LSD and its effect on the human brain. Some interesting facts

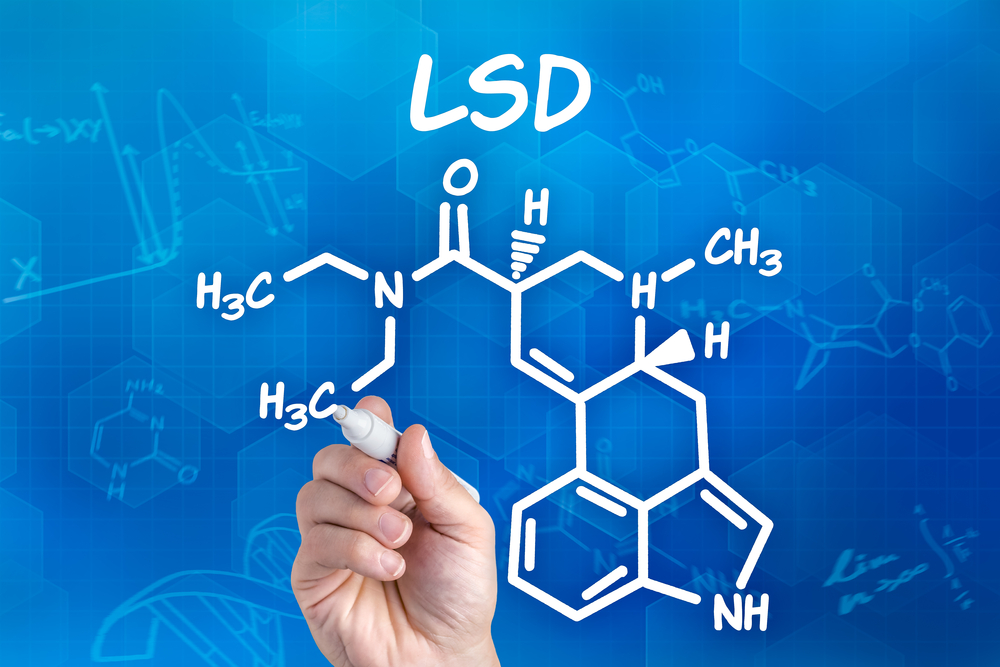
Probably, there are no such readers on Geektimes who would not hear about d-lysergic acid diethylamide (LSD). It was synthesized quite a long time ago, but the mechanism of influence on the consciousness is not fully revealed. True, recently the riddles of this chemical compound are gradually being revealed by man. In particular, scientists from the University of North Carolina have published information about the biochemical processes occurring in the human body after this compound enters, the chemical formula of which is C 20 H 25 N 3 O.
There are other works besides this one. For example, researchers who published an article on LSD in Current Biology studied the brain of volunteers who injected this substance for a long time. The brain of volunteers, scientists scanned with the help of MRI and other systems while listening to the test participants tunes that are important to them and tunes that they are indifferent. During the audition, the volunteers were influenced by psychedelics.
The results of such studies showed that LSD made a person susceptible to listening to music. The subjects began to consider interesting and important music, to which they were previously indifferent. In another study published in Cell , experts observed how a psychotropic drug interacts with certain brain receptors. As it turned out, LSD has a structural feature that binds a substance to the receptor for a long time, and this allows a person to be in a state of drug intoxication for many hours in a row.
')
The drug itself was discovered by chemist Albert Hofmann in 1938. Five years later, the scientist decided to check what effect LSD would have on him and took him inside. As it turned out, this connection almost completely changes the perception and mood of a person. Under the influence of psychedelics, people begin to experience, respectively, psychedelic experiences, which are called "trip". Such trips last for 6-15 (and sometimes longer) hours.
In America in the middle of the 20th century, a wave of enthusiasm for psychotropic substances and LSD, which greatly influenced the formation of the counterculture of the sixties and seventies, swept. The phrase of Dr. Leary, which turned into the motto of the use of psychedelics: “Turn on, tune in, drop out” (“Turn on, tune, drop out”) became widely known. The word dropout meant the departure from the conservative mores and way of life of the main part of society. Some researchers believe that the probable reason for the ban on LSD is the fright of conservative-minded societies and the government over the tendencies towards large-scale social changes that have arisen in the youth environment. The social and political realities of that time may have served as one of the reasons for banning LSD (the hippie movement developed at that time).
After it became clear that this is a psychedelic drug, the scientists decided that the substance could be used for medical purposes. But LSD quickly penetrated the masses, they were fond of young people and the substance was banned. True, despite the ban, experiments were conducted with him in many countries. In particular, this was done by the US military and the military of other countries.

The ratio of the possibility of becoming dependent on the ratio of the usual dose to the lethal dose of psychoactive substances
Despite the ban, now experts are conducting a large amount of research into the effects of LSD on the psyche and physiological state of people. Some of these studies are authorized by research institutes, and some are carried out at your own peril and risk. In particular, the psychedelic compound was given to people with so-called anxiety disorders, drug addiction or cluster headaches. This is quite a rare syndrome that causes very strong pain. Experts suggest LSD and psilocybin can not only reduce cluster pain, but in some cases interrupt the cluster cycle, and the syndrome is prevented in the future. Perhaps this is true, since many medications used to treat cluster pain include ergolins, which include LSD. This is confirmed by the results of a cluster pain patient survey conducted in 2006. True, only 53 patients with this syndrome who took LSD were interviewed. But almost all respondents reported that yes, the healing effect is positive.
Some scientists believe that LSD would be worth resolving for medical use. In particular, this was discussed in the publication of The British Journal of Psychiatry . Somewhat later, a similar problem was raised by the independent medical journal "The Lancet". A number of scientists believe that LSD should not be prohibited, because it has a significant therapeutic effect, it can be used to treat alcoholism, to soften migraines .
As for the physicochemical properties, the molecule of this chemical compound consists of an indole nucleus with an attached tetracyclic ring. The carbon atoms C-5 and C-8 in the molecule are asymmetric, and therefore the formation of 4 stereoisomers, of which only one - d-LSD - has psychoactive properties. LSD is relatively easy to dissolve in water.
This is a very active psychedelic, the estimated dose per person is millionths of a gram, and in other drugs the dosage is expressed in milligrams. The standard dose of LSD is in the range of 20 to 100 micrograms. Interestingly, LSD does not cause physical dependence, and also does not adversely affect the physical health of a person. However, it can in some cases cause or aggravate mental disorders.
The effects that the drug has on the person varies greatly depending on the characteristics of the organism and the psycho-physiological state. For example, there may be effects in which a person stops feeling the boundary between his own “I” and the outside world. In some cases, LSD leads to personality restructuring, and some experts believe that psychoactive substances can be very useful in psychotherapy. There is also a point of view that "the root of the therapeutic potential of LSD lies in its ability to induce a state of mind, in which positive self-esteem and rejection of selfish points of view easily occur."

Specialists managed to understand why a separate "trip" can last up to 10-15 hours. The fact is that when a psychedelic molecule enters the receptor, it closes there and cannot quickly exit. Over time, structural fluctuations lead to the fact that the molecules of LSD still leave the body, but this is a fairly long process.
A certain percentage of people taking LSD experience periods of spontaneous return of subjective symptoms (the so-called “flashback”, sometimes weeks, months, or years after ingestion. But the opinion that flashbacks are caused by the gradual accumulation of LSD in tissues is most likely erroneous — LSD is completely removed from the body within a few days. Scientists suggest that the cause of flashbacks may be in the ability of the human psyche to recall and relive super-strong emotional experiences and stresses (as denied both positive and positive) after some time after their occurrence under certain conditions, and since an LSD trip is an incredibly strong experience, a person can potentially recall and re-experience its details after a very long period of time.
In each person’s life, a similar “flashback” can occur, associated with long-past events from life and having no relation to psychedelics. A possible accelerator of the flashback can be listening to music that was previously heard during the LSD trip, viewing pictures similar to visual images that appeared in trip behind closed eyes, reading descriptions of similar experiences, taking other psychedelic substances and similar reasons.
During substance intake, the effect begins to appear when LSD binds to G-protein-coupled receptors. Serotonin receptors (5-HT2 family) also belong to this type of receptor. In particular, we are talking about receptors 5-HT2A and 5-HT2B. Their activation is closely related to such feelings and emotions as appetite, mood, perception of the world, libido, anxiety.
In one of the new studies, specialists decided to clarify the principle of the molecular mechanisms of interaction between psychedelic and serotonin receptors 5-HT2. To do this, scientists scanned using X-ray radiation crystals of a protein associated with LSD.
As it turned out, psychedelics and other ligands of serotonin receptors are conditionally divided into two functional groups. The first is ergolin, which consists of four rings and the second is diethylamide. The main role in the ligands belongs to ergolin. Moreover, despite the similarity, the effect of their reception is very different. For example, ergosterol relieves the pain of migraines. LSD - causes hallucinations. Perhaps this can be explained by the fact that the physiological barrier, which is called the hemato-encephalic, does not allow a number of ligands into the brain. For example, ergosterol is delayed by this barrier and does not cause hallucinations. Plus, a number of ligands interact in different ways with receptors. The same ergosterol goes deep into 5-HT2B a little deeper than LSD. And a lot depends on it.
What's next?
In general, most scientists who consider LSD effective in the fight against psycho-physiological disorders, alcoholism, cluster pains, consider it as a drug. At the same time, there is another group of scientists who believes that, having studied the effect of LSD, one can understand how various signal reactions are triggered that lead to one or another effect. The result is the possibility of developing synthetic drugs that can change the structure of the receptors, having a certain effect on the human brain.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/401265/
All Articles