Internet around the world - the countries with the fastest Internet in Europe

Romanian cat Pitzush, Instagram Star
The speed and availability of the Internet is associated not only with democratic freedoms and the development of high technologies in the country, but also with the general high standard of living of the society. And this is not by chance, because such Internet speed leaders as South Korea, Japan and Singapore only reinforce this stereotype. But everything becomes not so clear when faced with high rates in Europe. Stereotypes are crumbling, some social phenomena are completely logical, and the existence of fast Internet in a number of countries seems to be inexplicable.
Most of Western Europe (Germany, Italy, France, Ireland, Spain) shows average 4G LTE speeds of 20–30 Mbit / s, while Eastern European countries currently compete with Asian leaders. How have Eastern European countries managed to overtake the speed of the Internet Scandinavians, who have been leaders in Europe over the past few years? What are the reasons for such achievements? We will try to find the answer to this question.
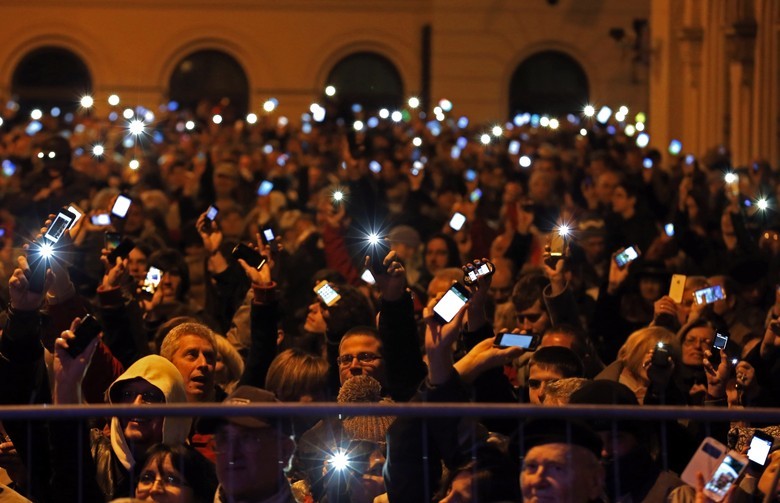
Hungarian protests for internet freedom
According to the OpenSignal report , the fastest mobile internet in Europe is Hungarian. Internet speed 4G LTE is 40.61 Mbit / s - the third place in the world. What is surprising, despite the increasing speed of the Internet every year, its availability is limited, and quite simple: with the help of price. Incomes are low, so this is quite an effective way to control traffic.
')
The national top-level domain .hu was registered in November 1990. By January 1, 2015, 656,185 domains were registered in the country.

A source
Little is known about the history of the Hungarian Internet. We know about the scandals associated with it. For example, in 2014, the Hungarian Prime Minister Viktor Orban proposed to impose a tax on the Internet, which would be charged on incoming traffic - for each gigabyte received. The fact is that people have become less likely to use the services of cellular operators for calls, switching to the Internet. Initially, the tax was explained as “good for the people”, but, after carefully weighing the consequences of its introduction, the residents predicted an increase in the cost of the Internet twice and took to the streets. For several days, Budapest was dominated by a crowd of many thousands opposing the tax. The protesters even threw the headquarters of the ruling party with details from old computers. As a result, the bill was withdrawn.
Phenomenon of the Romanian Internet

Romanian Cat Boss - PR manager of the local online store Catbox, a famous meme in Romania
Surely not everyone knows that for a long time Romania could boast the fastest internet in Europe until Hungary bypassed it (which is also quite unclear). The history of the phenomenon of the Romanian Internet originates in the nineties. The national top-level domain .ro was created in 1993. The state-owned company Romtelecom reigned in the provider market. The Internet was not very good, so local businessmen decided to create their own: high-speed and fiber-optic with overhead cables. As a result, Romania was one of the first countries to abandon the use of copper wires.
The technical revolution came there only in 2002; rather late, given that it swept around the world in 1989. But this did not prevent Romania from becoming a country with one of the most developed digital infrastructures. Now it ranks second in Europe and fourth in the world in terms of Internet speed 4G LTE (35.61 Mbit / s). For comparison, Russia is on the 58th place in this list (17.57 Mbit / s).
If the Internet is fast and cheap, then why did not Romania become a European startup center? The answer is simple - the country for this is still underdeveloped: poor financing of entrepreneurship, low purchasing power of citizens and big problems with infrastructure. But one can not fail to mention the advantages of Romania. Affordable Internet, good specialists (engineers and programmers) and low real estate prices can lead to the fact that the country will eventually become a European Silicon Valley.
Hackerville

It all sounds somehow too simple, even boring. But everything is simple only at first glance. In particular circles, Romania is associated with the city of Ramnicu Valcea, the European center of hackers. 120 thousand people live in it, and the locals call the only shopping center a “museum” (because it only comes to gaze, only fraudsters can buy something). In Ramnicu Valcea there was always a big shortage of work, but the spread of the Internet made it possible to find another way to get money - illegal.
The emergence of Internet cafes with cheap tariffs marked the beginning of hacking activities in the city. First of all, hackers mastered the basics: false advertising on eBay, which offered to purchase goods at a low price, transferring money to the scam accounts. Gradually, the small Romanian city became interested in the FBI, so it turned into Hackerville. According to the Romanian authorities, over the past ten years, hackers have “earned” more than 10 billion dollars. In 2014, they stole more than $ 1 billion — about 1/400 of the damage caused by Internet fraud in a year. But for Romania this is a lot of money. Separate groups of hackers can earn up to 50 thousand dollars a week.
And not even large hackers are sitting in the city, but small ones who steal credit card information, send bricks instead of smartphones to eBay customers, or create skimmers to remove credit card information from an ATM.

Marcel Lechel
But there are some special stars. Among them is the hacker Marcel Lechel under the pseudonym Guccifier. He became known for breaking into the mail of the sister of the former US President George W. Bush, Hillary Clinton, the Rockefeller family, and the general of the US Armed Forces, Colin Powell. True, the attacks on high-ranking and influential US citizens for Lechel are quite logical and “noble”: he, a conspiracy theorist, strongly believes that the Illuminati Mafia secretly controls society.
Bulgaria
The Internet in Bulgaria is widespread - more than half of the country's population have access to the Internet. In the global ranking, Bulgaria ranks sixth in the world and fourth in Europe for 4G LTE Internet speed - 34.26 Mbit / s. And all this is due to the fact that since 2009 at the state level the country has been actively promoting the National Strategy for the Development of Broadband Access.
The Bulgarian national top-level domain - .bg - was registered in 1991. The first commercial Internet provider (since 1991) is Digital Systems - Varna. He offered his services to subscribers via EUnet. The following year, e-mail became available in Bulgaria: the first public mail server was opened in the library of Varna, through which it was possible to send e-mails.
The law on electronic communications obliges Internet providers and cellular operators to keep data on traffic (date, hour, place, duration of communication) and on all communications of their subscribers for a year. By court decision, these data can be transferred to the State Agency of National Security, the Ministry of the Interior and the National Intelligence Service to search for persons and solve serious crimes: computer and those that involve five years in prison. Internet providers and mobile operators are not allowed to record information exchanged between subscribers without their personal consent.
The Netherlands is a technological gem of Europe
The Dutch are known to the whole world for their efforts in the introduction of technology in absolutely all areas of life. In the Netherlands, a lot of research is carried out related to the introduction of technologies in public transport, road infrastructure, the system of monitoring, planning and distribution of energy resources, etc.
Internet coverage in the country is very high: the second in Europe (after Lithuania) with an indicator of more than 82%, and the fifth in the world. In terms of speed 4G LTE, the seventh country in the world and fourth in Europe. One of the most important income items of the Netherlands is a start-up activity, because the state is interested in the continuous development of the technology industry. In December 2016, the Netherlands even sounded claims that high-speed Internet connection is a basic human need.
The manufacturability of the Netherlands is proved by the fact that in 2016 the country was the first in the world to successfully implement the Internet of things throughout its territory. KPN has stated that its LoRa Internet of Things network is now available everywhere. Previously, the network was used in test mode in Rotterdam and The Hague. What benefits did this implementation bring? For example, using the Internet of Things, Smartlog now controls the water level in the canals of Amsterdam. If the level is exceeded, the water discharge gates open automatically; This allows you to save from flooding many homes and shops of the city.
Another successful application of technology is the baggage tracking system at the large Schiphol airport. Instead of reading detailed descriptions it is better to watch the video how it works.
At the central station of the city of Utrecht, LoRa sensors are used to switch train hands. Sensors collect data on the position of the arrows and monitor everything that happens every second. Another successful example is the Mobilock project, which allows you to track bicycles in the city, minimizing the possibility of their theft.
Everyone knows that in the Netherlands they treat the environment with care and with particular love. Therefore, even waste disposal is automated with the help of the Internet of Things. Suez has equipped all types of waste with sensors and monitors their route from the collection site to the disposal site. This allows you to collect data on the load of services and reduce the cost of services, increasing the purity of the streets.
Conclusion
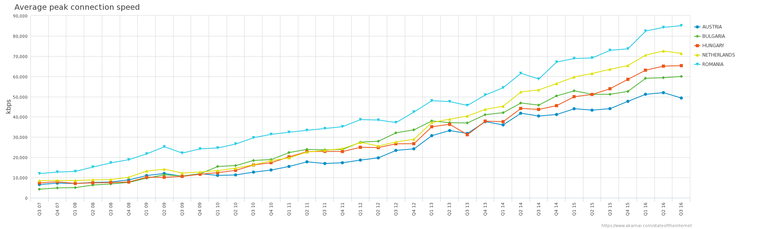
For completeness, the graphs below show the development of Internet penetration in the currently leading European countries and an increase in 4G LTE speed. Surprisingly, they are going quite evenly, even though the countries of Eastern Europe are very much inferior to their Western competitors in many ways: the development of the economy, the standard of living, the amount of investment, the freedom of the Internet and the transparency of the state. But this does not prevent them from rushing forward, very tightly competing even with the rich and very technological Scandinavians. Who knows, maybe very soon we will see these countries on a pedestal, and their example will be called the great miracle of Eastern Europe.

Past issues:
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/401799/
All Articles