Plasma in an oil well
Sometime in a geography lesson, I imagined that oil splashes in such underground lakes. And they mine it like this: they make a hole in the ground and it flows out. Later, I was surprised to learn that oil is often “squeezed out” of porous rocks enriched with hydrocarbons, and almost space technologies are used in oil production. Since the topic of oil production was recently discussed in the Experienced in the Kitchen podcast, in this article I would like to talk about one interesting technology in which you can artificially create ... a plasma in a well!
When a well is already producing oil, the flow from it will weaken over time. And it weakens for various reasons, including because of the so-called clogging. This is a complex process in which various phenomena take place to a greater or lesser degree: the formation of a mudcake on the walls of a well, the swelling of clay particles of a rock, the precipitation of chemical compounds, and the penetration of solid particles into a formation. How, then, to clean the pores? Workers cannot be blown into the well — the hole is too narrow, and the injection of chemical reagents does not always help well and can harm the environment. In addition, clearing the well, it would be desirable not to destroy the well itself. And in Russia, to all of the above, it is necessary to add severe climatic conditions for the work of personnel ...
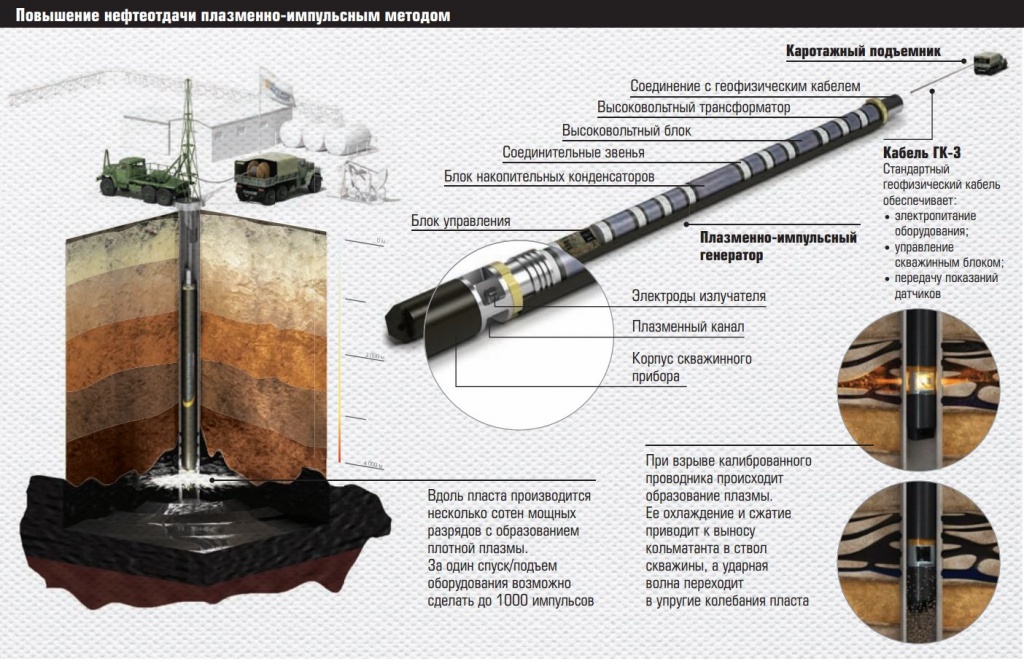
But in the mid-90s, an original method of well cleaning was invented - a plasma-pulse effect on the formation. Its essence is in an underwater spark discharge, in which shock waves occur, significant fluid movements, infrared and ultrasonic radiation, powerful electromagnetic fields (tens of thousands of oersted), as well as multiple ionization of the compounds and elements contained in the fluid, and the formation of low-temperature plasma with temperature to 4000 ° C. At the same time pressure reaches 1000 MPa.

Source: www.novas-energy.ru
')
How is such a discharge created and why such cosmic conditions do not destroy the well?
The process of plasma-pulse action occurs as follows: a cylindrical generator is lowered into the well, in a discharger of which there is a metal conductor. After that, so much current is passed through the conductor that the conductor instantly evaporates and turns into a plasma. Since the discharge occurs in water, an explosion takes place a chemical reaction of metallic vapor with water, and the current passes through the products of this reaction, which also explode. The result is a gas bubble. In these cases, the compression wave propagating in the liquid turns into a shock wave.
The expansion of the bubble occurs until the kinetic energy of the flow spreads completely into the potential energy of the bubble, the pressure of which is less than hydrostatic. Then, under the action of hydrostatic pressure, the reverse movement of the fluid occurs, the potential energy again passes into the kinetic energy of the converging flow. When the cavity collapses, the gas pressure in it sharply increases. Under the action of this pressure, the fluid is thrown back and the process is repeated in the form of subsequent damped pulsations. Virtually all of the energy in this case spreads horizontally, alternately compressing and stretching the medium, as a result of which the plugging gas is carried into the wellbore. Such horizontal pulses do not violate the integrity of the well, but they extend over long distances and can even increase production in neighboring wells.
Source: www.novas-energy.ru
The installation is a cylindrical case in which a high-frequency generator (creates a sequence of pulses), a high-voltage unit (creates high voltage), a storage capacitor unit, an instrument control unit, radiator electrodes and between them a plasma channel, and an electrode supply device to the plasma channel are sequentially located. To create a discharge using capacitors with a capacity of about 50 - 200 microfarads, charged up to 3,000 - 6,000 volts. Since a special cable (it still withstands high mechanical tensile loads) does not transfer more than 1 000 volts, then the capacitors and a voltage-raising transformer are located in the device itself, which requires the developers of devices with enchanting ingenuity.
It should be noted that the method was invented in Russia at the Mining University (St. Petersburg). So we are proud of the Russian engineers!
When a well is already producing oil, the flow from it will weaken over time. And it weakens for various reasons, including because of the so-called clogging. This is a complex process in which various phenomena take place to a greater or lesser degree: the formation of a mudcake on the walls of a well, the swelling of clay particles of a rock, the precipitation of chemical compounds, and the penetration of solid particles into a formation. How, then, to clean the pores? Workers cannot be blown into the well — the hole is too narrow, and the injection of chemical reagents does not always help well and can harm the environment. In addition, clearing the well, it would be desirable not to destroy the well itself. And in Russia, to all of the above, it is necessary to add severe climatic conditions for the work of personnel ...
But in the mid-90s, an original method of well cleaning was invented - a plasma-pulse effect on the formation. Its essence is in an underwater spark discharge, in which shock waves occur, significant fluid movements, infrared and ultrasonic radiation, powerful electromagnetic fields (tens of thousands of oersted), as well as multiple ionization of the compounds and elements contained in the fluid, and the formation of low-temperature plasma with temperature to 4000 ° C. At the same time pressure reaches 1000 MPa.

Source: www.novas-energy.ru
')
How is such a discharge created and why such cosmic conditions do not destroy the well?
The process of plasma-pulse action occurs as follows: a cylindrical generator is lowered into the well, in a discharger of which there is a metal conductor. After that, so much current is passed through the conductor that the conductor instantly evaporates and turns into a plasma. Since the discharge occurs in water, an explosion takes place a chemical reaction of metallic vapor with water, and the current passes through the products of this reaction, which also explode. The result is a gas bubble. In these cases, the compression wave propagating in the liquid turns into a shock wave.
The expansion of the bubble occurs until the kinetic energy of the flow spreads completely into the potential energy of the bubble, the pressure of which is less than hydrostatic. Then, under the action of hydrostatic pressure, the reverse movement of the fluid occurs, the potential energy again passes into the kinetic energy of the converging flow. When the cavity collapses, the gas pressure in it sharply increases. Under the action of this pressure, the fluid is thrown back and the process is repeated in the form of subsequent damped pulsations. Virtually all of the energy in this case spreads horizontally, alternately compressing and stretching the medium, as a result of which the plugging gas is carried into the wellbore. Such horizontal pulses do not violate the integrity of the well, but they extend over long distances and can even increase production in neighboring wells.

Source: www.novas-energy.ru
The installation is a cylindrical case in which a high-frequency generator (creates a sequence of pulses), a high-voltage unit (creates high voltage), a storage capacitor unit, an instrument control unit, radiator electrodes and between them a plasma channel, and an electrode supply device to the plasma channel are sequentially located. To create a discharge using capacitors with a capacity of about 50 - 200 microfarads, charged up to 3,000 - 6,000 volts. Since a special cable (it still withstands high mechanical tensile loads) does not transfer more than 1 000 volts, then the capacitors and a voltage-raising transformer are located in the device itself, which requires the developers of devices with enchanting ingenuity.
It should be noted that the method was invented in Russia at the Mining University (St. Petersburg). So we are proud of the Russian engineers!
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/400901/
All Articles