What is antibiotics

Spring is a time of catarrhal diseases, so many of us keep a package of antibiotics “just in case” in the first-aid kit. According to a VTsIOM survey in 2011, 48% of women and 43% of men, and this is almost half of Russians, believe that viruses, like bacteria, are unstable to antibiotics.
Let's see what kind of an antibiotic this animal is, and for whom it is dangerous.
First we turn to the term "microbiology". Microbiology is a science, the subject of study of which are microscopic organisms, their structure, relationships and everything else associated with them that can be studied. We now turn to a narrower concept - bacteriology. What she studies, I think, is clear.
')
Bacteria, like protists (more complexly organized microorganisms), consist of a single cell and are independent viable organisms. Although they tend to form clusters - colonies, which, by the way, may well be visible to the naked eye.
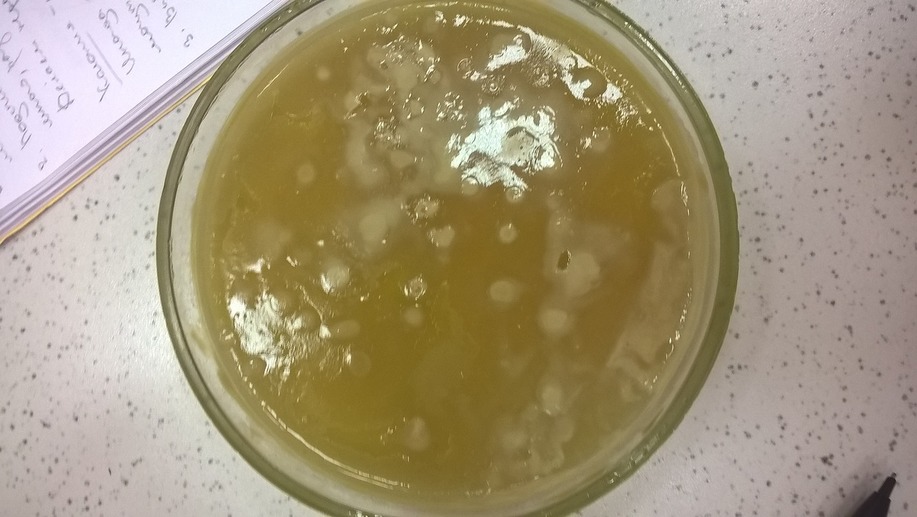

In the photo there is a Petri dish with bacteria overgrown on it, collected by me at one of the stations of the St. Petersburg metro.
Bacteria do not have a decorated nucleus and organelles that would perform all functions (analogous to our organs, so to speak). They are also called prokaryotes (pre-nuclear organisms), and those who have nuclei are called eukaryotes (which we also belong to).
All that consists of bacteria:
- protoplast - cytoplasm (all internally the contents of the cell) and the membrane covering above
- cell wall , around which there may be a mucous pouch and / or capsule
- there may be flagella for movement

Anyone who has read this far may ask a fair question: “And where does antibiotics come in?”.
So, antibiotics are substances with bactericidal activity. As it was said above, they will not help from viruses, as well as from the simplest ones. But it is rather an exception.
Now let's understand why they act on bacteria and how.
Mechanisms of action:
- The very first of those studied is the effect on the cell wall.
In their chemical composition, the cell wall of bacteria is different from the cell wall of eukaryotes. The main component is murein , which forms the murein network on the surface.
Danish microbiologist Hans Gram proposed a method for staining bacteria smears, which was named after him. The smear was stained with gentian violet (dye) and fixed with iodine solution. Next, the bacteria behave differently, which is why they were divided into two groups: those whose dye is kept in the cell when treated with alcohol or acetone (gram-positive), and those who discolor (gram-negative).

Staphylococcus aureus - Staphylococcus aureus (gram-positive cocci, dark) and Escherichia coli - E. coli (gram-negative bacilli, pink).
I will not bore any additional features of the wall structure, it is obvious from the image below.
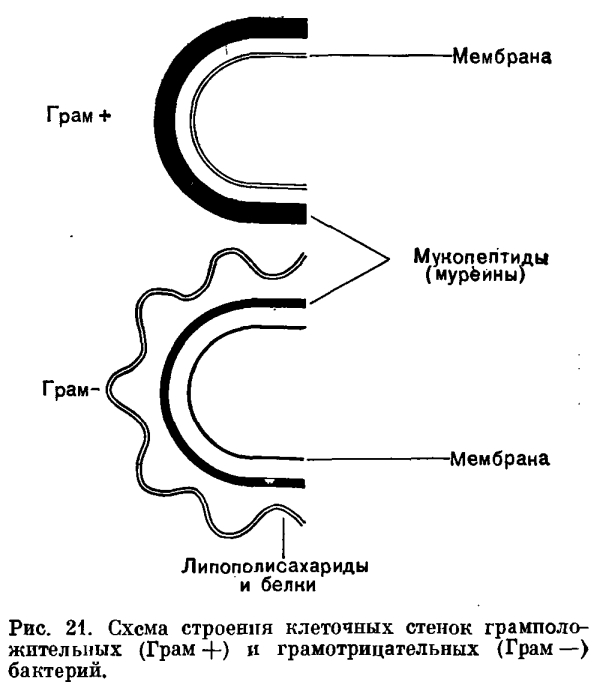
The wall performs a barrier function and establishes the contact of bacteria with the environment. Gram-negative bacteria are a higher stage of evolution, they are more resistant to toxins, including antibiotics, than gram-positive ones, although they have a thicker (and at the same time more vulnerable) wall.
Some antibiotics (a group of penicillin and cycloserine) inhibit cell wall synthesis, which leads to the formation of protoplasts (see above) and spheroplasts (the cell wall is destroyed, but not completely). When they stop taking antibiotics, they reverse (turn) into normal cells again or transform into L-forms, but they may die.
L-forms do not have a cell wall, but can develop, grow and divide. The formation of L-forms is one of the causes of chronic recurrent diseases. If the antibiotics are not taken correctly, the patient's condition may improve, but after complete abolition, reversion occurs to full-fledged forms of the original species with the restoration of their pathogenicity. By the way, immunity to these antibiotics may also appear, which means that they will not help with relapse.
To understand why taking antibiotics has a particular dosage, you should look at this chart:
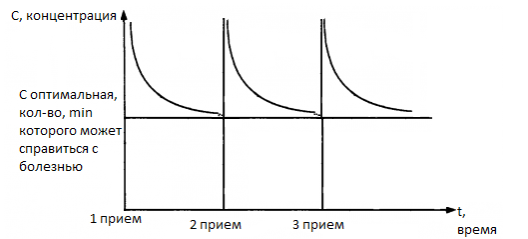
the concentration is always higher than the optimal one at first, but is eventually excreted from the body, so you need to take the pills again. Therefore, it is important to select antibiotics in which their effectiveness would be stronger, or at least on a level with possible risks and side effects.
It is in this way that antibiotics affect representatives of lobar and focal pneumonia, meningitis, urinary and biliary tract infections, syphilis, gonorrhea, diphtheria, scarlet fever, sore throats, ENT diseases and many others.
- Another mechanism of action is the violation of protein synthesis in the cell: inhibition (suppression) of the functions of ribosomes and protein synthesis (streptomycin). Tuberculosis of the lungs and other organs is treated, brucellosis, plague.
- Violation of the integrity of the membranes, i.e., violation of ion channels, which can make the cell permeable to substances that should not get inside, or vice versa - block the access of important substances. (gramicidin, polymyxin). Used for diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, sepsis, and, like penicillin, for meningitis and ENT diseases.
- Inhibition of the synthesis of nucleic acids (DNA and RNA) due to disruption of the enzymes that "direct" the process. With leukemia, lymphoma, lymphosarcoma, neiloblastoma in children. It is used together with other anticancer drugs.
- Violation of DNA and RNA synthesis, but due to the violation of the nitrogenous bases themselves - the components of the nucleic acids themselves (sarcomycin). Suppresses the growth of culture of Ehrlich cancer cells.
- And finally, the inhibition of respiratory enzymes of bacteria (antimycin). Used in crop production for the destruction of agricultural pests.
Now it is worth discussing such a thing as antibiotic resistance, i.e. the resistance of the microorganism to the action of the antibiotic. May occur due to mutations and after exposure to the antibiotic is fixed in the whole group of organisms.
Mechanisms of opposition:
- blocking the entrance to the cell is an additional membrane in most gram-negative bacteria, which makes them immune to penicillin.
- a decrease in pore size (the antibiotic does not pass inwards) or a protein appears, which immediately removes the antibiotic from the cell.
- some bacteria have learned to inactivate antibiotics. For example, in staphylococci (R. Staphylococcus), a substance β-lactonase is produced for this substance, which destroys the β-lactam ring in most penicillins. To do this, they add folic acid to inhibit β-lactonase.
- Well, the cell wall itself, which is affected by an antibiotic, may be absent, such as the genus Mycoplasma (Mycoplasma)
Finally, it is worth mentioning that the fact that antibiotics do not affect viruses does not mean that they are harmless to humans. They can not be taken just like that, without making sure that the causative agent of the disease is a bacterium, because antibiotics affect the liver (it is she who is engaged in detoxifying the body), the intestine (the microflora dies, and the first thing that gets caught in its place). Also, the fact that the treatment of this group of drugs can not be drunk, everyone knows. Alcohol affects the activity of antibiotics and their excretion from the body by the liver. Some antibiotics can interact with alcohol and cause side effects, starting with diarrhea and vomiting and ending with convulsions and even death.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/402795/
All Articles