Future prediction systems

( c )
The best neural networks that beat a person in poker, Go, chess and Dotu have one thing in common - they can predict the near future.
The ability of machines to predict behavior can far exceed the capabilities of a person. In the space of different probabilities, algorithms are better than a person subject to the influence of emotions.
What can neural networks predict? Before us is an endless field of possibilities: the stock exchange, crime, weather, health, transportation — everywhere, the ability to calculate a few steps ahead will be useful. Already today, some algorithms are superior to human experts. The dawn of tomorrow's neurodne will not leave any trace of the "fog of uncertainty."
Researchers from the company DeepMind published a scientific paper in which they presented a new method of teaching a neural network with reinforcements. It turned out that if in the process of self-learning, a neural network begins to “ fantasize ” about various options for the future, then it learns much faster. The “fantasy” of the neural network is that for the three last known frames, the neural network must predict the reward it will receive in the fourth unknown time interval. AI uses its memory and applies new strategies as if in its own imagination.
The more efficient the systems become, the better they make the predictions. Now we can not only predict the weather (in the short term). We can even “see” the future of macroeconomic situations in different areas of the city, measuring the consumption of water, electricity, traffic (how many passengers are in public transport and how many in our cars), increase / decrease in resource consumption.
It is already difficult to imagine a sphere in which we could do without predictions. And is it worth rejecting them if the algorithms make it possible to choose the right behavior strategy?
Behavior on the roads
Researchers at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology have built a system that can predict a huge number of real-world events. At first, the program was trained on a choice of 2 million online videos. Each video program analyzed, classifying all subjects and actions in the subjects.
Then neural networks showed a static image. The program, in turn, generated 1.5-second video clips, demonstrating the vision of the near future.
Obviously, this solution can be used not only to create gifs. Algorithms, in principle, allow you to "look into" the future of complex systems, which will find application in autonomous cars, analyzing the constantly changing situation on the road.
The computer will be able to understand that it sees something unusual - for example, the animal ran out onto the road. Even if the car has never been in this situation before, it will “understand” that something strange is happening - you should either stop or transfer control to the driver.
Human health

( c )
Scientists from Stanford University have developed an artificial intelligence system that can predict the probability of death of a seriously ill patient during the year with an accuracy of up to 90%.
The researchers analyzed the records of 160,000 patients in order to collect data on past diagnoses, prescribed procedures, and forecasts made by doctors.
After processing the dataset, an algorithm was developed for deep learning of the neural network. The grid then made predictions of all-cause mortality for a period of 3 to 12 months for 40,000 patients.
A year later, the researchers summed up: in 90% of cases, the neural network correctly predicted the condition of the patient (regardless of whether he waited for death or recovery). This indicator significantly exceeds the capabilities of even a group of medical experts.
The brand Theraflu has developed a system that predicts the probability of catching a cold in the territory of several countries, including Russia. Daily, the system analyzes posts in social networks, search queries, data from the Research Institute of Influenza , as well as demand data from pharmacies for funds specific to combat common cold symptoms. The result is a graph of "cold danger" in a particular region with a forecast for several days. However, such platforms are finding more valuable applications: in Virtual Singapore, it is already possible in real time to view and analyze a country's life and predict, for example, the spread of dangerous infections or the reaction of large masses of people to an explosion in a shopping center.
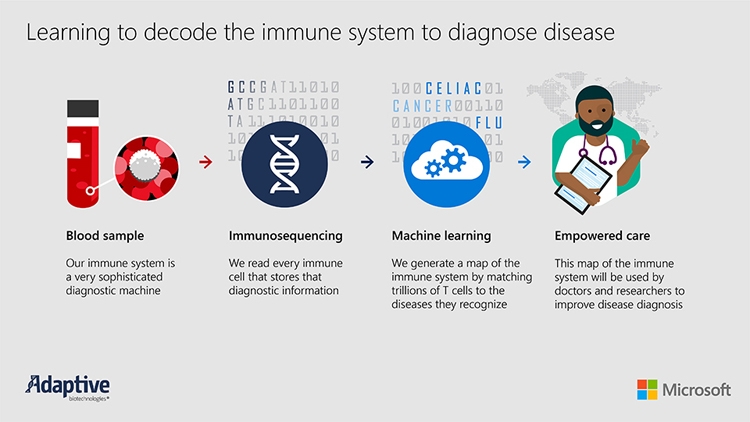
Microsoft and Adaptive Biotechnologies plan to create a system that, based on a blood test, will be able to detect diseases in the early stages. By analyzing the genetic code in trillions of T-lymphocyte receptors, the system will detect diseases that the body has encountered at an asymptomatic stage. It is assumed that the test will be able to identify a wide range of diseases at a time, including diseases that are usually diagnosed at very late stages.
A research team from the Institute of Molecular Biology, Russian Academy of Sciences, Russian Gerontological Research and Clinical Center, MIPT and other research centers, presented a method for predicting a person’s biological age (which differs from a passport one) based on human carotid artery ultrasound and tonometry data. With the help of machine learning , a complex formula was obtained , capable of predicting age in healthy people with an accuracy of 6.9 years for men and 5.9 years for women, which is a very high figure compared to other known methods.
Danish scientists have developed the Corti Signal neural network, which tracks sound messages to diagnose a heart attack. First of all, the system should help people who called the ambulance. The operator is not always able to detect a heart attack in a person on the other end of the wire (he copes in 73% of cases), but the neural network solves this problem with an accuracy of 95%! The AI not only listens to the conversation, but also collects non-verbal cues, such as breathing patterns.
Apparently, in the future, systems based on neural networks (and other methods) will make it possible to predict diseases much earlier - in some cases decades before the onset of the disease itself.
Clever things know what will happen to them.

Imagine a building that may, even before an accident, say that heating, for example, will soon fail. Some companies use machine learning to do just that. This procedure is called predictive maintenance.
CGnal, located in Milan, Italy, recently analyzed data for the year from heating and ventilation systems in an Italian hospital. From the sensors were obtained data on temperature, humidity, use of electricity. The algorithm was trained on a sample for six months, then the researchers checked it with data from the second half of the year. The system predicted 76 out of 124 real faults, including 41 out of 44, where the device temperature has risen above acceptable levels.
Other companies also use a similar approach to data. Finnish startup Leanheat places a wireless sensor for temperature, humidity and pressure to remotely control heating and monitor device health. Instead of adjusting the heating simply by the outdoor temperature, the Leanheat models take into account changes in the weather: the temperature dropped to zero from 10 degrees or rose from -10.
In the US, Augury developed Shazam for Machines, installing acoustic sensors in cars to listen for audible changes and identify potentially unavoidable failures. However, the gadget can work with different devices: customers can connect the sensor to commercial refrigerators or industrial heaters. The Augury gadget records vibrations and ultrasounds, loads them into the cloud service, where the data is analyzed to make a prediction about the health of the monitored machine.
The audio and data are analyzed and stored so that the sound of the device of one client can be compared with the sound of everyone else. The idea is that Augury does not need to configure software for each type of device. Instead, you can simply install the sensors and listen to the device to get an idea of how it sounds when it functions normally. Over time, the database of sounds will let you know which specific sounds precede specific types of failures.
Weather forecast
Weather forecasting remains a challenge for science. We have already got the hang of using convolutional neural networks for this, but progress does not stand still. In the Top-500 list of the most powerful computing systems in the world, as of November 2016, 23 supercomputers were engaged in weather forecasting.
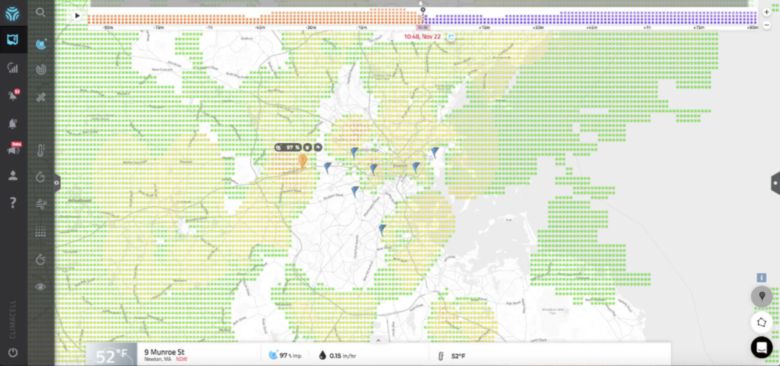
ClimaCell uses an approach that is not related to neural networks and super-complex algorithms: wireless communication networks act as sensors for weather prediction - all this is done within the framework of the nowcasting concept, in which the super-short-term forecast of weather phenomena is made within 0-6 hours from the observation period .
ClimaCell combines several levels of data from wireless networks, satellites, weather radar and other sensors to create high-definition maps. Using data from approximately 5,000 stations operated by several telecommunications firms, the company creates very accurate and reliable weather maps.
Dangerous Algorithms

Not that compass , but close in meaning
Various crime prediction systems have been tested in the US for several years now. One of the first systems of this type - COMPAS - was created in 1998. COMPAS analyzes 137 parameters of the convicted person’s biography, including the severity of previous crimes, the level of education and income, marital status and dependency. The program also takes into account the results of psychological tests, including temperament, willingness to take risks, the degree of narcissism and a penchant for guilt. Based on these data, COMPAS predicts the likelihood of a criminal relapse in the next two years.
However, Dartmouth College conducted a thorough COMPAS study and concluded that the algorithm is actually no more accurate than any average person. The program was able to identify repeat offenders in 65% of cases. People without special education and experience of sentencing coped with this task in 67% of cases, knowing only the age, gender and history of the crimes of the accused. Moreover, it turned out that the accuracy of COMPAS can be improved if we leave only two parameters in it: a person's age and information about previous convictions.
Algorithms can make decisions and build predictions much more efficiently than humans. People take into account non-essential factors and ignore the really important ones, give in to emotions, and also allow themselves to make decisions in accordance with their inner “instinct”, intuition, or without any logic at all.
However, this does not mean that we must completely trust the machines, because they also do not have 100% accuracy.
')
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/410933/
All Articles