New ARM Processors Ready for AI Applications

The British corporation ARM improved the heterogeneous computing architecture of ARM big.LITTLE , on which all the leading ARM microprocessors since Cortex-A7 (2011) are based - and yesterday presented a new heterogeneous architecture DynamIQ big.LITTLE . On the microcircuits, space is allocated for special hardware accelerators of machine learning applications. Perhaps in the future, hardware support for neural networks will become a new trend among microprocessor developers and the inherent quality of new smartphones.
The ARM big.LITTLE architecture feature consists of two types of processor cores: relatively slow, energy efficient (LITTLE) and relatively powerful and voracious (big). Usually the system activates only one of two types of cores: only large or only small. It is clear that background tasks on a smartphone or other device are conveniently solved with small cores that consume very little energy. If necessary, the processor activates powerful voracious kernels, which, in multi-threaded mode, working together, demonstrate particularly high performance. In principle, all cores have access to shared memory, so that tasks can be set to run on both types of cores simultaneously. That is, large and small will switch on the fly.
Such a heterogeneous architecture and task switching on the fly from one type of core to another are designed to create dynamic changes in power and processor power consumption. ARM itself stated that in some tasks that architecture saves up to 75% of energy.
')
DynamIQ big.LITTLE is an evolutionary step forward. The new architecture allows you to use a variety of combinations of large and small cores that were not previously possible. For example, 1 + 3, 2 + 4 or 1 + 7, or even 2 + 4 + 2 (cores of three different capacities). A typical future smartphone can have an eight-core system on a chip with two powerful cores, four medium and two low-capacity cores for the background mode.
With hardware support for machine learning and AI, new special processor instructions (for example, calculations with limited accuracy) will be available to developers. ARM promises that in the next three to five years, Cortex-A processors on the new architecture will provide up to 50-fold increase in performance in AI applications, in comparison with current Cortex-A73-based systems and an additional increase due to the integrated accelerators on the chip. The special access port with low latency between the CPU and accelerators has a 10-fold performance.
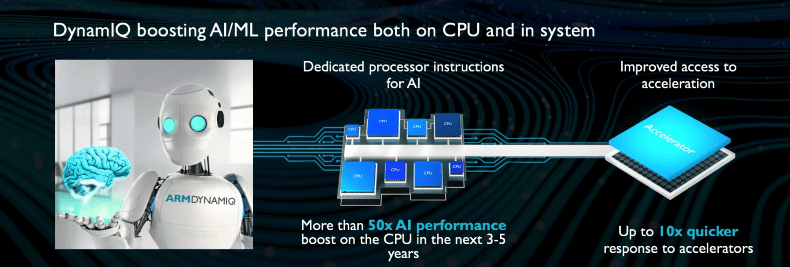
This means that trained neural networks will work much better on smartphones, including those that cheat graphics and video, computer vision applications and other systems that process large data streams.
Each cluster can contain up to eight cores of different characteristics. This can also be used to speed up AI applications, compared to current systems. In addition, the redesigned memory subsystem will provide faster data access and improve energy efficiency. By the way, it is not necessary to include LITTLE kernels with weak performance, which are usually used in mobile devices to save battery power, into clusters of cores. If you need very high performance regardless of power consumption - no one bothers to make clusters of eight large cores, and combine them into especially powerful computer systems. ARM believes that this will expand the scope of application of ARM processors beyond smartphones.
Almost unlimited scale DynamIQ clusters with shared memory is a proposal to create the most powerful computing systems of various purposes.

Additional flexibility in dynamic power / power adjustment will be provided by the function of individual changes in the clock frequency of individual processors in a cluster of multiple ARM processors. Developers from Cambridge believe that this is especially important in virtual reality helmets, which are in a state of low power consumption for long periods of time. Transitions of the processor to one of the three energy states (ON, OFF, SLEEP) are carried out much faster, automatically at the hardware level.
In the end, the advanced DynamIQ architecture allows you to build more reliable systems with duplication of functions, which increases the level of security in autonomous systems that need to respond to failures. For example, these are computer vision systems in unmanned vehicles - Advanced Driver Assistance Systems (ADAS). When one cluster of nuclei fails or the accelerator fails, the other cluster automatically takes over its functions.

The ARM processor architecture is licensed in its chips by many manufacturers, including Samsung, Qualcomm, Nvidia, Intel and Apple (iPhone, iPad). Between 2013 and 2017, more than 50 billion microchips were sold on the ARM architecture in the world, and English developers hope that in the next four years this number will double to more than 100 billion.
Most devices on ARM processors do not need active cooling. The company is confident that with the increase in the power of these systems and the transition to the DynamIQ architecture, everything will remain the same.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/402501/
All Articles