Great post about projectors: technology, appointment, choice, development prospects
Multimedia projector has long become a familiar gadget for offices, presentations, meeting rooms, museums, educational institutions. Increasingly, projectors are used at home. These devices survive in a fairly complex competitive climate (plasma, LCD and laser panels - competitors of projectors), while having only one huge advantage - the large diagonal of the projected image.

The abundance of technologies used for the production of projectors gives rise to the problem of choice. As Pult.ru specialists note, buyers who intend to buy a projector rarely have what they want, which is not rarely leads to mistakes in choosing. This post is about the main criteria for the selection of projectors and the prospects for the development of modern technologies that are used in their production.
While the most common light sources in the projectors are high-pressure discharge lamps. And these lamps are recognized as the Achilles' heel of most modern projectors, since most of them require replacement after 1000 - 4000 (in rare cases, 8000) hours of operation.
')
This impressive cost of consumables has to be changed every 3-4 years, and with intensive use more often. Engineers from leading world manufacturers tried to solve the problem of a not too resource-intensive light source.
Uhp
The most commonly used projection lamps are UHP (Ultra High Performance). The principle is simple - a discharge in the lamp that occurs between tungsten electrodes in mercury vapor, which are under high pressure. The main advantages of these lamps are the relative high intensity of light radiation with a fairly compact source size, as well as good color rendering.

The disadvantages of UHP lamps are a gradual decrease in the intensity of radiation throughout the entire period of operation and a relatively short lifetime (2000 hours). Partly, the first deficiency was compensated by the addition of special reagents that contribute to the restoration of tungsten on the electrodes. Partially extends the life of the lamp using glass from high-purity quartz, which allows you to maintain a balance of thermal energy produced by the lamp.
HCX
HCX projection lamps or metal halide lamps, like others, emit light due to the discharge of an electric arc plasma produced in high-pressure gas. They are distinguished from UHD by the addition of certain metals to the mercury vapor of the halides, which makes it possible to make the spectral characteristic of the light emission more uniform.
The problem with these lamps is a gradual, but at the same time, permanent loss of brightness, up to 50% during the operation of the source. The operating time of these lamps is comparable with other gas-discharge analogues.
P-VIP
P-VIP is another variation on “Mercury discharge lamps for a projector”. This type can be considered the pinnacle of the evolution of mercury projector lamps. The service life of these lamps can reach 6000 - 8000 hours, the radiation intensity and spectrum uniformity is comparable to HCX, while the P-VIP does not have the disease "age-related decrease in brightness", the lamp shines equally coolly throughout the entire service life. Despite the success in extending the full life of this type of lamps, their problems have not been solved at the root.

Xenon
Another type of discharge lamps for projectors is Xenon. As the name suggests, instead of mercury vapor in the lamp is compressed xenon. Xenon lamps are many times superior to mercury in power, pressure and, as a result, in light intensity.

The power of xenon lamps is in the range from 2 to 15 kW, and the gas pressure in the lamp reaches 300 atmospheres, which predetermined their use in professional cinema projectors and extremely rarely in extremely expensive demonstration and home models. As the saying goes, “All the best tochildren’s cinemas.”

Fortunately, the use of high-pressure discharge lamps gradually dies away, giving way to more advanced light sources. Their use allows for relatively high levels of brightness and contrast, but, as I have already noted, they are expensive and require replacement from time to time.
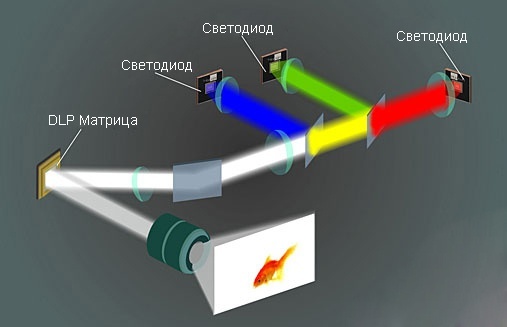
An alternative to gas discharge lamps, which appeared at the beginning of the last century, were LEDs and lasers. Each of these sources has the advantage of long-term work. In fact, both LEDs and lasers are able to provide at least 20,000 hours of work, and in some cases work longer. In addition, LED and laser projectors can reduce the minimum distance to the screen. The great advantages of laser projectors over the other types are high image quality and the complete absence of “fastidiousness” to the surface on which the image is projected. Sadly, both alternatives have characteristic drawbacks.
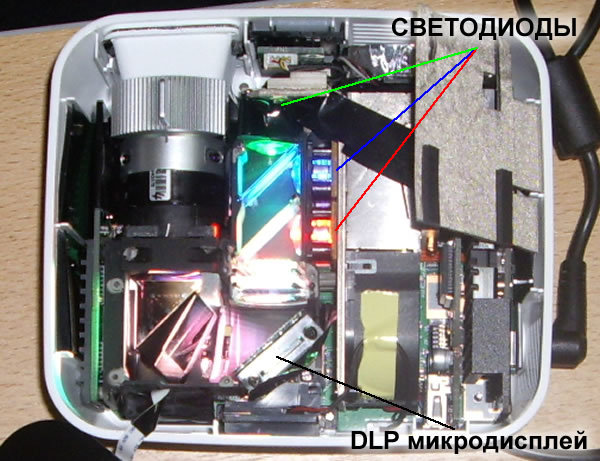

Disadvantages of LED
Despite the impressive progress over the past 8 years, most LED projectors with an equal cost are inferior to tube ones in luminous intensity. For most models, the luminous flux of the source does not exceed 1000 -1200 ANSILm, and in most cases is within 1000. Another problem with Led-projectors is the noise level during operation, which often exceeds 35 dB. However, these shortcomings are gradually eliminated, it is worth remembering that at the time of the release of the first mass-produced serial led-projectors (2008 - 2009), the record brightness of the latter was 350-400 ANSILm.
Disadvantages of laser projectors
The main disadvantage of laser projectors is the price. Despite the serial production of laser projectors for the last 10 years, the price has not decreased to the figures imputed to the average person. Also tangible disadvantages of laser devices include source flicker and unnatural saturation of some colors. In some models, there are quite sharp transitions in the color palette, which can be annoying during long-term viewing. It is also worth noting that some of the difficulties in color rendering can be easily eliminated by additional configuration.

Hybrid schemes
Increasingly, hybrid models are emerging on the market, which use both laser and LEDs as sources of luminous flux. The use of this approach makes it possible to compensate for the shortcomings of one source by another. Most of the reviews and comparative tests of such systems are at the level of lamp projectors, while maintaining the main advantage of alternative sources - an enormous operational resource. Lack of one - indecently high cost.
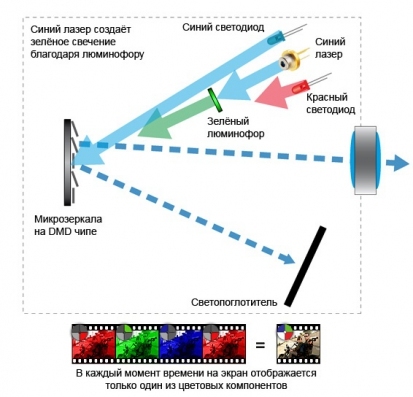
Before making specific recommendations on the choice of projectors, it is necessary to tell a little about the types of these devices. The following types of projectors are most widely represented on the market today:
It makes no sense to describe each of the principles in detail, as there is more than enough encyclopedic material in the network. I believe that it is better to dwell on the advantages and disadvantages of each of them. To get into a rather prolonged dispute with biased lovers to say nothing about what is actually steeper than 3DLP (DLP), LCD (3LCD), LCOS or 3LED will not. In connection with the different tasks that are put before projectors, the advantages of one technology or another determine the choice, and in the premium segment, the disadvantages of technology are leveled a little less than completely. I can only note that several chips are better than one, as they allow to increase the image quality for a number of parameters.
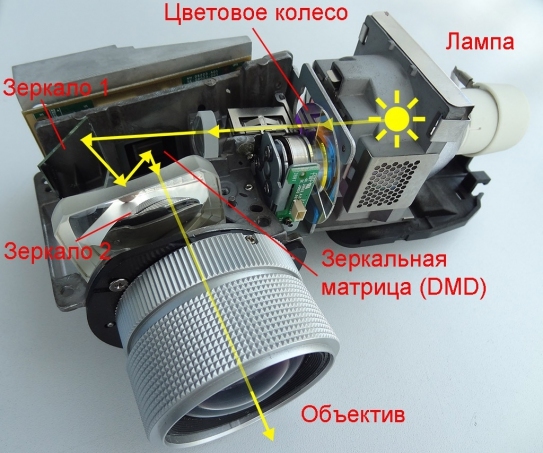
DLP and 3DLP are the champions in contrast
DLP advantages:

Disadvantages of DLP:
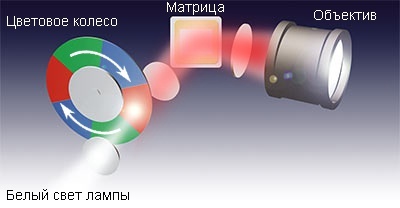
3LCD - color brightness leaders
Advantages of 3LCD:
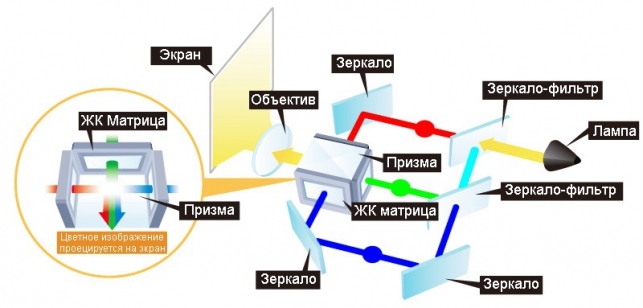
Disadvantages of 3LCD:
LCOS - expensive "golden mean"
The merits of LCOS

Disadvantages of LCOS:
3LED - winners of marathon distances
Advantages of 3 led:
Disadvantages 3 LED
When choosing a projector it is worth considering a number of characteristics on which the result will depend.
Brightness
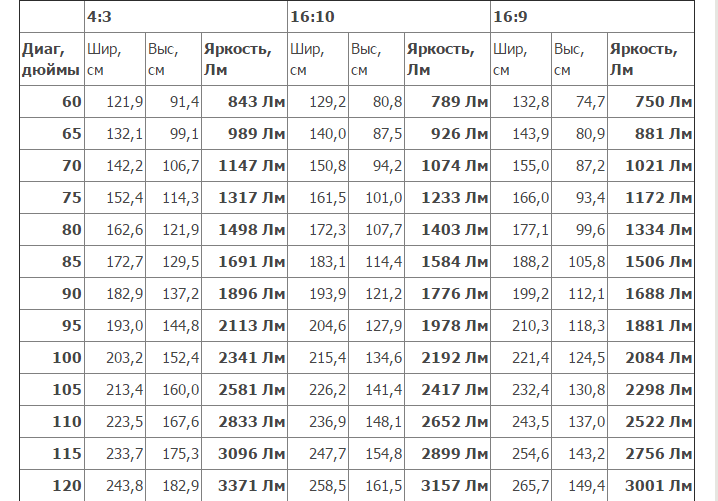
If necessary, calculate the luminous flux of the projector for an audience or a room where the lighting complies with current sanitary and hygienic standards (the room where you can read and work, you can multiply 756 by the square of the screen in square meters.
Below is a table calculating the brightness required by the projector, depending on the screen area when the light is sufficient to read.



Resolution
Below are the standards and permissions according to the format.
1. Aspect ratio 4: 3:
2. Image format 16: 9, 16:10, 15: 9 or others:
Uniform lighting
Rarely indicated parameter that demonstrates the ratio of the minimum peripheral illumination of the screen to the maximum in the center. In the projector for watching movies and games and in professional devices, the value of uniformity must exceed 70%.
And a little more about the contrast
Contrast has the maximum effect on image quality in darkened rooms. In many respects, therefore, high-contrast models of projectors are used as an element of systems for home theaters. If you need to get a distinguishable image in the lighted interiors, you should rely on the brightness.
As I have already noted, people who buy projectors rarely imagine which one they need, which not so decent sellers sometimes use.
I will start with educational institutions where the projector allows you to show presentations and educational films. Requirements for quality are minimal, while, as a rule, there are requirements for the price and in some cases for brightness. For rooms where dimming is possible, single-chip DLP, 3 LED or 3 LCD projectors and with a brightness of 700 - 1000 ANSIlm are suitable; in rooms where there is a problem with dimming, a more powerful luminous flux, respectively, from 1000 ANSIlm and higher is needed. As a rule, in the ratio of brightness / price win 3 LCD projectors. At the same time for rooms with the possibility of darkening DLP are considered preferable.

The choice of a business projector for presentations will also be related to the working conditions and tasks, with the only difference that, as a rule, a higher resolution (HD) is required for business, and the cost will increase accordingly.
For professional presentations and long-term work, laser and hybrid 3 DLP, 3 LCD and LCOS projectors can be used, which provide long-term operation and high-quality images, usually with FullHD and WUXGA, 4 K HD resolution. The values of the luminous flux in such projectors, designed to work in illuminated rooms, as well as during the day outside can reach 20,000 ANSIlm.
Despite the tough competition from LCD TVs and plasma panels, projectors are no longer exotic at home. For home theater and gaming systems, most experts recommend DLP and 3DLP projectors, since the latter distort the picture less and work much more efficiently in 3D mode.

The most attractive and promising light sources in projectors are lasers and LEDs, which, all other things being equal, give odds to the rest of the operational resource. Experts say that the future is behind them and this future is near. According to the calculations of a number of manufacturers, gas-discharge lamps will be abandoned in the next 10 years.
The material is built on the comments of experts pult.ru, used graphic materials sites: myprojector.ru, projector-lamps.ru, viking.ru, giga-line.ru, stereo.ru
PS The cost of projectors, depending on the destination, varies widely, our catalog contains projectors from 19,790 to 10,452,850. If we talk about training, office, the average cost of the latter (depending on the characteristics and the technology used) varies from 19,790 to 300 000. In the case of equipment for home theaters and games, if not to affect professional and HI END lines, the average cost of such a projector will be about 90 000 - 150 000 (again, depending on the characteristics and technology used ogii). The presented information on prices is rather arbitrary, the price largely depends on the manufacturer, functions, design and capabilities of the device.

The abundance of technologies used for the production of projectors gives rise to the problem of choice. As Pult.ru specialists note, buyers who intend to buy a projector rarely have what they want, which is not rarely leads to mistakes in choosing. This post is about the main criteria for the selection of projectors and the prospects for the development of modern technologies that are used in their production.
Lamps
While the most common light sources in the projectors are high-pressure discharge lamps. And these lamps are recognized as the Achilles' heel of most modern projectors, since most of them require replacement after 1000 - 4000 (in rare cases, 8000) hours of operation.
')
This impressive cost of consumables has to be changed every 3-4 years, and with intensive use more often. Engineers from leading world manufacturers tried to solve the problem of a not too resource-intensive light source.
Uhp
The most commonly used projection lamps are UHP (Ultra High Performance). The principle is simple - a discharge in the lamp that occurs between tungsten electrodes in mercury vapor, which are under high pressure. The main advantages of these lamps are the relative high intensity of light radiation with a fairly compact source size, as well as good color rendering.

The disadvantages of UHP lamps are a gradual decrease in the intensity of radiation throughout the entire period of operation and a relatively short lifetime (2000 hours). Partly, the first deficiency was compensated by the addition of special reagents that contribute to the restoration of tungsten on the electrodes. Partially extends the life of the lamp using glass from high-purity quartz, which allows you to maintain a balance of thermal energy produced by the lamp.
HCX
HCX projection lamps or metal halide lamps, like others, emit light due to the discharge of an electric arc plasma produced in high-pressure gas. They are distinguished from UHD by the addition of certain metals to the mercury vapor of the halides, which makes it possible to make the spectral characteristic of the light emission more uniform.

The problem with these lamps is a gradual, but at the same time, permanent loss of brightness, up to 50% during the operation of the source. The operating time of these lamps is comparable with other gas-discharge analogues.
P-VIP
P-VIP is another variation on “Mercury discharge lamps for a projector”. This type can be considered the pinnacle of the evolution of mercury projector lamps. The service life of these lamps can reach 6000 - 8000 hours, the radiation intensity and spectrum uniformity is comparable to HCX, while the P-VIP does not have the disease "age-related decrease in brightness", the lamp shines equally coolly throughout the entire service life. Despite the success in extending the full life of this type of lamps, their problems have not been solved at the root.

Xenon
Another type of discharge lamps for projectors is Xenon. As the name suggests, instead of mercury vapor in the lamp is compressed xenon. Xenon lamps are many times superior to mercury in power, pressure and, as a result, in light intensity.

The power of xenon lamps is in the range from 2 to 15 kW, and the gas pressure in the lamp reaches 300 atmospheres, which predetermined their use in professional cinema projectors and extremely rarely in extremely expensive demonstration and home models. As the saying goes, “All the best to

Comparison of the spectra of "xenon" and "mercury"
Axis X - wave length in nm
Y axis - recoil
blue graph - "xenon", red - "mercury"
Fortunately, the use of high-pressure discharge lamps gradually dies away, giving way to more advanced light sources. Their use allows for relatively high levels of brightness and contrast, but, as I have already noted, they are expensive and require replacement from time to time.
Not lamps - led vs laser
An alternative to gas discharge lamps, which appeared at the beginning of the last century, were LEDs and lasers. Each of these sources has the advantage of long-term work. In fact, both LEDs and lasers are able to provide at least 20,000 hours of work, and in some cases work longer. In addition, LED and laser projectors can reduce the minimum distance to the screen. The great advantages of laser projectors over the other types are high image quality and the complete absence of “fastidiousness” to the surface on which the image is projected. Sadly, both alternatives have characteristic drawbacks.

Disadvantages of LED
Despite the impressive progress over the past 8 years, most LED projectors with an equal cost are inferior to tube ones in luminous intensity. For most models, the luminous flux of the source does not exceed 1000 -1200 ANSILm, and in most cases is within 1000. Another problem with Led-projectors is the noise level during operation, which often exceeds 35 dB. However, these shortcomings are gradually eliminated, it is worth remembering that at the time of the release of the first mass-produced serial led-projectors (2008 - 2009), the record brightness of the latter was 350-400 ANSILm.
Disadvantages of laser projectors
The main disadvantage of laser projectors is the price. Despite the serial production of laser projectors for the last 10 years, the price has not decreased to the figures imputed to the average person. Also tangible disadvantages of laser devices include source flicker and unnatural saturation of some colors. In some models, there are quite sharp transitions in the color palette, which can be annoying during long-term viewing. It is also worth noting that some of the difficulties in color rendering can be easily eliminated by additional configuration.

Hybrid schemes
Increasingly, hybrid models are emerging on the market, which use both laser and LEDs as sources of luminous flux. The use of this approach makes it possible to compensate for the shortcomings of one source by another. Most of the reviews and comparative tests of such systems are at the level of lamp projectors, while maintaining the main advantage of alternative sources - an enormous operational resource. Lack of one - indecently high cost.

The advantages and disadvantages of the basic principles of work
Before making specific recommendations on the choice of projectors, it is necessary to tell a little about the types of these devices. The following types of projectors are most widely represented on the market today:
- DLP (3DLP)
- LCD (3LCD)
- LCOS (SXRD, D-ILA)
- 3LED
It makes no sense to describe each of the principles in detail, as there is more than enough encyclopedic material in the network. I believe that it is better to dwell on the advantages and disadvantages of each of them. To get into a rather prolonged dispute with biased lovers to say nothing about what is actually steeper than 3DLP (DLP), LCD (3LCD), LCOS or 3LED will not. In connection with the different tasks that are put before projectors, the advantages of one technology or another determine the choice, and in the premium segment, the disadvantages of technology are leveled a little less than completely. I can only note that several chips are better than one, as they allow to increase the image quality for a number of parameters.
DLP and 3DLP are the champions in contrast
DLP advantages:
- high contrast, realistic black;
- high color rendering options;
- the widest range of models and manufacturers among those on the market;
- more suitable for creating home theaters, due to a more realistic picture transfer;
- there are no optical distortions in the older lines;
- does not demand additional service, is protected from dust;
- can be effectively used for gaming and 3D.

Disadvantages of DLP:
- Sufficiently low brightness (especially the values of the so-called color brightness) budget models, which loses to other technologies;
- In budget models, the rainbow effect is manifested;
- The image of single-chip DLP projectors flickers, which is noticeable when shooting video and may be more tedious to view;
- Higher cost solutions with high quality image.

In fact, all the shortcomings, except for the high cost, single-matrix DLP do not apply to projectors with three chips, the so-called. 3 DLP, which at the same time maintain high contrast, as one of the main advantages.
3LCD - color brightness leaders
Advantages of 3LCD:
- High brightness when comparing lower lines;
- As a rule, higher convenience when setting up optics;
- Some of the budget models can be used in non-darkened rooms;
- In terms of price / performance ratio, they are ideal for use as an office presentation projector and a training projector for small audiences;
- In the budget lines provide more realistic color reproduction (except for black and gray tones)

Disadvantages of 3LCD:
- Limited range, monopoly on the use of technology;
- Low contrast, unrealistic (gray) black;
- Vulnerability to dust, the need to replace filters with a specialist;
- Artifacts (concave at the top) are noticeable on screens with a large diagonal;
- The appearance of artifacts (loops) when playing dynamic scenes in games and 3D.
In the older lines solved the problem of low contrast (technology C2Fine)
LCOS - expensive "golden mean"
The merits of LCOS
- The LCoS is superior to LCD and DLP at the maximum available resolution;
- Due to the placement of control elements behind the reflective layer, they are rid of the effect of the “comb” characteristic of LCD (3LCD);
- Efficiency technology is higher than that of the LCD (3LCD);
- The fill factor (the ratio of the working area to the total area of the matrix) is higher for LCoS than for DLP and LCD projectors;
- Due to the use of a cooling substrate, the resistance of LCoS chips to temperature is higher than that of DLP and LCD matrices, which allows you to create more powerful devices designed for installations;
- Contrast and black are better than LCD;
- Does not flicker like DLP;
- The response time of the LCoS matrix is shorter than that of the LCD.

Disadvantages of LCOS:
- Presented only in Hi End and professional segments, which naturally affected the price, there are practically no budget models;
- The technology is monopolized by several companies, which seriously affects the product range;
- In the older segments, it has almost no advantages over 3 DLP and 3 LCD, except for the resistance of the chip to the loads, while at the same image quality it is more expensive;
- Are widely demanded only for expensive installations, as a technique of high reliability.
3LED - winners of marathon distances
Advantages of 3 led:
- No flicker;
- Contrast higher than 3 LCD;
- The use of an almost eternal source of light;
- Lack of rainbow effect and other artifacts;
- High reliability.

Disadvantages 3 LED
- Low brightness level;
- Noise at work, reaching 35 - 40 dB;
- Limited range: 2 - 3 projectors from a few manufacturers;
- In a number of cases, spectrum instability;
- The high cost of a few high-brightness solutions.
Main characteristics
When choosing a projector it is worth considering a number of characteristics on which the result will depend.
Brightness
If necessary, calculate the luminous flux of the projector for an audience or a room where the lighting complies with current sanitary and hygienic standards (the room where you can read and work, you can multiply 756 by the square of the screen in square meters.
Below is a table calculating the brightness required by the projector, depending on the screen area when the light is sufficient to read.




Resolution
Below are the standards and permissions according to the format.
1. Aspect ratio 4: 3:
- VGA (640x480),
- SVGA (800x600),
- XGA (1024x780),
- SXGA (1280x1024),
- SXGA + (1400x1050),
- UXGA (1600x1200),
- QXGA (2048x1536).
2. Image format 16: 9, 16:10, 15: 9 or others:
- W XGA (1280x768 or 1280x780),
- HD720 (1280x720)
- W VGA (864x480),
- W SVGA (1024x576),
- Full HD (1920x1080),
- WUXGA (1920x1200),
- HD 4K (4096x2400).
Uniform lighting
Rarely indicated parameter that demonstrates the ratio of the minimum peripheral illumination of the screen to the maximum in the center. In the projector for watching movies and games and in professional devices, the value of uniformity must exceed 70%.
And a little more about the contrast
Contrast has the maximum effect on image quality in darkened rooms. In many respects, therefore, high-contrast models of projectors are used as an element of systems for home theaters. If you need to get a distinguishable image in the lighted interiors, you should rely on the brightness.
Dry residue - what and to whom
As I have already noted, people who buy projectors rarely imagine which one they need, which not so decent sellers sometimes use.
I will start with educational institutions where the projector allows you to show presentations and educational films. Requirements for quality are minimal, while, as a rule, there are requirements for the price and in some cases for brightness. For rooms where dimming is possible, single-chip DLP, 3 LED or 3 LCD projectors and with a brightness of 700 - 1000 ANSIlm are suitable; in rooms where there is a problem with dimming, a more powerful luminous flux, respectively, from 1000 ANSIlm and higher is needed. As a rule, in the ratio of brightness / price win 3 LCD projectors. At the same time for rooms with the possibility of darkening DLP are considered preferable.

The choice of a business projector for presentations will also be related to the working conditions and tasks, with the only difference that, as a rule, a higher resolution (HD) is required for business, and the cost will increase accordingly.
For professional presentations and long-term work, laser and hybrid 3 DLP, 3 LCD and LCOS projectors can be used, which provide long-term operation and high-quality images, usually with FullHD and WUXGA, 4 K HD resolution. The values of the luminous flux in such projectors, designed to work in illuminated rooms, as well as during the day outside can reach 20,000 ANSIlm.
Despite the tough competition from LCD TVs and plasma panels, projectors are no longer exotic at home. For home theater and gaming systems, most experts recommend DLP and 3DLP projectors, since the latter distort the picture less and work much more efficiently in 3D mode.

The most attractive and promising light sources in projectors are lasers and LEDs, which, all other things being equal, give odds to the rest of the operational resource. Experts say that the future is behind them and this future is near. According to the calculations of a number of manufacturers, gas-discharge lamps will be abandoned in the next 10 years.
The material is built on the comments of experts pult.ru, used graphic materials sites: myprojector.ru, projector-lamps.ru, viking.ru, giga-line.ru, stereo.ru
PS The cost of projectors, depending on the destination, varies widely, our catalog contains projectors from 19,790 to 10,452,850. If we talk about training, office, the average cost of the latter (depending on the characteristics and the technology used) varies from 19,790 to 300 000. In the case of equipment for home theaters and games, if not to affect professional and HI END lines, the average cost of such a projector will be about 90 000 - 150 000 (again, depending on the characteristics and technology used ogii). The presented information on prices is rather arbitrary, the price largely depends on the manufacturer, functions, design and capabilities of the device.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/403175/
All Articles