Software AI learns how to do AI: scientists report on the progress in self-learning artificial intelligence
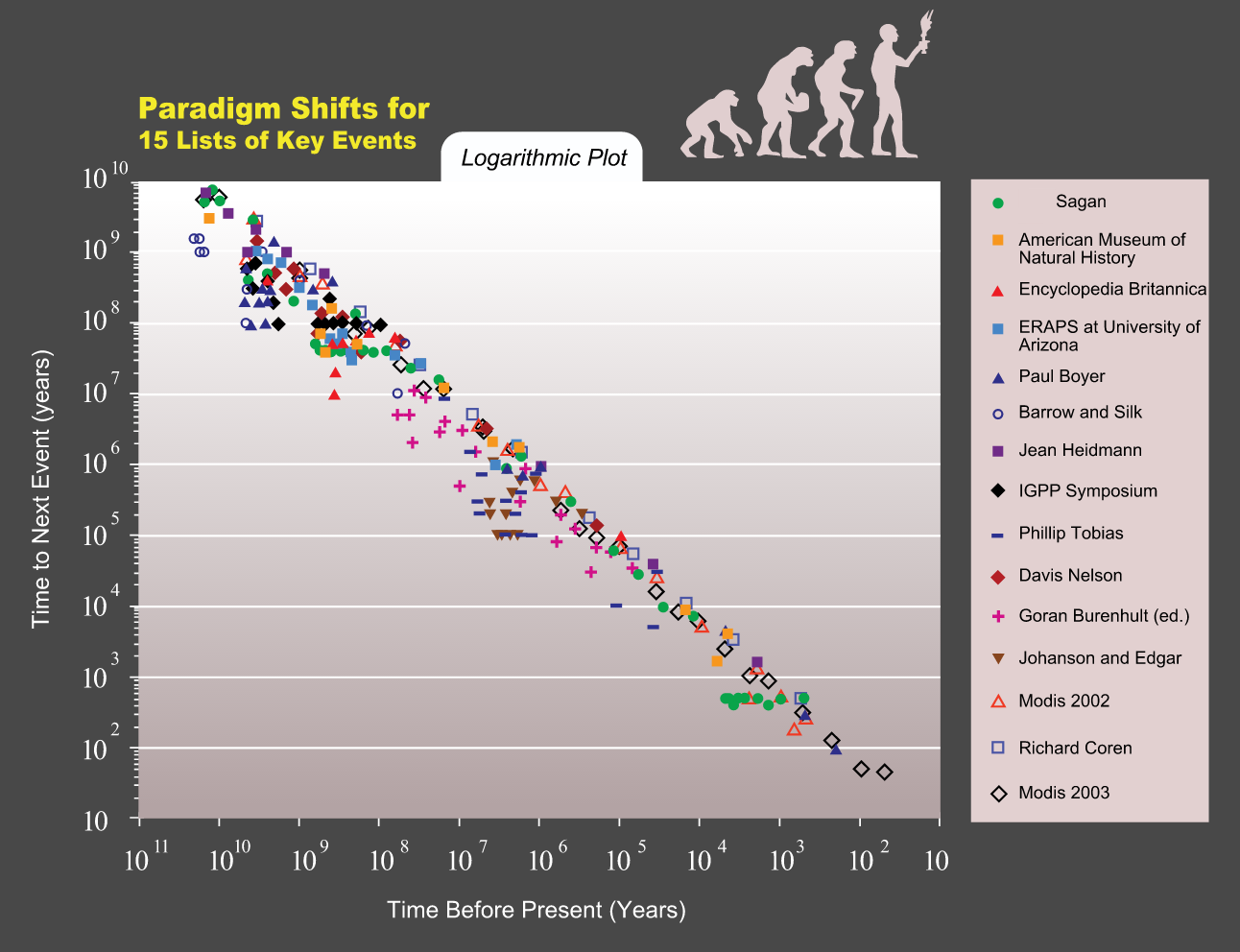
According to Kurzweil, the logarithmic paradigm shift scale for key historical events exhibits an exponential trend.
The key element for the emergence of technological singularity is the launch of an uncontrolled AI self-improvement cycle, where each new, smarter generation of AI will appear faster than the previous one. According to the theory of singularity according to Verner Vinge, as a result of the explosive development of the intellect , a superintelligence will appear in the cycle of exponential self-improvement, which will far exceed the capabilities of the human mind and in fact will be incomprehensible to it. Different approximate dates for the onset of a singularity are called, based on the extrapolation of technological progress. Ray Kurzweil believes that this will happen around 2045 (although he does not consider exponential self-improvement of AI necessary), and the average median value according to expert polls for strong AI is 2040.
It is possible that the singularity comes earlier than predicted. Engineers from Google and AI system developers from other companies report successes that have been achieved in a key area - the creation of AI systems designed to design other AI systems.
In one experiment, AI researchers from the Google Brain division developed a program that designed the neural architecture of a neural network so that it showed the highest possible results in speech recognition. The system designed by software method showed better results than human-created neural networks .
')
The publication of MIT Technology Review reports that in recent months several research teams have reported successes in creating AI systems for designing other AI systems, including from the nonprofit organization OpenAI (funded by Ilon Mask), the Massachusetts Institute of Technology , the University of California at Berkeley , and Google’s other artificial intelligence unit, DeepMind . Obviously, this area of research is considered one of the most promising, many want to succeed in it.
According to MIT Technology Review , such developments primarily have an economic goal. Creating a program for designing AI applications will significantly accelerate the use of such technologies in various sectors of the economy. Now, many companies cannot afford to implement an AI system, because there are no specialists with such competence in the state. Trite, AI experts are in great short supply. But neural networks can be used practically in a huge number of applications: in the automotive industry, in the banking sector, in telecommunications, in security systems and video surveillance, in a wide variety of consumer products for speech recognition and gestures, machine vision, etc.
The development of AI systems with software methods will allow replacing part of these deficient programmers.
It is also important that AI develops neural networks more efficient than humans, so the introduction of such programs makes sense even where live developers used to work.
Jeff Dean, head of the Google Brain research group, recently reasoned on this topic. In his speech at the AI Frontiers conference in Santa Clara (California), he suggested that some of these programmers can be replaced by software, because at the moment companies have to pay very high money and salary to these professionals, which are extremely scarce.
For example, DeepMind’s research article “ Learning to reinforcement learn ” from DeepMind describes a set of self-learning experiments for AI, which researchers call “deep meta-reinforcement learning”. The bottom line is to use standardized training with reinforcement of a closed-loop neural network so that this recurrent neural network develops its own external-free learning procedure with reinforcement for another recurrent neural network.
Experiments have shown that the second-order neural network, created by the efforts of the first neural network, in some cases demonstrates efficiency and qualities that the first-order neural network does not possess.
In total, seven such experiments are described in DeepMind’s scientific work. As usual, they spend them in the space of computer games. According to researchers, similar AI agents, created with the help of other AI programs, are able to quickly adapt to new tasks, using previously acquired knowledge on similar tasks. Experiments have also shown that the result of learning a second-order AI can be considered unpredictable: its architecture does not depend on the first-order AI architecture and can be very different from it. In particular, second-order AIs are able to use environmental features that were not known or which were not taken into account by the developers themselves.
DeepMind experts believe that their experiments with deep meta-learning with reinforcements are important in studying the human brain, in particular, they “provide an integrative framework for understanding the relevant roles of dopamine and the prefrontal cortex in biological reinforcement learning processes”.
The idea of self-study of AI was put forward earlier, but so far scientists have failed to demonstrate such impressive results. For example, one of the pioneers in this field, Professor Yoshua Bengio, said that such experiments require too much computing power, so until recently they had no practical meaning. For example, in the Google Brain experiments, 800 high-performance graphics processors were used to run software that designs an AI system for computer vision.
Researchers at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology are planning to publish the source code of the program, which was used in their experiments . Perhaps over time, the use of such tools will make economic sense and it will reduce the burden on professionals who develop models for data processing. Highly skilled programmers will be able to escape from coding and concentrate on ideas of a higher order.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/400965/
All Articles