Anabiosis for long space travel will soon become reality
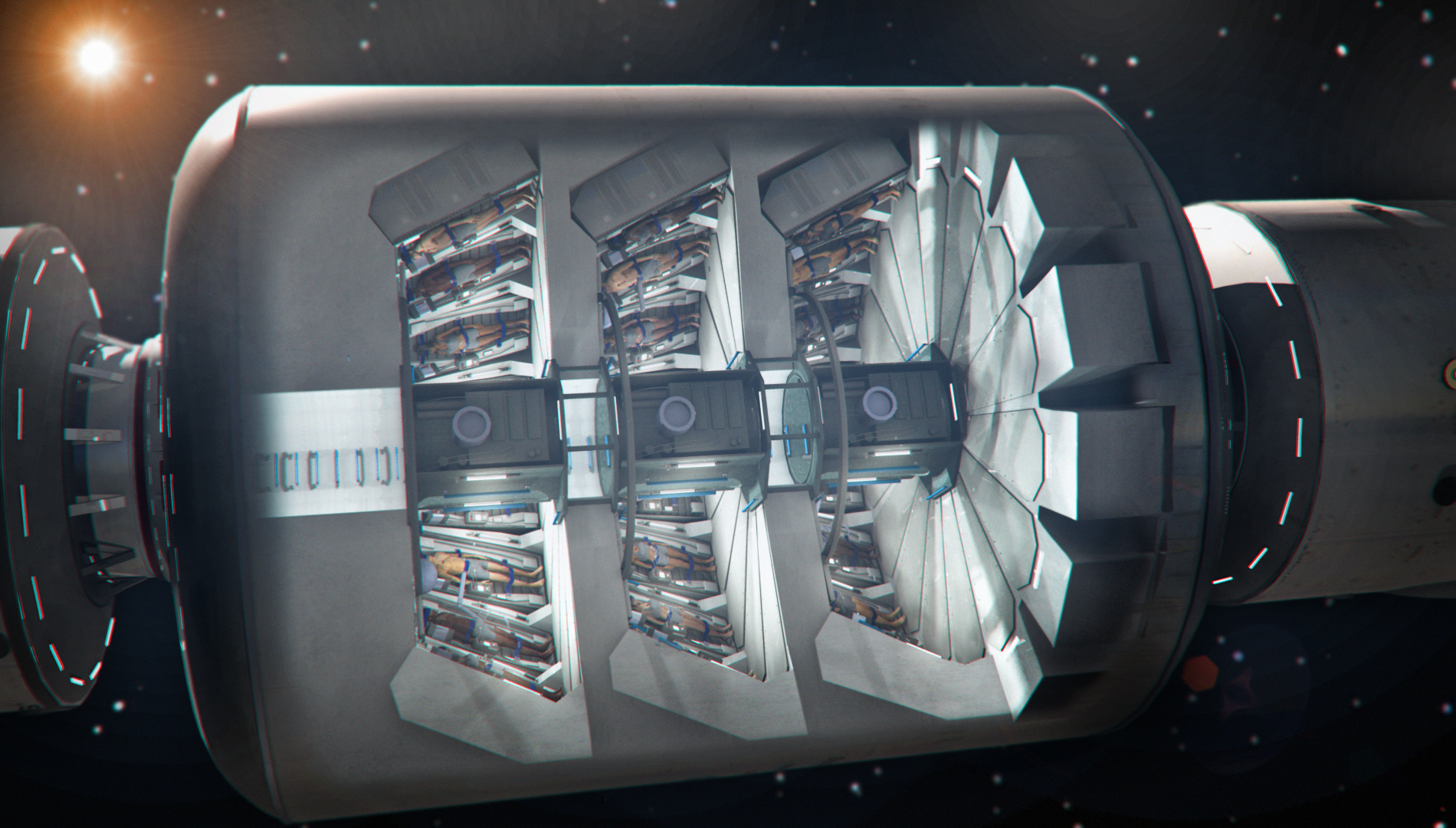
The artist's presentation of cameras for anabiosis from Spaceworks
On October 7, 2006, Mitsutaka Uchikoshi, after eating shashlik on Mount Rocco in western Japan, decided to go down the mountain on foot rather than ride the cable car. He was lost, slipped, broke his pelvis, and since there was no one around who could help him, he lost consciousness. After 24 days, a passing climber found Utikosi. His body temperature dropped to 22 ° C, his pulse was barely detectable, and his metabolism almost stopped. Despite the failure of many organs and the serious loss of blood, he survived without food and water, and then fully recovered.
The case of Utikosi was called the first documented case of hibernation . His story immediately attracted the attention of the medical community, hoping to develop new therapies.
')
Among the medics was John Bradford, President of the American company Spaceworks from Atlanta, pcs. Georgia, developing space exploration technology. Bradford, however, was not going to develop new treatments; He wanted to find a way to introduce people into anabiosis on long interstellar flights.
“I'm a big fan of science fiction, so the point is to make a small part of it real,” Bradford says. “But I’m primarily an engineer working on manned missions to Mars and other areas in our solar system.” From this point of view, anabiosis is fully justified. ” If the team is sleeping, it needs less food and life support systems, and this significantly reduces the overall weight of the ship and the cost of the mission.
Bradford and his team focused on “therapeutic hypothermia,” a well-established procedure used in hospitals around the world, conducted on thousands of patients to fight heart attacks and brain injuries. According to this scheme, the body is slowly cooled to temperatures of 32-34 ° C, about 1 degree per hour, and this slows down the heartbeat and reduces blood pressure, which gives physicians more time to work with difficult problems in the heart and brain. Usually, the patient remains in this state of stasis for 2-4 days, although there have been cases when doctors prolonged it for up to two weeks - without any complications. The Uticoshi case showed that it is possible to survive even with a longer cooling procedure.
“Our goal is to go from days and weeks to months,” says Bradford. He argues that medical equipment used for therapeutic hypothermia can be easily converted to automatic mode and prepared for space. It is already small, consumes little energy, is easy to use and portable enough to be transported in ambulances.
Hypothermia equipment
The spaceworks hibernation room from Spaceworks will look something like the way it is portrayed in n / f films, but with some key differences. “Individual cameras for anabiosis have advantages. You can control the temperature of each person. They will come in handy in case of danger, for example, the spread of a pathogen, ”says Bradford. But this option will add too much weight to the ship. Therefore, the company's engineers tend to open and shared rooms for anabiosis. “There will be robotic manipulators and tracking systems that care for passengers. They will have small nasal tubes for cooling, as well as systems for heating, bringing them back from anabiosis. ”
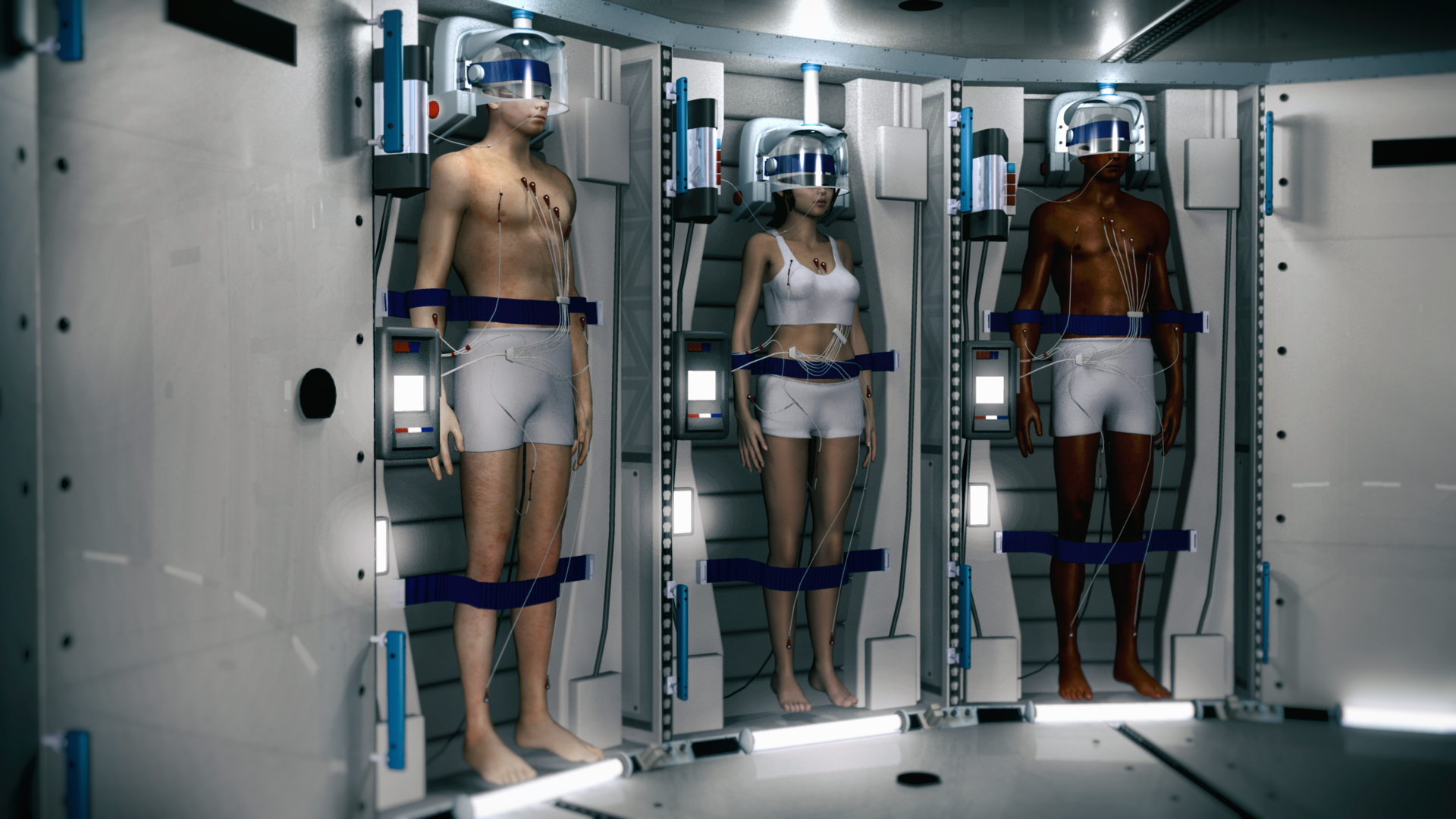

The artist's presentation of the camera for anabiosis
In reality, the scheme of anabiosis will also be different from the Hollywood presentation. The team will not sleep all the way. The company talked with medical experts, and most of them agree that short repeated cycles of entry and exit from anabiosis will be safer than one long one. One of the reasons is that one of the crew members will always stay awake and be able to monitor ship systems and react to unforeseen events. "Therefore, in the near future, in 20-40 years, we will be able to achieve anabiosis lasting a couple of weeks," says Bradford.
But there are difficulties. Our bodies are not adapted to low gravity. Bones and muscles, freed from the need to maintain weight, gradually lose weight to a state in which people become disabled. The heart, designed to pump blood up to the brain, struggling with gravity, copes with work too well in space. Therefore, astronauts suffer from increased intracranial pressure, which leads to vision problems. One solution is to build a ship with artificial gravity, but this is likely to be very expensive. Another thing is to force the team to do a lot, as they do on board the ISS. But after all, they will not be able to perform the exercises while in hibernation. Or will they?
“We have ideas on how to exercise them,” says Bradford. One of the ideas is “neuromuscular electrostimulation,” during which small electrical impulses are transmitted through the body and cause the muscles to contract. “The results of using this technique to prevent muscle atrophy in patients in a coma are promising,” says Bradford. In space, this can be supplemented with drugs to reduce the effect of weightlessness on bone mass.
And to combat the increased intracranial pressure, therapeutic hypothermia is used.
The company wants to begin tests on animals in 2018, and then go to tests with healthy people, and possibly conduct experiments on the ISS. But the company's vision extends much further than flights to Mars or Jupiter. They are already thinking about supporting the ship with hundreds of passengers for interstellar flight. Bradford considers a realistic system, reducing body temperature by several degrees, metabolism by 50-70%, and extending the time of suspended animation from several weeks to several months.
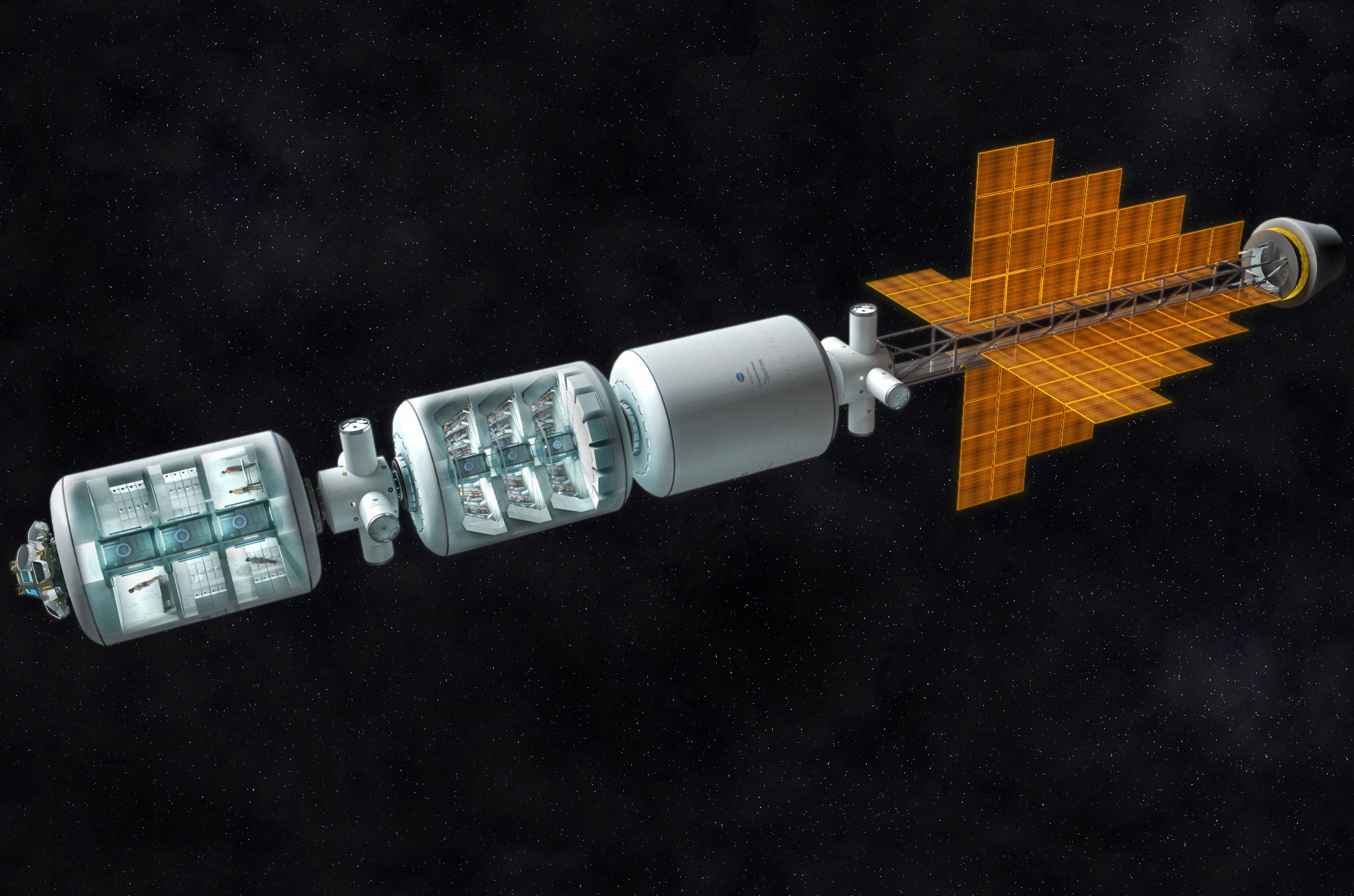
What about cryocapsules from Hollywood films in which interstellar travelers are able to sleep for years? After all, a journey into a truly deep space will take dozens, if not hundreds and thousands of years, right?
But Hollywood is not so understood, the reality is much crazier.
“Our plans for the colonization of the universe are simple, we don’t need fashionable things that violate the laws of physics,” says John Alice, a physicist at CERN. As he told me at a conference in 2015:
This allows the theory of relativity. Take Alpha Centauri, 4.3 light-years away. If we could accelerate the ship to 0.8 from the speed of light, a slowdown in time would have come into play. The journey would have taken five years on the Earth clock, but only a few months on the ship’s clock. And the closer the speed to the speed of light, the shorter the path will be for the team. The astronauts of the future will need only a few months of flight. "
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/402141/
All Articles