In the atmosphere of exoplanets WASP-39b was three times more water than on Saturn
Artistic concept: NASA, ESA, G. Bacon, A. Feild (STScI), H. Wakeford (STScI / Univ. Of Exeter)
With the help of the Hubble and Spitzer telescopes, astrophysicists analyzed (pdf) the atmosphere of the WASP-39b exorbitant “hot Saturn” type — and made up the most complete transmission spectrum that can be compiled using modern tools. Starlight passes through the planet's atmosphere, while partially absorbed by waves with lengths characteristic of the energy states of matter in the atmosphere. Thus, by absorption spectroscopy, it is possible to determine which chemical compounds are present in the atmosphere.
So, astrophysics from the University of Exeter (United Kingdom), with the cooperation of colleagues from other universities and NASA staff, have demonstrated the presence of a significant amount of water vapor in the atmosphere.
')
Although the presence of water in the atmosphere was predicted in advance, but such a large amount is surprising - three times more than on Saturn. This suggests that the planet was formed much farther from its star and was bombarded with icy material.
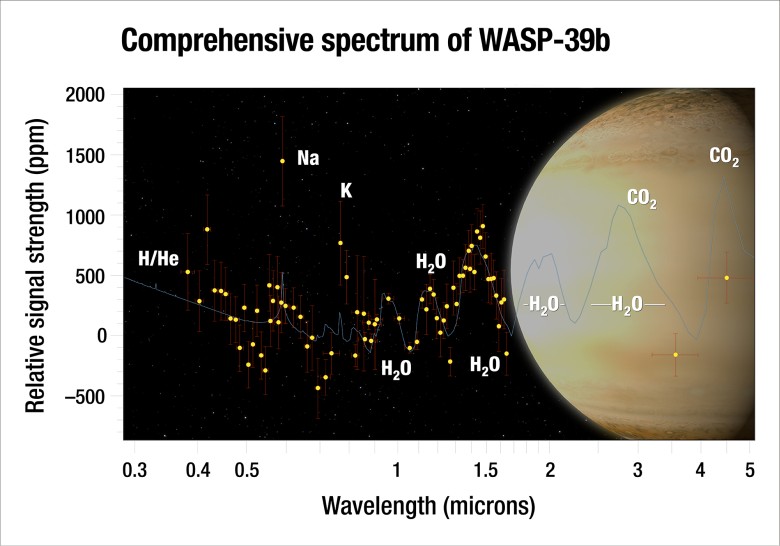
The illustration below shows the full transmittance spectrum of the WASP-39b (black dots).
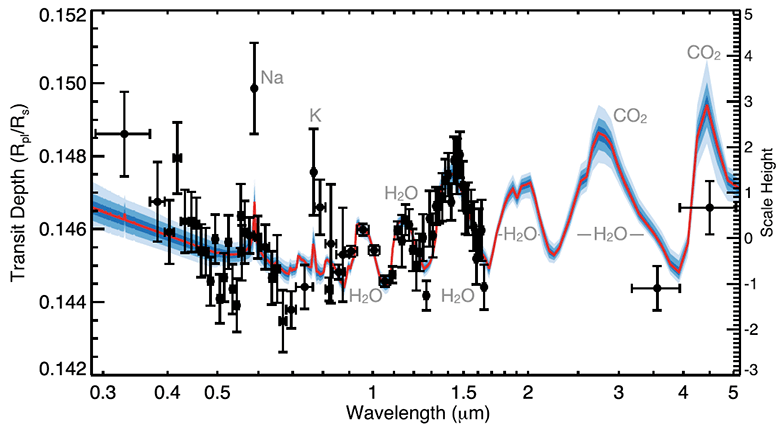
The transmittance spectrum includes the HST STIS and WFC3, Spitzer IRAC and VLT FORS2 data, complementing the spectrum from 0.3 to 5.0 µm with all available tools. Based on the isothermal profile and the equilibrium chemical state, scientists have compiled the most likely atmospheric model for the planet WASP-39b. It is indicated in red, indicating the confidence intervals 1, 2 and 3σ (from dark blue to blue).
Although there are no planets like WASP-39b in the Solar System, but studying it can provide new information about where and how planets are formed relative to their stars. Exoplanet is unique in its kind. The more information you can gather about it and about other unusual planets, the clearer their origin will become.
WASP-39b is interesting because it must have a very unusual evolutionary history. Judging by the amount of water in the atmosphere, it was formed far from the star, but then made an epic journey through its planetary system and, possibly, destroyed some other planetary objects in its path.
“We need to study other planets in order to understand our own solar system,” explains lead researcher Hannah Wakeford (Hannah Wakeford) from the Space Research Institute (USA) and the University of Exeter (United Kingdom). “But exoplanets show that the formation of planets is more complicated and confusing than we thought. And this is fantastic! ”The example of WASP-39b shows that exoplanets can differ greatly in the composition of the atmosphere from the planets in our solar system.
WASP-39b is located in the constellation Virgo in the orbit of a quiet solar-type star at a distance of about 700 light-years from the Sun. The rotation period (sidereal period) is four Earth days. Currently, it is located more than 20 times closer to its star than the Earth to the Sun, and rotates synchronously with the star, that is, it is always turned to it by the same side.
The temperature on the sunny side is 776.7 ° C. Strong winds carry heat from the day side all over the planet, so the other side heats up almost as much as the day. Although the planet is called "hot Saturn", it does not have the same ring. But on the other hand, it has a large atmosphere, devoid of high-altitude clouds, which made it possible to use instruments for absorption spectroscopy.
Scientists are hoping to take a significant step forward in studying WASP-39b and other exoplanets after the launch of the James Webb telescope, scheduled for 2019. According to the latest schedule, the launch should take place in the window between March and June 2019. Unfortunately, according to the latest report of the US Accounting Chamber of February 28, 2018, the Northrop Grumman contractor will need an additional four months to prepare the telescope for work. Therefore, the launch of the telescope can once again be postponed. Now Northrop Grumman employees are working on JWST in three shifts 24 hours a day. Since September 2017, the volume of work on the project has already exceeded the original figures by five times.

Telescope "James Webb" after cryogenic testing in the vacuum control chamber of the Space Center. Johnson in Houston, December 1, 2017. Photo: NASA / Chris Gunn, CC BY-NC-ND 2.0
"James Webb" will provide information about the content of carbon in the atmosphere, which absorbs light at longer wavelengths than is recorded by Hubble. Then scientists will be able to determine the proportion of carbon and oxygen in the atmosphere - and make even more accurate assumptions about the origin and evolutionary history of the planet.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/410771/
All Articles