A new type of battery at the same time serves as a heat sink for elements of computer equipment.

A joint team of researchers from the IBM Research Zurich laboratory and ETH Zurich (Swiss Higher Technical School of Zurich) has created a new type of liquid battery. According to the developers, these miniature elements can simultaneously serve as a source of energy and a heat sink for the hottest components of electronic devices. The novelty suggests the possibility of a dense vertical placement of chips on the boards to save space and energy.
This battery uses two electrolytes that circulate inside a closed system in a closed circuit. “The chips are efficiently cooled and receive the necessary energy to work,” said Dimos Poulikakos, a professor of thermodynamics from ETH Zurich.
The battery, created by scientists, is very thin. Its thickness is only 1.5 millimeters. Its parameters make it possible to fully realize the idea of developers, which consists in creating a multi-layered “sandwich” from batteries and chips. The chip is installed first, then the battery, then the chip again, and so on.
')
Liquid batteries for all sorts of devices - not new, they exist. But, basically, they are used as energy storage in wind and power plants. Here they temporarily store energy in order to later give it to the network. “We are the first to build such a thin battery that is capable of supplying energy to the board and cooling it,” says one of the project’s authors. A battery of this type can both convert the energy of chemical reactions into electricity, and vice versa.
The power element is pretty good: 1.4 watts per square centimeter square. This should be enough to provide energy for small mobile devices. Tests have already been conducted that proved that electrolytic fluids are indeed capable of cooling a chip.
According to the developers, the main difficulty in creating such batteries was to make them suitable for use with modern electronics. Another complication is to reduce the energy consumption of a fluid circulation circuit. The movement of electrolytes requires energy, and if such an element consumes too much energy, then it simply would not be suitable as a battery.
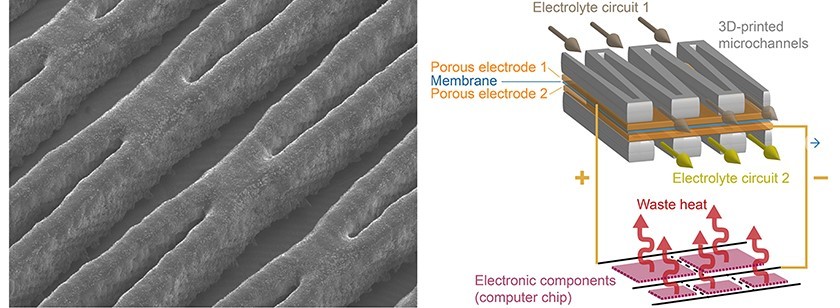
Electrochemical reactions in the battery occur due to the presence of two thin porous electrodes, which are separated by a membrane. Scientists have used 3D printing technology to create batteries. This was needed in order to create from polymer a system of channels through which electrolytes circulate.
So far, scientists have been able to prove only the potential performance of a liquid battery cooler. The fact is that he was able to simultaneously cool equipment and supply individual elements with energy. But for modern chips this energy is still too little - the system needs to be improved. Nevertheless, experts are confident of success. In addition, the liquid battery keeps the temperature of the entire system at an optimum level.
The technology is called Redoxflow.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/403049/
All Articles