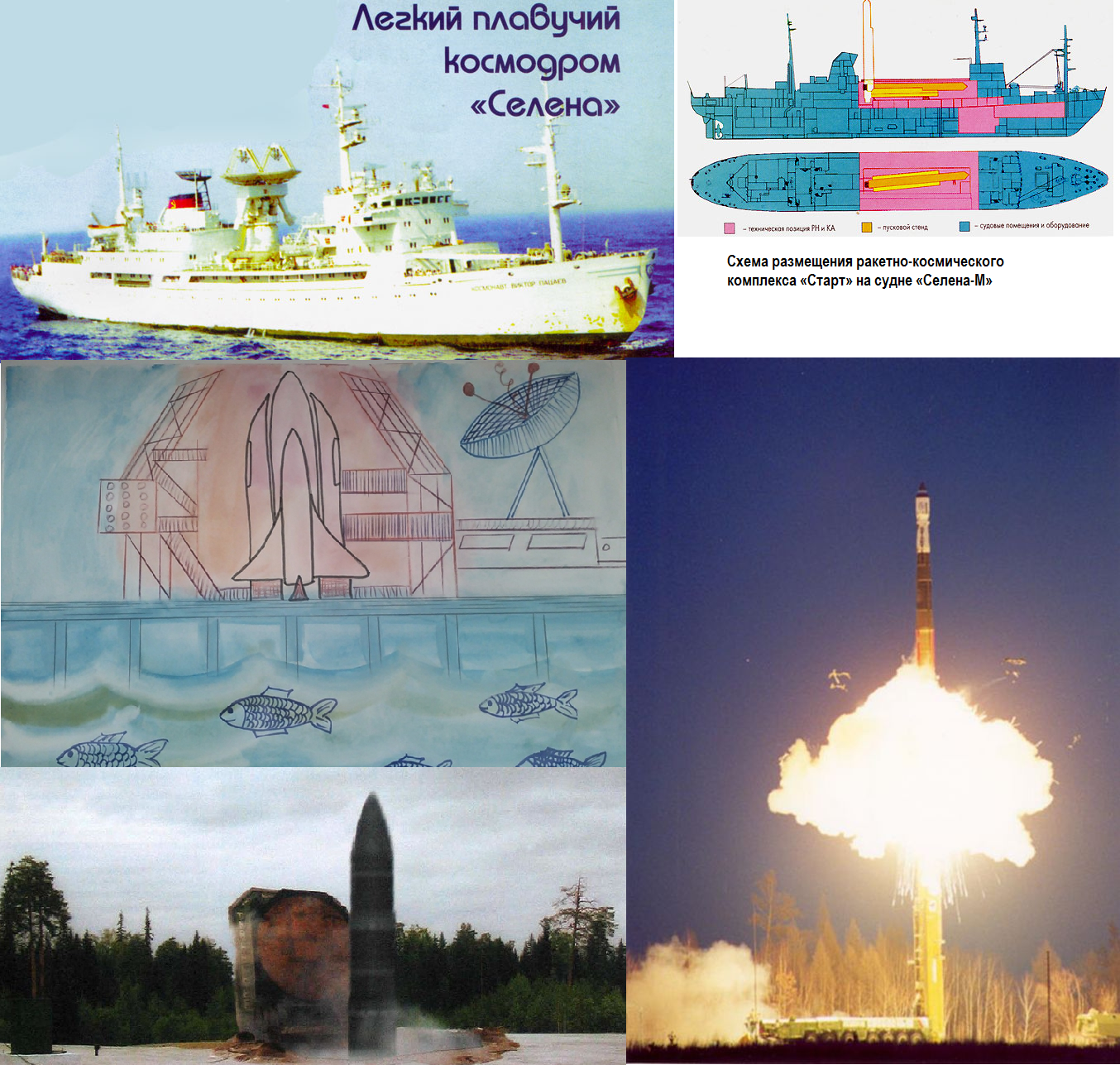
Launch pad in the ocean - light floating cosmodrome "Selena"
“... What seemed unrealizable for centuries, what yesterday was only a bold dream, today is becoming a real task, and tomorrow - an accomplishment.S.P. Korolev
There are no barriers of human thought! "
In continuation of the topic how to get into orbit (or into space) in a non-trivial way, voiced in the articles:
Underwater launch systems: how to get out of water into orbit?
Underwater launch systems: how to get out of water into orbit? Ending
')
The launch of a BR or PH from an offshore platform or a ship (aircraft carrier) is not “Russian” know-how
The first were most likely Americans. V2 rocket launch from USS Midway Aircraft Carrier (1947):
This is understandable: a large stock of expropriated V-2 (Vergeltungswaffe-2) and a large number of aircraft carriers.
Advantage: logistics, any launch width, large spaces for falling missiles and their stages. There are disadvantages.
Other significant American projects:
Sea Dragon ("Sea Dragon") from Aerojet - a project of 1962 to create a fully reusable two-stage sea-based launch vehicle. One of the designs created by Robert Truax was a rocket launched from a free-floating position in the ocean.
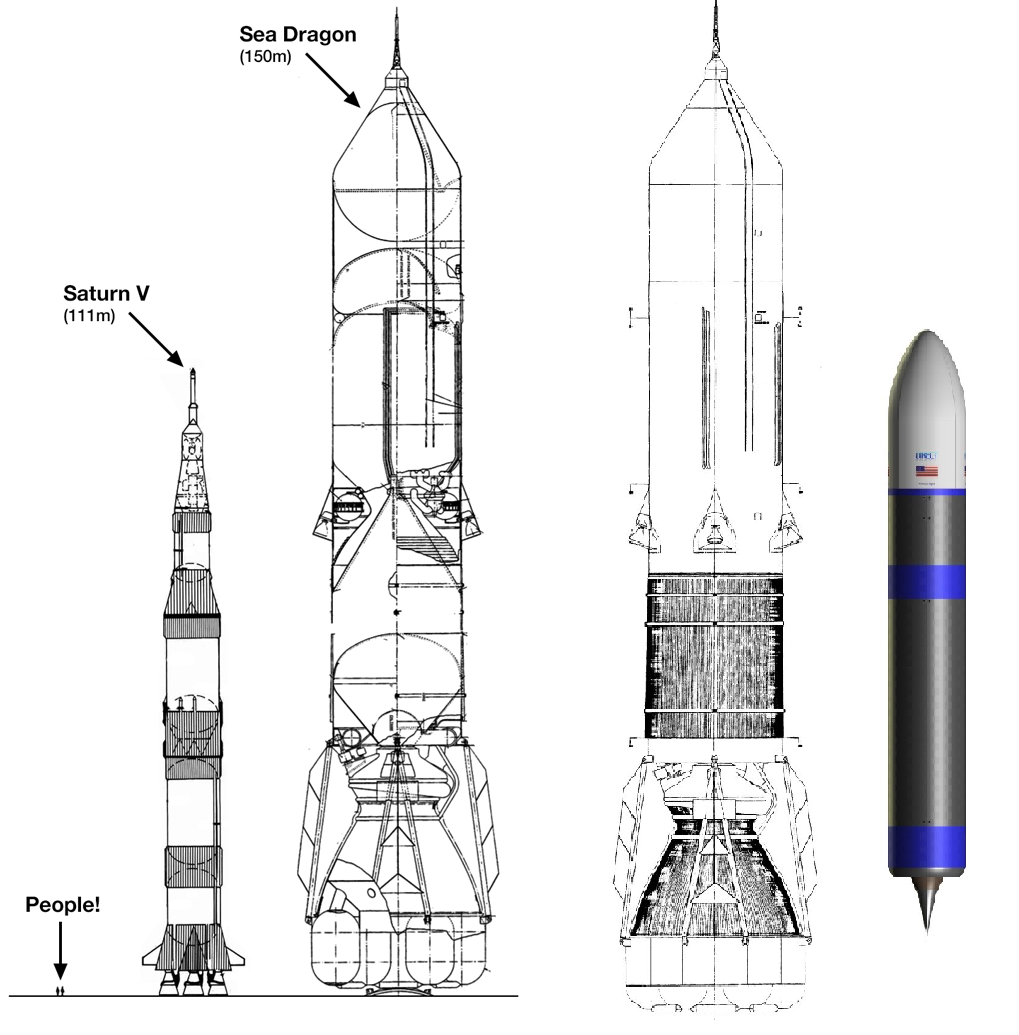
The main idea of Truax was to create a cheap heavy carrier, now called “big silly carrier” .
Before the dragon, Robert experimented with Sea Bee and Sea Horse .
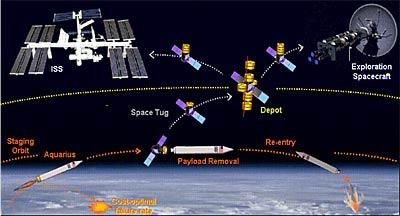 From the “latest” US offers, this is probably the PH Aquarius (Aquarius), developed by Space Systems / Loral, Aerojet, Microcosm in the 2000s.
From the “latest” US offers, this is probably the PH Aquarius (Aquarius), developed by Space Systems / Loral, Aerojet, Microcosm in the 2000s.Purpose: The cost of the withdrawal of the payload (for the supply of the ISS) per NOU 1000 kg (2200 pounds) not more than $ 1,000,000.00. Disposable media.
Low-cost launch and orbital depots: the Aquarius system.
The preface is over, I return to Selene.
Very little information and good quality photos. More likely to get about the ships and about the PH.
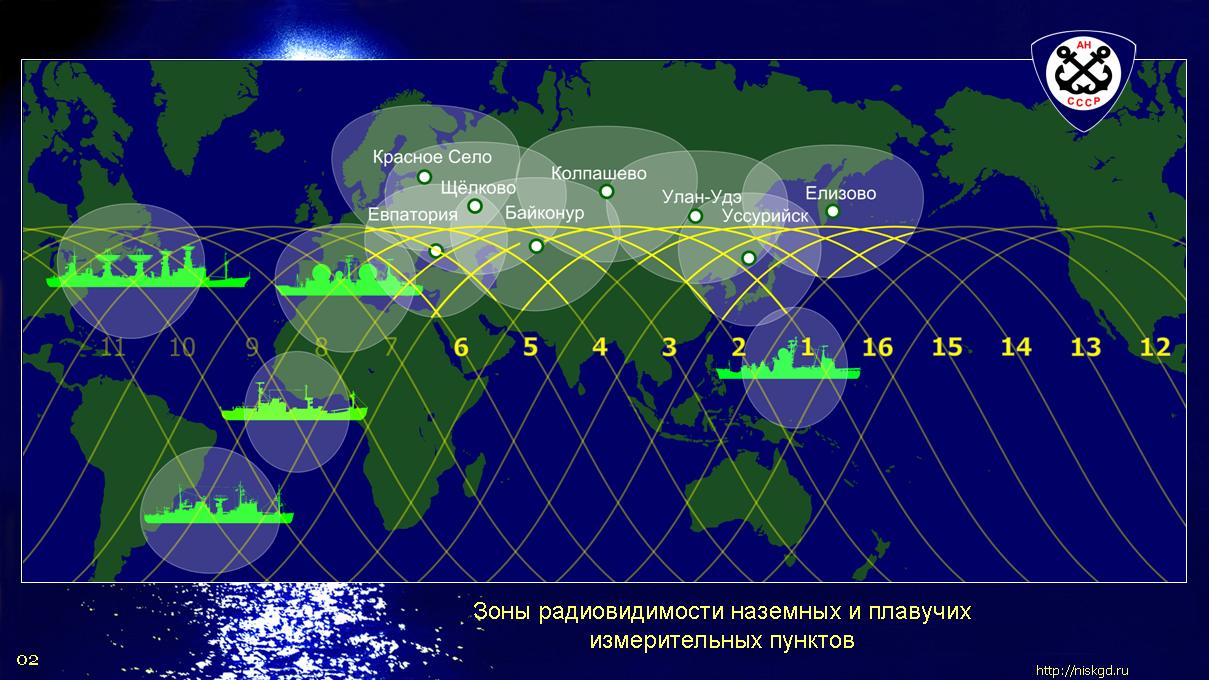
It will be a question of one of the options for using the fleet of the Space Research Service of the Department of Marine Expeditionary Works of the Academy of Sciences of the USSR ( SKI OMER USSR Academy of Sciences ).
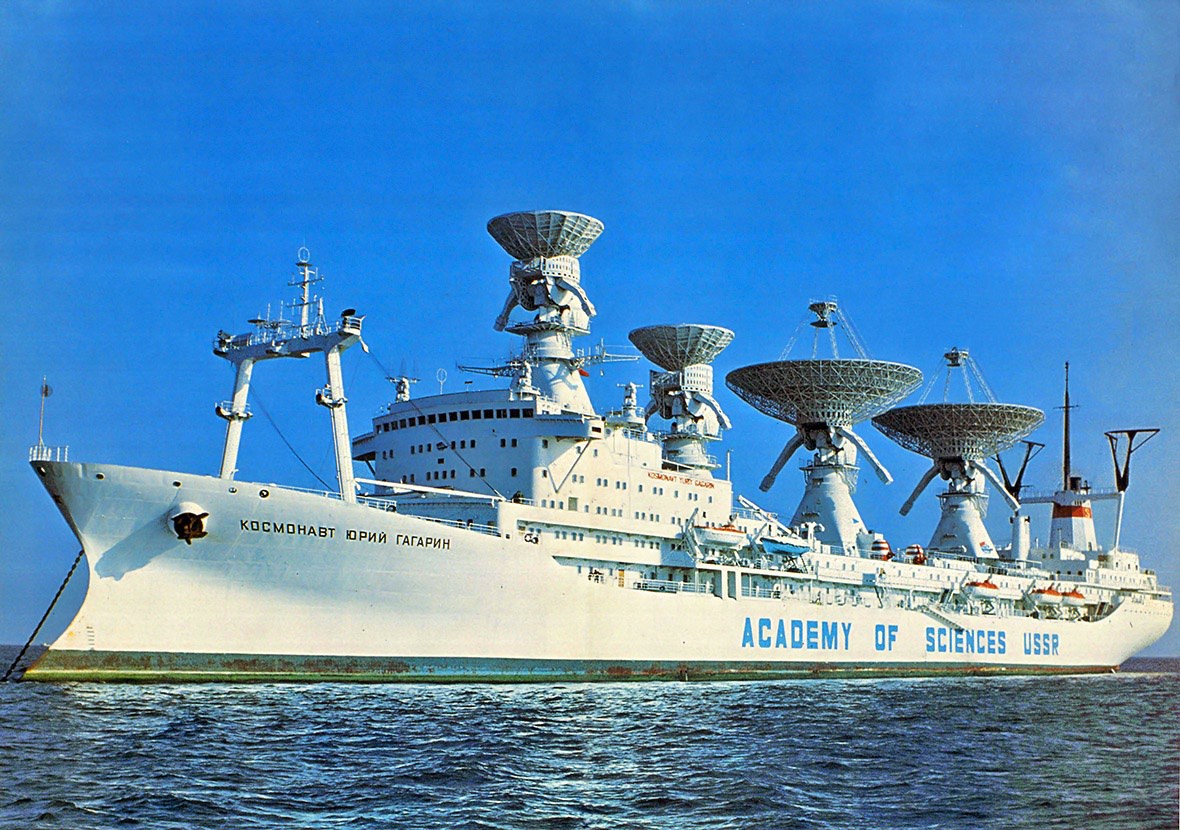

"Sea space fleet", ships "Star Flotilla", floating measuring points, space service vessels. What is this fleet? What kind of trial?[one]
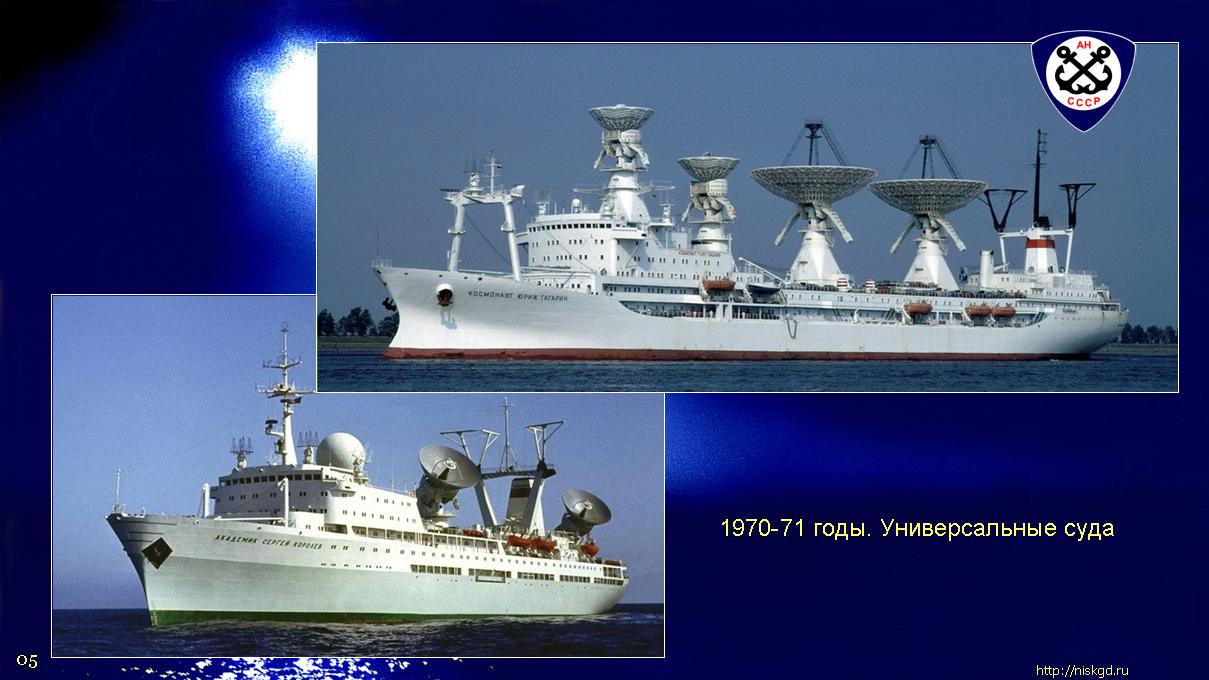

Questions and answers. [one]
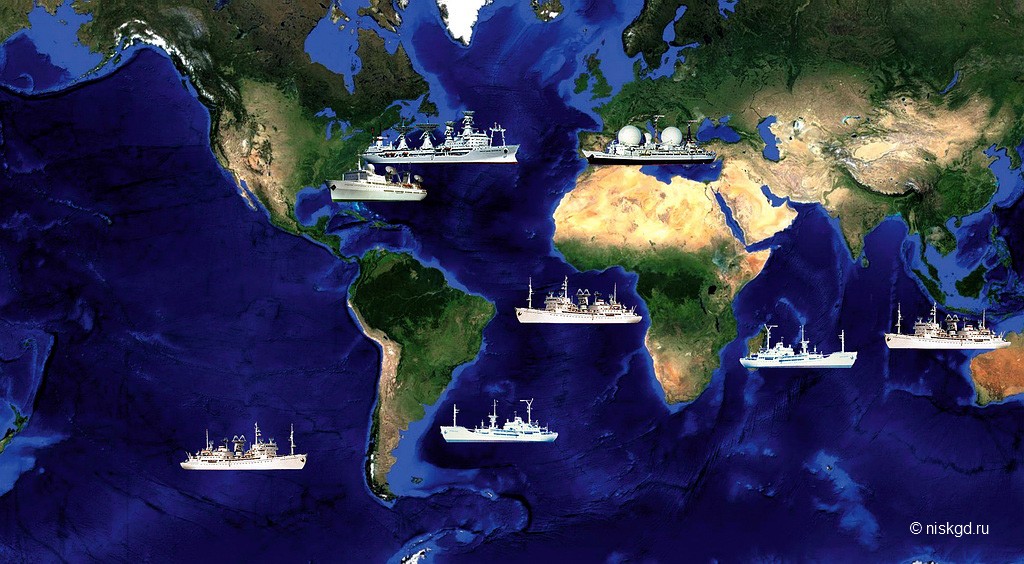
The ships with the significant names "Cosmonaut Yuri Gagarin", "Academician Sergey Korolev", "Cosmonaut Georgy Dobrovolsky" and the others were once subordinate to the Ministry of Defense, although they went "under the roof" of the Academy of Sciences:[3]

In addition to communication with manned spacecraft, they also performed other tasks, including the provision of flight tests of rocket and space technology products.
After the collapse of the USSR, three large ships, the Gagarin, Korolev, and Komarov, were sold for scrap. Approximately at the same time, the Ministry of Defense transferred the remaining four ships of the Selena type to the NPO measuring equipment of the Russian Space Agency.
“Cosmonaut George Dobrovolsky” and “Cosmonaut Viktor Patsayev” were equipped with TM measurement and communication equipment, and two ships - “Cosmonaut Vladislav Volkov” and “Cosmonaut Pavel Belyaev” - without scientific equipment, since Former owners managed to remove special equipment and some equipment.

In the second half of the 1990s, the Cosmonaut Georgy Dobrovolsky was prepared for use in the Sea Launch project as a spacecraft measurement complex.
According to the original scheme, it should have telemetry from a rocket in the most critical areas: separation of the stages, separation of the upper stage, launching the object into orbit.
Until October 1998, everything was moving according to plan. Additional equipment of the vessel was held for Russian money, taking into account that the Americans will sign a contract. Indeed, they even allocated a bit of finance in advance. But at the last moment they unexpectedly changed their minds and offered to abandon his services, equipping the rocket with an American satellite relay unit, and use their TDRS satellite for transmitting telemetry.

Maybe this is true from the point of view of a business decision: the day of operation of a telemetric vessel cost only $ 10,000.
This includes the cost of fuel, water, food, navigation services and only a small proportion of the salary of Russian personnel.
However, the savings of Americans did not take into account that the launch of the Zenit launch vehicle from the Sea Launch platform has a number of features:
- for the first time, a land-based PH will start from an ocean platform;[2]
- for the first time, refueling and storage of fuel components will be carried out in the ocean on a platform from which the launch vehicle starts;
- for the first time, the volume of telemetry adopted for normal operation at the tested RN will be reduced for transmission via the TDRS radio link;
- for the first time on the tested complex in the first launch, an experimental telemetry measurement system based on the use of TDRS will be used.
- The savings offered by the Americans cannot be compared with the possible losses. --- Telemetry information is vital for commercial launches. Its absence “hits the pocket”: in case of unsuccessful start-up, insurers do not pay compensation until they unequivocally determine the cause of the accident.
Russian partners advocated the use of Selena, at least in the first launches. The negotiations ended in nothing. In March 1998, the Zenit launch vehicle launched a spacecraft from the platform without the involvement of the Selena-M telemetric vessel.
To prevent the ships from disappearing, their crew, at every opportunity, took the ships out to sea, performing many tasks, including working with the Mir station.
A possible way out of the impasse was outlined, as always, “at the junction of two elements” - the sea and space, the ship and the rocket.
The project of the FSUE “Scientific and Production Association of Measuring Equipment” ( NPO IT ) was very simple and low-cost. In the docks of Kaliningrad and St. Petersburg there were two of the three remaining (in Soviet times there were 11) vessels of the Selena-M series intended for space communications, Cosmonaut Viktor Patsayev and Cosmonaut Georgy Dobrovolsky.
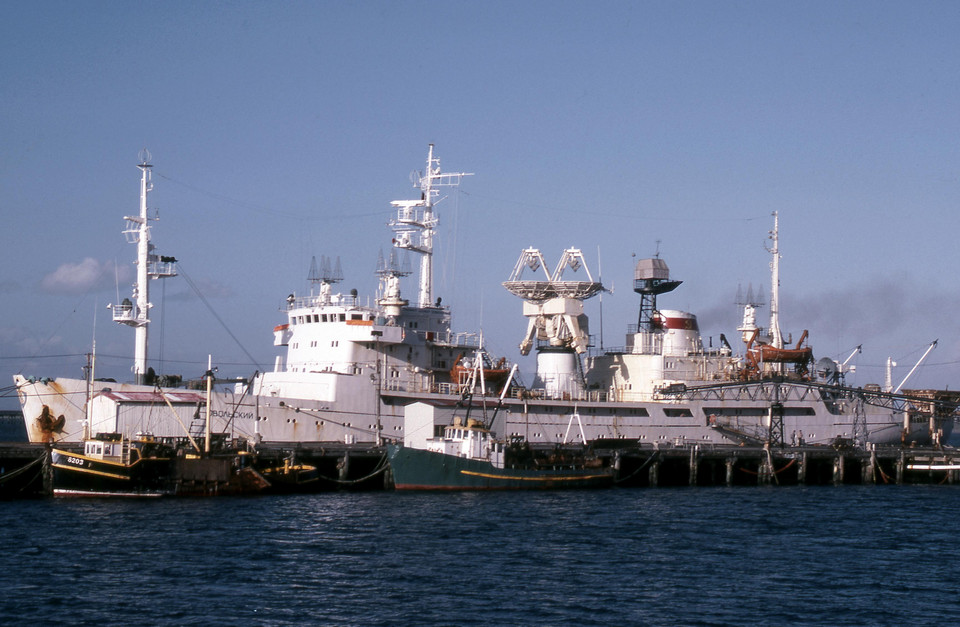

NPO IT specialists suggested one of them to re-equip to launch launch vehicles ( corrected on March 13, 17 on sticks from
The ships could be based anywhere from the Baltic to the Canary Islands - as more convenient for the customer.
The difference is only in the speed of reaching the starting point (closer to the equator): in the first case it is two or three weeks, in the second - up to 10 days.
More benefits:
- in the geographical breadth of the launch. Starting from the equator, in the vicinity of which the floating cosmodrome can easily be located, allows you to increase the mass of the satellite being put into orbit and the lower the orbit, the greater the difference in mass: for example, two hundred-kilometer height can be sent from the Plesetsk to 535 kg, and from the equator - 742.
- some specific-purpose satellites cannot be launched from the territory of the Russian Federation:
- - The law of conditions for the export of high technology from 1979;
- - Military items controlled by the US Munitions List
- - Dual-use items, the list of which is defined by the US Commercial Control List.
- great difficulty in carrying out commercial launches from Baikonur or Plesetsk is represented by customs procedures (duties on the import of foreign satellites for launches by Russian missiles constitute a significant fraction of the cost of the launch itself).
EAEC EA: 10% duty and 18% VAT.
The mobile complex, which independently arrives at the customer’s port, plunges aboard the spacecraft together with the escort team and, under its own power, goes to the launch point of the Offshore and is relieved of such a moth.
Comfortable conditions on board (single and double cabins) make it possible to accommodate customer representatives, even the most demanding ones.

Of course there are also disadvantages
The main one: the sea launch was losing (at that time), and even now it loses (Space X is the same) in price to the earth cosmodromes. Sea launch is more expensive by about $ 2-4 million ($ 12-14 million versus $ 10 million from the launch site).
Partial “difference” was paid by extra satellite kilograms launched from the equator.
Launch class launch vehicles ( corrected on March 13, 177 by sticks with
ILV (conversion version RT-2PM / 15Zh58 (SS-25 SICKLE)) are compact in size and have an acceptable mass, which made it possible to place two missiles on the ship at once.
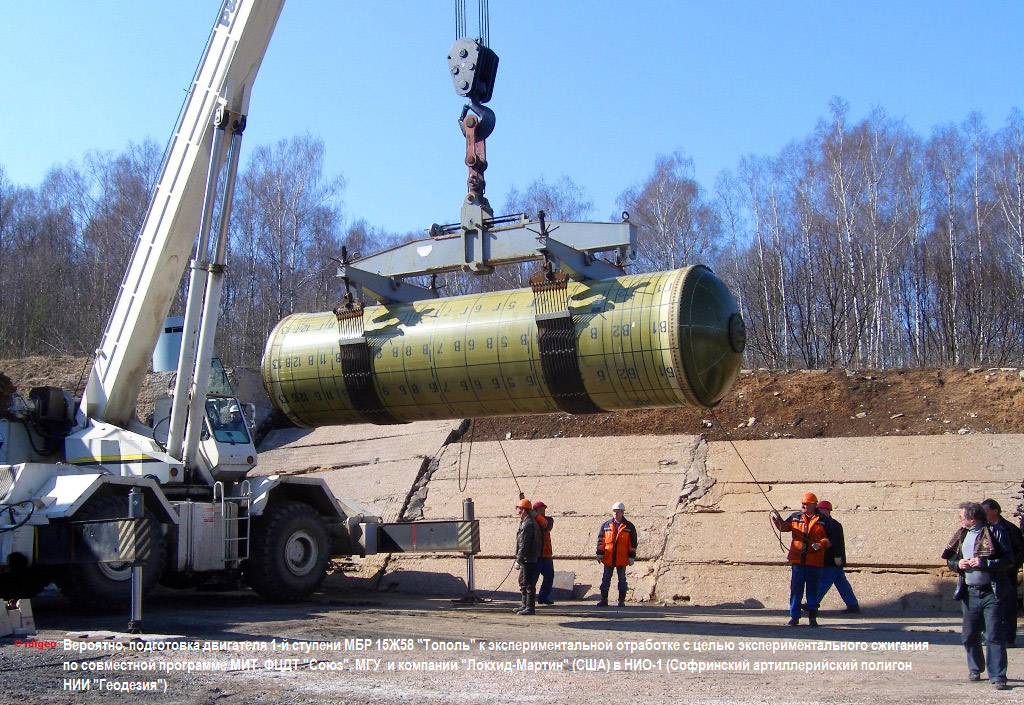

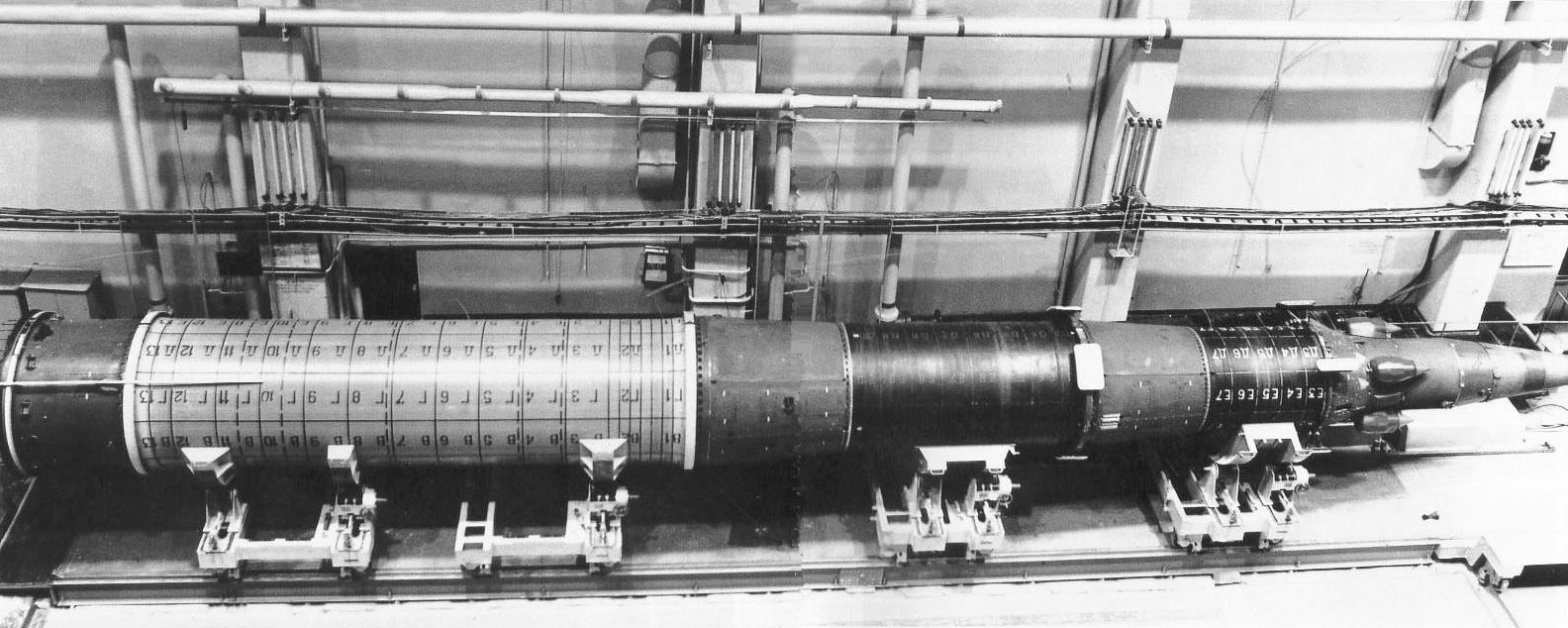

The degree of automation of prelaunch preparation is very high (at 100%).

The total cost of the project "easy" sea launch: 20-25 million dollars (almost the price of one space tour), which includes a complete re-equipment of the spaceport, the output of two ships at sea and their work.
For the year, according to the designers, you can make up to 10 starts.

There is also a security problem: the ship is a land site of the cosmodrome.
The designers used the “mortar” principle of launch in the ICBM: the charge of the TPK in which the rocket is located will be the first to fire and fire it into the air, then the main engines of the launch vehicle turn on at a safe height ( corrected on March 13, 17 sticks from the
For complete safety, the option of a remote launch without the presence of the crew was also provided: the legacy of the combat ICBM.
The marine launch complex, called Selena, includes a transportable rocket-space complex with a solid launch rocket of the Start family, a Selena-M project transport and launch vessel, a complex of rocket launch process measurement systems and a ground-based technical base for preparation and assembly of the RKK in the port of registry.

The current measuring points are completely different. Places on the ships of this class will be a lot. The trouble ships almost gone.
Mobile measuring points (MIPs) are developed and exist. Since not every country allows them to be brought into their territory, they are made in a mobile version on a gyro-stabilized platform.
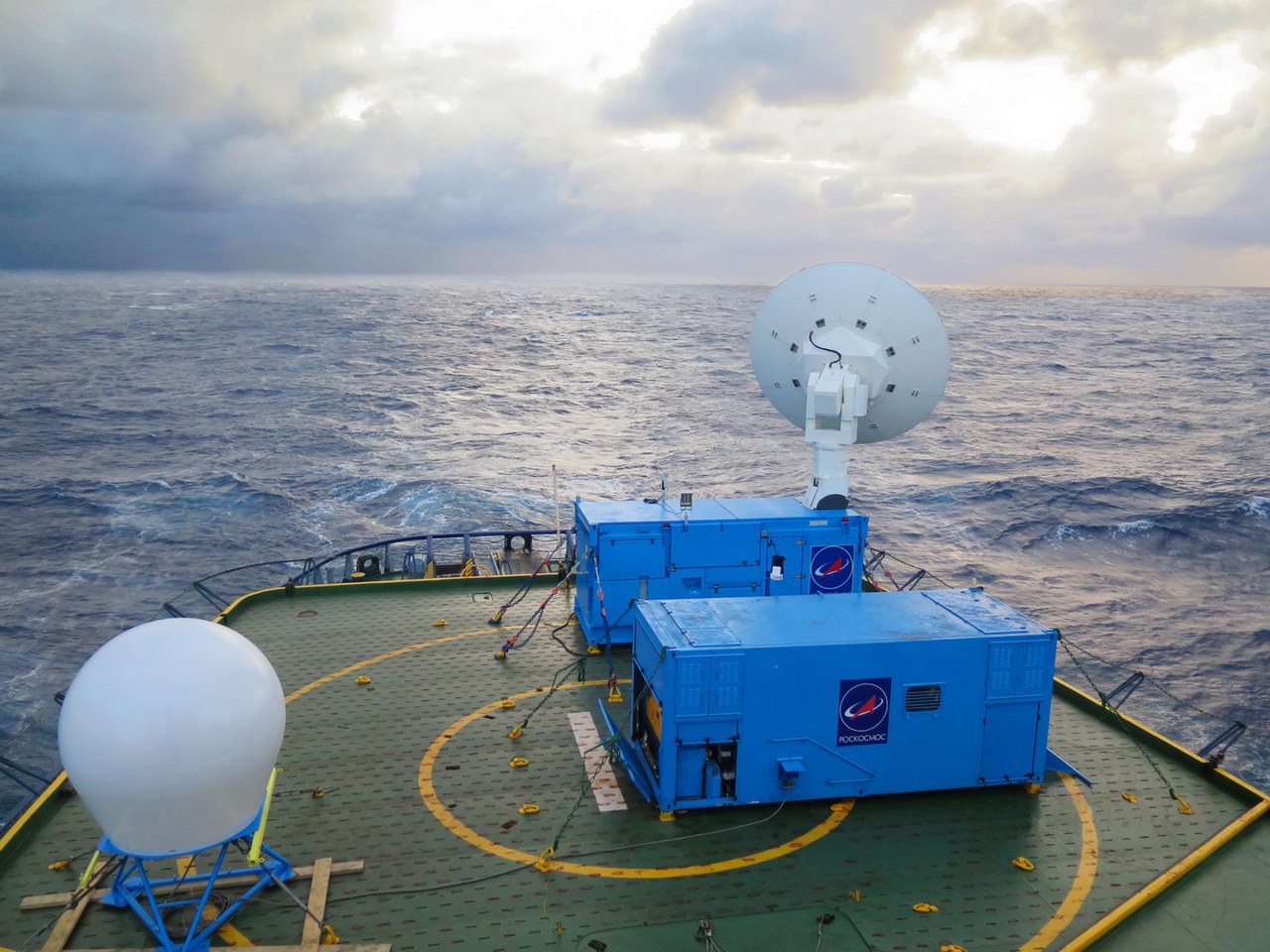

In August 2015, the sea-based MIP (MIP MB), produced by NPOIT, was tested in the Sea of Japan video aboard the “Admiral Makarov.
The infrastructure of the complex is largely ready. The reliability of the RSC is confirmed during the operation of the original missiles and launch vehicles from Svobodny and Plesetsk.
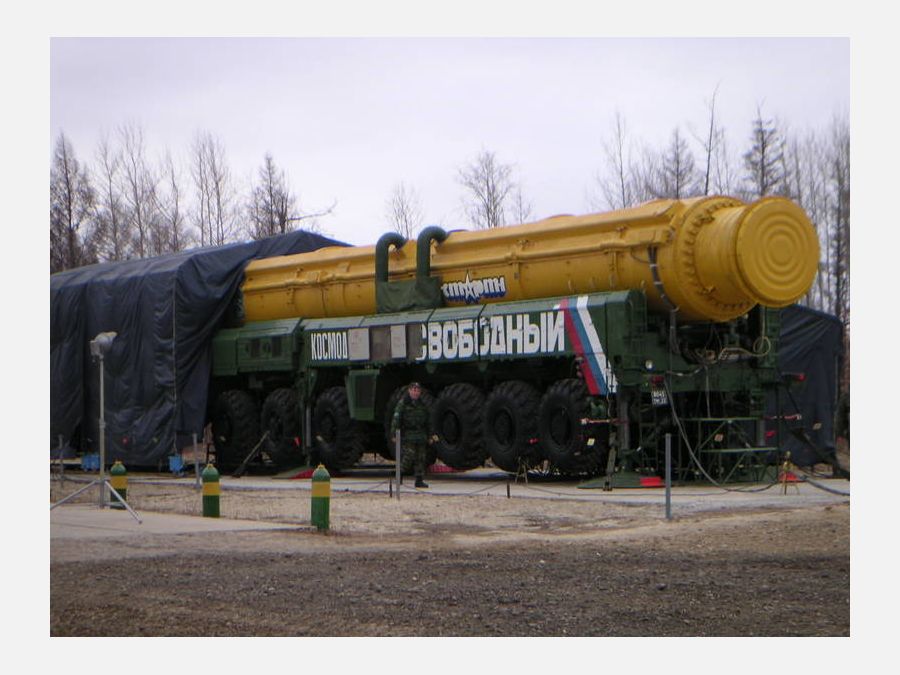
All launches of Topol ICBMs (RS-12M Topol, RT-2PM / 15Zh58-SS-25 SICKLE) / RN Start-1.2 rocket
There were two modifications of Start media:
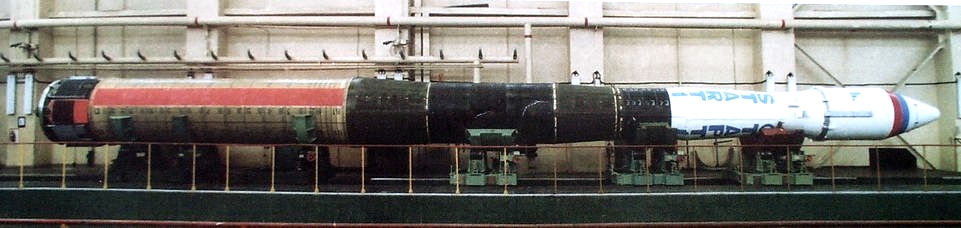
Four-step "Start-1" and five-step "Start".
The latter had only one launch from Plesetsk - emergency - on March 28, 1995 (the EKA-2 dimensional and weight mock-up and the Gurwin Techsat 1A and UNAMSat A. satellites were not put into orbit.
Start-1 from Plesetsk had only one launch: on March 25, 1993, with the launch of the satellite into orbit orbit (or, according to other data, the overall weight model) of ECA-1.

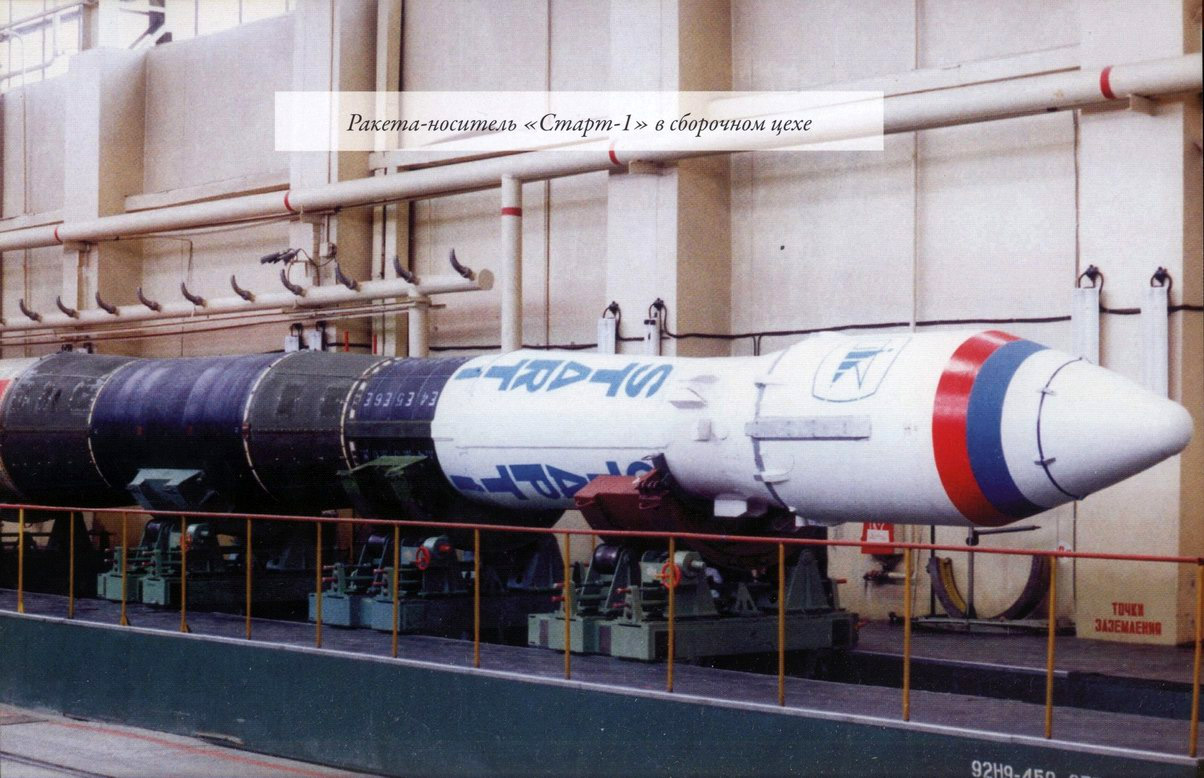
The remaining five Start-1 launches were performed from the Svobodny space center:
March 4, 1997 (satellite Zeya), December 24, 1997 (EarlyBird), December 5, 2000 (EROS A), February 20, 2001 (Odin) and April 25, 2006 (EROS B).

Already at that time, and now even more so, there is a boom of interest in low-orbit satellite communication systems based on small satellites and ultra-small satellites.

The first satellite in the world made by primary school students was launched into space.
Satellites-microchips (“star dust”) will go into orbit
Another giant project SpaceX, arithmetic and common sense
The devices are launched on large carriers in “bundles” and wait for their turn when the “elder brothers” are ready.
But the life of such dwarfs is very limited. Starts are required to maintain the orbital constellation.
Probably small rocket carriers based on conversion marine or land ICBMs will be especially effective here.
Launch of NROL-55 spysat:
...
Cosmonaut Georgy Dobrovolsky (Project 1929 (Selena-2), No. IMO: 6910245) in 2005 sold for scrap. In March 2006, under the name “Cosmos” came to Alang (India), where it was dismantled.

He survived his eldest friend for 10 years:
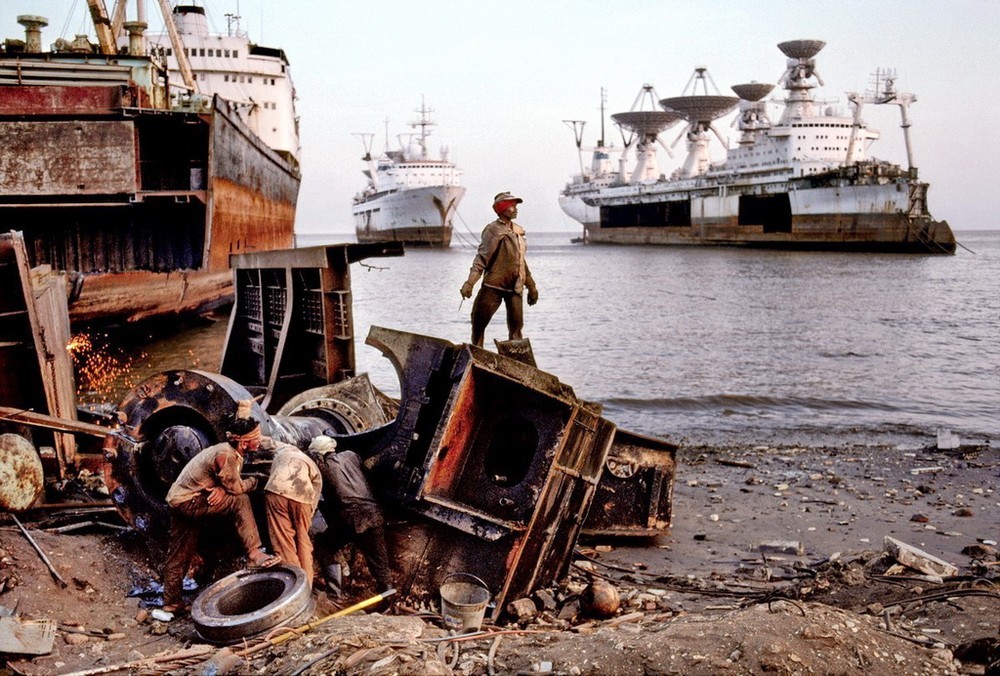


Instead of an afterword I quote Vladimir Proshchenko:
Do I need a "Marine Space Fleet"? What in return?
A little boy was playing in the field, he was digging a hole with a scoop.[2]
The satellite is gone! No signals from GLONASS! Long laughed at the NASA Directorate
Telemetry, launched by the PH and SC, again:
The rocket flew - fell into the swamp ...
Why fell? And who is to blame? And most importantly: "What to do?" And "How to fix?"
No data-guessing on the coffee grounds
Cosmonaut Georgy Dobrovolsky-TV Studio Roscosmos
Original sources, links and borrowed photos / videos
[1] V.Proshchenko Report to the Korolev readings, January 2016. Section 10. “Astronautics and Culture”
The site “KIK USSR” Alexander Neom 2009-2016
[2] Forum NIS "Cosmonaut George Dobrovolsky"
Appendix to NIS CGD website
TV studio Roscosmos
RV "Georgiy Dobrovolsky" Vladimir Proshchenko
[3] COSMODROMES
Starting place - the ocean / V.M. Filin. - 2000
Children's drawing competition
Launch of the 15Zh65 missile from the converted Voevoda ICBM R-36M2 mine. Polygon Plesetsk. / Research and Development "Universal" / OCR "Topol-M", 15Zh55 / 15Zh65 rocket - SS-X-27 SICKLE-B /
www.nnm.me
www.dimmi-tomsk.livejournal.com
www.militaryrussia.ru
www.novosti-kosmonavtiki.ru
www.wikipedia.org
www.itogi.ru
www.ski-omer.ru
www.space.hobby.ru
www.sslmda.com
www.americaspace.com
The site “KIK USSR” Alexander Neom 2009-2016
[2] Forum NIS "Cosmonaut George Dobrovolsky"
Appendix to NIS CGD website
TV studio Roscosmos
RV "Georgiy Dobrovolsky" Vladimir Proshchenko
[3] COSMODROMES
Starting place - the ocean / V.M. Filin. - 2000
Children's drawing competition
Launch of the 15Zh65 missile from the converted Voevoda ICBM R-36M2 mine. Polygon Plesetsk. / Research and Development "Universal" / OCR "Topol-M", 15Zh55 / 15Zh65 rocket - SS-X-27 SICKLE-B /
www.nnm.me
www.dimmi-tomsk.livejournal.com
www.militaryrussia.ru
www.novosti-kosmonavtiki.ru
www.wikipedia.org
www.itogi.ru
www.ski-omer.ru
www.space.hobby.ru
www.sslmda.com
www.americaspace.com
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/402213/
All Articles