Internet around the world: Korean Peninsula
South Korea today is associated with high technology, high-quality medicine, a high human development index and one of the strongest economies. And her neighbor, North Korea, is firmly connected with the Juche ideology, repression, poor quality of life, undernourishment of the population and the cult of personality. But still, high technologies have not bypassed the most closed country in the world. We decided to compare how in these kindred countries things are with such an important resource in the modern world - the Internet.
Echo of War
Until 1945, North and South Korea did not exist - there was a single state of Korea that occupied the entire Korean Peninsula. From 1910 to 1945, it was part of the Japanese Empire, and after Japan’s capitulation, the territory of Korea was divided into Soviet and American zones of influence. In 1948, the creation of two states was proclaimed - the Republic of Korea (South) and the Democratic People’s Republic of Korea (North). In 1950, a war broke out between them, which went down in history as the Korean. Three years later, a cease-fire agreement was signed, which ended hostilities. But technically both Koreas are still in a state of war.

')
All these events were reflected in further, completely different ways of development of the countries. They are similar only in one thing - in warming up hostility towards each other in order to be ready to repel the blow of the enemy at any moment. This vector is very clearly seen in the history of the development of the Internet in both South and North Korea.
The fastest internet in the world
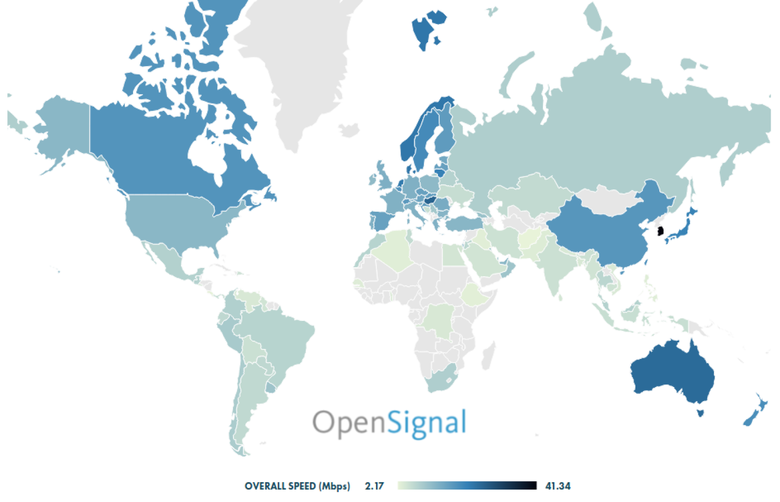
According to the report of the British company Opensignal, in South Korea today is the highest average mobile Internet speed - 41.3 Mbit / s. Then Singapore (31.19) and Hungary (26.15) are far behind. South Korea also has the best 3G / 4GA signal. At the same time, the country ranked third in terms of Wi-Fi usage by the population.
A brief history of the development of the Internet in South Korea
The first Korean Internet system SDN appeared quite a long time ago - May 15, 1982: a computer at the Computer Science Department of Seoul National University was connected to another computer at the Korean Electronic Technology Institute (KIET) at Gumi via a 1200-bit dedicated line. In 1983, SDN was connected to various networks in Asia as well as North America (HPLABS and Seismo in the USA, CDNNET in Canada) and Europe (MCVAX in the Netherlands). The network linking Asian countries was called ASIANNET. It included: Australia, Indonesia, Japan, Korea and Singapore.

In July 1986, the first IP address (128.134.0.0) was assigned to South Korea. At the same time, the national top-level domain, .kr, was formally submitted. In 1989, the University of Hawaii became the focal point for the PACCOM (Pacific Communications Networking Project) project, connecting Australia, Hawaii, Japan, South Korea and New Zealand. This is how the HANAnet network appears, and the SDN is no longer used since 1993. In the 1990s, the World Wide Web began to spread rapidly. In 1993, the first cair.kaist.ac.kr website was created in South Korea, hosted at the Center for Artificial Intelligence Research (CAIR) at KAIST.
Until the late 1990s, South Korean users had a maximum Internet speed of about 64 Kbps. In 1998, Thrunet began providing broadband Internet services at a speed of 1 Mbit / s. In 2004, the number of home users with broadband access exceeded 11 million (more than 70% of households). High availability of broadband Internet allowed Korea to become one of the foremost Internet nations. This led to the development of telecommunication technologies and online commerce. For example, the first Internet cafe appeared in Seoul in 1995, and already after 4 years their number reached 15 150. In turn, this affected the growth of popularity of online games.
But the rapid development of the Internet quickly appeared a lot of negative consequences. In 1995, the Center for Internet Addiction was established, which is still functioning. Today, South Korea leads the number of Internet dependent people. The magnitude of the problem is such that Internet addiction is considered a clinical disease, and the number of rehabilitation centers is increasing every year.
In order to prevent Internet addiction in adolescents, access to game servers is restricted by law from midnight to six in the morning for people under 16 years of age. Players must enter their ID numbers to gain access.
Netizenes
Since the beginning of the 1990s, the Netizenes ( Setyans ) movement has emerged , which has begun to actively defend certain political and social views. Anonymity and easy access to the network prompted people to be more relaxed and socially active. The Netizens very quickly react to acute social and political situations in the country, involving more and more people into their ranks and creating popular network power. In particular, the Netizens influenced the announcement of impeachment of South Korean President Park Geun-hye.
Nationwide Internet of Things
In 2016, the country launched the second in the world (after the Netherlands) nationwide Internet of Things . The network is based on the LoRaWAN (Long Range Wide Area Network) technology, which provides significant energy savings. First of all, the network will integrate the equipment in the utility organizations and in the homes of their clients. As a result, it will be possible to remotely take meter readings and connect and disconnect services.
Ban on cheating
South Korea is famous not only for its advanced technologies, but also for its rather tough laws. In 2016, Parliament adopted amendments to the law on the promotion of the gaming industry: for the production and distribution of cheat programs you can go to prison for 5 years or pay a fine of $ 43 thousand. And since the majority of cheat programs in the world are being created in South Korea, the new law can make life easier for all honest players.
Censorship
Despite the status of a country that is at the forefront of high technology, South Korea became the first state to pass a law on Internet censorship. This happened in 1995, and in 2002 the powers of the supervisory authorities were expanded.
Today in South Korea one can get a jail for saying the approval of some opposition rally, or sympathy with North Korea, on the Internet. First of all, all information about North Korea (DPRK) is subject to censorship, and opinions that are different from the official are not allowed. Also in South Korea blocked the news resources of the DPRK.
North Korea
North Korea's own national domain appeared only in 2007 - .kp. Prior to this, government sites, which were counted on the fingers, were hosted in China, Japan, Germany and the USA.
I must say that the DPRK knowingly bears the title of "the most closed country in the world." All computers that fall or are assembled in North Korea are put on state records. Wireless networks are prohibited in the country (mobile Internet is allowed only for embassies and foreign companies) and the sale of laptops (“for the sake of state security”).
The only main channel connecting the DPRK to the Internet is in the capital, Pyongyang. Access to the network is available only from some organizations that have received official permission. First of all, it is the party apparatus, the Foreign Ministry, several scientific institutions and enterprises engaged in foreign economic activity. Moreover, the head of state personally - Kim Jong-un - confirms the list of those who are allowed access to the Internet. But even if an organization has received permission, only a select person is allowed access to the network within it.
However, North Korea also has its own internal national network, Gwangmyeong . It is mainly used for e-mail and the operation of internal sites that are subject to total censorship. Most sites belong to the propaganda and scientific and technical areas. There is information that Gwangmyeong is available to ordinary Koreans today.
A curious touch: on all official sites a script is used that checks for the presence of the name Kim Jong-un in the text and slightly increases its font.
But even under total control, the North Koreans manage to somehow get information from the outside world. True, all the tricks work only in areas bordering with China and South Korea. For example, flashballs tied to balloons sometimes fly from a related country, on which South Koreans record entertainment content or news information. A few kilometers from the Chinese border, daredevils are calling on smuggled mobile phones. It is rumored that a call with a duration of more than two minutes is very dangerous for the intruder, since the risk that the signal is intercepted and the source is greatly increased.
Nevertheless, experts note that with the coming to power of Kim Jong-un, North Koreans are getting more and more indulgence in various spheres of life, including access to high technology and the Internet. Perhaps in a couple of decades, the heir to the DPRK will make the DPRK a sufficiently open country, so that its inhabitants have at least a quarter of the network freedoms available today to the people of China. Our next article will be devoted to the Chinese Internet. Do not switch!
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/400815/
All Articles