Dear hackers, where are your autonomous lawn mowers?

It is impossible to establish when the society began to care for their lawns. To be honest, cutting grass was, and remains, a necessity. But weed control, trimming and other excesses are not. A beautiful lawn is a status symbol in modern suburbs around the world. When aliens arrive to us, they will surely immediately notice how tidy our lawns are. And this achievement of civilization became possible with the arrival of special machines for cutting grass.
The first lawnmowers were representatives of cattle. The problem is that they are very difficult to maintain, they cut the grass unevenly, which is why they did not take root in families fighting for the perfect lawn. If we recall the unpleasant smell of the by-products of their activities, it becomes clear why animals have ceased to be popular and gradually moved to the backyards. To maintain the look of a prestigious courtyard, people began to look for other means.
The first mechanical lawn mower was invented in 1830 by Edwin Budding, no doubt, in order to surpass his neighbor, who used a scythe. His mower was very similar to today's options, in which the blades are fixed in a cylinder that rotates when the mower moves forward. Budding was granted a patent for the device, which greatly upset his neighbors - most of them had to buy a Budding mower, since almost everyone bought themselves the same one, even though they were not necessary.
')
By 1930, the cold war between Budding and his neighbor had spread to almost every yard of the planet, and there was no end in sight. If we go back in our time, then in 2014 alone, $ 10 billion in sales in the garden and lawn care market was made. Technological progress led to the emergence of very advanced machines chewing grass. For small areas, most people use mowers with single-cylinder internal combustion engines that need to be pushed in front of them. Many mowers are equipped with cloth bags for collecting pieces that everyone hates, as they gradually fill up, which makes it harder to push the mower. But since the neighbors use it, we have to. Larger areas require expensive mowers to ride. Many owners of such mowers can boast at a neighbor's party that they have a hydrostatic transmission, although they have no idea what it is.
We hackers are no better than them. We, like everyone, also have lawns. But, unlike all the others, we have soldering irons. And we know how to use them. I propose to undermine the foundations of the neighborhood war just as Budding did 85 years ago. Take out your favorite microcontroller, and get to work!
Truly autonomous lawn mowers - please raise your hands
First, let's figure it out with something. These stupid "robotic lawn mowers" using wire-terminator and mowing the grass, moving along random paths , we do not need. Any hacker worth this title is clear that the mower needs a positioning system. “Why?” - you ask. Watch any video about how such a thing is tossed around like an insect in the wind, and you will say to yourself: “You know, this thing would work much better if you knew where it is.” This is what we are going to do. To create an autonomous lawn mower, we need a positioning system. If we can find the XY coordinates of the mower, then the automation will be much easier.
Of course, there are other ways to achieve autonomy, and I suggest you discuss them in the comments, but in this article I will describe autonomy through positioning. Specifically, through satellite positioning.
GPS, RTK and DGPS
The first thing that comes to mind for solving the problem of obtaining coordinates outside buildings is GPS. The second thing that comes to mind in about 25 ms is the accuracy of this system. Everyone knows that the accuracy of GPS varies within 15 meters. With an autonomous lawnmower, this will not work. But there are two more options: RTK and DGPS . And these methods already have the accuracy we need.
Standard GPS
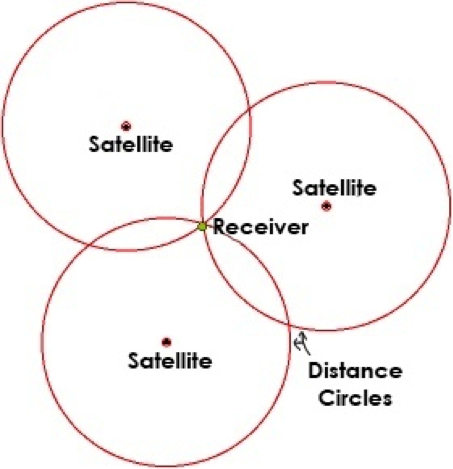
Before plunging into other systems, consider the simple and familiar GPS. GPS in the phone measures the distance from it to at least three satellites. This allows him to find his position by trilateration (not to be confused with triangulation). Naturally, the accuracy depends on the accuracy of measuring distances to satellites. This distance is determined by the time stamps specified with the accuracy of the atomic clock coming from the satellites. The receiver simply takes the difference between the transmission time and the receiving time, and multiplies it by the speed of light to get the distance from it to the satellite.
In addition to the timestamp, the satellite transmits its location. Armed with the distance to the satellite and its position, the recipient, in fact, knows the radius of the circle, in the center of which is the satellite, and on the perimeter - the recipient. And when three such circles unite - broads! You get your location using trilateration.
Several things limit the accuracy of the method; one of the main things is the atmosphere. The ionosphere can delay signals, causing problems. The greater the thickness of the atmosphere needed to overcome the signal, the greater this effect. Therefore, the signal from the satellite above the horizon is more susceptible to distortion than the signal from the satellite above the head. This interference is constantly changing and because of them there is a fatal positioning error - up to 10 meters.
RTK and differential GPS
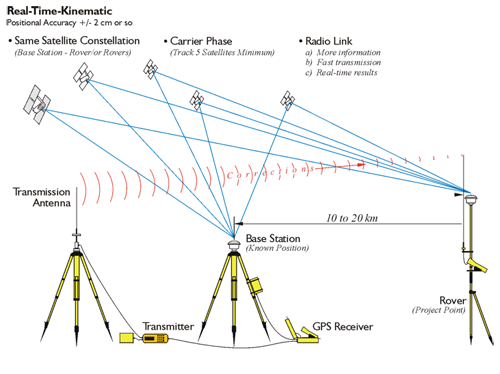
Now, knowing the GPS operation scheme and its fundamental limitations, we can figure out how to fix them and improve positioning accuracy. This can be done by including in the circuit a second, fixed receiver. He does not move, and his location is known for sure. A mobile receiver that needs to know its location should be fairly close to the fixed one so that these two receivers can compare signals from the same GPS satellites and then communicate on this topic.
The fixed receiver compares the GPS signals received by itself and the mobile receiver. Since the fixed receiver already knows its location, it can catch an error in the signal and send a correction to the mobile receiver. This is how real-time kinematics (RTK) and differential GPS systems work.
Differential GPS can achieve an accuracy of up to 10 cm, while the RTK estimates the analog part of the signal along with the digital one and therefore achieves an accuracy of 2 cm. Which is quite accurate for an autonomous lawn mower.
Free market options
There are several available types of equipment for such precise positioning. They are not cheap, but not very heavy for those who want to succeed in this project. The cheapest system we have found is the REACH RTK , which costs $ 570, but all of the kits sell very quickly after they go on sale. There is also a Swift Navigation Piksi , a more expensive option, already under $ 1000. If you know other options, please report them in the comments.
Using RTK GPS for autonomous lawn mowers is already available to you or your team. If you know where exactly your mower is in real time, then code writing and mechanical engineering problems are solved head-on. Why did not they decide? What are you waiting for?
CNC mower
Imagine what happens if you cross your lawn mower with a G-code . If you attach the remote on / off blades, then instead of mowing the grass, you can control the mower remotely.
The picture I have drawn makes sense in large spaces where small battery powered mowers are not as effective. If the area is too large, it is unlikely that it would make sense to set the perimeter around it, and this makes the GPS option more acceptable (although the signal from this perimeter can be faked , which allows us to attach the GPS to the finished robotic mower).
From a consumer point of view, in order to enter a large-scale lawn market, small problems need to be addressed, for example, safety, avoiding obstacles (fallen limbs, people, cattle), tracking fuel levels, etc. But for hackers, this concept is too interesting to get around. We are pleased to hear about your adventures with automatic lawn mowers, and we expect to someday see a jolly Roger carved on the grass the size of half a hectare.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/402221/
All Articles