What will thawing permafrost lead to?
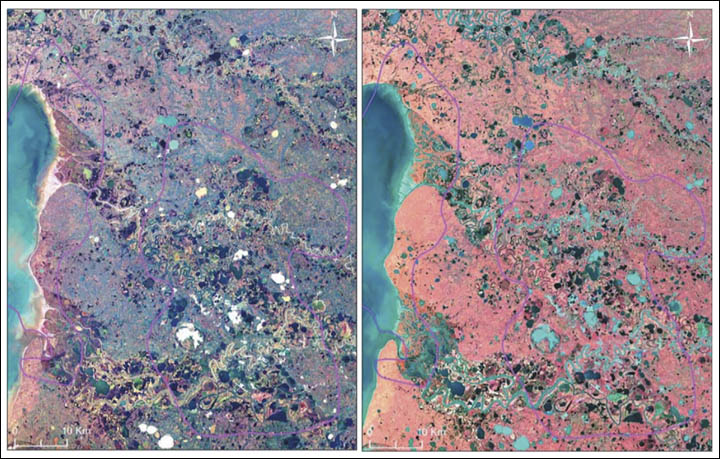
The lakes in the area of the Bovanenkovskoye and Kruzenshternskoye gas and condensate fields in the photographs from the satellite Landsat-8 (on the left - the visible spectrum, on the right - IR, synthesis). Photo: Professor Vasily Bogoyavlensky
Satellite photographs revealed more than 200 bright blue lakes formed in the thawed permafrost areas (“permafrost”) on the Yamal Peninsula and the Gydan Peninsula, found in the areas of thawed permafrost. Like giant whirlpools, these lakes of unusual color are blowing methane bubbles, The Siberian Times newspaper writes , citing the latest research by Professor Vasily Bogoyavlensky from the Russian Academy of Sciences.
The lakes were formed as a result of thermokarst - subsidence of the earth's surface due to melting of icy frozen rocks. When thawing "permafrost" formed dips, which are filled with melted water. At the same time, natural gas begins to flow out of the ground.
Scientists note that the lakes on Yamal are very different from normal thermokarst lakes of dark color. These lakes are bright blue and contain bubbles of gas that enters the water before it is released into the atmosphere.
')
More than 200 blue lakes in the Far North are located in close proximity to the large Bovanenkovskoye and Kruzenshternskoye gas condensate fields. According to the professor, these lakes have a number of characteristic features by which they can be distinguished from other lakes. This is an abnormal blue color of water, the presence of a crater at the bottom and gas emissions from water, traces of gas in the seasonal ice cover, active coastal erosion and swelling of permafrost at the water's edge.
Professor Bogoyavlensky suggests that the formation of lakes is also associated with seismic activity. For example, over one of the deposits on the Yamal Peninsula they formed along two lines, forming a giant cross.
Tellingly, new dips and lakes are formed even at temperatures around 0 ° C.
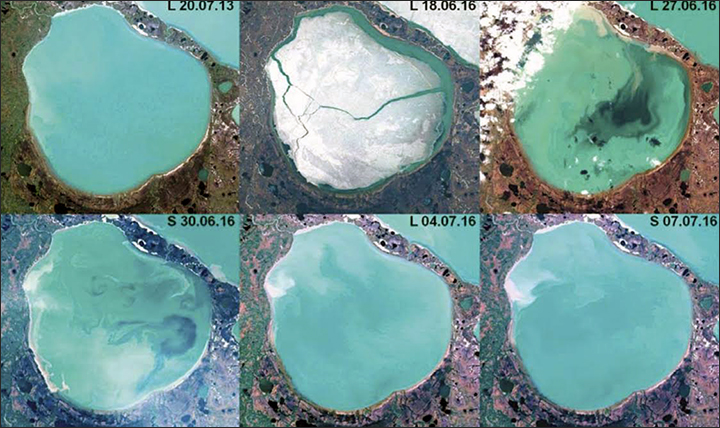
The illustration shows satellite images of one of these lakes from photographs of Landsat-8 and Sentinel-2 satellites.
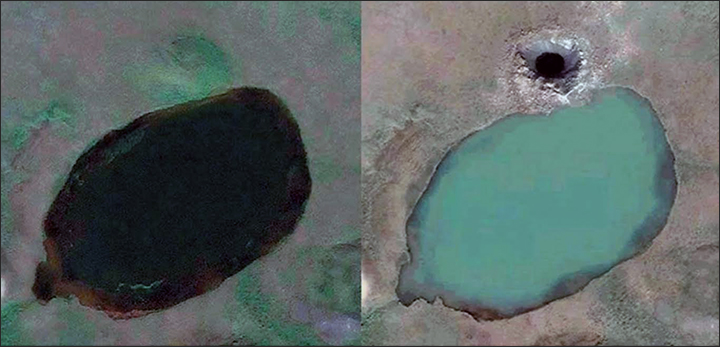
The photo on the right shows that a giant crater formed in the ground near one of the lake. Perhaps from the "explosion" of a bubble with gas, although scientists can not say for sure what was inside the bubble before the rupture - water, ice or something else. This is the key question, after the answer to which it will be possible to make any predictions about the appearance of such new craters.
At least 10 such craters are already known in the region. Here is what a crater looks like when shooting from a helicopter.
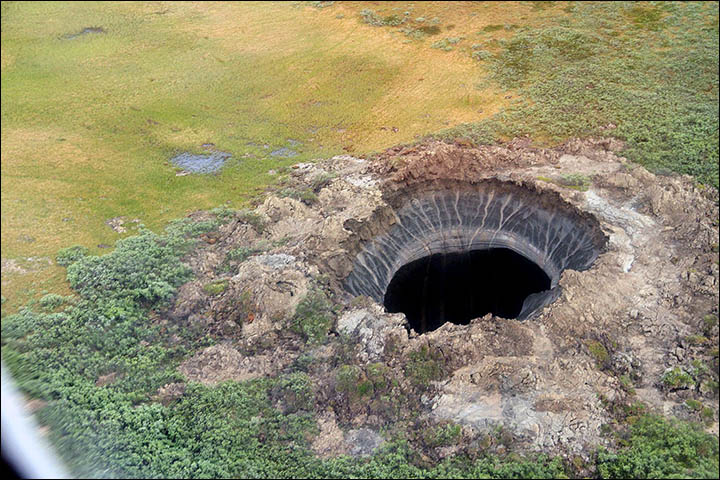

Photo: Press Service of the Governor of the Yamalo-Nenets Autonomous District
Vasily Bogoyavlensky and his colleagues actively studied the appearance of these lakes on satellite photographs of 2015-2016.
Thawing of "permafrost" goes not only on the Yamal Peninsula and the Gydan peninsula, but also in Siberia. For example, in Yakutia, the giant Batagai crater is gradually expanding, which is called the “ gateway to hell ” or “ failure to the past .”
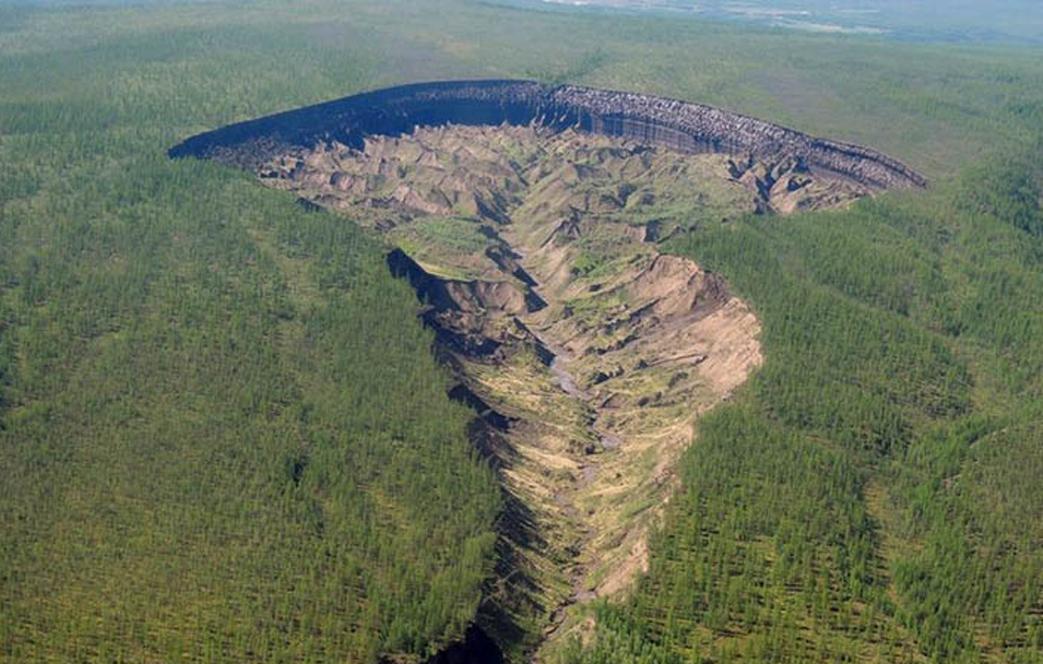

Photo: NKFU named after M.Ammosov
The thermokarst basin with a depth of about 100 meters in the Verkhoyansk district of the Yakutsk region exposes ancient geological strata of different eras. The cleft reaches a kilometer in length and up to 800 meters in width. It was formed in the 1960s after a section of the taiga was cut down 8 km south-west of the village of Batagai. Since then, as the temperature rises, the permafrost continues to melt, and the cleft grows by about 15 meters per year.
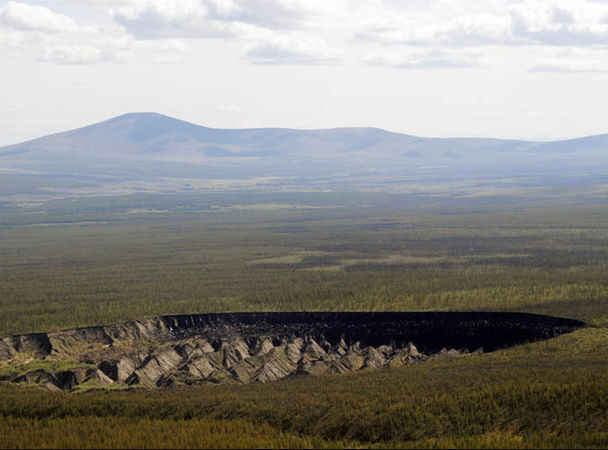

Photo: NKFU named after M.Ammosov
The Batagai crater is very interesting for paleontologists. For example, in 2009, a well-preserved wreck of a foal, 4400 years old, and the remains of a baby bison were found here. Among other finds - the bones of mammoths and deer.
Global warming and the constant rise in global average temperatures make it possible to predict that the thawing of permafrost will continue. Probably, such gigantic failures in the future may also occur in other places of the taiga.
The thawing of permafrost on Yamal and Gydan Peninsula is dangerous because the reserves of methane, one of the greenhouse gases, are released into the atmosphere. According to its ability to retain heat transfer, methane is 30 times more efficient than CO 2 .
This will make it harder to heat the atmosphere and increase the greenhouse effect, which will cause the surface of the planet to heat up faster, so that the greenhouse process will accelerate itself. Scientists have already tried to estimate the effect of hydrocarbon release into the atmosphere due to melting of permafrost. According to one study , by the year 2100, up to 205 billion tons of hydrocarbons will be released into the atmosphere if the melting of permafrost accelerates with an increase in world temperature, as is happening now.
Previous studies have suggested that permafrost thawing will begin if the global temperature rises another 1.5 ° C. But the formation of methane bubbles in the soil and bright blue lakes on Yamal may be a sign that the process has already begun.
In Siberia, scientists have found more than 7,000 methane bubbles in the soil, as shown in the video. Such bubbles can break free and cause a crater to form.
Thawing permafrost does not bode well for mankind. We can recall the mass Permian extinction - one of the largest disasters of the biosphere in the history of the Earth, which led to the extinction of 96% of all marine species and 73% of terrestrial vertebrate species. According to one version, the mass Permian extinction arose due to the lack of oxygen in the oceans, which led to a chain of events. Perhaps it began with a massive release of methane or sulfur from the crust into the atmosphere.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/402593/
All Articles