Smart cars: the story of the sequel
Along with the development of the mechanical systems of the car, engineers were constantly striving to add something to the electronic filling, to make the car safer, more manageable and smarter. Today, there are all the prerequisites for this: the IT industry is developing at a tremendous pace, automakers are ready to cooperate and conduct promising developments, corporations are investing in the development of vehicles. Meanwhile, the "mind" of cars developed progressively over more than half a century. All this time he took different forms and went into different concepts: from security to entertainment. The modern stage of evolution has gone so far that it is already incomprehensible, software defines iron, or iron - software. So, it's time to write about cars on Hiktayms.

The first technological revolution in the automotive industry was the interest of automotive companies to electric starters - they were first installed in 1911. Then innovations began to concern the convenience of the driver and even his entertainment behind the wheel: in 1925 the cigarette lighter appeared, in 1930 - the radio, in 1956 - the power steering, in 1970 - the cassette deck, in 1984 - the airbags. A year later - CD players, in 1994 - the instrument panel of computer diagnostics of the car, in 1995 - GPS, in 2000 - USB and Bluetooth, the first signs of the “connected” car to the whole.
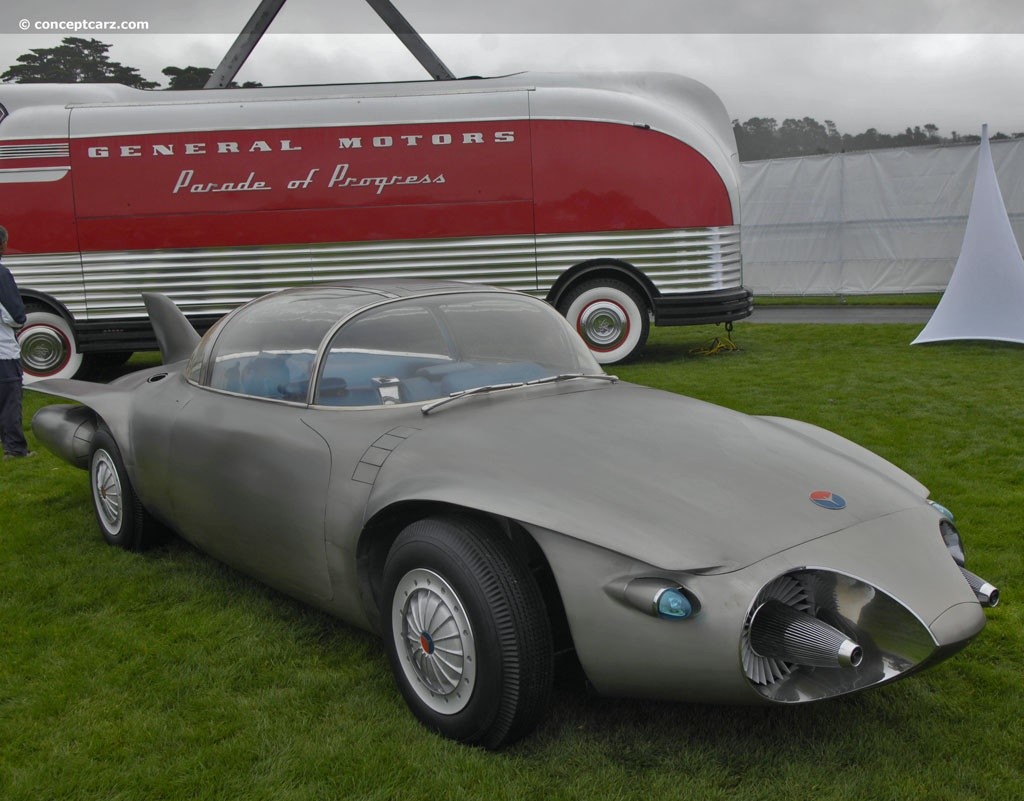
The first experience of creating a smart car occurred in the middle of the twentieth century. General Motors Firebird II - four-seater car in 1956 with independent suspension. Under the titanium case, there was a Whirlfire GT-304 gas turbine engine for 200 hp, electric equipment and an integrated level air conditioning system no worse than at the beginning of the XXI century. In terms of design and ergonomics, Firebird II continued the 1953 version of the car, which was called the “jet airplane on wheels” (the developers and engineers were really inspired by the concepts of the fighters of that time). However, in Firebird II, the structure was used for the first time on the road of the future — a complex control system that had to interact with the electrical wire built into the carriageway to send signals and serve as a guide for newer cars. It was assumed that the electromagnetic field minimizes dangerous situations on the road, reducing the human factor. In those times, it was too bold a model that caused a sensation at the exhibitions, but never got into mass production.
')

Future highways were built in Europe and the USA. The first production car that really began to interact with them was the Citroen DS, the legendary passenger car that ranked third in the ranking of cars of the century. Low-power engine 75 hp Nothing stood out in those days, but the car was distinguished by an advanced transmission combined with steering, brakes and hydropneumatic suspension. This design ahead of the development of the automotive industry for many years to come. The Citroen DS was able to interact with the highway using an electric signal, but there was no question of any independent autopilot — it was more fun. By the way, it is incredible popularity, advanced technology and, albeit a relatively illusory one, but the autopilot made this Citroen a flying car of Fantômas.

Experiments with on-board computers in the 60-70 years. were held, but never entered the series. It is worth remembering the experimental Chrysler Plymouth, which was equipped with an on-board computer (well, as far as can be called an on-board computer, which occupied half of the rear seat) and a generator to power the system, placed on the roof of the car. Laboratory tests were carried out for 10 years, but there could be no question of any serial production.
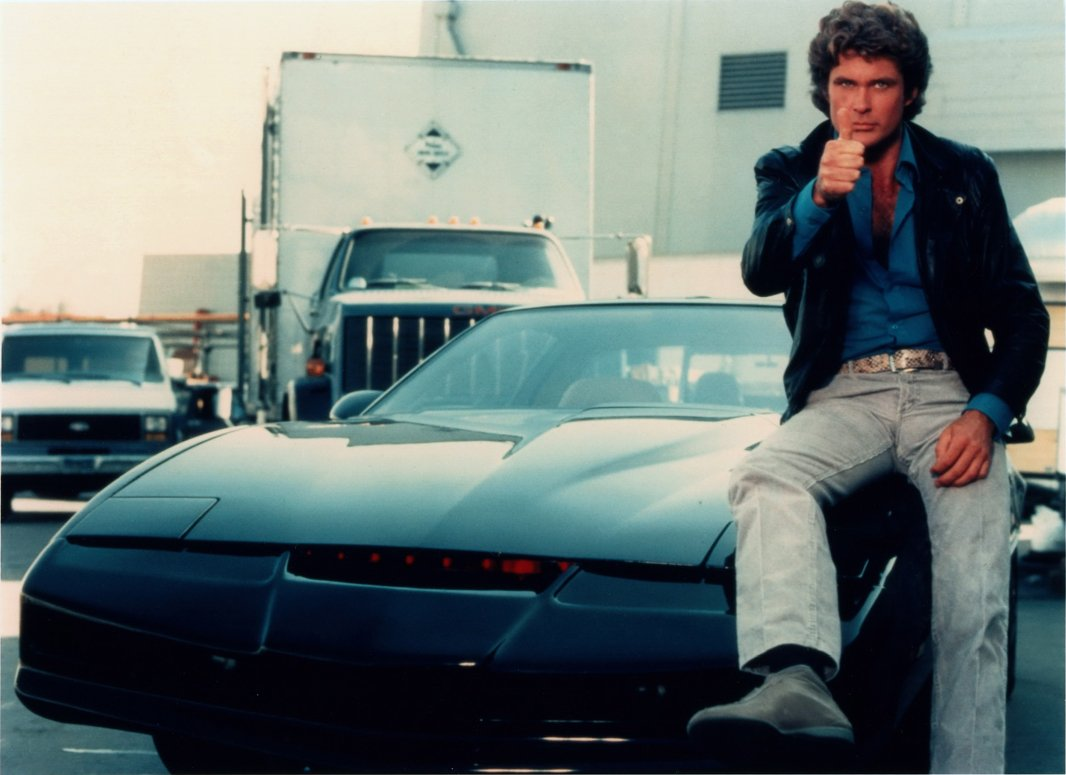
However, neither engineering thought nor futurist fantasy stopped for a minute - mankind was looking for cars not only a luxury or a means of transportation, but also a clever helper who could make life easier, make roads safe, work for a man. Such a desire was reflected in the movies - after several films with “talking” cars, the James Bond series of films with his heaped cars and, of course, the legendary “Knight of the Roads” became real hits. The smart, humorous KITT based on the Pontiac Firebird Trans AM not only accelerated at 500 km / h and was almost invulnerable, but also knew how to talk, ride full autopilot and control all electronic devices from a distance.

Kitt inside
Surely, the utilitarian reality did not coincide with the dreams of the engineers of the past - commerce and the notorious business expediency influenced the shaping of modern smart cars.
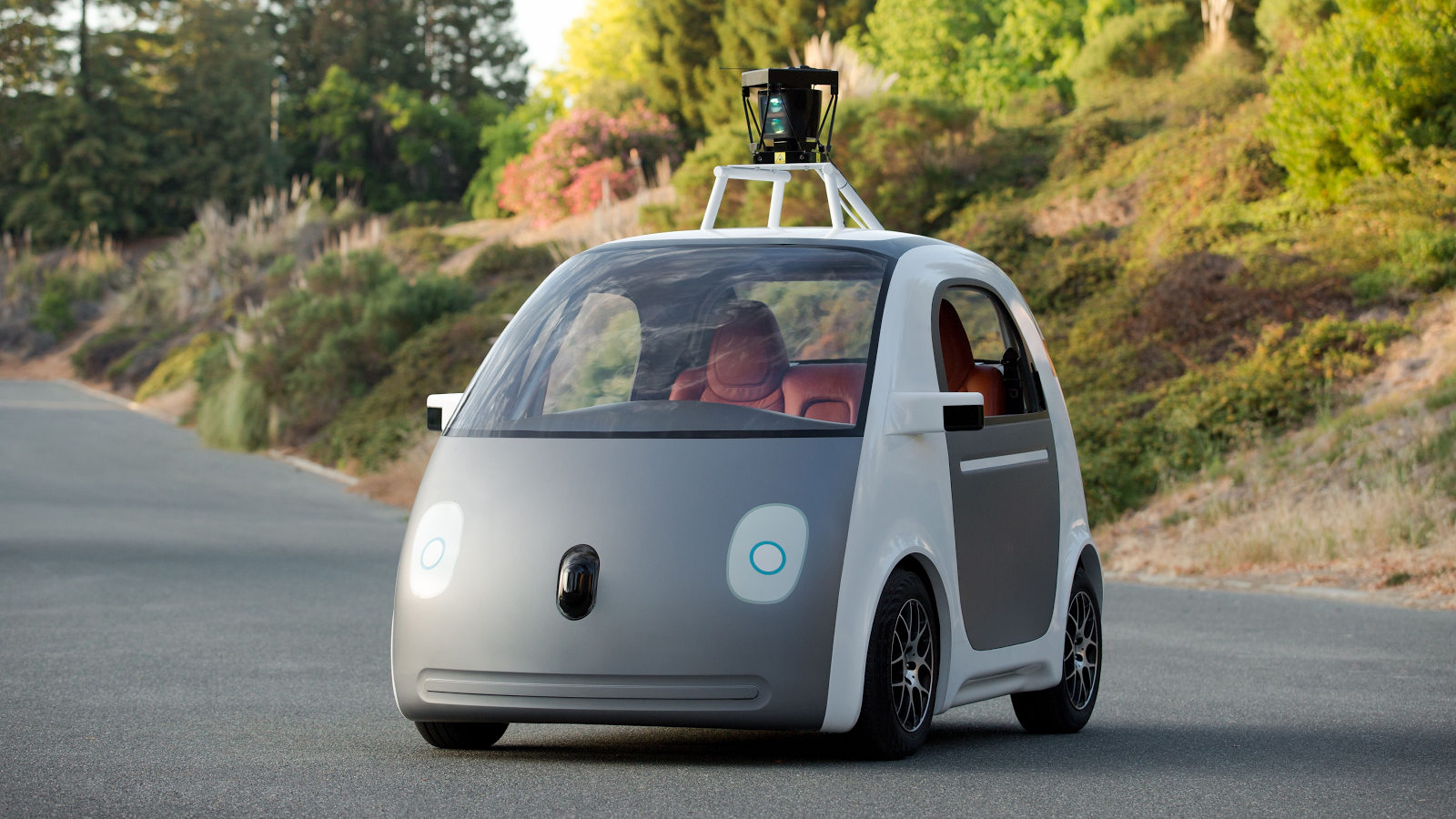
One of the first prototypes proposed by Google - Google Car. This is a mini-car with an unprecedented level of autonomy. The machine is designed for two people, has two engines, non-standard body materials, is fully electric, reaches a speed of 25 miles / hour (a little more than 40 km / h), is controlled from the start button and does not require the presence of a person except as a passenger. Naturally, it is integrated with Google services - on the central console you can watch videos and movies on Youtube, work with mail, search in Chrome. By the way, the car was also built by Google, since previous partners Lexus and Toyota expectedly imposed many restrictions on risky experiments. Exit to the mass market of personal vehicles is extremely difficult, and in December 2016, Google (more precisely, the holding Alphabet) turned the project to create your unmanned vehicle. The company continues to develop autopilots, but for ordinary automakers.

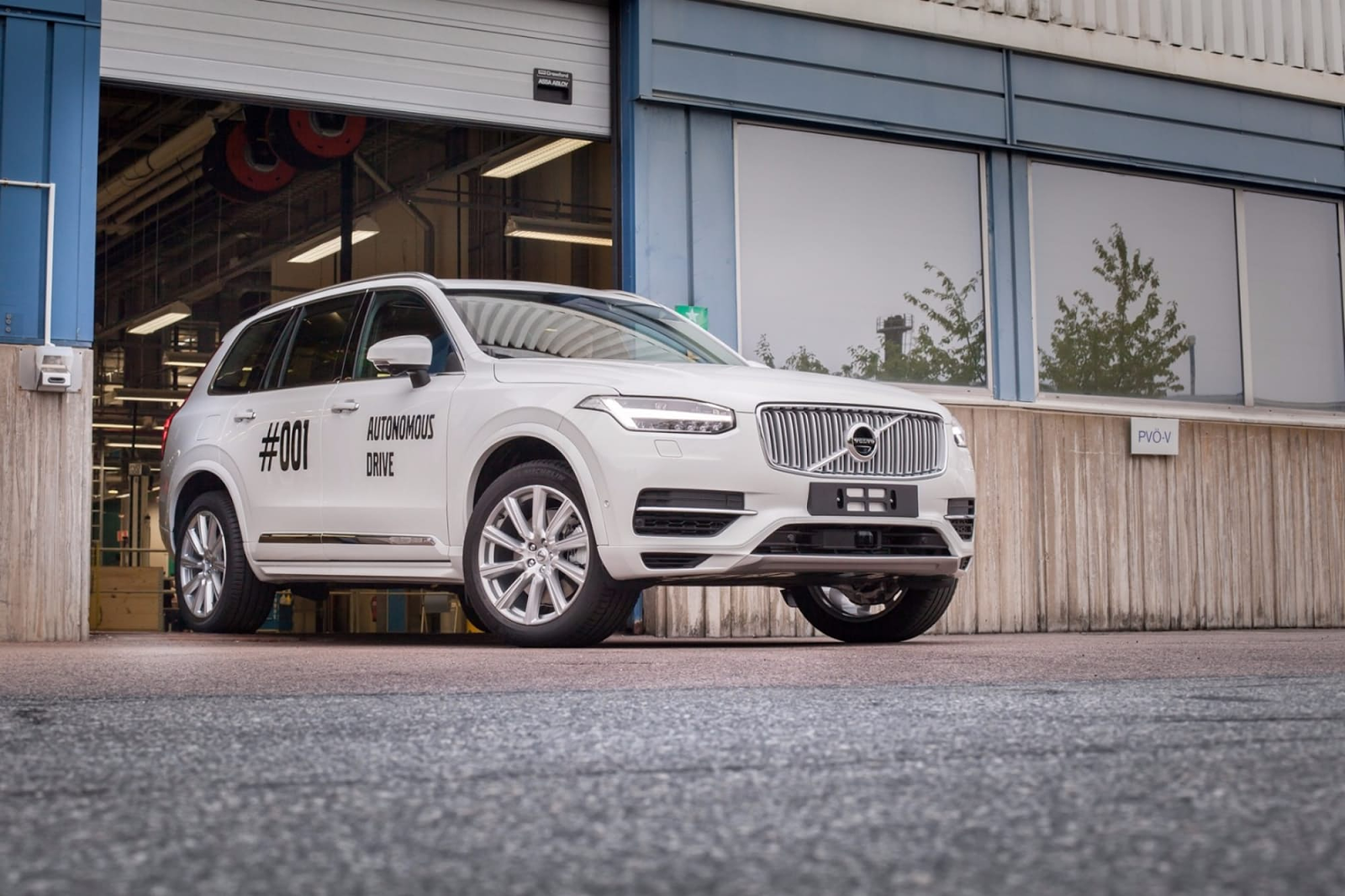
Already this year, will be tested autonomous driving system Drive Me from Volvo. Again, the purpose of autonomy - while the convenience of the driver and driving safety in the event that the owner of the car wants, for example, have lunch at the wheel or type a couple of messages in the messenger. Monitoring the environment, including the movement of pedestrians, will be possible with the help of a clever combination of radar, cameras and lasers. Volvo focuses on the fact that they make real systems for real roads and consumers.
To test Volvo plans to attract the most ordinary people of different sexes, ages, with different driving experience. During testing, the company plans to collect "terabytes of data" about security, usability, consumer experience, traffic flows, energy efficiency. Based on these data, the system will be refined. The base car for testing is the XC90s.

In 2015, at the Geneva Motor Show, the Italian studio Italdesign Giugiaro presented the GEA car (there is a version that it was partly a prototype Audi A9, someone refers to Audi in the near future) with fully autonomous control. Due to the fact that the driver behind the wheel (the joystick wheel) has nothing to do, the GEA has three modes: a study, a gym and a rest room. In Business mode, the cabin provides two 19-inch monitors and a turntable for comfortable conversation. Wellness-mode gives instructions for the exercises on the handles built into the rear seat. Finally, Dream mode provides the driver with an extensive bed for sleeping. For all the options work is selected atmosphere and lighting. The car can be controlled from a smartphone through a special application. The technical characteristics of the concept are also outstanding: 4 engines with a total capacity of 775 hp, length 5370 mm, maximum speed of 250 km / h.

Audi traits are clearly read.
You can not leave the review of smart cars without attention to the legendary and, perhaps, the most German mark - BMW. The Bavarian automaker rarely looks back on others and is at the forefront of the market through design and technology. According to the KPMG report, the concern is leading in smart and unmanned vehicle technology.
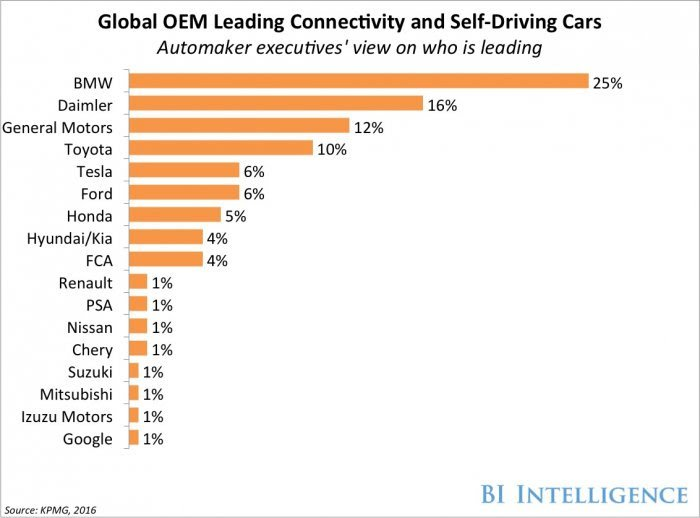
In the case of smart cars, the story is this: in addition to the unmanned versions, which we’ll talk about below, there are production cars that use everything that was created for the smart cars of our time. At the beginning of 2017, among the leaders are the BMW i8, the hybrid BMW X5 PHEV and BMW 7 (which, among other things, projects the dashboard data onto the windshield, has a heavily updated iDrive and perceives the control of the sensor with gestures). These BMW models (like others) are equipped with a large number of sensors and are smart precisely from the point of view of safety - they analyze the situation on the road and, having in mind a huge amount of information, literally predict adverse events, thereby preventing them. Also, BMW has a built-in Vodafon operator SIM card, which roams in the networks of almost any cellular operator in the world (in Russia - everyone) and conveys important information: to the driver - about the need for another THAT, battery charge level, nearest car services, help points and even hotels, restaurants, etc., and from the driver - about critical situations on the road. So, you can call for help with one SOS button and the operator will receive the data of the owner and the exact coordinates of the incident. If it is impossible to reach the button - the car itself will transmit a distress signal to special services.

X5 with hybrid engine
Together with Mobileye and Intel, BMW is developing the iNEXT unmanned software and network platform, which will be designed both for installation on the concern’s cars and for sale to other automakers. In 2021, BMW plans to release a third-level mobile vehicle, which will continue to require the presence of a person (fourth level - it is possible to do anything other than driving, fifth level - the car will go where you (he?) Need it).

From the wheels is simply impossible to tear off
About Tesla is written so much and in detail that it is even boring to tell. But not to mention this project is simply impossible. First of all, because of the autonomy unique to the production car: a set of sensors protects the car from collisions, and the 360-degree camera recognizes road markings, intersections, other cars and vehicles, and pedestrians. Thus, the car independently regulates the controls and speed. In the process of using the car, the autopilot learns itself and at the same time transmits data to the servers of Tesla Motors, whose employees analyze and improve the system.
The Tesla Model S electronic filling is based on the information and control system on two Tegra3 processors, the first of which is responsible for devices and sensors, and the second is for entertainment and informing the driver through a 17-inch display. The software is based on the Linux kernel and a special shell developed by Tesla Motors. Software updates are released quite often and downloaded "over the air."
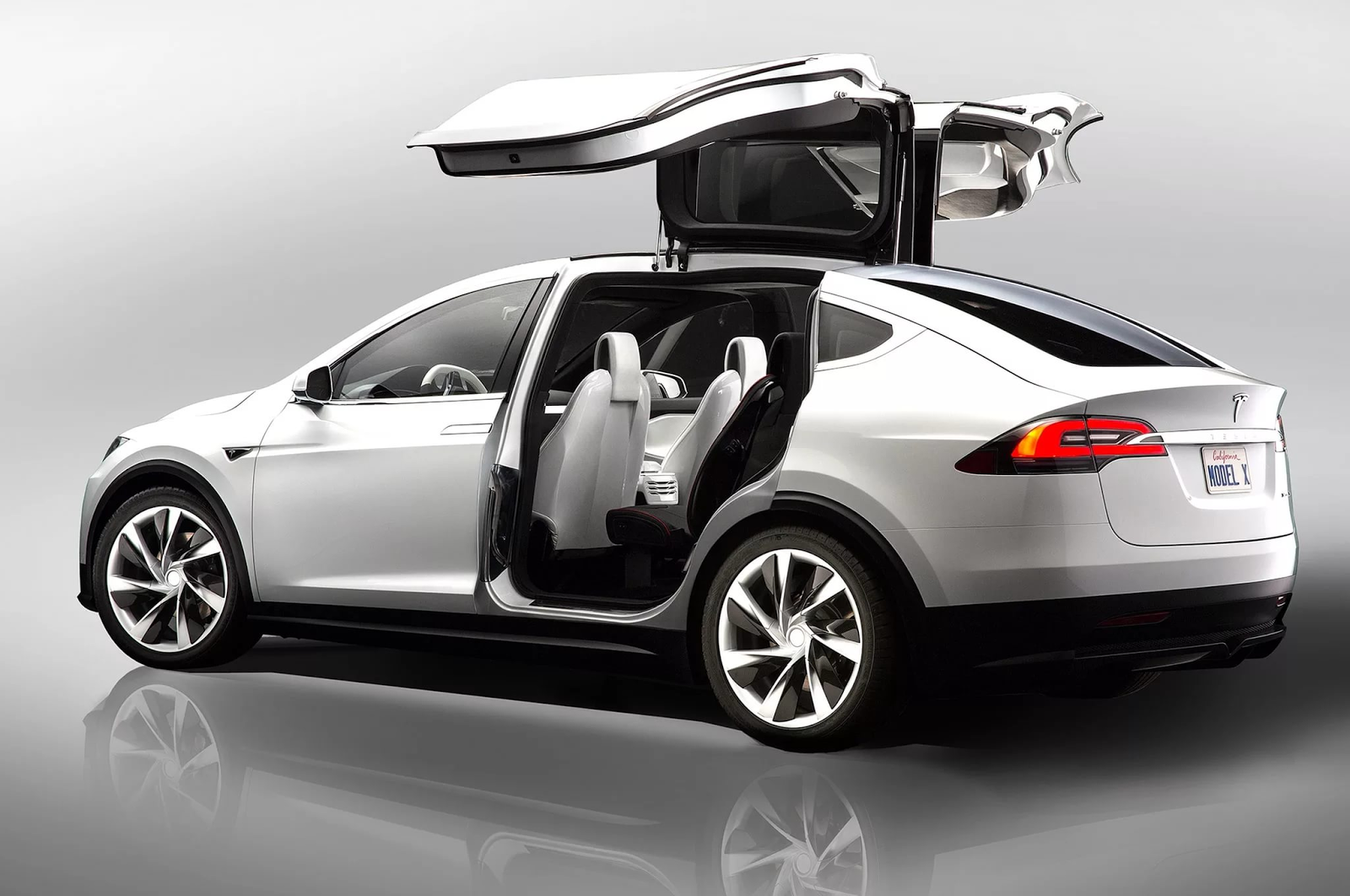

Tesla Model X
Faraday Future is a California startup funded by a Chinese company LeEco, which is trying to create its own ecosystem and produce literally everything. Already from the name of the project it is clear that we are talking about an intelligent electric car and from it it is obvious that the creator of a startup considers Tesla to be the main competitor. After a series of rumors about bankruptcy and the failure of the project, the company presented the Faraday Future FF 91 serial all-electric crossover in a rather unusual streamlined body design. The car turned out to be overall (5250 mm long, 3200 mm wheelbase) and ergonomic, with a low (0.25) drag coefficient. The native platform Variable Platform Architecture (VPA) includes 4 electric motors and a battery pack. Power of electric motors in the aggregate - 1050 hp, acceleration to a hundred in 2.4 seconds.
Faraday technology is also impressive: 10 cameras of circular view, 13 radar sensors, 12 ultrasonic sensors and one 3D LIDAR scanner (laser version of the radar, the same pipka on the hood). In the car, you can set up FFID accounts, which “recognize” the driver in person and immediately set up the car options for him.
By the way, this crossover is still a mild version of a Chinese electric car, the first concept had a super bold design. The company is doing something with varying success: in November 2016, LeEco announced a lack of funds and austerity, and just a few days ago at CES in Las Vegas, the crossover was presented to the public, but not without technical failures. The launch of mass production is scheduled for 2018 - we will soon see how the story of the Chinese rival Tesla will end.

One of the most promising applications of platforms for unmanned vehicles is freight transport, which is used in construction, industry and agriculture. Mercedes has created a drone Future Truck 2025, designed to move on major routes. Autopilot functions are implemented on the basis of dual cameras, sensors, radar and dead point technology. Special radar listens and looks at the road, assessing the terrain or, for example, catching the special signals of emergency vehicles. During autopilot, the driver should be inside but can relax comfortably with the tablet in hand. To drive a car in an urban setting, such a wagon needs a driver.

This is how we represent the truckers of the future.
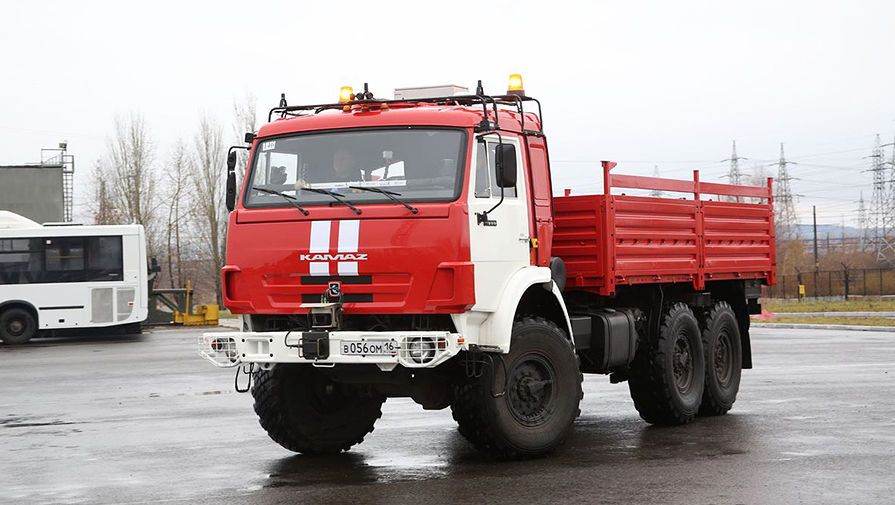
The Russian KamAZ also began testing the unmanned version. KamAZ, together with Cognitive Technologies and VIST Group, is implementing a project of an unmanned vehicle that will control the gas and brake pedals itself, the steering wheel drive and the automatic transmission. The basis for the prototype was a serial KAMAZ-5350, which has four video cameras, three radars and a lidar - an active optical sensor that performs the role of a laser range finder. The cockpit contains control drives and two computers connected by an Ethernet network. Unmanned KamAZ uses the technology of passive computer vision: in less than 0.3 seconds the truck detects obstacles in its path, recognizes traffic signs and traffic lights. In contrast to foreign unmanned vehicles, KAMAZ imbued with the Russian reality and does not work based on the recognition of road markings on a perfectly flat highway.

We can confidently say that we live in the era of smart cars that will fall into one of three groups: familiar cars stuffed with electronics, unmanned vehicles and electronic assistants. An extra example is not mentioned above, but present on the market smart cars VW iBeetle with the Apple ecosystem - all the onboard electrical systems are integrated with the iPhone, and even the bulky and clumsy Ford F-150 pickup with voice control. These are production cars, available for purchase and ready to work for their owner. In any case, it is obvious that the development of electronic and software components of cars will develop, seeking a compromise between the needs for security, information component and entertainment.
But most of all I want to, despite the enormous possibilities of electronics, the subjective remains, but the main thing is driving pleasure.

Remember how it all began
The first technological revolution in the automotive industry was the interest of automotive companies to electric starters - they were first installed in 1911. Then innovations began to concern the convenience of the driver and even his entertainment behind the wheel: in 1925 the cigarette lighter appeared, in 1930 - the radio, in 1956 - the power steering, in 1970 - the cassette deck, in 1984 - the airbags. A year later - CD players, in 1994 - the instrument panel of computer diagnostics of the car, in 1995 - GPS, in 2000 - USB and Bluetooth, the first signs of the “connected” car to the whole.
The first experience of creating a smart car occurred in the middle of the twentieth century. General Motors Firebird II - four-seater car in 1956 with independent suspension. Under the titanium case, there was a Whirlfire GT-304 gas turbine engine for 200 hp, electric equipment and an integrated level air conditioning system no worse than at the beginning of the XXI century. In terms of design and ergonomics, Firebird II continued the 1953 version of the car, which was called the “jet airplane on wheels” (the developers and engineers were really inspired by the concepts of the fighters of that time). However, in Firebird II, the structure was used for the first time on the road of the future — a complex control system that had to interact with the electrical wire built into the carriageway to send signals and serve as a guide for newer cars. It was assumed that the electromagnetic field minimizes dangerous situations on the road, reducing the human factor. In those times, it was too bold a model that caused a sensation at the exhibitions, but never got into mass production.
')

Future highways were built in Europe and the USA. The first production car that really began to interact with them was the Citroen DS, the legendary passenger car that ranked third in the ranking of cars of the century. Low-power engine 75 hp Nothing stood out in those days, but the car was distinguished by an advanced transmission combined with steering, brakes and hydropneumatic suspension. This design ahead of the development of the automotive industry for many years to come. The Citroen DS was able to interact with the highway using an electric signal, but there was no question of any independent autopilot — it was more fun. By the way, it is incredible popularity, advanced technology and, albeit a relatively illusory one, but the autopilot made this Citroen a flying car of Fantômas.

Experiments with on-board computers in the 60-70 years. were held, but never entered the series. It is worth remembering the experimental Chrysler Plymouth, which was equipped with an on-board computer (well, as far as can be called an on-board computer, which occupied half of the rear seat) and a generator to power the system, placed on the roof of the car. Laboratory tests were carried out for 10 years, but there could be no question of any serial production.
However, neither engineering thought nor futurist fantasy stopped for a minute - mankind was looking for cars not only a luxury or a means of transportation, but also a clever helper who could make life easier, make roads safe, work for a man. Such a desire was reflected in the movies - after several films with “talking” cars, the James Bond series of films with his heaped cars and, of course, the legendary “Knight of the Roads” became real hits. The smart, humorous KITT based on the Pontiac Firebird Trans AM not only accelerated at 500 km / h and was almost invulnerable, but also knew how to talk, ride full autopilot and control all electronic devices from a distance.

Kitt inside
Surely, the utilitarian reality did not coincide with the dreams of the engineers of the past - commerce and the notorious business expediency influenced the shaping of modern smart cars.
- Car manufacturers began to strive to meet the requirements of the mass consumer, which is spoiled by the IT industry. Cruise control, media devices for playing content, built-in phones in the 80s-90s and so on became the mind of cars.
- Manufacturers of tablets and smartphones began to lobby their interests in order to integrate into cars (for example, Samsung tablets are built into some BMW cars).
- Users began to impose increased requirements for e-stuffing: from entertainment content to security systems and the ability to work with alerts on the condition of the car.
Modern smart cars
One of the first prototypes proposed by Google - Google Car. This is a mini-car with an unprecedented level of autonomy. The machine is designed for two people, has two engines, non-standard body materials, is fully electric, reaches a speed of 25 miles / hour (a little more than 40 km / h), is controlled from the start button and does not require the presence of a person except as a passenger. Naturally, it is integrated with Google services - on the central console you can watch videos and movies on Youtube, work with mail, search in Chrome. By the way, the car was also built by Google, since previous partners Lexus and Toyota expectedly imposed many restrictions on risky experiments. Exit to the mass market of personal vehicles is extremely difficult, and in December 2016, Google (more precisely, the holding Alphabet) turned the project to create your unmanned vehicle. The company continues to develop autopilots, but for ordinary automakers.

Vehicle Operating Systems
Surely most readers will come up with the first Android OS. Indeed, this operating system is present in cars, and not only on embedded tablets. The distribution of the system began with the creation of the Open Automotive Alliance, which included Google, NVIDIA, Audi, General Motors GM, Honda and Hyundai. We must not forget about Tesla, on board which are large 17-inch displays based on Android. However, for the time being, the use of this operating system is mainly aimed at creating information and entertainment filling of the car, including navigation functions. In the near future, the new platform will have to provide an increase in comfort and an increase in the level of vehicle safety.
iOS does not lag behind its competitor, and while the whole world is waiting for the first i-mobile or i-Car by 2020 (they say it will be something unmanned on the basis of the BMW i3), Apple has implemented the Apple Carplay system, which allows you to connect iPhone 5th and above. Not all cars support the system yet, but most of the top manufacturers are already on the list. Of course, there is no talk about the operating system here either - just the integration of iOS devices into the infrastructure of the onboard computer. Again, the entertainment aspect comes out on top - here are both hands-free conversations, and iTunes voice control. By the way, the development of the drone Apple is strictly classified - try to find something, besides common phrases, about the Project Titan project.
Microsoft didn’t make a revolution either, but chose a different vector of development and set its sights on voice control of the car’s functions so as not to distract the driver from the road. What is happening with the Microsoft software for cars can be described as a fully embedded smartphone in the car. Well, that is, you can wait for jokes from the category of "wait, I will park the phone."
Already this year, will be tested autonomous driving system Drive Me from Volvo. Again, the purpose of autonomy - while the convenience of the driver and driving safety in the event that the owner of the car wants, for example, have lunch at the wheel or type a couple of messages in the messenger. Monitoring the environment, including the movement of pedestrians, will be possible with the help of a clever combination of radar, cameras and lasers. Volvo focuses on the fact that they make real systems for real roads and consumers.
To test Volvo plans to attract the most ordinary people of different sexes, ages, with different driving experience. During testing, the company plans to collect "terabytes of data" about security, usability, consumer experience, traffic flows, energy efficiency. Based on these data, the system will be refined. The base car for testing is the XC90s.

In 2015, at the Geneva Motor Show, the Italian studio Italdesign Giugiaro presented the GEA car (there is a version that it was partly a prototype Audi A9, someone refers to Audi in the near future) with fully autonomous control. Due to the fact that the driver behind the wheel (the joystick wheel) has nothing to do, the GEA has three modes: a study, a gym and a rest room. In Business mode, the cabin provides two 19-inch monitors and a turntable for comfortable conversation. Wellness-mode gives instructions for the exercises on the handles built into the rear seat. Finally, Dream mode provides the driver with an extensive bed for sleeping. For all the options work is selected atmosphere and lighting. The car can be controlled from a smartphone through a special application. The technical characteristics of the concept are also outstanding: 4 engines with a total capacity of 775 hp, length 5370 mm, maximum speed of 250 km / h.

Audi traits are clearly read.
You can not leave the review of smart cars without attention to the legendary and, perhaps, the most German mark - BMW. The Bavarian automaker rarely looks back on others and is at the forefront of the market through design and technology. According to the KPMG report, the concern is leading in smart and unmanned vehicle technology.

In the case of smart cars, the story is this: in addition to the unmanned versions, which we’ll talk about below, there are production cars that use everything that was created for the smart cars of our time. At the beginning of 2017, among the leaders are the BMW i8, the hybrid BMW X5 PHEV and BMW 7 (which, among other things, projects the dashboard data onto the windshield, has a heavily updated iDrive and perceives the control of the sensor with gestures). These BMW models (like others) are equipped with a large number of sensors and are smart precisely from the point of view of safety - they analyze the situation on the road and, having in mind a huge amount of information, literally predict adverse events, thereby preventing them. Also, BMW has a built-in Vodafon operator SIM card, which roams in the networks of almost any cellular operator in the world (in Russia - everyone) and conveys important information: to the driver - about the need for another THAT, battery charge level, nearest car services, help points and even hotels, restaurants, etc., and from the driver - about critical situations on the road. So, you can call for help with one SOS button and the operator will receive the data of the owner and the exact coordinates of the incident. If it is impossible to reach the button - the car itself will transmit a distress signal to special services.

X5 with hybrid engine
Together with Mobileye and Intel, BMW is developing the iNEXT unmanned software and network platform, which will be designed both for installation on the concern’s cars and for sale to other automakers. In 2021, BMW plans to release a third-level mobile vehicle, which will continue to require the presence of a person (fourth level - it is possible to do anything other than driving, fifth level - the car will go where you (he?) Need it).

From the wheels is simply impossible to tear off
Car software
AUTOSAR (AUTomotive Open System ARchitecture) is an organization that has as its goal the creation of a standardized open software structure for car electronics, except for infotainment systems. Such software should be scalable (extend to different vehicles and platforms), localized, relevant security requirements and maintainable for the entire life of the vehicle. The AUTOSAR standard extends to body electronics, powertrain, chassis and security systems, as well as multimedia systems, telematics, and the driver-vehicle interface.
The standard onboard electronics protocol FlexRay is a high-speed network protocol for automobiles developed by the global consortium FlexRay, founded by NXP in partnership with BMW, DaimlerChrysler, Bosch, GM and Volkswagen. The data transfer rate on it reaches 10 Mbps. It is ten times faster than the modern CAN bus (Controller-Area Network) and even more so - the already outdated and very slow diagnostic OBD (On Board Diagnostic). FlexRay controllers will work for the control of those parts of the car in which the question of modern diagnostics is equal to the question of life and death: engine, transmission, suspension, brakes, steering. Also, the protocol should in principle expand the capabilities of the onboard control.
The Automotive Safety Restraints Bus specification (ASRB 2.0) is a standard for vehicle electronic systems that are also responsible for the physical safety of the driver and passengers.
Auto pilots, car parks and navigation systems - software and hardware, without which driving will soon be difficult to imagine. In addition, these systems are already assigned the function of security and protection (for example, calling special services in the event of a serious accident), and in the future this functionality will only increase.
They are also used in automobiles and typical for IoT (Internet of Things) solutions: for example, GM collaborates with IBM in order to use Watson for smart cars.
Not to mention the main problem of software for cars - it must take into account the peculiarities of iron, which can even be used for more than ten years, which means there must be advanced updates. And even better - software, ahead of time.
Details on the software of smart cars can be found in the material Compress .
About Tesla is written so much and in detail that it is even boring to tell. But not to mention this project is simply impossible. First of all, because of the autonomy unique to the production car: a set of sensors protects the car from collisions, and the 360-degree camera recognizes road markings, intersections, other cars and vehicles, and pedestrians. Thus, the car independently regulates the controls and speed. In the process of using the car, the autopilot learns itself and at the same time transmits data to the servers of Tesla Motors, whose employees analyze and improve the system.
The Tesla Model S electronic filling is based on the information and control system on two Tegra3 processors, the first of which is responsible for devices and sensors, and the second is for entertainment and informing the driver through a 17-inch display. The software is based on the Linux kernel and a special shell developed by Tesla Motors. Software updates are released quite often and downloaded "over the air."

Tesla Model X
Faraday Future is a California startup funded by a Chinese company LeEco, which is trying to create its own ecosystem and produce literally everything. Already from the name of the project it is clear that we are talking about an intelligent electric car and from it it is obvious that the creator of a startup considers Tesla to be the main competitor. After a series of rumors about bankruptcy and the failure of the project, the company presented the Faraday Future FF 91 serial all-electric crossover in a rather unusual streamlined body design. The car turned out to be overall (5250 mm long, 3200 mm wheelbase) and ergonomic, with a low (0.25) drag coefficient. The native platform Variable Platform Architecture (VPA) includes 4 electric motors and a battery pack. Power of electric motors in the aggregate - 1050 hp, acceleration to a hundred in 2.4 seconds.
Faraday technology is also impressive: 10 cameras of circular view, 13 radar sensors, 12 ultrasonic sensors and one 3D LIDAR scanner (laser version of the radar, the same pipka on the hood). In the car, you can set up FFID accounts, which “recognize” the driver in person and immediately set up the car options for him.
By the way, this crossover is still a mild version of a Chinese electric car, the first concept had a super bold design. The company is doing something with varying success: in November 2016, LeEco announced a lack of funds and austerity, and just a few days ago at CES in Las Vegas, the crossover was presented to the public, but not without technical failures. The launch of mass production is scheduled for 2018 - we will soon see how the story of the Chinese rival Tesla will end.

One of the most promising applications of platforms for unmanned vehicles is freight transport, which is used in construction, industry and agriculture. Mercedes has created a drone Future Truck 2025, designed to move on major routes. Autopilot functions are implemented on the basis of dual cameras, sensors, radar and dead point technology. Special radar listens and looks at the road, assessing the terrain or, for example, catching the special signals of emergency vehicles. During autopilot, the driver should be inside but can relax comfortably with the tablet in hand. To drive a car in an urban setting, such a wagon needs a driver.

This is how we represent the truckers of the future.
The Russian KamAZ also began testing the unmanned version. KamAZ, together with Cognitive Technologies and VIST Group, is implementing a project of an unmanned vehicle that will control the gas and brake pedals itself, the steering wheel drive and the automatic transmission. The basis for the prototype was a serial KAMAZ-5350, which has four video cameras, three radars and a lidar - an active optical sensor that performs the role of a laser range finder. The cockpit contains control drives and two computers connected by an Ethernet network. Unmanned KamAZ uses the technology of passive computer vision: in less than 0.3 seconds the truck detects obstacles in its path, recognizes traffic signs and traffic lights. In contrast to foreign unmanned vehicles, KAMAZ imbued with the Russian reality and does not work based on the recognition of road markings on a perfectly flat highway.

We can confidently say that we live in the era of smart cars that will fall into one of three groups: familiar cars stuffed with electronics, unmanned vehicles and electronic assistants. An extra example is not mentioned above, but present on the market smart cars VW iBeetle with the Apple ecosystem - all the onboard electrical systems are integrated with the iPhone, and even the bulky and clumsy Ford F-150 pickup with voice control. These are production cars, available for purchase and ready to work for their owner. In any case, it is obvious that the development of electronic and software components of cars will develop, seeking a compromise between the needs for security, information component and entertainment.
But most of all I want to, despite the enormous possibilities of electronics, the subjective remains, but the main thing is driving pleasure.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/403291/
All Articles