The greatest "Dome" of science from Istra

Archaeologists are amazed at the craftsmanship of ancient architects. Not having modern tools, they could build objects of amazing imagination. Buildings of the distant past do not fit into our ideas about the life of previous generations so much that they give rise to the growth of alternative theories about Atlantes, newcomers, and chrononauts. If after many years, when only plastic fragments scattered on a petrified bed between the Burgeshes shale and a thousand-year layer of mud are left from humanity, aliens will fly to Earth, they will study our reinforced megalithic structures with the same distrustfulness.
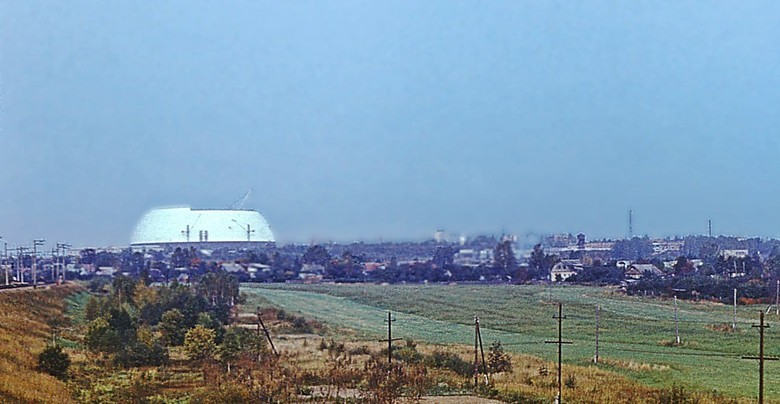
There is no need to go far in order to experience emotions from contact with history. Enough to go to the suburbs, where under the bushes, the earth and the ancient concrete slab are the remains of the largest mysterious structures. Today we will talk about one of these places - the main testing ground of the All-Russian Electrotechnical Institute.
High voltage projects
In the 70–80's of the last century, the Soviet Union launched a large-scale project to build a super-powerful energy bridge, which was supposed to connect Siberian power stations, Ekibastuz energy center, where the largest thermal power station of Kazakhstan is located, with the industrialized Urals and the European part of Russia.
In 1978, the construction of the longest power lines in the world began - a 2414-kilometer DC line would link Ekibastuz and Tambov cities. The maximum power should have been 6000 MW.
In 1988, a unique high-voltage AC line with a rated voltage of 1150 kV Barnaul-Ekibastuz-Kokshetau-Kostanay-Chelyabinsk was built. This is the only power line in the world of this class of voltage, the capacity of which reaches 5500 MW.
Projects of such a scale could not be implemented without real checks of high-voltage equipment, but at that time there was no test bench equipped with necessary equipment and corresponding to a high level of safety.
In addition, as part of the preparation of an “asymmetric response” to Reagan’s “Strategic Defense Initiative”, the military considered various theories of creating weapons based on artificial lightning. The platform, where free megawatt electrical discharges could be generated, would be the answer to all the questions for both civilian scientists and the army.
The period from the late 1960s to the late 1980s is one of the most interesting in the history of architecture of the USSR. It was a time of bold, unusual, futuristic projects. We on Real Estate Mail.Ru even somehow did a selection of projects in the form of flying saucers and fancy tents.
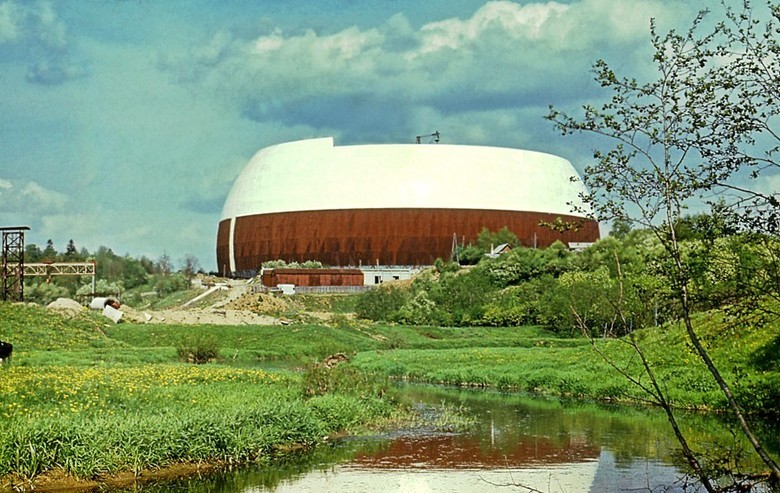
Istra dominant

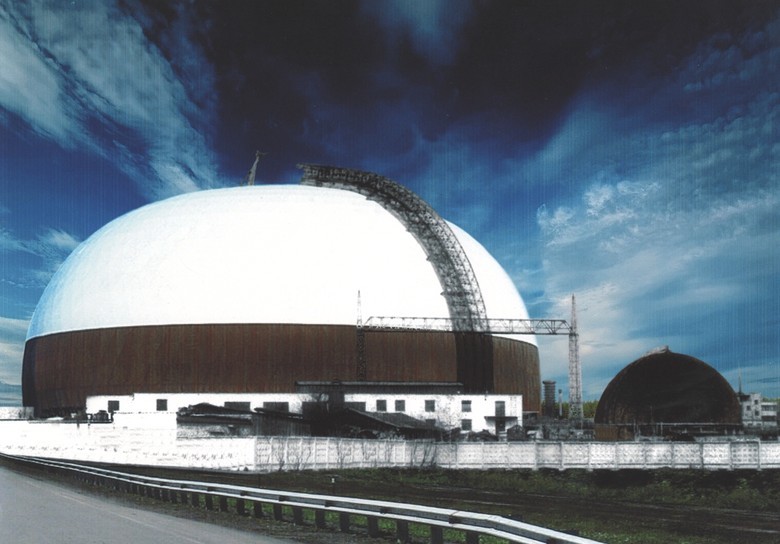
The diameter of the base - 236.5 meters. Height - 118.4 meters
The project, called the High Voltage Test Stand of Enterprise R-6511, was built for the All-Union Energy Institute named after V. Lenin (VEI) on the site already owned by VEI, near the city of Istra, on the high bank of the river of the same name. Various organizations participated in the construction of the high-voltage test center. The project of the metal part was developed by the leading organization of the country in the field of metal structures - the Central Order of the Red Banner of Labor Research and Design Institute of Construction Metal Structures named after N. P. Melnikova.
Glavspetsstroy, the leading construction organization working for the country's military-industrial complex, has become a general contractor. Virtually all construction work on the dome was carried out by the 168th Military Construction Directorate. The most difficult part of the project, the installation of metal structures, was entrusted to “Special Steel Construction” (Ministry of Special Construction Works of the USSR).
The VEI decided that the building should be made in the form of a dome structure - it was the sphere that the waves from the electromagnetic impulse generator should propagate during the tests, and the envelope was supposed to shield the impulses. Construction began in 1982, and two years later the largest dome in the history of mankind was erected, built without the use of internal supports.
Challenging uniqueness
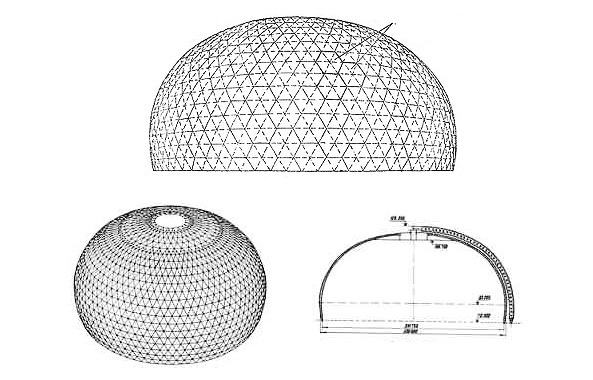
Since the installation was carried out without the use of supporting structures, it was necessary to introduce special technical solutions. The clue was given by nature itself. The shape of the structure was chosen as a drop lying on a flat surface. A drop is a very stable structure due to surface tension. The walls of a huge dome, towering above emptiness, were supposed to work similarly to the “walls” of a drop.
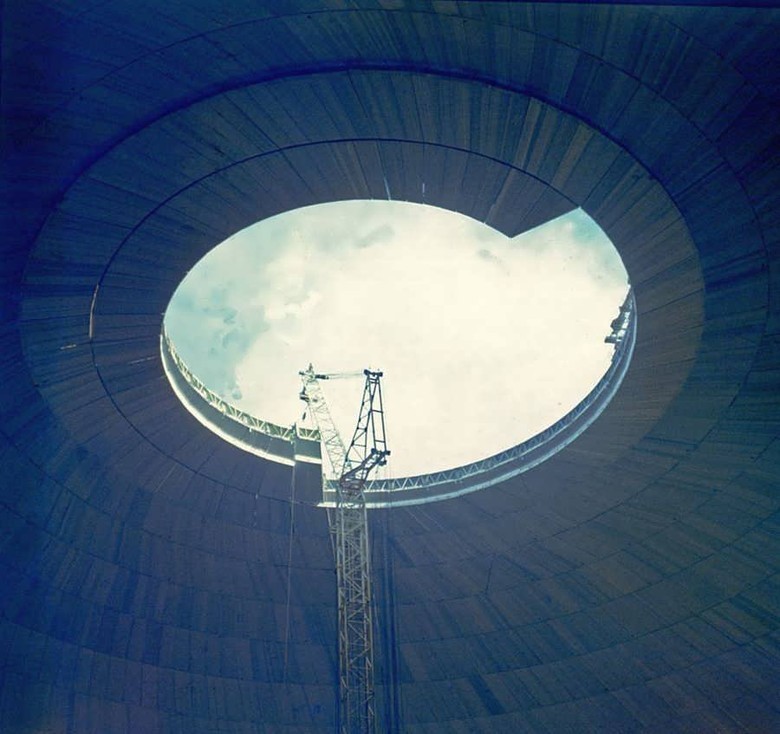

The first 10 tiers of the building were assembled by two tower cranes moving along an annular path outside the dome, and further installation was carried out with one mounted inside crane. The inclined part of the sphere with its weight pressed on the lower layers and so remained stable. There were no obvious reasons for abandoning the supporting structures, they took into account the progressiveness and technological advantages of the method of mounted installation, which allowed building a huge structure in the shortest possible time and at the same time reducing the consumption of necessary materials.
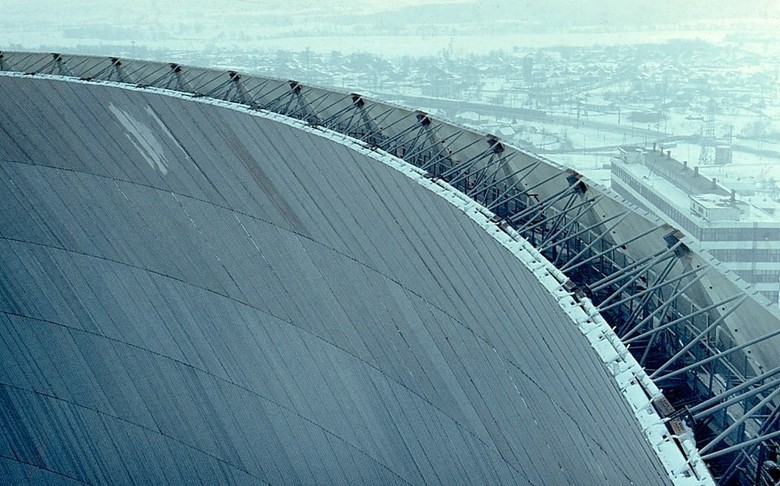

The thin “shell” of the dome was a network of massive steel rods forming isosceles triangles. The core bars were made in the form of trusses with parallel steel belts consisting of paired angles. Aluminum panels with mineral wool for thermal and sound insulation were fastened to the inner side. The total thickness of the shell was 2.5 meters.
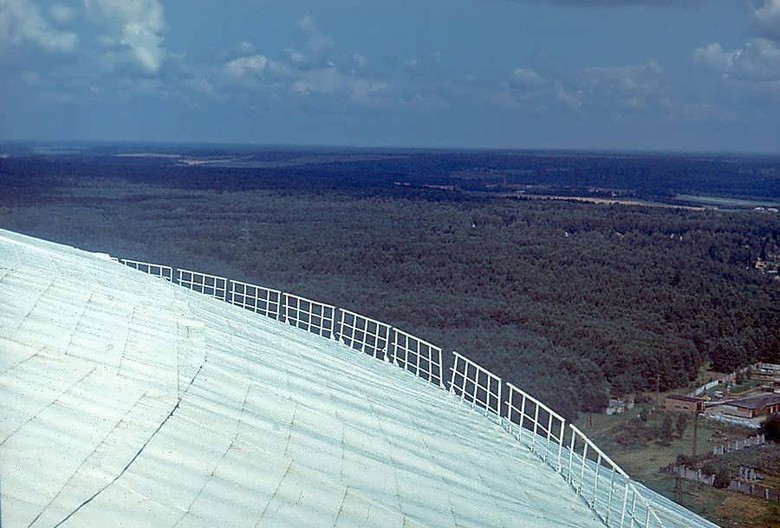

A membrane of weatherproof steel, just one and a half millimeters thick, was welded to the outer chords of the framework, which was immediately painted in a light color, giving the appearance of the dome a resemblance to an egg shell.
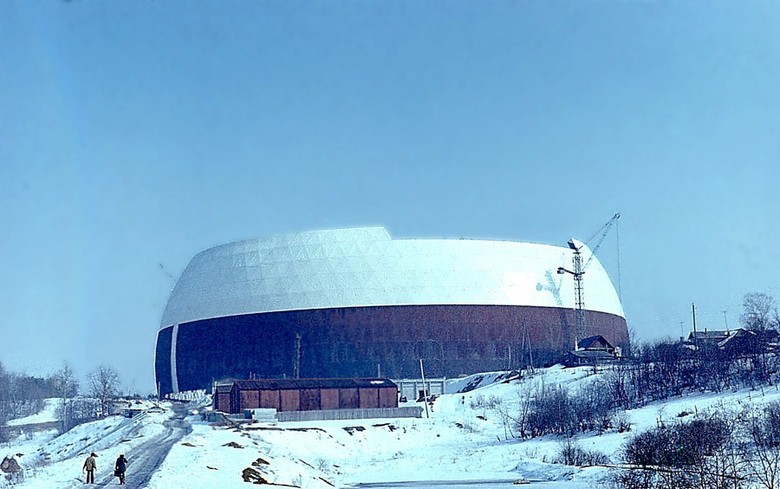

The dome took about 10 thousand tons of steel and 363 tons of aluminum, 21 symmetric block tiers were mounted, a box-shaped ring with a diameter of 34 m was installed on it, and the central part of the shell weighing over 600 tons was lifted. The foundation of the dome was made of 63 concrete supports of which survived to this day.
At the top of the dome, a technological room with a diameter of 34 m with a floor area of 900 m² and a weight of 110 tons was assembled. To it, in the very center of the dome, a high-power impulse voltage generator was attached to the hangers.

On the inner surface of the dome were equipped with cargo lifts of 5, 25 and 100 tons, installed at an altitude of 106.7 meters. For the purpose of servicing the outer surface of the dome, a device was designed in the form of a semi-arch, inside of which a passenger-and-freight elevator and stairs were located.
Disaster and investigation
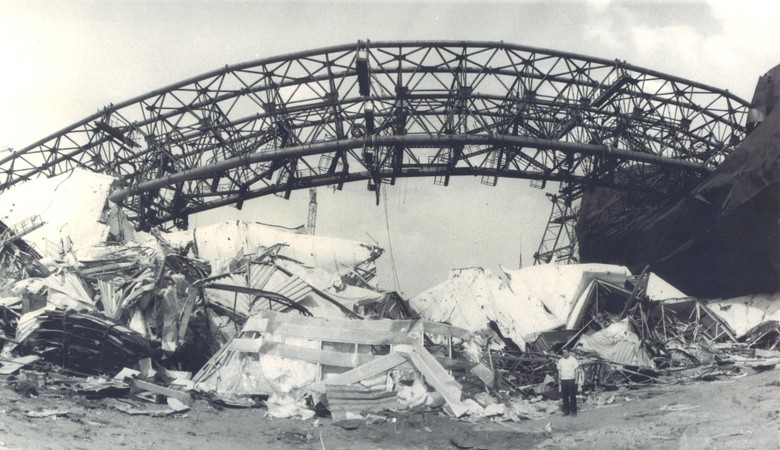

At the site of the collapse of the structure. Above - the remnants of the self-propelled semiarks, located on the outside of the dome
By the fall of 1984, the main work was completed, but after only a few months, on January 25, 1985, the dome collapsed. Only the early time of the disaster (7:30 am) made it possible to avoid casualties. Over 16 thousand tons of metal structures were destroyed.
The technical commission for investigating the causes of the accident considered many versions of what happened, from tectonic shocks to sabotage. It was checked that the actual shape of the dome was significantly different from the design. If initially there were errors in the project, then over time they accumulated, reducing the curvature of the upper part of the dome. As a result, the "cover" of the dome could press on the rest of the structure as a plate.
During installation, some compressed rods really lost stability. The cause of the overload was eliminated, and the deflections apparently remained. In addition, before the collapse, severe frosts gave way to thaw. Cold air gathered under the dome, and on the surface it began to press warm. The desire to save on time and money led to the fact that some rods were made not from steel of increased strength, but from ordinary steel. Not all supporting high-strength bolts were supplied.
However, experts of the commission came to the conclusion that all these defects could not have caused the collapse. At the project stage, the statistical calculations of the dome were made in the Paradox program, which took into account the upper part of the dome, as a flat slab supported along the contour. Thus, the mere additional impact of snow, water or air, not to mention its own weight, could not bring down the "roof" of the dome. The technical commission concluded that the accident occurred as a result of an unfavorable combination of dozens of small errors in the design, manufacture and installation of structures. One of the most important factors in the critical accumulation of errors was the ignoring by the customer of research and experimental work on real models. And already during the installation, there were not enough instruments to monitor the deformations of the dome in automatic mode - they simply did not exist in the USSR.
Effects
Gosstroy of the USSR tried to make Glavspetsstroy build the dome again in two years. Moreover, they were going to build on the previous project. However, before all the issues related to financing were resolved, a restructuring took place, followed by the collapse of the USSR, and there was no money left for ambitious research projects.
A few years after the fall of the dome in Istra, the currently valid national standard “Reliability of building structures and foundations” was developed. The following very important lines appeared in it: “for unique structures that do not have reliable calculation methods or similar solutions tested earlier in Russia, the calculation of structures and bases must be made on the basis of specially designed experimental studies on models or full-scale structures” .
To monitor the possible deformation of materials during construction at the end of the 90s, Russia began to use non-reflecting electronic total stations. They were used, for example, in the construction of the Lefortovo tunnel in Moscow.
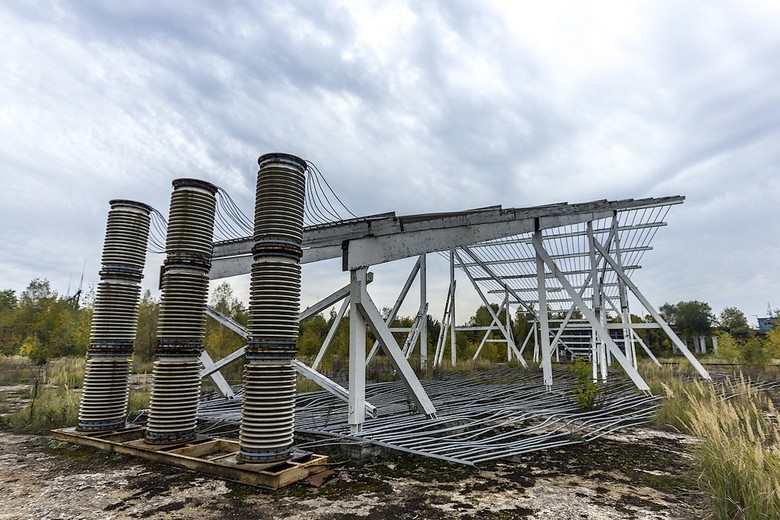

Thousands of tons of reinforced concrete structures were removed from the site of collapse. There was only a concrete pit. Later, a “Stationary electromagnetic impulse“ Allure ”simulator will be built on it, intended for testing and research of objects of aviation, radar, armored and automobile vehicles, rocket complexes, communication systems, power supply and combat control, computing equipment and various equipment for resistance to powerful electromagnetic pulses of man-made and natural origin.
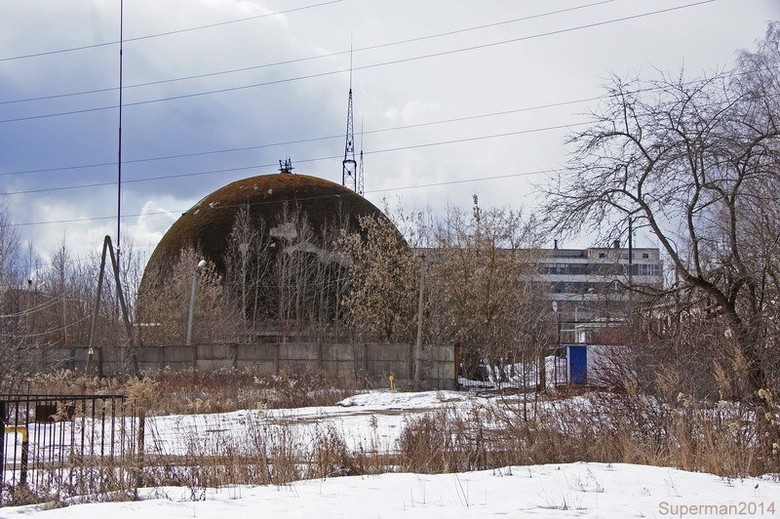

On the territory of VEI there is another test building with a dome completion, the so-called “Small Dome”, but its dimensions are not commensurate with the collapsed large dome.
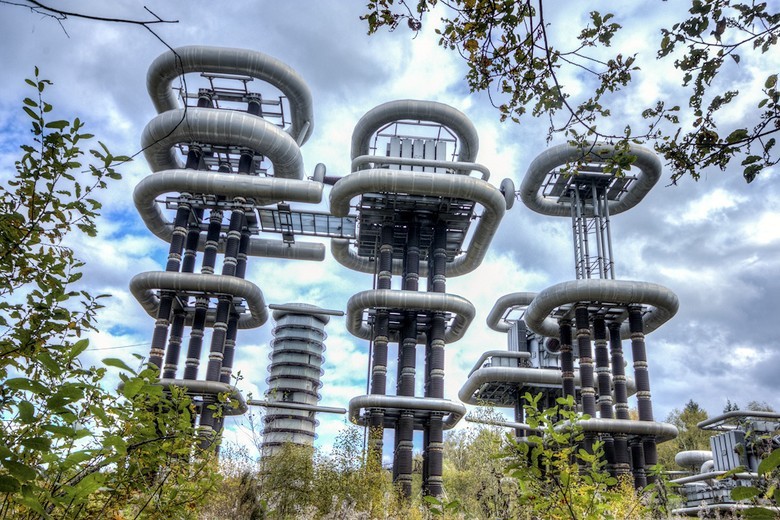

In the foreground is the Arkadieva-Marx generator, setting a constant voltage to 2.25 megavolts. Marx pulse voltage generator is seen in the background.
Nearby there is an open test site, on which a 43-meter tower is installed - a Marx impulse voltage generator with a power of 9 MV. It was used for research on the physics of lightning.
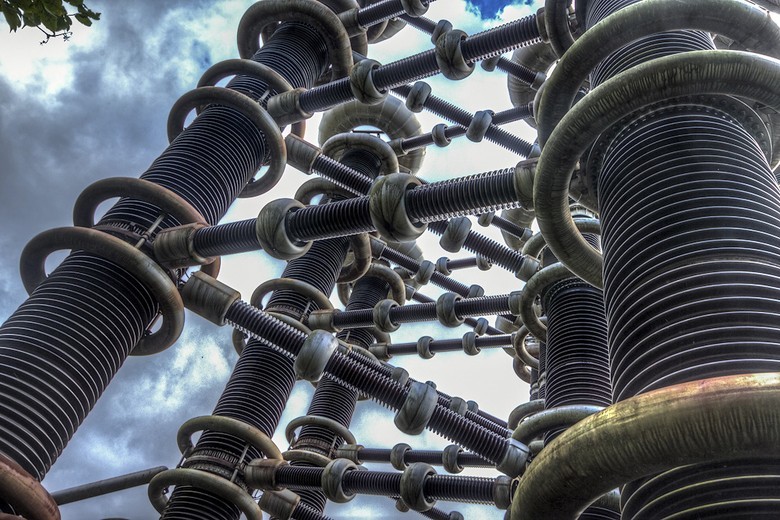

In recent years, the facility is in a semi-abandoned state, and the VEI itself is struggling hard for its own survival and has no money for the maintenance of infrastructure.
Sources:
" Secrets of steel structures ", M. Aroshenko, V. Gordeev, I. Lebedev.
"The secret dome in the vast Moscow region, " deletant .
“ Modern automated systems for controlling the deformation of large-span structures ”, G. E. Ryazantsev, I. A. Sedelnikova, I. A. Nazarov.
“ Fallen drop ”, magazine “Spetsstroy”, Oleg Dogadin.
“The Big Dome in Istra on the territory of the All-Union Energy Institute named after Lenin (VEI) "
')
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/402165/
All Articles
