Where do water and oxygen come from on the ISS?

Anthem 13 division.
We are not astronauts, not pilots,
Not engineers, not doctors.
And we water plumbers:
We drive water from the urine!
And not fakirs, brothers, like us,
But, without boasting, we say:
The water cycle in nature we
In our system, repeat!
Our science is very accurate.
You just give thought a turn.
We will overtake waste water
On casseroles and compote!
Having passed all the roads Milky,
Do not lose weight with it
With full self-sufficiency
Our space systems.
After all, even the cakes are excellent,
Lula kebab and rolls
Ultimately - from the original
Material and urine!
Do not refuse, if possible,
When we ask in the morning
Fill the flask in total
At least one hundred grams each!
We must confess in a friendly way
What is beneficial to be friends with us:
After all, without utilization
In this world not live !!!
(Author - Varlamov Valentin Filippovich - pseudonym V.Vologdin)

Water is the basis of life. On our planet for sure. On some sort of "Gamma Centaurus" everything is possible differently. With the advent of space exploration, the importance of water for humans has only increased. Very much depends on H2O in space, starting with the work of the space station itself and ending with the generation of oxygen. The first spacecraft did not have a closed "water supply" system. All the water and other "consumables" was taken on board from the very beginning, from Earth.
')
“The previous space missions - Mercury, Gemini, Apollo, took with them all the necessary supplies of water and oxygen and dumped liquid and gaseous waste into space ,” explains Robert Bagdigian from the Marshall Center .

If we formulate briefly: the life support systems for astronauts and astronauts were “open-ended” - they relied on support from their home planet.
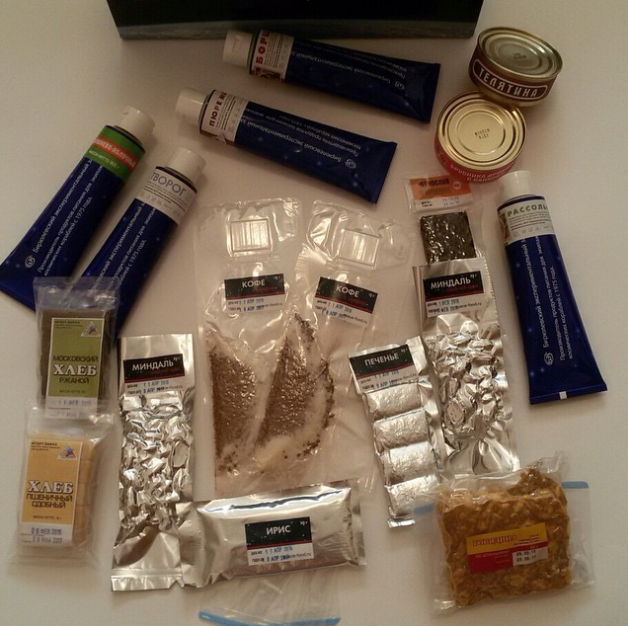

About iodine and the spacecraft "Apolon", the role of toilets and options (UdSSR or USA) of waste disposal on early spacecraft I will tell you another time.
In the photo: Apollo 15 crews life support portable system, 1968.
Leaving the reptiloid I swam up to the locker of sanitary facilities. Turning his back to the counter, he took out a soft corrugated hose, undid the pants.
- The need for waste disposal?
Lord ...
I certainly did not answer. He turned on the suction and tried to forget about the curious look of the reptiloid, who drilled his back. I hate these petty domestic problems.
"Stars - cold toys", S. Lukyanenko
I will return to the water and O2.
Today on the ISS is a partially closed system of water regeneration, and I will try to talk about the details (as far as I figured this out myself).

In accordance with GOST 28040-89 (I don’t even know if it still works) "The life support system of an astronaut in a manned spacecraft" - the LSS of the cosmonaut is "A collection of functionally interrelated means and measures intended to create conditions in the habitable compartment of a manned spacecraft providing maintaining the energy and mass transfer of the cosmonaut’s body with the environment at a level that is necessary to maintain its health and working capacity. ” The cosmonaut LSS includes the following systems:
* SOGS - gas supply system,
* CBO - water supply system,
* SSGO - system of sanitary and hygienic maintenance,
* SOP - power supply system,
* SOTR - system for ensuring thermal conditions.
You can be proud. Robyn Carrasquillo, ECLSS technical project manager:
“The Russians were ahead of us in this area, even the Salyut and Mir spacecraft were able to condense moisture from the air and used electrolysis — passing an electric current through water — to produce oxygen.”
How it all began (with us).
1. LIFE SUPPORT SYSTEMS IN THE HERMETIC CABINS OF STRATOSTATS, MISSILES AND THE FIRST ARTIFICIAL EARTH SATELLITES
The first human visit to the space beyond the Karman line in a spacecraft was preceded by launches of stratostats, rockets and artificial earth satellites, in which there were life support systems for people and animals (mostly for dogs).
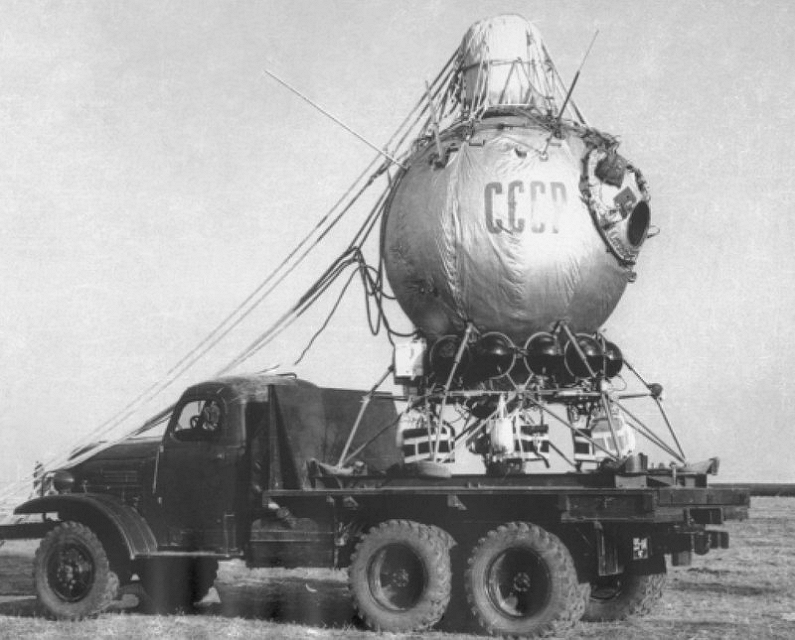

In the stratostatos "USSR-1" (1933) and "Osoaviakhim-1" (1934), life support systems included reserves of cryogenic and gaseous oxygen; the latter was in cylinders under a pressure of 150 atm. Carbon dioxide was removed with the help of KPI - chemical lime absorber in accordance with the reaction: Ca (OH) 2 + CO2 = Ca (CO2) + H2O
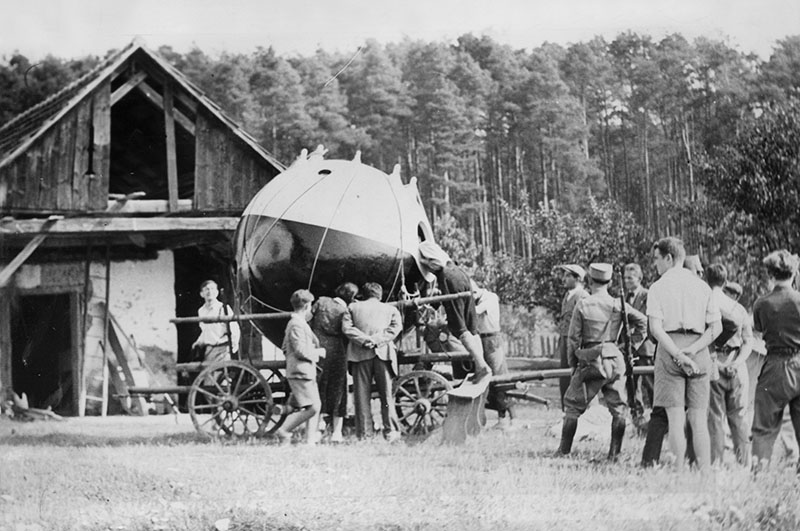

The composition of the KPI includes 95% Ca (OH) 2 and 5% asbestos.
In the rockets, with the help of which the near space was probed, there was an airtight cabin with animals, having in its composition three cylinders for a mixture of air and oxygen. Carbon dioxide emitted by the animals was removed with the help of KPI.
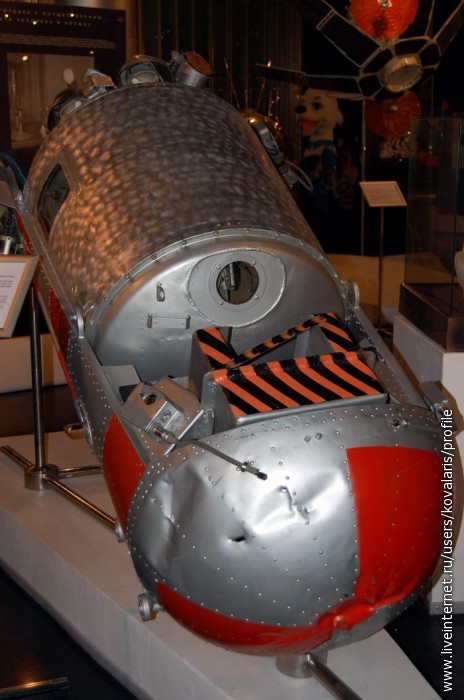

In the photo: Belka and Strelka star dogs capsule, in which they returned to Earth.
On board the first artificial earth satellites, the life support systems for dogs included some elements of future life-support systems for astronauts: a meal device, a cesspool device; purification of the atmosphere and the provision of oxygen was carried out using supraperoxide compounds, which, when absorbing carbon dioxide and water vapor, released oxygen in accordance with the reactions:
4KO2 + 2 H2O = 3O2 + 4 KOH
2KON + CO2 = K2 CO3 + H2O
K2 CO3 + H2O + CO2 = 2 KNSO3
2. LIFE SUPPORT SYSTEMS OF BIOLOGICAL SATELLITES OF THE EARTH OF THE TYPE “BION” AND “PHOTON”
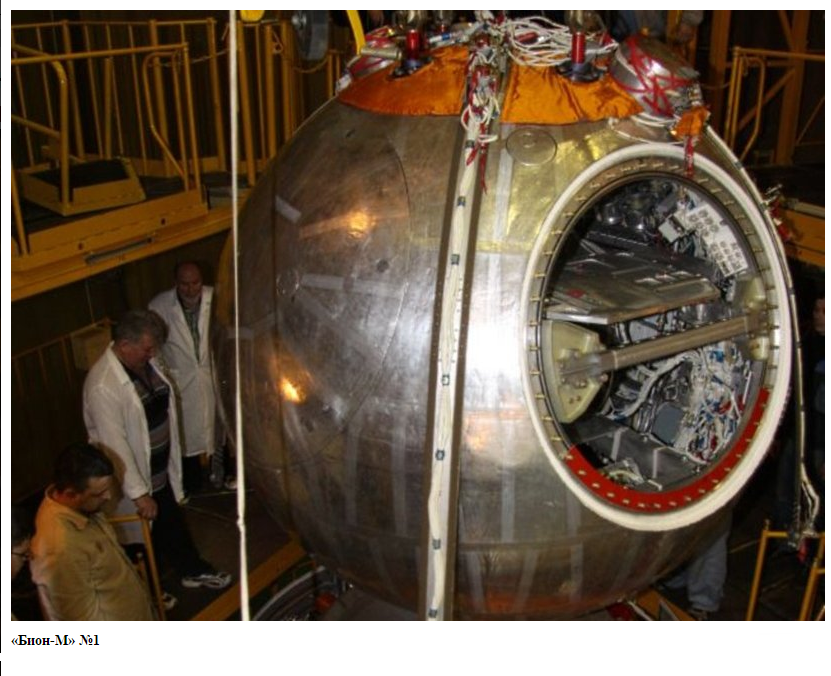
Biological satellites of the Earth - the automatic space vehicles "BION" and "PHOTON" are intended for studying the influence of space flight factors (weightlessness, radiation, etc.) on the animal organism. It is noteworthy that Russia is essentially the only country in the world that has automatic spacecraft for research on biological objects. Other countries are forced to send animals into space on our vehicles.

Over the years, the scientific leaders of the BION program were O.G. Gazenko and E.A. Ilyin. At present, the scientific director of the BION program is OI Orlov, alternates - E.A. Ilyin and E.N. Yarmanova.
The biological satellite "BION" is equipped with water supply and animal feeding systems, a thermal and moisture regulation system, a day-night system, a gas composition support system, etc.

The system for ensuring the gas composition of the automatic spacecraft "BION" and "PHOTON" is intended to provide animals with oxygen, remove carbon dioxide and gaseous trace impurities in the descent vehicle.
Composition:
- cartridges with an oxygen-containing substance and an absorber of harmful trace impurities;
- cartridge with carbon dioxide absorber and harmful trace impurities;
- electric fans;
- sensors for indicating the operability of the fans and the tightness of the gas paths;
- gas analyzer;
- control unit and control.
The system provides comfortable conditions in the gaseous environment of the descent vehicle (closed hermetic volume containing 4.0–4.5 m3 of air) and consists of three regenerative cartridges and an absorption cartridge with an electric fan for each cartridge, providing air regeneration for CO2, O2, CO and other harmful impurities. Turning on and off the microcompressors allows you to provide a given composition of the atmosphere of the object.
Principle of operation: the air of an object is pumped through a fan through a regenerative cartridge, where it is cleaned of CO2 and harmful impurities and enriched with oxygen.
Excess carbon dioxide is removed by periodically turning on the absorption cartridge. Absorption cartridge also provides cleaning from harmful impurities. The system works with a control and monitoring unit and a gas analyzer for oxygen and carbon dioxide. When the partial pressure of oxygen drops to 20.0 kPa, the first regenerative cartridge is activated.
If the oxygen partial pressure is greater than or equal to 20.8 kPa, the regenerative cartridge is switched off and switched on again at an oxygen partial pressure of 20.5 kPa. The inclusion of the second and subsequent cartridges occurs at a partial pressure of oxygen of 20.0 kPa (subject to a fall in concentration), and the previously included cartridges continue to work.
The absorption cartridge is switched on periodically with a partial pressure of carbon dioxide of 1.0 kPa; it is switched off at a partial pressure of carbon dioxide of 0.8 kPa, regardless of the operation of the regenerative cartridge.
3. SYSTEMS OF LIFE SUPPORT ON THE BASIS OF RESERVES FOR CREWS OF SPACE SHIPS OF TYPE “VOSTOK”, “VOSKHOD”, “SOYUZ”, “MERCURY”, “GEMINI”, “APOLLO”, “SHATTLE”, OGRETTE, OUR, OGRET, OGRET, OGRET, OUR, OGRET, OUR)
Life support systems for Soviet spacecraft of the Vostok, Voskhod, Soyuz types, as well as the American Mercury, Gemini, Apollon and the Shuttle transport ship, were fully based on stocks of consumable materials: oxygen, water, food, CO2 removal and harmful trace contaminants.
4. REGENERATION SYSTEMS OF LIFE SUPPORT ON THE BASIS OF PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROCESSES FOR CREWS OF ORBITAL SPACE SALUT, MIR, MKS
The operation of life support systems based on reserves of consumable substances taken from the Earth has a significant drawback: their weight and dimensions increase in direct proportion to the duration of the space mission and the number of crew members. Upon reaching a certain duration of the flight, the life-age system on the basis of reserves may be an obstacle to the implementation of the expedition.
The table shows the mass characteristics of LSS, based on stocks of consumable substances in relation to the expedition with a duration of 50, 100 and 500 days for a crew of 6 people:

Based on the consumption rates of the main components of the LSS, obtained as a result of long-term practice of long-term orbital flights at the SALUT, MIR and MKS stations (oxygen — 0.96 kg / person-day., Drinking water — 2.5 kg (man. days., food - 1.75 kg / person days., etc.), it is easy to calculate that the necessary mass reserves for the crew, consisting of 6 - and people in a 500-day flight without taking into account the tare weight and storage systems would be more than 58 tons (see tab.). In the case of life support systems based on supplies of consumables, it would be necessary to create storage systems for cosmonauts' vital products: feces, urine, condensate of atmospheric moisture, used sanitary and kitchen water, etc.
What is in fact difficult to implement or not at all possible (flight to Mars for example).
In 1967-1968, a unique annual medical-technical experiment was conducted at the Institute of Biomedical Problems of the Ministry of Health with the participation of three testers: G.A. Manovtsev, A.N. Bozhko and B.N. Ulybysheva. In the thermocamera experiment, which lasted 365 days, a biomedical and technical evaluation of a new complex of regenerative life-support systems took place.


The LSS of the ground-level laboratory complex included:
carbon dioxide removal system, atmospheric cleaning system from harmful trace impurities,
oxygen generation system, water recovery system from moisture-containing products of vital functions of testers, sanitary and hygienic equipment, greenhouse, system of instrumentation equipment.
Experimental regeneration life support systems based on physicochemical processes, tested in an annual medical and technical experiment, were the prototype of the standard LSS for crews of the Salyut, MIR and MKS orbital stations.
For the first time in the world practice of manned flights on the Salyut-4 space station, the CPB-K regeneration system operated — a system for obtaining drinking water from condensate by an atmosphere of moisture. The crew consisting of A. A. Gubarev and G. M. Grechko used the water regenerated in the “SRV-K” system for drinking and preparing food and drinks. The system operated during the entire manned flight of the station. Similar systems such as SRV-K operated at the Salyut-6, Salyut-7, and MIR stations.

Note 02.28.17: thanks for the help in editing and understanding the etymology of artyums
Retreat:
On February 20, 1986, the Soviet Mir space station entered orbit.

March 23, 2001, it was flooded in the Pacific Ocean.
Our station "Mir" flooded when she was 15 years old. Now the two Russian modules that are part of the ISS are already too 17. But no one is going to sink the ISS yet ...
The efficiency of the use of regeneration systems has been confirmed by the experience of many years of operation, for example, the MIR orbital station, on board of which the LSS subsystems successfully operated, such as:
SRV-K is a system for the regeneration of water from atmospheric moisture condensate,
"SRV-U" - the system of water recovery from urine (urine),
"SPK-U" - a system for receiving and preserving urine (urine),
Electron is an oxygen generation system based on water electrolysis,
Air is a carbon dioxide removal system
"BMP" - block removal of harmful trace impurities, etc.
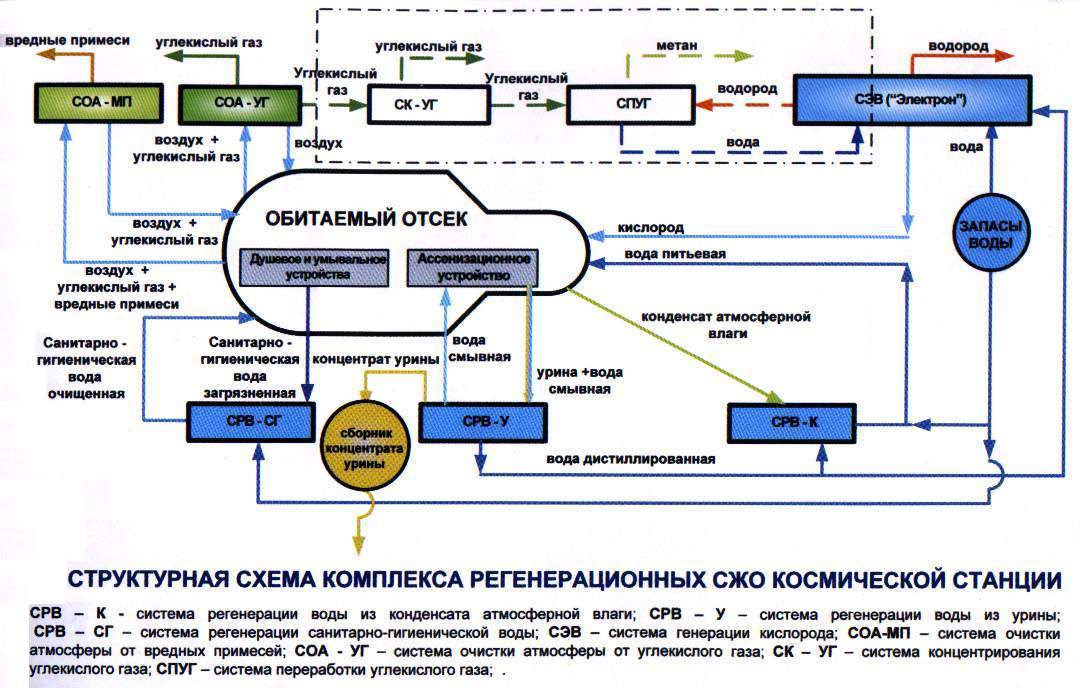
Similar regeneration systems (with the exception of the "SRV-U") are currently operating successfully on board the International Space Station (ISS).

The structure of the life support system (coolant-cutting fluid) of the ISS includes the gas composition support subsystem (SGS). Composition: means of controlling and regulating atmospheric pressure, means of pressure equalization, equipment for depressurization and pressurization of PSO, gas analysis equipment, system for removing harmful impurities from the BMP, system for removing carbon dioxide from the atmosphere “Air”, means for cleaning the atmosphere. An integral part of the SOGS is the oxygen supply means, including solid fuel oxygen sources (TIC) and the system for producing oxygen from Electron-VM water. At the start-up, there was only 120 kg of air and two solid-fuel TGK oxygen generators on board the SM.
→ Live online broadcast from webcam to ISS.
To deliver 30,000 liters of water on board the MIR and MKS orbital stations, it would be necessary to organize an additional 12 launches of the Progress transport ship, the payload of which is 2.5 tons. If we take into account the fact that the Progresses are equipped with spring water tanks of 420 l capacity, then the number of additional launches of the Progress transport ship would have increased several times.
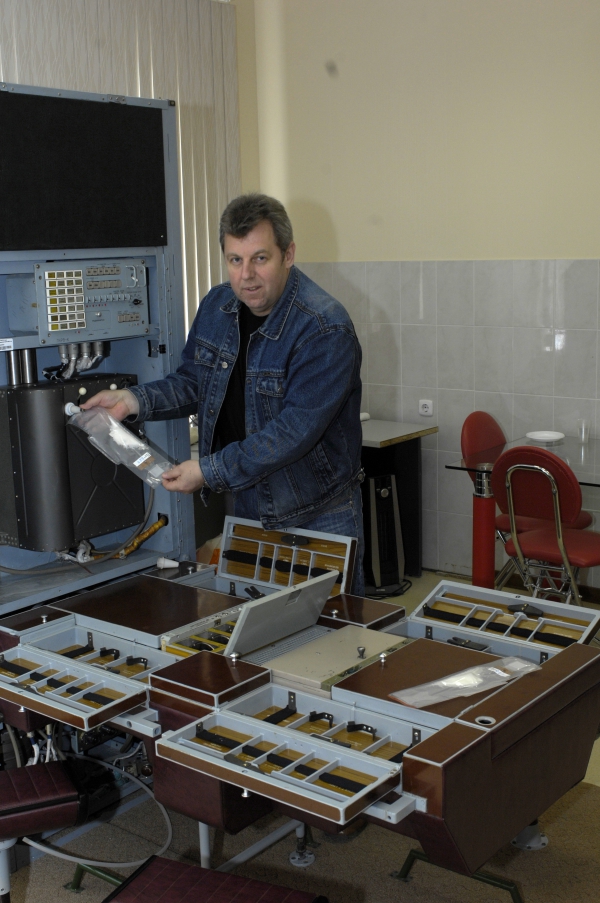


On the ISS, zeolite scavengers of the Air system capture carbon dioxide (CO2) and release it into the overboard space. The oxygen lost in the composition of CO2 is replenished due to the electrolysis of water (decomposition of it into hydrogen and oxygen). This is done on the ISS by the Electron system, which consumes 1 kg of water per person per day. Hydrogen is now being dumped overboard, but in the future it will help to convert CO2 into valuable water and methane emitted (CH4). And of course, just in case there are oxygen checkers and tanks on board.

In the photo: oxygen generator and simulator for running on the ISS, which failed in 2011.

In the photo: the astronauts are setting up a system for degassing liquids for biological experiments under microgravity conditions in the Destiny laboratory.

In the photo: Sergey Krikalev with the Electron water electrolysis device
Unfortunately, the full cycle of substances in orbital stations has not yet been achieved. At this level of technology using physicochemical methods it is not possible to carry out the synthesis of proteins, fats, carbohydrates and other biologically active substances. Therefore, carbon dioxide, hydrogen, moisture-containing and dense wastes of cosmonauts are removed into the vacuum of outer space.

The bathroom on the space station looks like this
In the service module of the ISS, the Air and BMP purification systems, advanced systems for the recovery of water from the SRB-K2M condensate and the Electron-VM oxygen generation, as well as the SPK-UM urine reception and preservation system are introduced and function. The productivity of advanced systems has been increased by more than 2 times (it provides the crew with up to 6 people), while energy and mass costs are reduced.
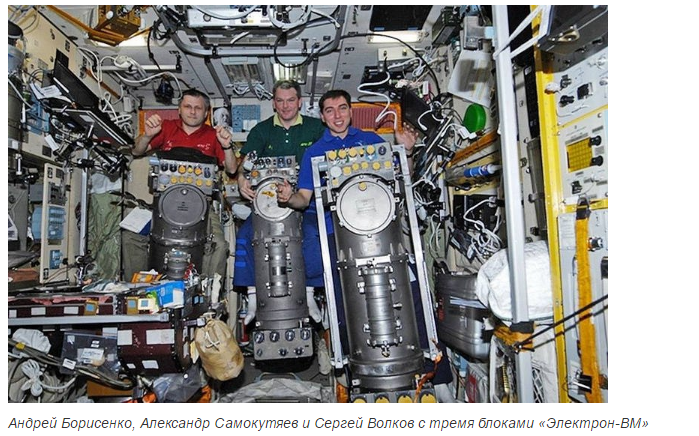

Over the five-year period (data for 2006) of their operation, 6.8 tons of water, 2.8 tons of oxygen were regenerated, which made it possible to reduce the mass of cargo delivered to the station by more than 11 tons.
The delay in the inclusion of the system for the recovery of water from urine CPB-UM into the LSS complex did not allow for the regeneration of 7 tons of water and reduce the mass of delivery.
"Second Front" - Americans
The process water from the American ECLSS apparatus is supplied to the Russian system and the American OGS (Oxygen Generation System), where it is then “processed” into oxygen.

The process of recovering water from urine is a difficult technical task: “Urine is much dirtier than water vapor ,” explains Carrascillo, “It is capable of corroding metal parts and littering pipes.” The ECLSS system uses a process called vapor compression distillation to cleanse urine: the urine is boiled until the water turns into steam. Steam - naturally purified water in the vapor state (with the exception of traces of ammonia and other gases) - rises into the distillation chamber, leaving concentrated brown mud of impurities and salts, which Carrascillo mercifully calls "brine" (which is then thrown into outer space). The steam is then cooled and the water is condensed. The distillate obtained is mixed with moisture condensed from the air and filtered to a state suitable for drinking. The ECLSS system is able to recover 100% of moisture from air and 85% of water from urine, which corresponds to a total efficiency of about 93%.
Described above, however, refers to the operation of the system in terrestrial conditions. An additional complexity appears in space - the steam does not rise up: it is not able to rise into the distillation chamber. Therefore, in the ECLSS model for the ISS, "... we rotate the distillation system to create artificial gravity to separate the pairs and the brine ," explains Carrascillo.
Perspectives:
Attempts to obtain synthetic carbohydrates from the cosmonauts vital activity products for the conditions of space expeditions are known according to the scheme:
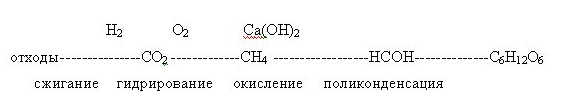
According to this scheme, waste products are burned to form carbon dioxide, from which methane is formed as a result of hydrogenation ( Sabatier reaction ). Methane can be transformed into formaldehyde, from which carbohydrate-monosaccharides are formed as a result of a polycondensation reaction ( Butlerov reaction ).
However, the obtained carbohydrate-monosaccharides were a mixture of racemates - tetrose, pentoses, hexoses, heptoses, which do not possess optical activity.
Note I'm even afraid to delve into the "wiki-knowledge" to understand their meaning.
Modern LSS, after their corresponding modernization, can be used as a basis for creating LSS necessary for the development of deep space.
The LSS complex will ensure almost complete reproduction of water and oxygen at the station and can be the basis of the LSS complexes for scheduled flights to Mars and the organization of a base on the Moon.




Much attention is paid to the creation of systems that provide the most complete circulation of substances. To this end, the process of carbonation hydrogenation by Sabatier or Bosch-Boudoir will most likely be used, which will allow the circulation of oxygen and water:
CO2 + 4H2 = CH4 + 2H2O
CO2 + 2H2 = C + 2H2O
In the case of an exobiological prohibition of the release of CH4 into the vacuum of outer space, methane can be transformed into formaldehyde and non-volatile monosaccharide carbohydrates by the following reactions:
CH4 + O2 = CH2O + H2O
polycondensation
n2 -? (CH2O) n
Ca (OH) 2
It should be noted that the sources of pollution of the environment at orbital stations and during long-term interplanetary flights are:
- interior construction materials (polymeric synthetic materials, varnishes, paints)
- man (with perspiration, transpiration, with intestinal gases, with sanitary and hygienic measures, medical examinations, etc.)
- working electronic equipment
- life support systems (ascenisation device-ACS , kitchen, sauna, shower)
and much more.
Obviously, the creation of an automatic system of operational control and management of habitat quality will be required. Some ASOKUKSO?
Oh, it was not for nothing that in Baumanka the specialty on LSS KA was called by students:
What was meant as:
F izne O bespechenii P ilotiruemyh A pparatov
I don’t remember the code, Department E4.

The end: maybe I did not take everything into account and confused facts, figures somewhere. Then supplement, correct and criticize.
An interesting publication pushed me into this “verbiage”: Vegetables for astronauts: how fresh greens are grown in NASA laboratories .
My younger son at school today started making a “research gang group” to grow Beijing salad in an old microwave. Probably decided to provide themselves with greenery when traveling to Mars. Old microwave will have to buy on AVITO, t. To. my while all function. Do not break it specifically?
Note in the photo, of course not my child, and not the future victim of the microwave experiment.
As I promised marks @ marks, if something comes out, pictures and the result will throw on the GIK. Grown lettuce can be sent by RF mail to those who wish, for a fee, of course.
Primary Sources:
, , .. () «
(, )» / 2008.
« » (http://livescience.ru)- .
«» (www.niichimmash.ru). «».
- « »
(, )» / 2008.
« » (http://livescience.ru)- .
«» (www.niichimmash.ru). «».
- « »
Used photos, videos and documents:
—
www.geektimes.ru/post/235877 ( @lozga)
www.gctc.ru
www.bezformata.ru
www.vesvks.ru
www.epizodsspace.no-ip.org
www.techcult.ru
www.membrana.ru
www.yaplakal.com
www..
www.fotostrana.ru
www.wikipedia.org
www.fishki.net
www.spb.kp.ru
www.nasa.gov
www.heroicrelics.org
www.marshallcenter.org
www.prostislav1.livejournal.com/70287.html
www.liveinternet.ru/users/carminaboo/post124427371
www.files.polkrf.ru
(www.bse.uaio.ru)
www.vokrugsveta.ru
www.geektimes.ru/post/235877 ( @lozga)
www.gctc.ru
www.bezformata.ru
www.vesvks.ru
www.epizodsspace.no-ip.org
www.techcult.ru
www.membrana.ru
www.yaplakal.com
www..
www.fotostrana.ru
www.wikipedia.org
www.fishki.net
www.spb.kp.ru
www.nasa.gov
www.heroicrelics.org
www.marshallcenter.org
www.prostislav1.livejournal.com/70287.html
www.liveinternet.ru/users/carminaboo/post124427371
www.files.polkrf.ru
(www.bse.uaio.ru)
www.vokrugsveta.ru
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/401893/
All Articles