Google introduced a new quantum processor
Google Inc. introduced the 72-qubit Bristlecone quantum processor. Using this processor, the Google Quantum AI lab, responsible for developing a quantum computer, will test system errors and scalability of technology, as well as the field of quantum simulation, optimization and machine learning “to solve real-world problems,” as the company writes in a blog .
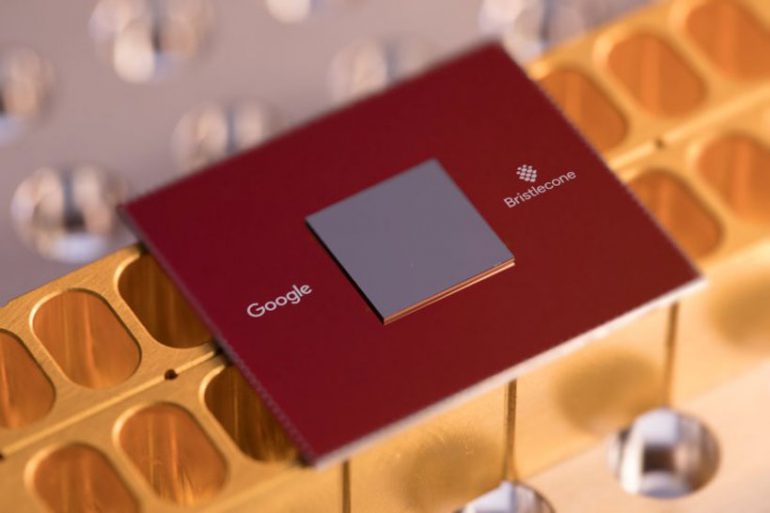

The new 72-qubit Google Bristlecone quantum processor is built on the principle that allowed the previous 9-qubit processor to show a low error rate when reading data (1%), while the single-qubit gate is working - 0.1% and when the two-qubit gate is working - 0.6 % that, as noted by Google, was the best result of the company. Before applying a new processor, it is important to understand its capabilities: the team created a tool that checks it for errors by solving identical problems on a quantum processor and in a classic simulation. With a low number of errors, "quantum superiority" can be achieved.

Google forecast: dependence of the number of errors on the number of qubits in the processor
')
Quantum computers use quantum superposition and quantum entanglement to transmit and process data. One of the main tasks of quantum computers will be the strengthening of artificial intelligence . Quantum processor qubits are quantum analogs of bits. Two adjacent qubits have four states - both on, both off, on / off and off / on, each of them has a weight or “amplitude” that can play the role of a neuron; the third qubit in such a system allows us to represent eight neurons, and the fourth - sixteen. Changing the state of four qubits leads to the processing of sixteen neurons at a time, while a classical computer would process these numbers one by one.
One of the problems with the operation of a quantum computer is the number of errors that occur when computing, reading and writing information in qubits. In June 2016, researchers from Google built a processor of 9 qubits, which showed high reliability. They were able to scale this development by March 2018, increasing the number of qubits to 72. In the processor, the qubits are arranged in two 6x6 layers one above the other. The Google Quantum AI lab is testing development.
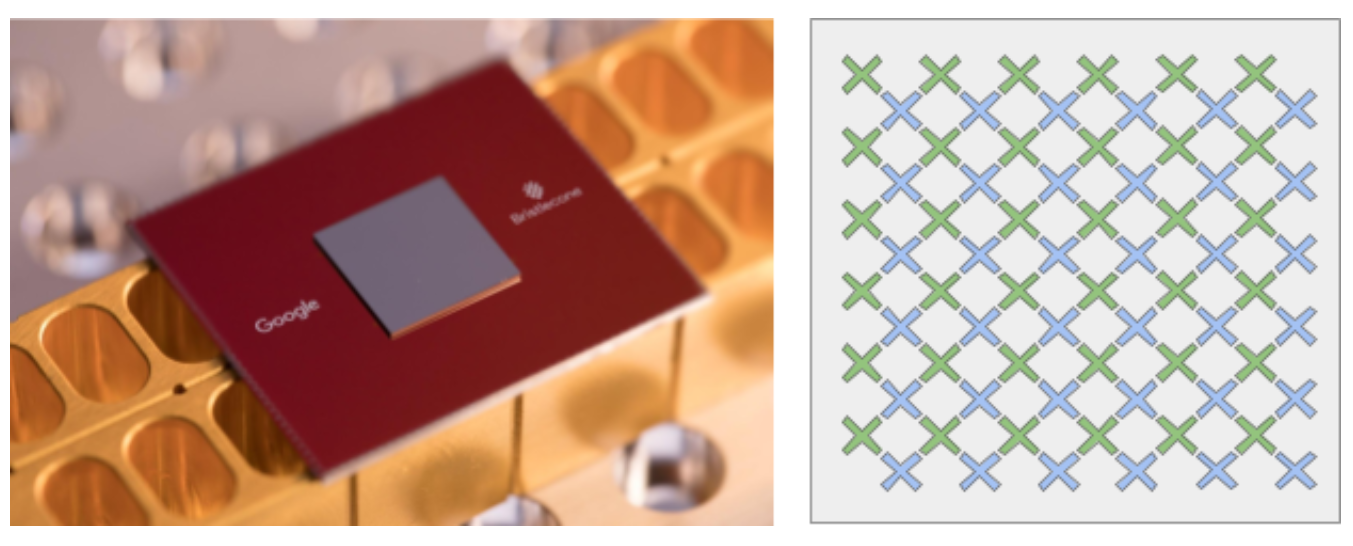
The Bristlecone quantum processor consists of 72 qubits, shown in the diagram (right) in the form of "X", where the points of contact between the ends of the symbol represent the connection of the qubit with the nearest "neighbors"
At the moment, a number of research teams are engaged in quantum computers, including IBM. In March 2017, the company announced the launch of the IBM Q project, and by June introduced two processors: 16-qubit for work in the scientific field and 17-qubit for commercial use. In 2017, IBM Research developed the 49-qubit processor.
In July 2017, a team of Russian and American scientists from Harvard University, led by the co-founder of the Russian Quantum Center (RCC), Mikhail Lukin, announced the creation of a 51-qubit quantum computer.
In Russia, in March 2018, Vnesheconombank, VEB Innovations, the Foundation for Advanced Studies (FPI), Lomonosov Moscow State University and ANO Digital Economy signed an agreement on the development of a 50-qubit quantum computer.

The new 72-qubit Google Bristlecone quantum processor is built on the principle that allowed the previous 9-qubit processor to show a low error rate when reading data (1%), while the single-qubit gate is working - 0.1% and when the two-qubit gate is working - 0.6 % that, as noted by Google, was the best result of the company. Before applying a new processor, it is important to understand its capabilities: the team created a tool that checks it for errors by solving identical problems on a quantum processor and in a classic simulation. With a low number of errors, "quantum superiority" can be achieved.

Google forecast: dependence of the number of errors on the number of qubits in the processor
')
Quantum computers use quantum superposition and quantum entanglement to transmit and process data. One of the main tasks of quantum computers will be the strengthening of artificial intelligence . Quantum processor qubits are quantum analogs of bits. Two adjacent qubits have four states - both on, both off, on / off and off / on, each of them has a weight or “amplitude” that can play the role of a neuron; the third qubit in such a system allows us to represent eight neurons, and the fourth - sixteen. Changing the state of four qubits leads to the processing of sixteen neurons at a time, while a classical computer would process these numbers one by one.
One of the problems with the operation of a quantum computer is the number of errors that occur when computing, reading and writing information in qubits. In June 2016, researchers from Google built a processor of 9 qubits, which showed high reliability. They were able to scale this development by March 2018, increasing the number of qubits to 72. In the processor, the qubits are arranged in two 6x6 layers one above the other. The Google Quantum AI lab is testing development.

The Bristlecone quantum processor consists of 72 qubits, shown in the diagram (right) in the form of "X", where the points of contact between the ends of the symbol represent the connection of the qubit with the nearest "neighbors"
At the moment, a number of research teams are engaged in quantum computers, including IBM. In March 2017, the company announced the launch of the IBM Q project, and by June introduced two processors: 16-qubit for work in the scientific field and 17-qubit for commercial use. In 2017, IBM Research developed the 49-qubit processor.
In July 2017, a team of Russian and American scientists from Harvard University, led by the co-founder of the Russian Quantum Center (RCC), Mikhail Lukin, announced the creation of a 51-qubit quantum computer.
In Russia, in March 2018, Vnesheconombank, VEB Innovations, the Foundation for Advanced Studies (FPI), Lomonosov Moscow State University and ANO Digital Economy signed an agreement on the development of a 50-qubit quantum computer.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/410909/
All Articles