of your house, and look at this very interesting computing device. For example, in my house there was a heat meter Thermotronic TV7 :

This device has quite large capabilities, such as connection via Ethernet, USB, RS-232, but most importantly it has an SD card reader. Simply insert the SD card into it, and it automatically records the entire history of the readings — pressure, temperature, coolant volume, and other characteristics necessary to calculate the cost of heating. By the way, in my case, it also turned out that if native flow meters were used (a sensor that calculates the mass of the coolant), then it would be possible to automatically fix leaks in the house and send sms to the plumber - you have a flood, run to the house!
And so we downloaded the data from the heat calculator, and now with the help of the Archiver program we can process the data from the meter:

The program itself is quite primitive, and does not even know how to build graphs, and does not even export to Excel. But the good old ctrl-c ctrl-v make it easy to deal with the problem!
Draw graphics
Now that we have data in Excel, we can draw graphs and draw some conclusions. Oh, how much you can see on the charts! For example, in the first graph, two subsidences in the heat carrier volume (upper dark blue and gray lines) passing through the house are most likely pipe failures in the area. Just coincides with the increase in feed temperature (frost!)

The right axis is Q, showing heat in daily gigcalories. As I said at the rate of 1, the Gigakaloriya in Vladimir costs 1987.40 rub. On the graph Gigacalorie marked with a yellow line. That's how much a month the gigacalories house accumulates, this amount is multiplied by 1987.40 rubles, then it is broken into apartments and you pay it in your receipts for communal.
The red and blue lines are the flow temperature and the return temperature. Values on the left scale. The green line is the delta, i.e. that temperature, how much your house took for heating. As you can see the temperature of the feed in the cold above 100 degrees And if it does, it is life threatening!
It can be noted that despite the jump in flow temperature, the return temperature is always about the same. This is an interesting phenomenon. Does anyone know why? I have a version, but for now I'll leave it with me, go in the comments! :) It's a shame actually, it’s not possible to save on the obvious, on the temperature difference.
The dark blue and gray lines are the volume of coolant passing per hour through the inlet and outlet, respectively. For some reason, it takes us a little more than it comes. Either the measurement error, or something flows somewhere ... I will understand this issue.

And the second figure is the hourly consumption for the last 24 hours. Here, basically all the peaks in gigacalories (orange line) are connected with the life of the house. At 7 in the morning they get up, at 12 o'clock, at 17 at dinner, and around 9-10 in the evening, everyone takes a shower and actively pours hot water. What disciplined neighbors I have! :)
Well, now, when it is possible to track the heat consumption of an apartment building, you can raise the issue of energy efficiency. First of all, I plan to wrap all the pipes in the house into an energy-flex, as well as install weather-dependent automation, remove the prehistoric elevator assembly from the scheme, install a modern three-way valve that can be controlled automatically or via the Internet. I spend this whole thing with thermal imaging control. About the thermal imager, I think I will also publish several posts if the audience accepts this topic. Well, in general, I plan to tackle the issue of energy saving in a dense way, as at the moment the readings of energy consumption at home are extremely high, which we clearly see on the chart.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/411009/
All Articles