Vision correction equipment
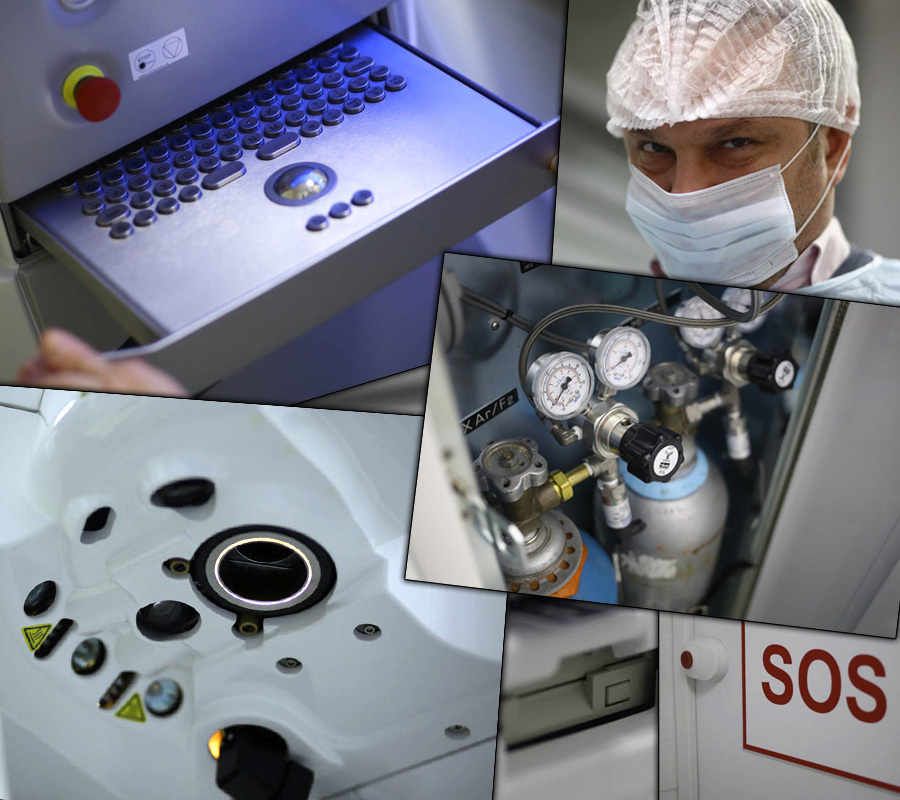

This is a photo excursion , then there will be 70 photos from two operating units for laser vision correction.
Different options for expander:
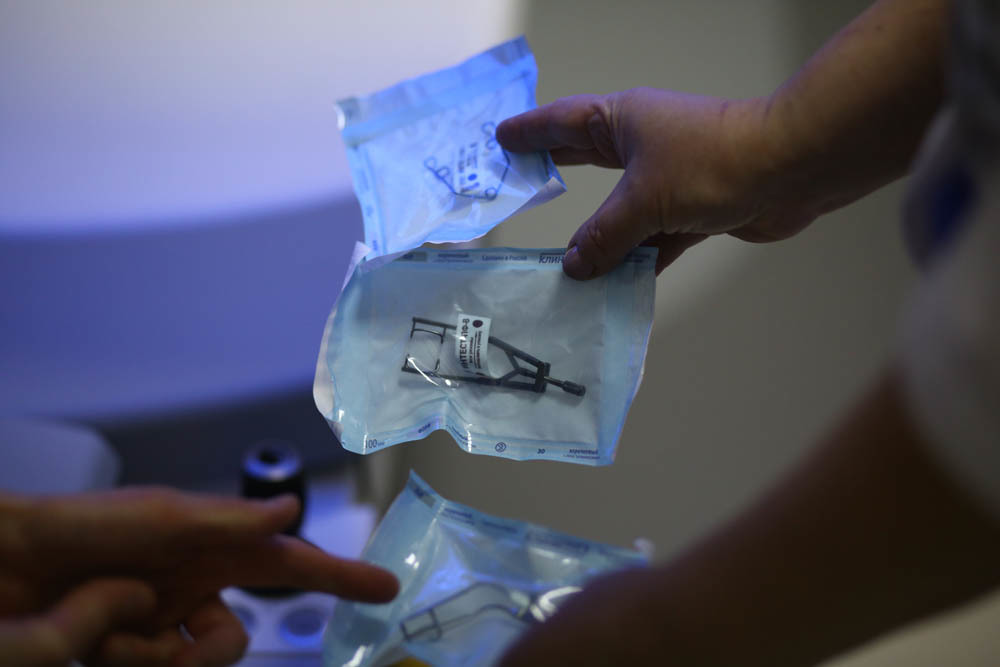
')

Packaging with a disposable blade, which is charged in microkeratome to form a valve in the cornea during mechanical (non-laser) operations:

But the microkeratome head, where the blade is inserted:
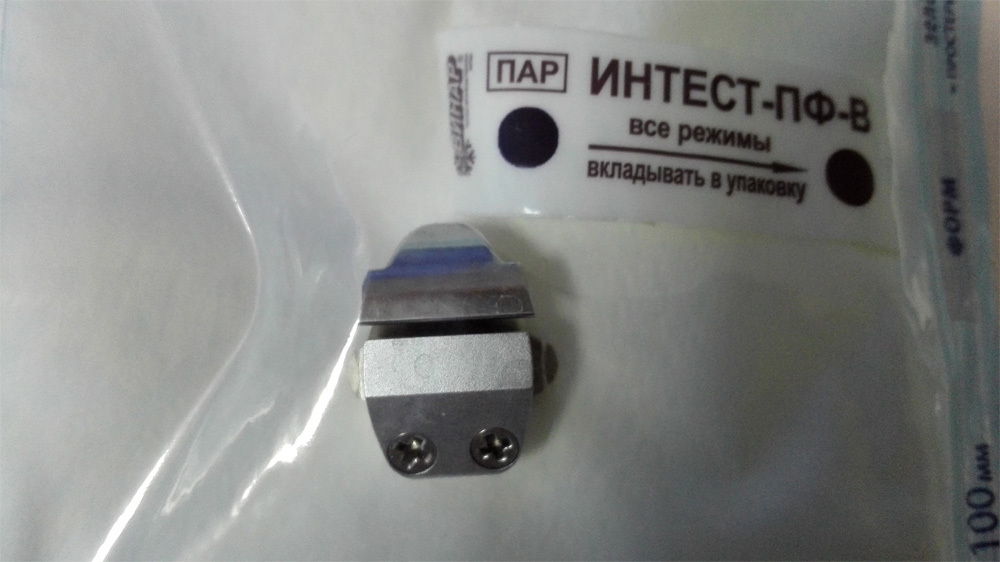

Here is a set of "accessories" for the working part - it is reusable:
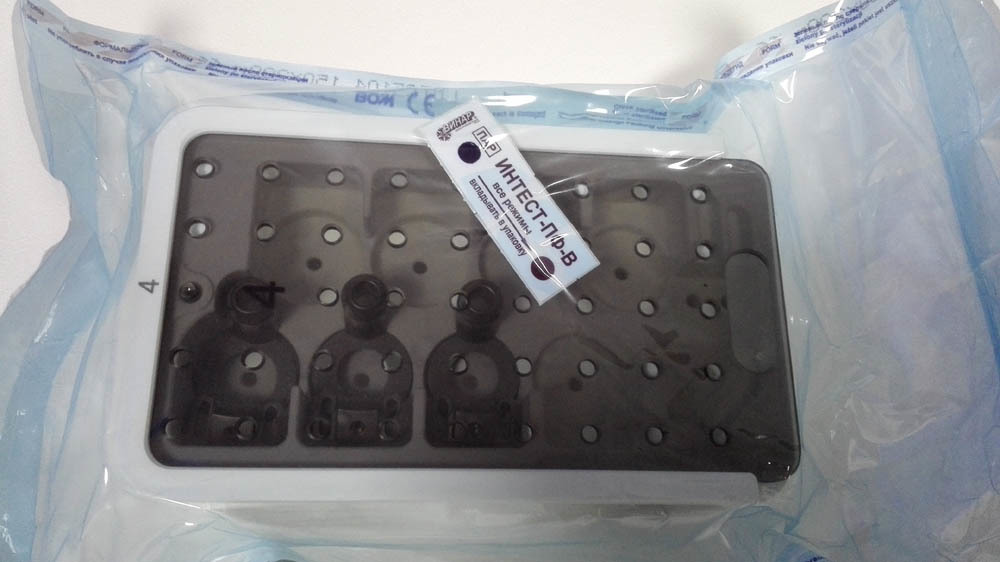


Motor for driving the head with the blade:

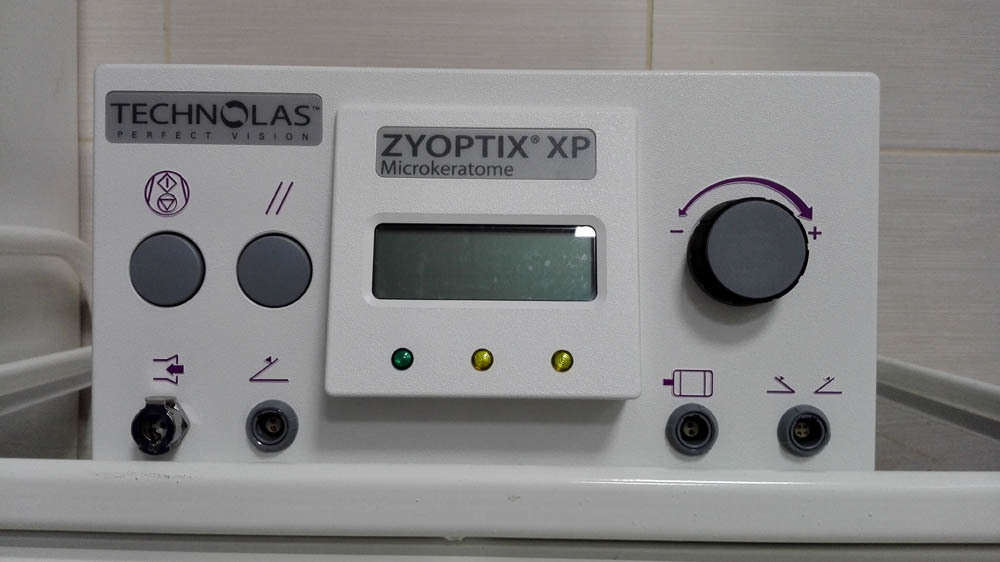
And this is a console with an indicator of operation parameters:

Now compare with the tools for SMILE. This is what disposable packaging with a cone looks like, in the same place - a vacuum tube for the removal of gas:
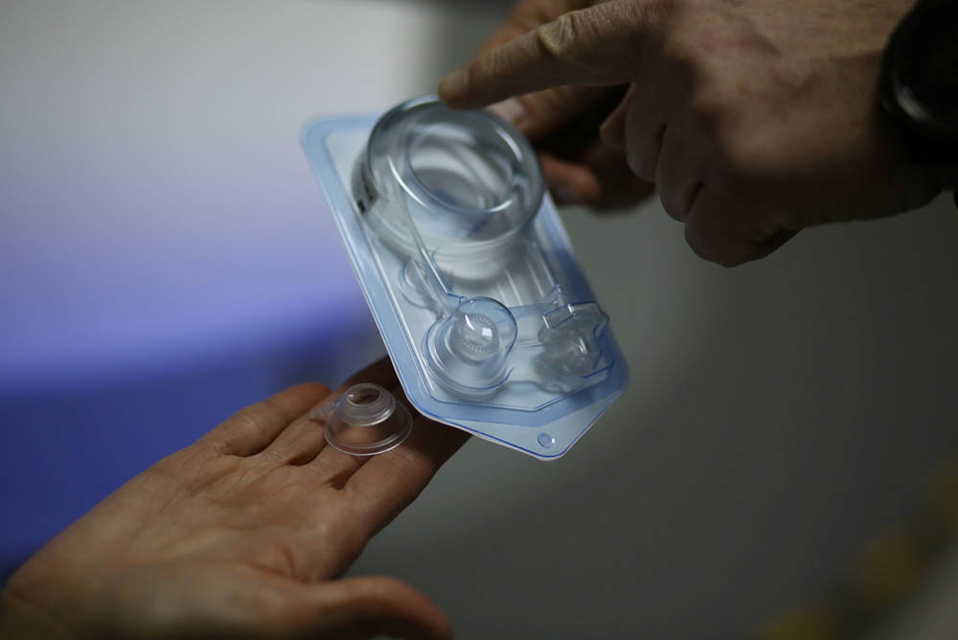
Spatula for separation to scale:
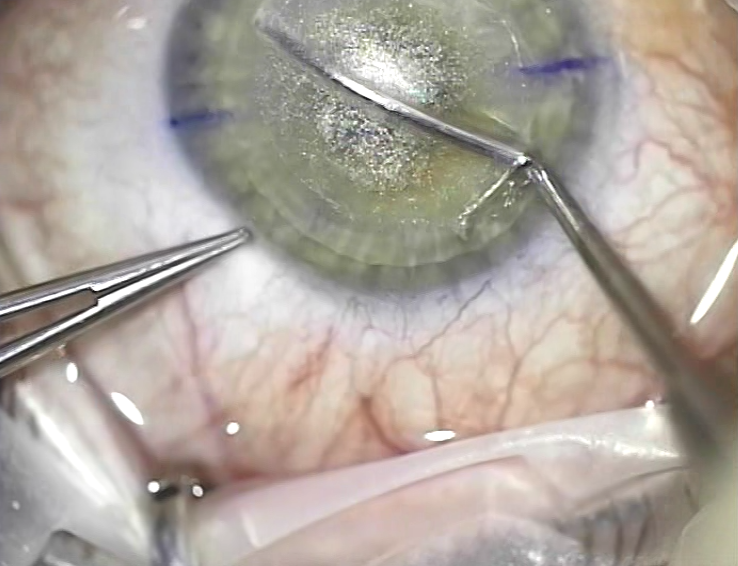
The very first spatula was made by Dr. Bloom, who, together with Walter Secundo, invented the technology. Today they do not use it, because it was spiny, because then they were cutting at other frequencies, there were no modern lasers. Now the cut is much cleaner, and there are already about 10 different modifications of tools. The most popular is according to Chansu (this is a Thai surgeon who performs a wild number of operations, 8 or 10 thousand one per year, he has a “conveyor” type clinic in Bangkok). There are interesting Russian ones, in particular, Kostin's spatula from Yekaterinburg. There is no huge difference between them. Walter enjoys just like the photo, this is his author’s model just under his arm. Let me remind you that this is what it looks like (in the photo below during the operation, the Chansu spatula):
Micro-sponges from hydrophilic material that frightened someone in the second post (these are not blades):

What the patient takes home after correction:
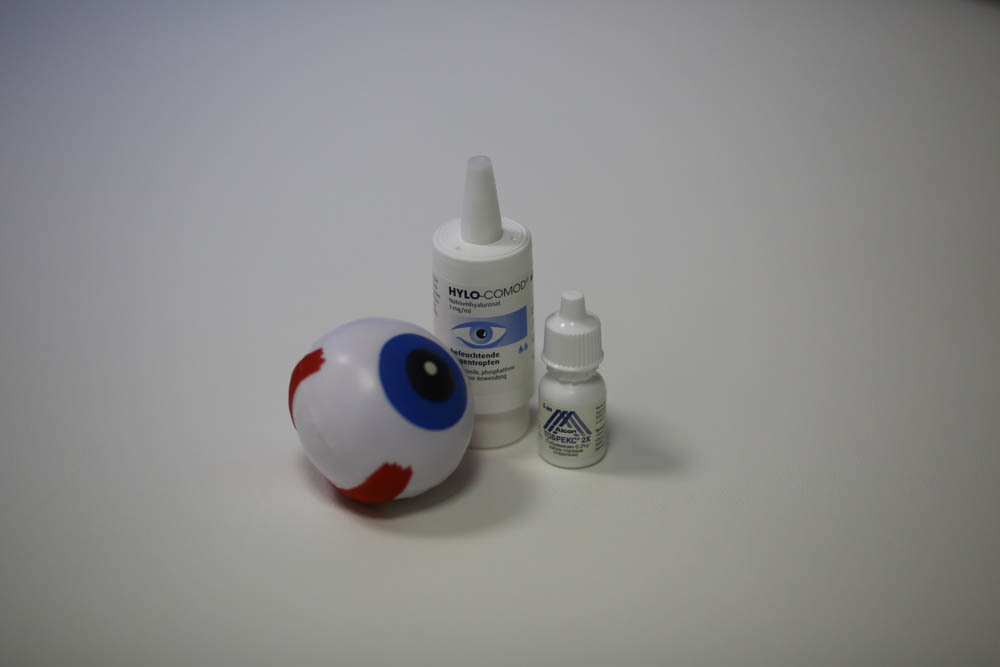
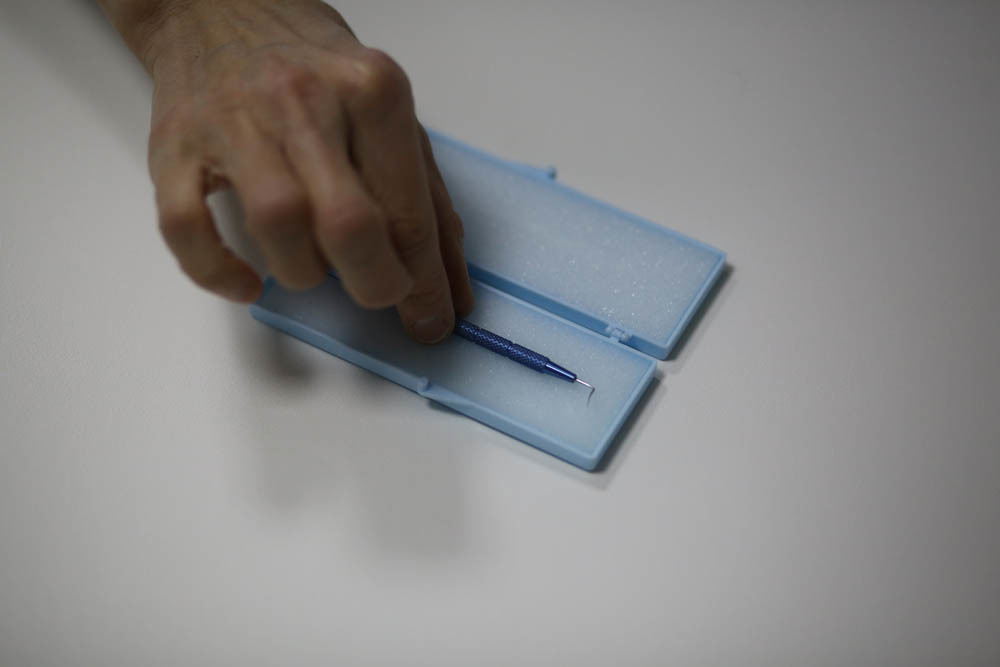
Here is a disposable scalpel for the cornea, which is practically not needed (its functions are performed by a laser):

For the patient, everything begins after a corridor with such a bed. Here the patient lies a little before the correction (to calm the motility) and rests a couple of hours after.
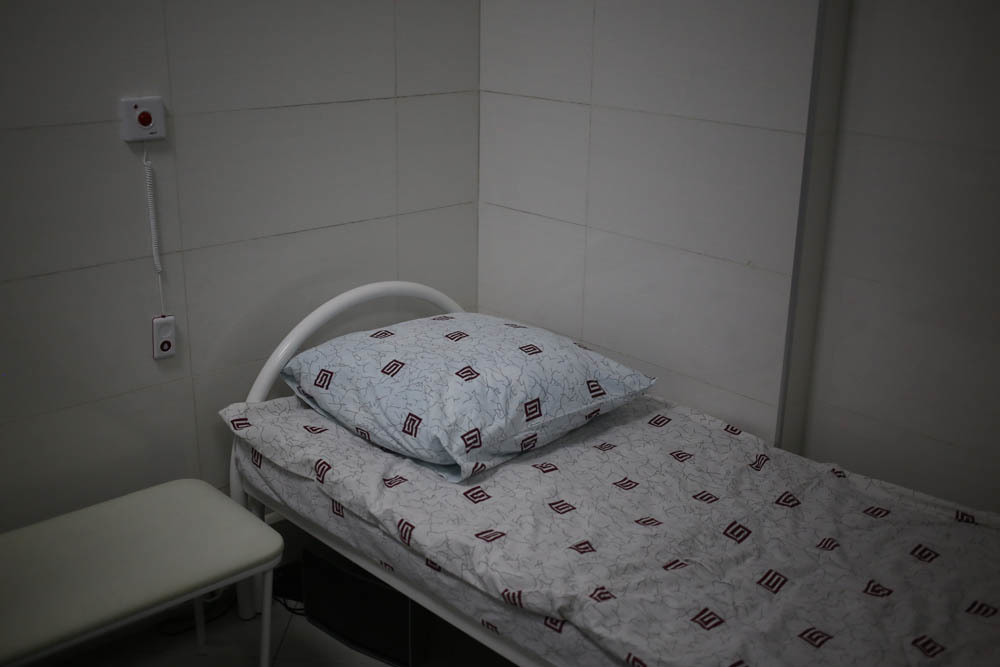

On the wall are two buttons: call sister and SOS. SOS includes an alarm in all rooms, except for other operating rooms.

On the wall for viewing pictures:

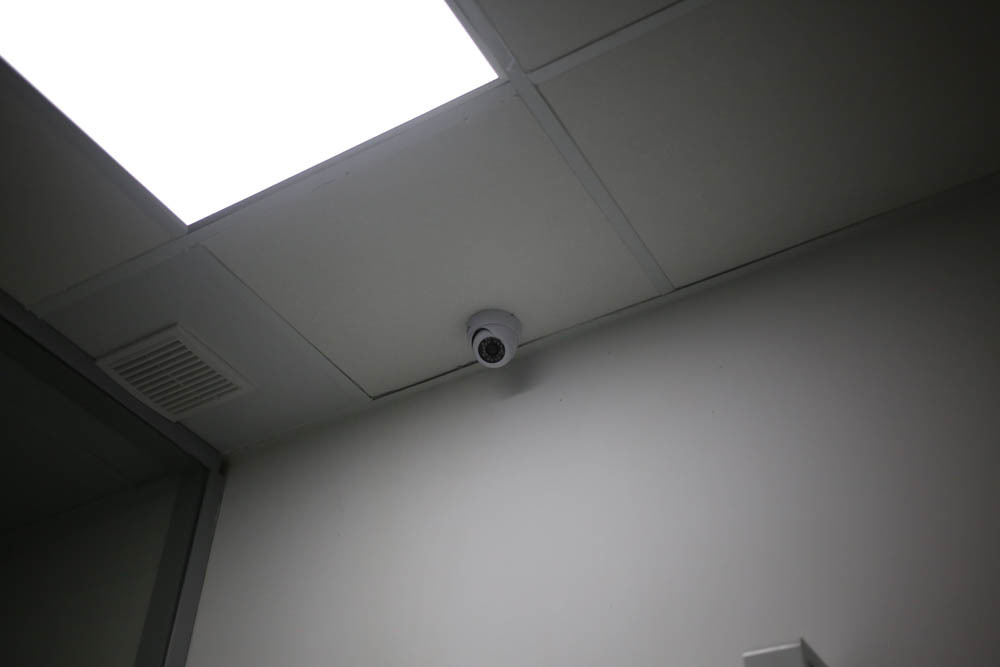
There is a video camera monitoring the patient in the ward. The image is broadcast on the post of a nurse, so that we always know what is happening with the patient. It is especially needed for those long operations, after which the patient wakes up after anesthesia is not quite in a normal state of consciousness.

The first operating room with an excimer laser:

The couch (more precisely, the operating table, it is also a smart bed):

Excimer laser:

He is the "face" of the patient (this part is located under a microscope):
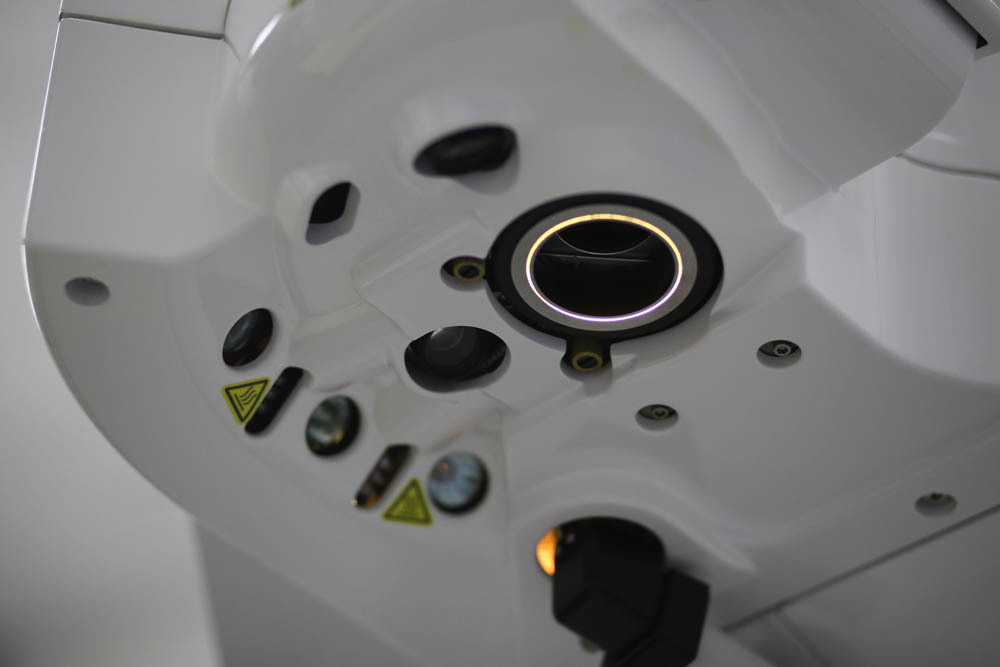

This is how the laser is visible to the surgeon:
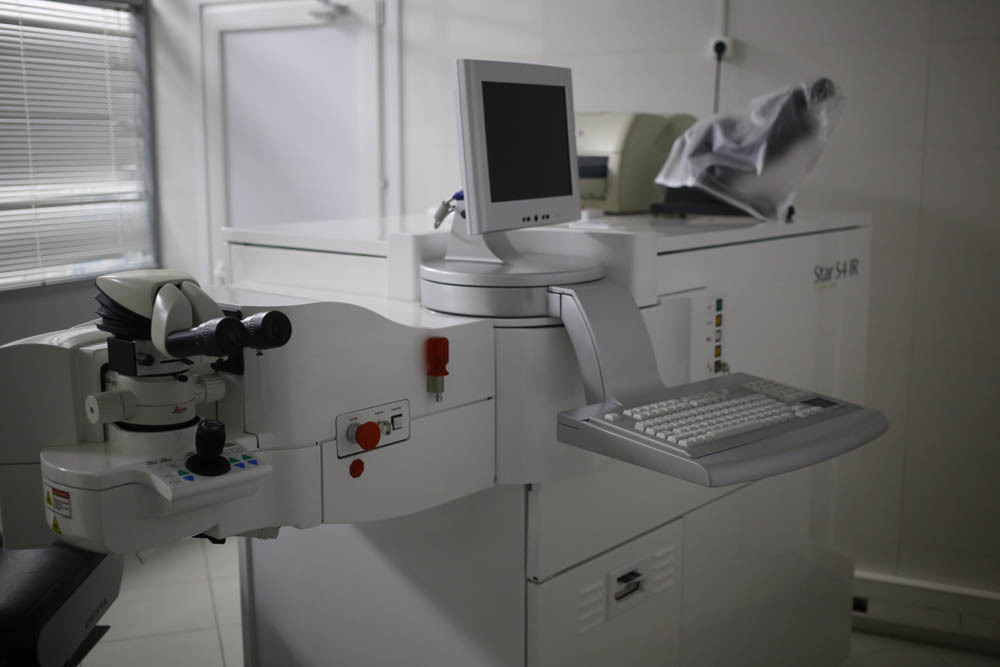

In this microscope is monitored. The data is also displayed for the assistant on the screen on the operating room wall.
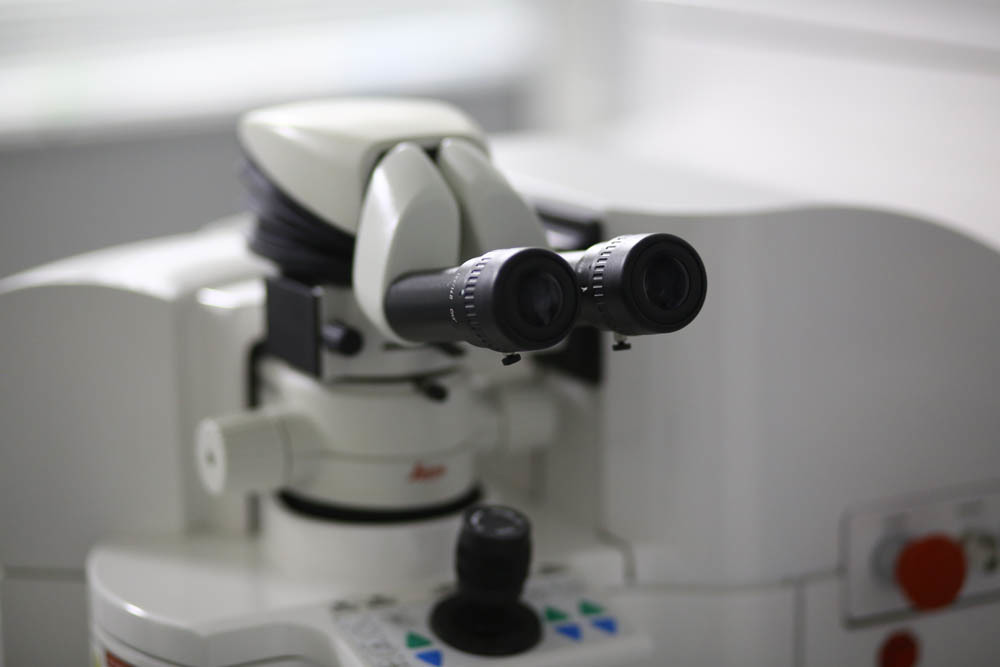
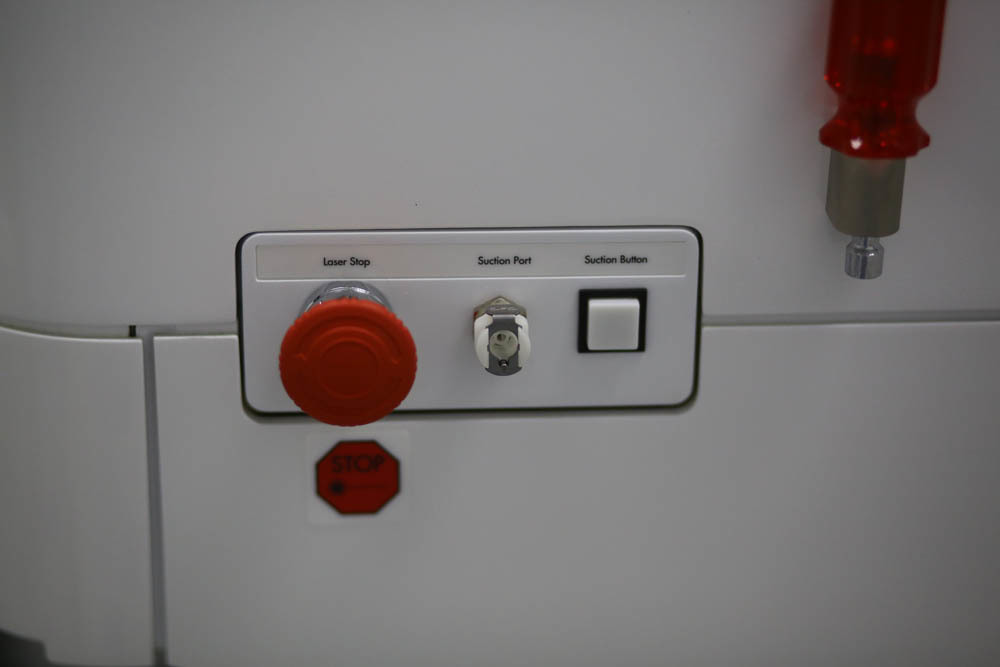
On hand at the doctor - the laser stop button:

This is the key to the start and pre-calculated profile for the operation:

Vibration protection:
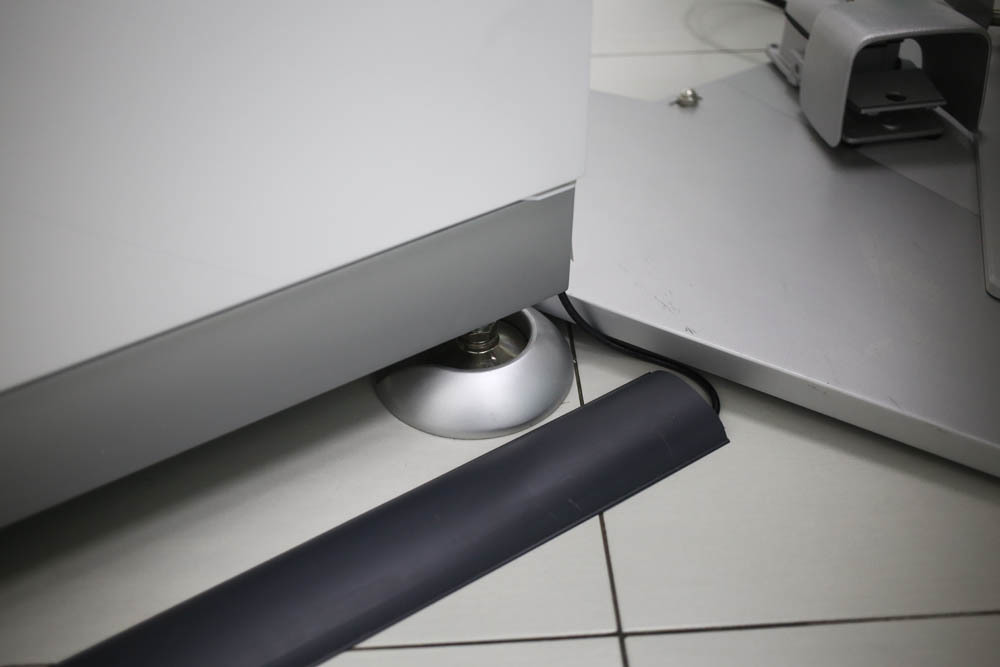

Laser control pedal (during the operation, it is under the foot of the doctor):
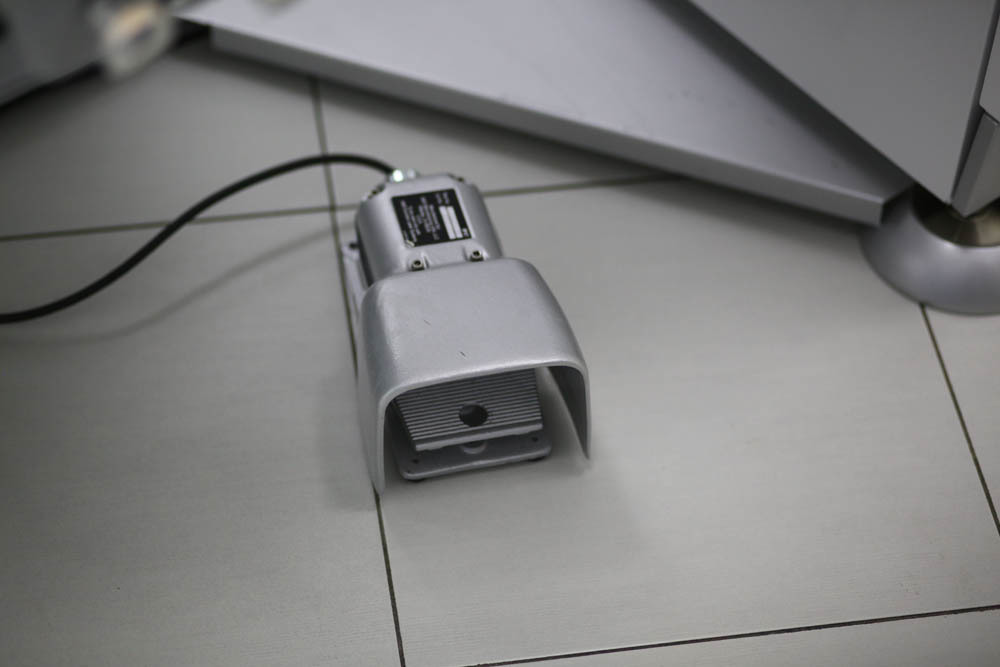

Vacuum suction to remove excess moisture and fat secretions glands:


Excimer laser control knob:
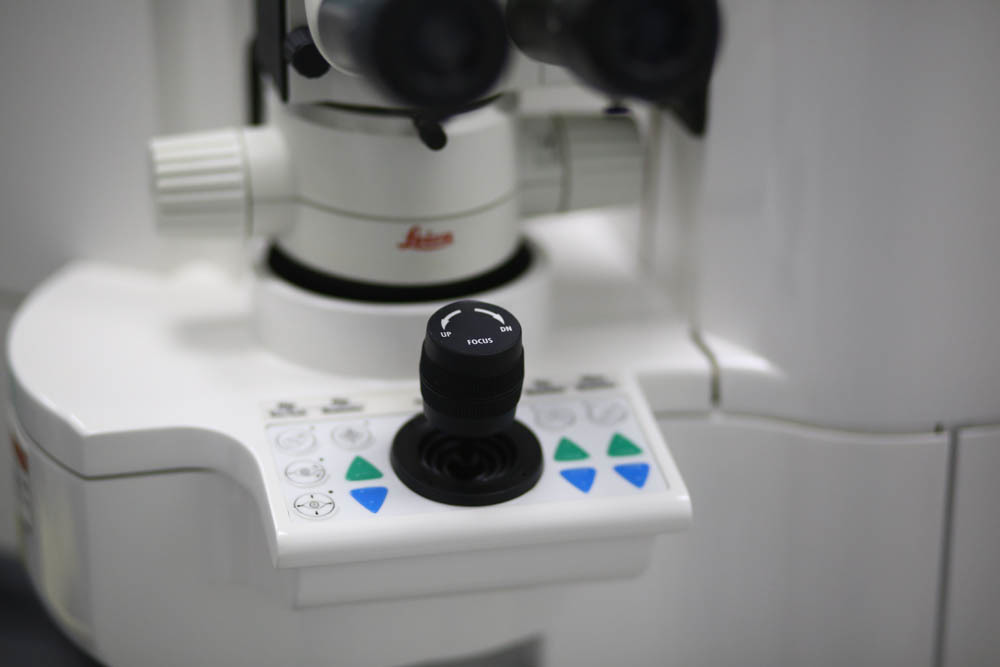
A diopter for evaluating laser calibration (a laser burns out special test calibration lenses of various diopters).
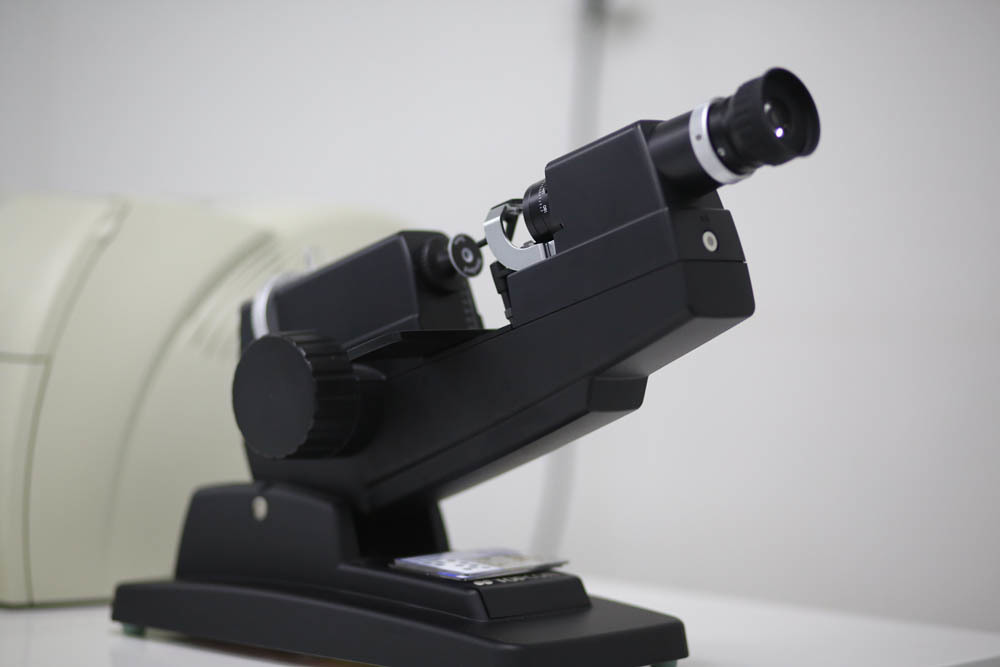

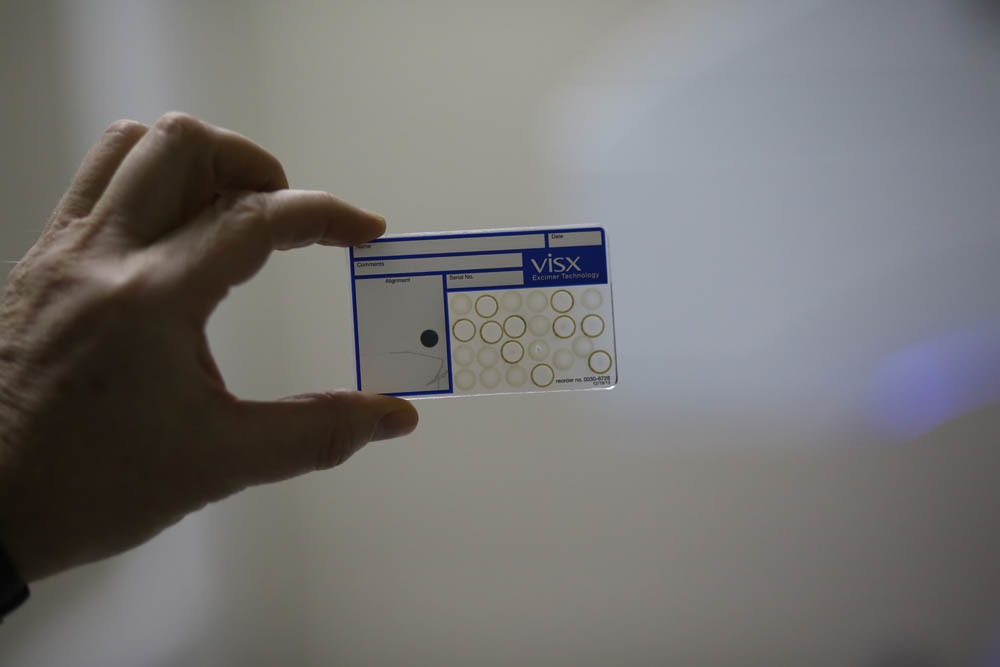
These are the cards, on them the laser burns the lenses of different dioptries:

Put warnings:

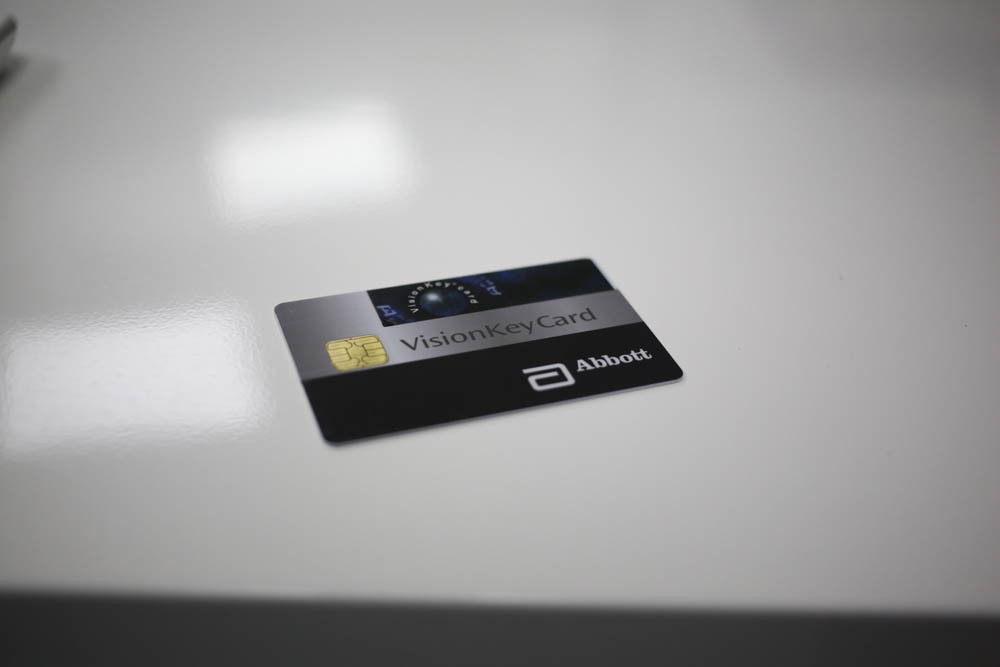
License card (on a femtosecond laser, the license is already fully digital):

Guess who is under it:

The keyboard is almost normal, but with a trackpad - needed to work with the interface. Until the very work of the laser is a Windows-program, then - laser firmware.

Testing:
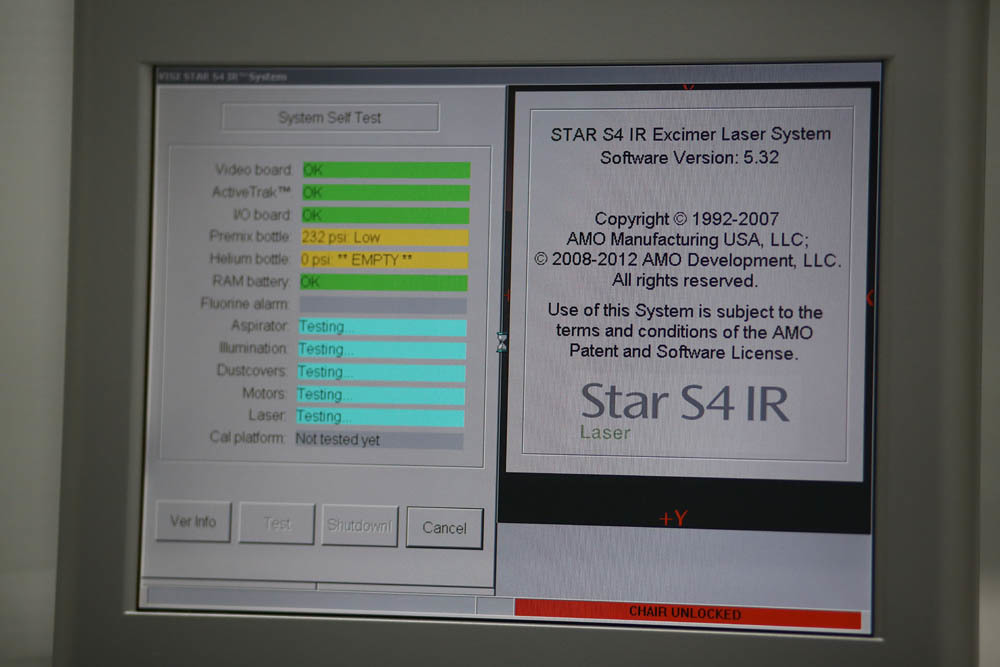
Here is visible marking for aiming:

It is activated by pressing the key on the upper left of the joystick. It is positioned on the cornea of the patient during the operation - it is also a “blinking red dot” (its intensity can be changed) during the excimer laser correction operation:

In the left row are three buttons. The top left includes the red line, which is projected onto the patient's face for laying in a strictly longitudinal position without lateral displacement. On the side of the head end there is a label for positioning at eye level. Thus, an accurate styling of the head along the XY axis occurs. Vacuum cushion firmly enough fixes the head in the selected position. From the left to the right eye, the position is changed by pressing the button with an assistant on the bed of the bed. Next, the surgeon proceeds to centering the eye under a microscope.
The left lower control button for capturing the image of the iris is the control button for the iris recorder (controls the XY position). The left middle one is the cyclothoria control button (by rotating the eyeball around its axis when the patient changes the position from vertical to horizontal).
On the right is the illumination regulation button of the operative field - direct and side illumination. Often, the surgeon almost completely turns off the illumination of the surgical field, since the camera monitoring the individual iris card works in the infrared range and the “pattern” of the iris and pupil in the dark is determined by the device more quickly.
Here is the main position of the table during the operation:
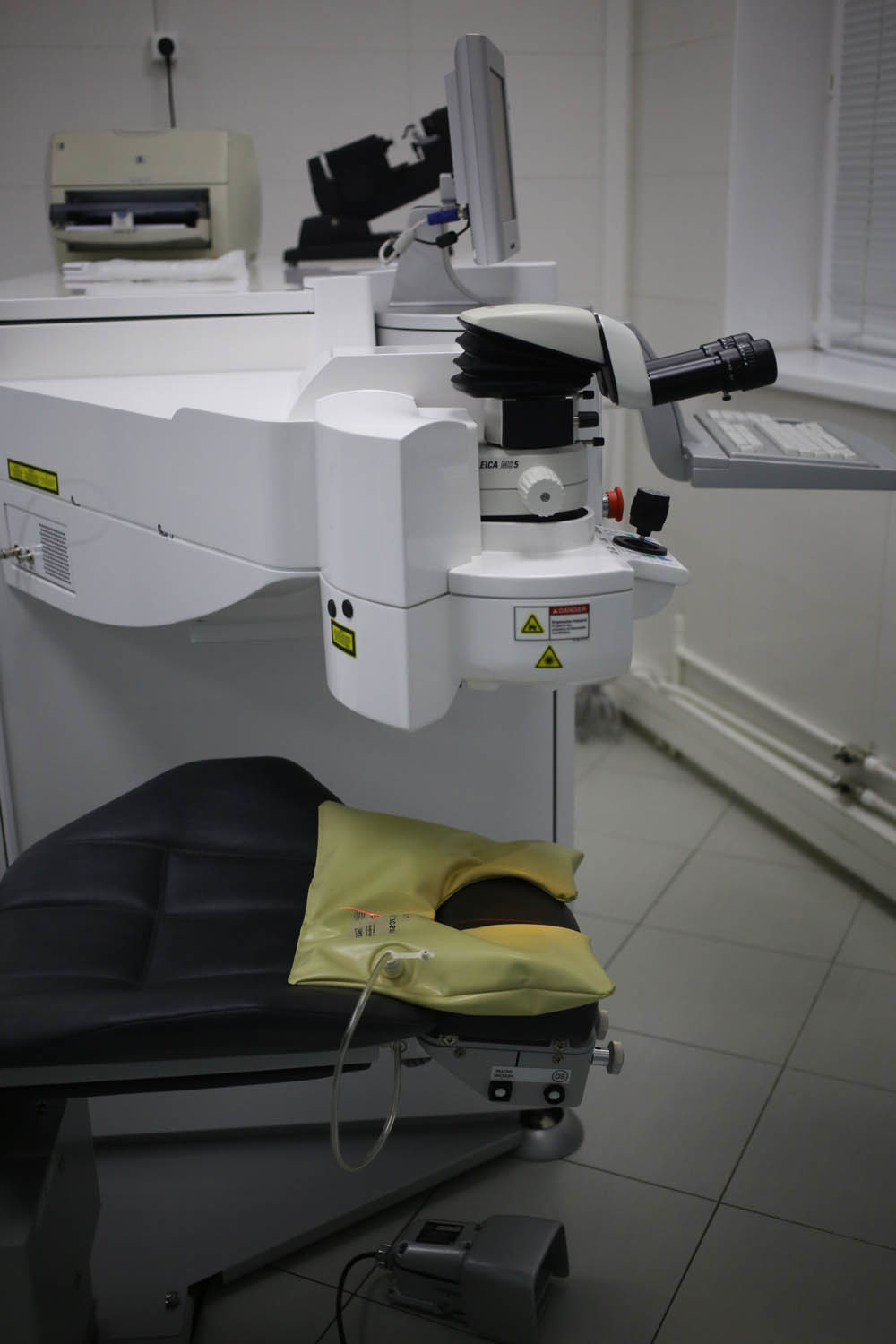
It adjusts in height and other parameters:

The laser screen is completely normal:
Excimer lasers are extremely sensitive to temperature and humidity variations in the operating room. Also, no ether and alcohol solutions in the excimer laser operating room should not be. Put constant monitoring of thermometers and hygrometers.

License Card:


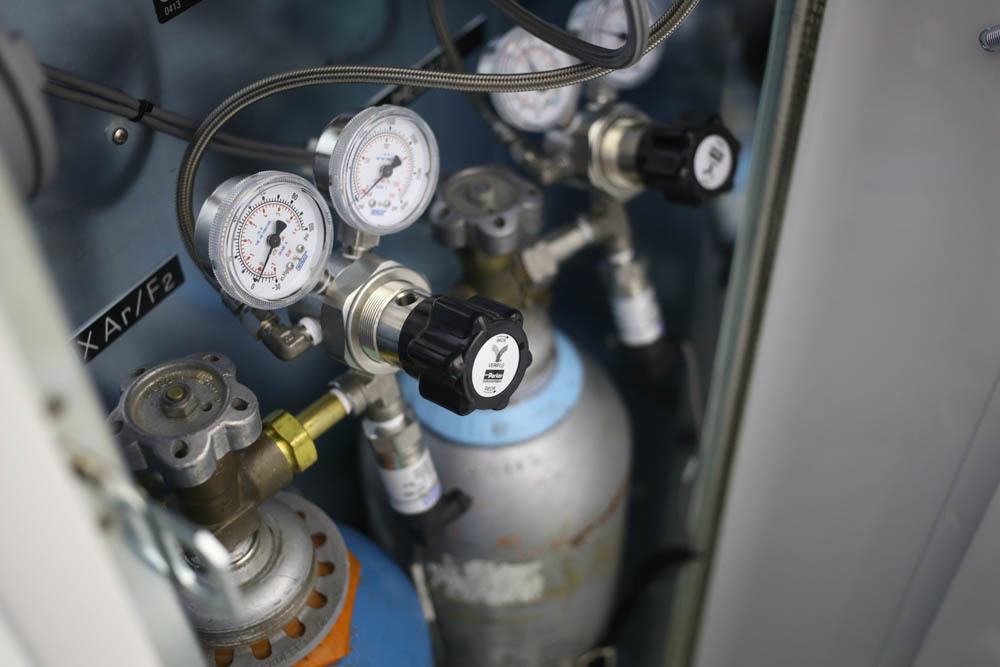
Gas cylinders for laser:
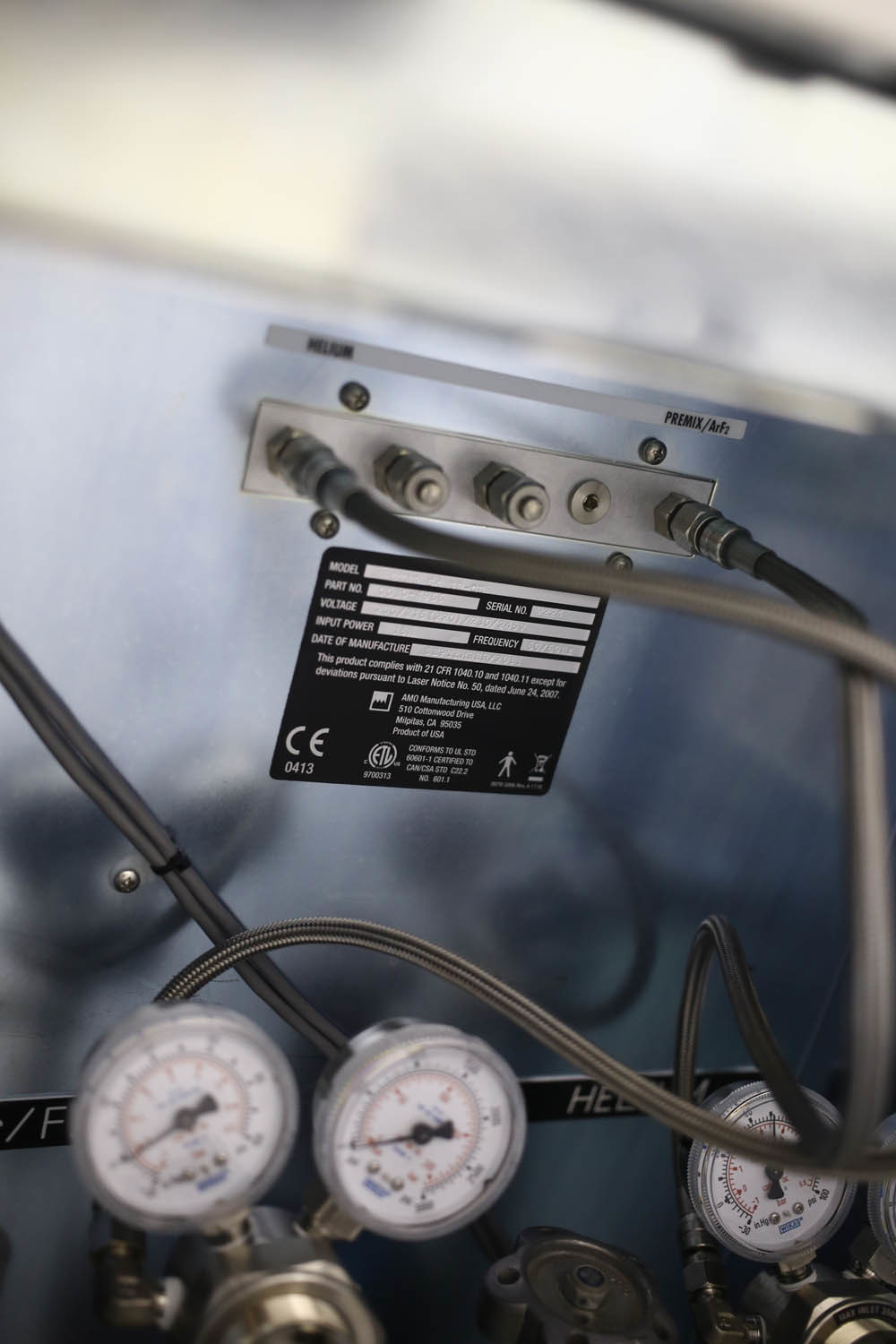



Assistant Screen:

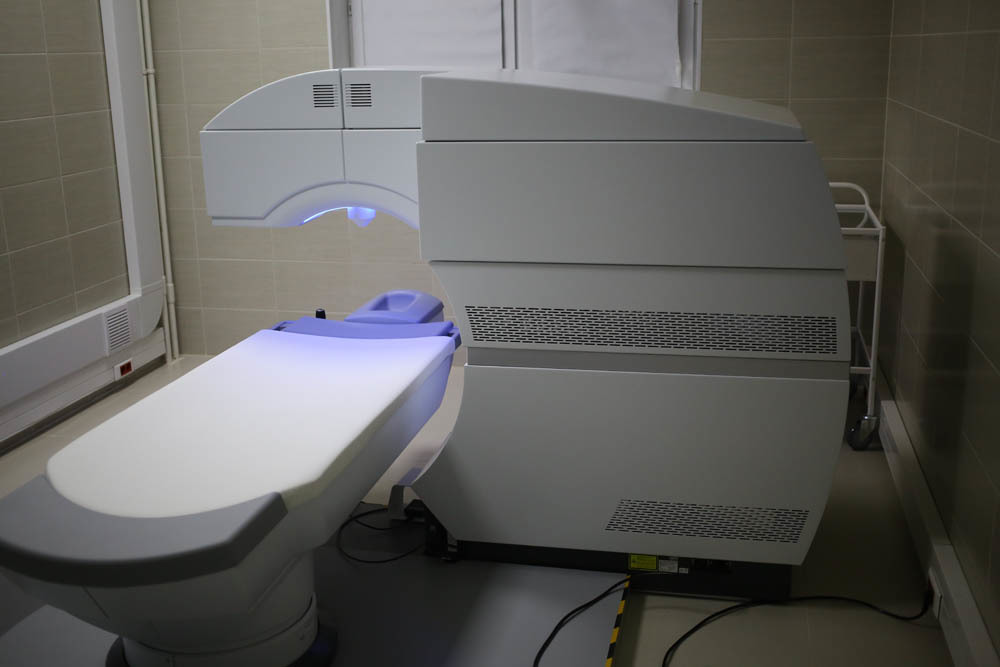
Everything with the excimer is finished. Go to the next operating room, where there is a femtolaser VisuMax. It is used to form a flap with femtoLASIK (then the patient goes to the operating room described above as an excimer), for FLEX and SMILE laser correction (then you don’t need to move anywhere — everything is done under one laser), as well as for any corneal cuts, for example, for intracorneal rings with keratoconus). In the case of a common manufacturer of femtolaser and excimer laser installations, in some cases they use one bed for two devices, then they move it in the process of performing different stages.
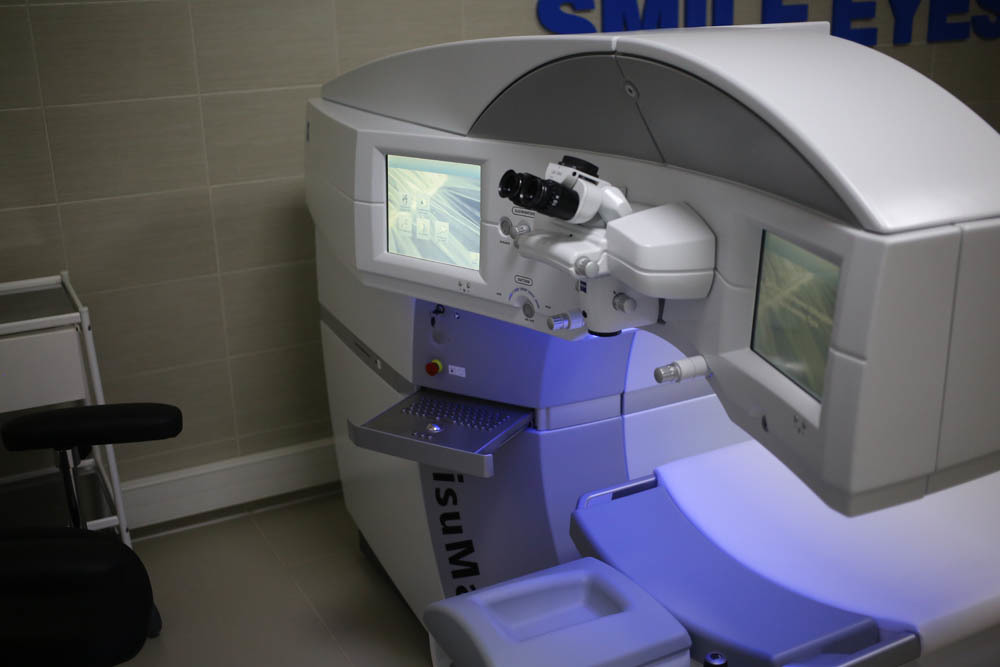
So, this is VisuMax:

The laser was created to impress with a view - Zeis ordered ergonomics at the design bureau of Mercedes (this laser had both design and cost like Maybach, they not only made the controls very comfortable, but also worked with the appearance). This was motivated very simply: if the patient feels that he is sitting in Maybach, then he is somehow more calm than when landing in something from the films about “Alien.”
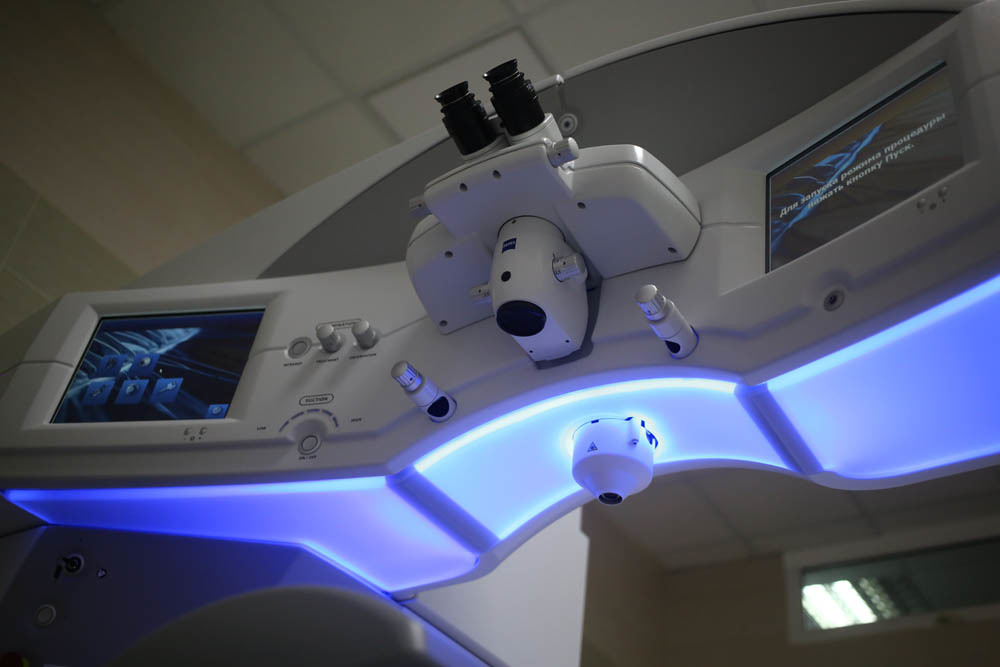
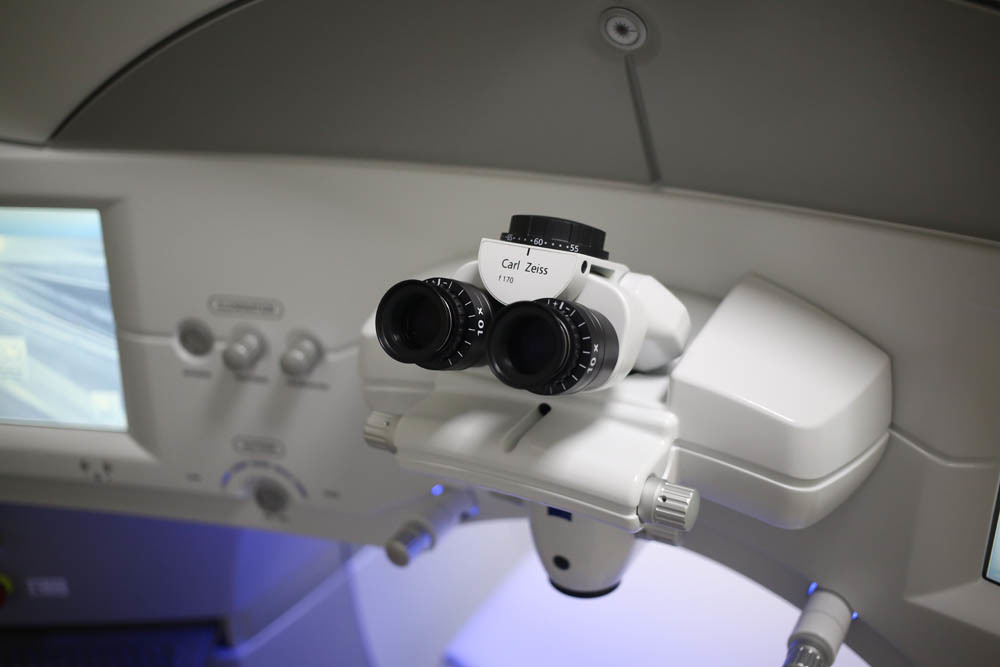
Ergonomics is really great, everything is at hand (or rather, hands):
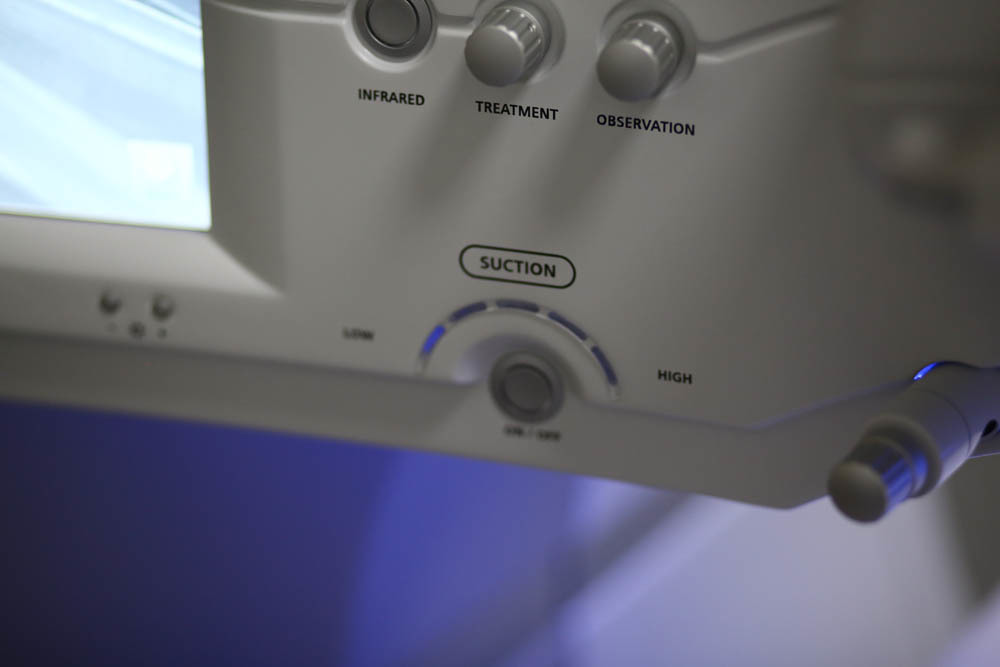
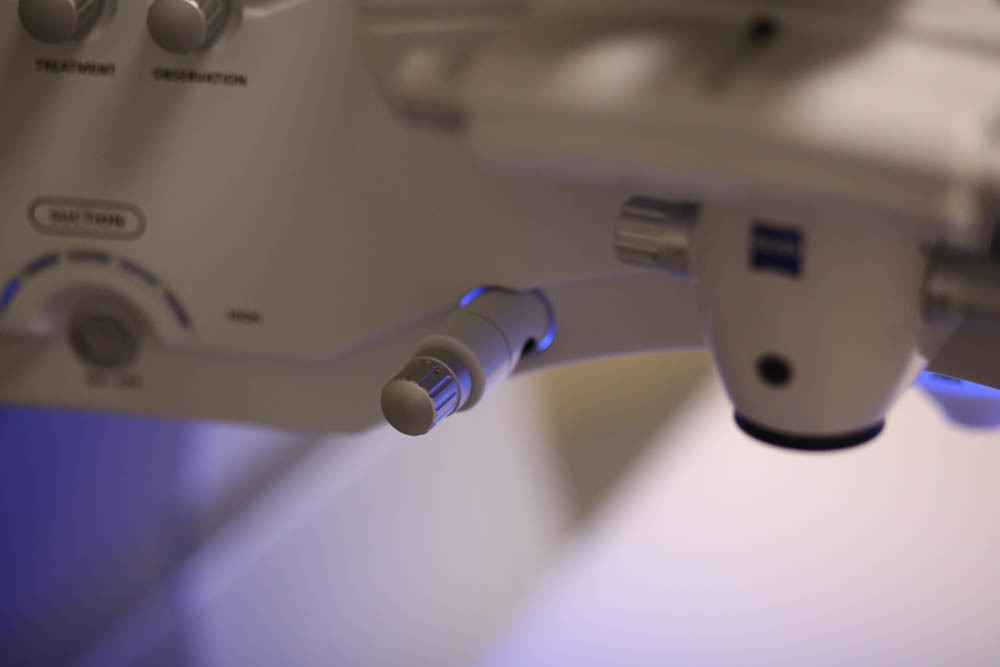
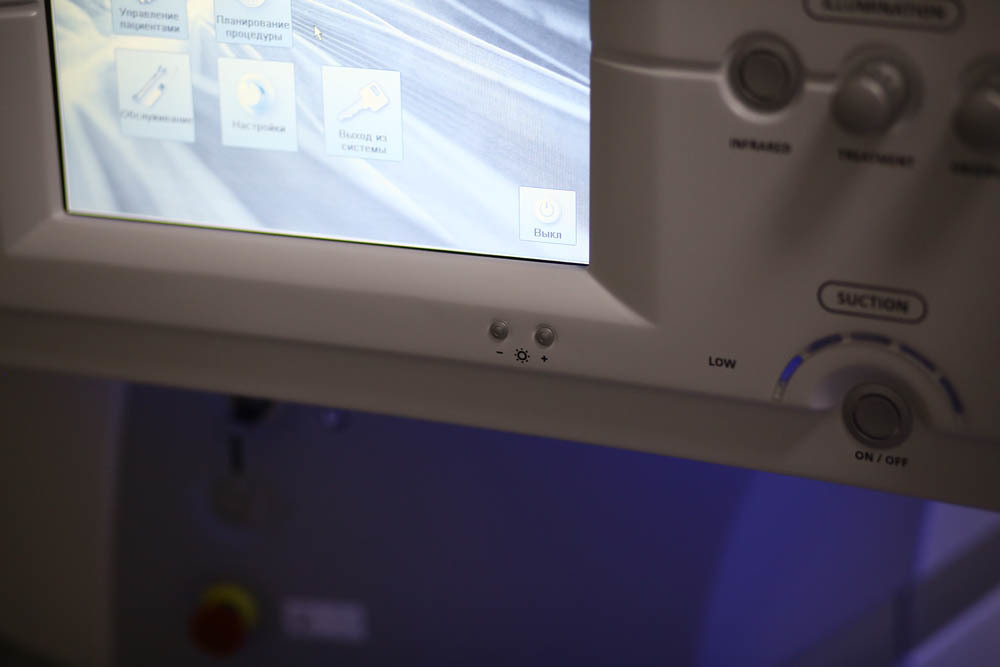



The keyboard is almost not needed here, touch screens:
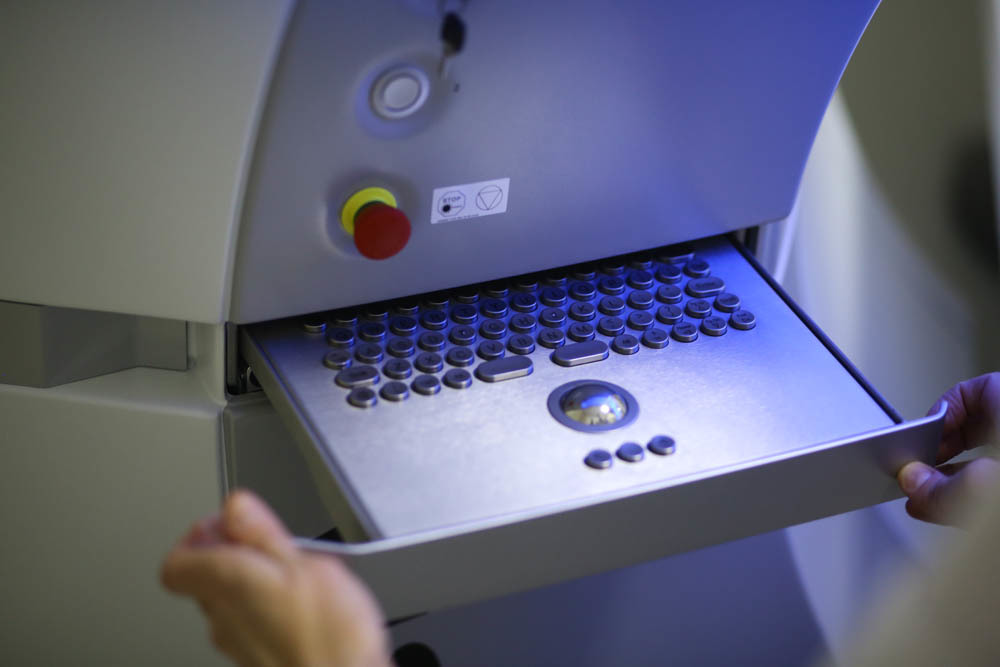


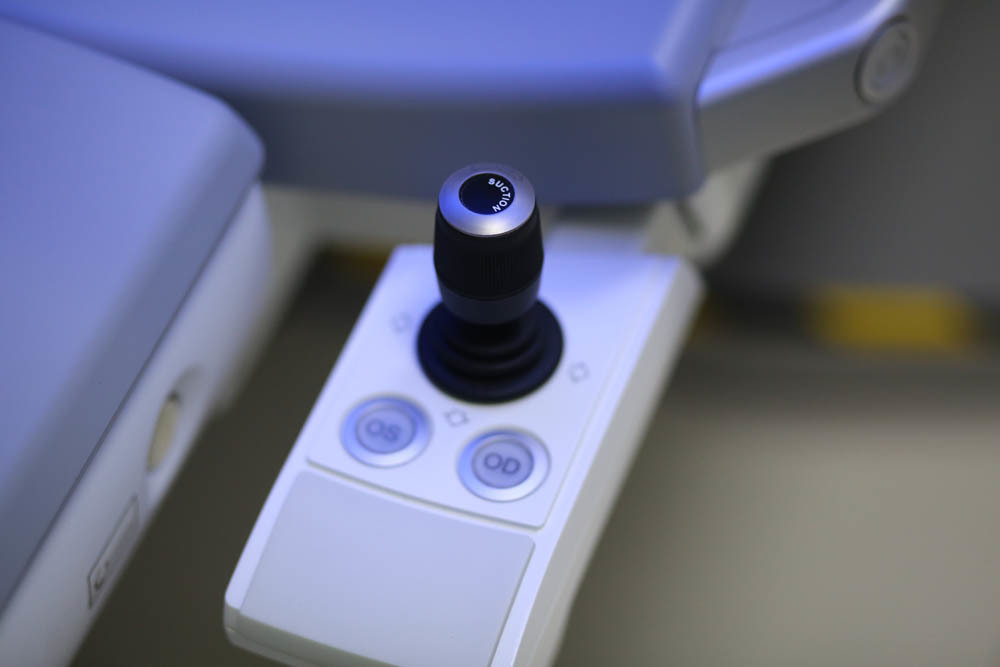
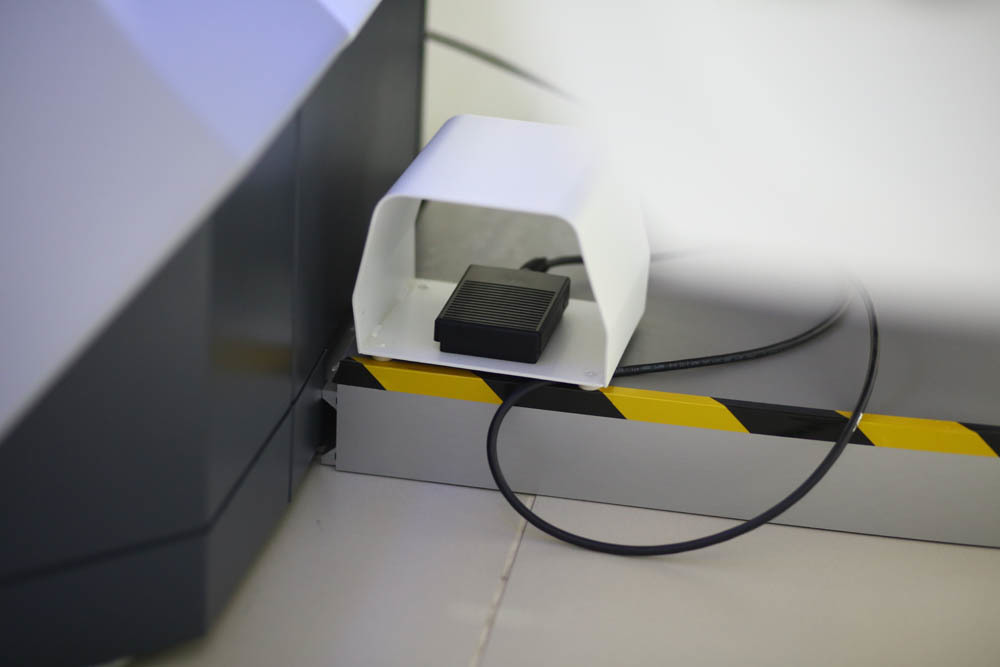
The pedal is slightly different. From the moment of its pressing, the license for a specific operation is considered to be used:

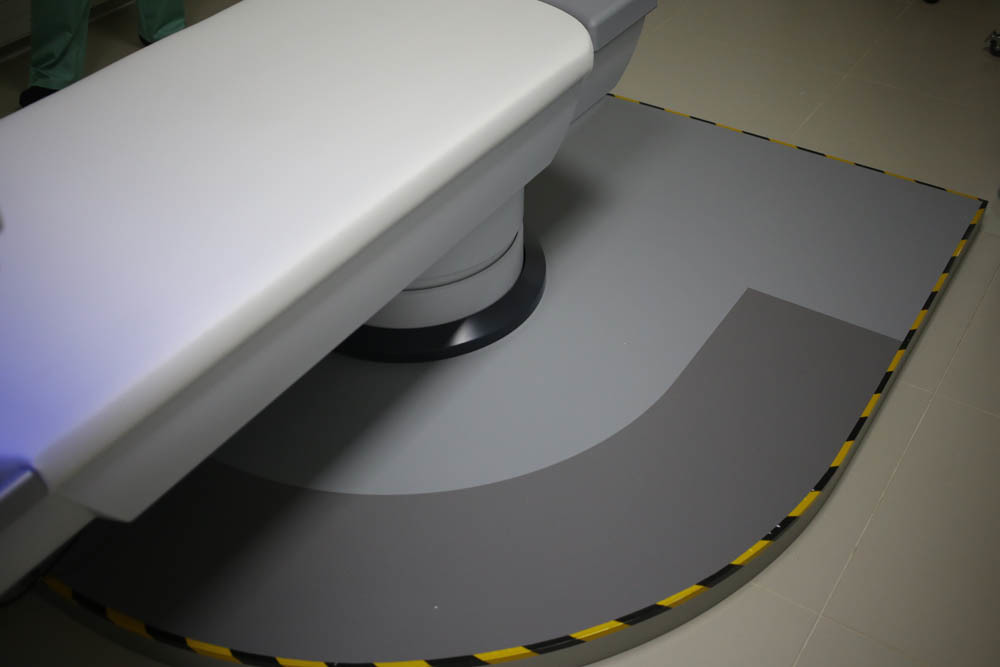
Landing here is this:
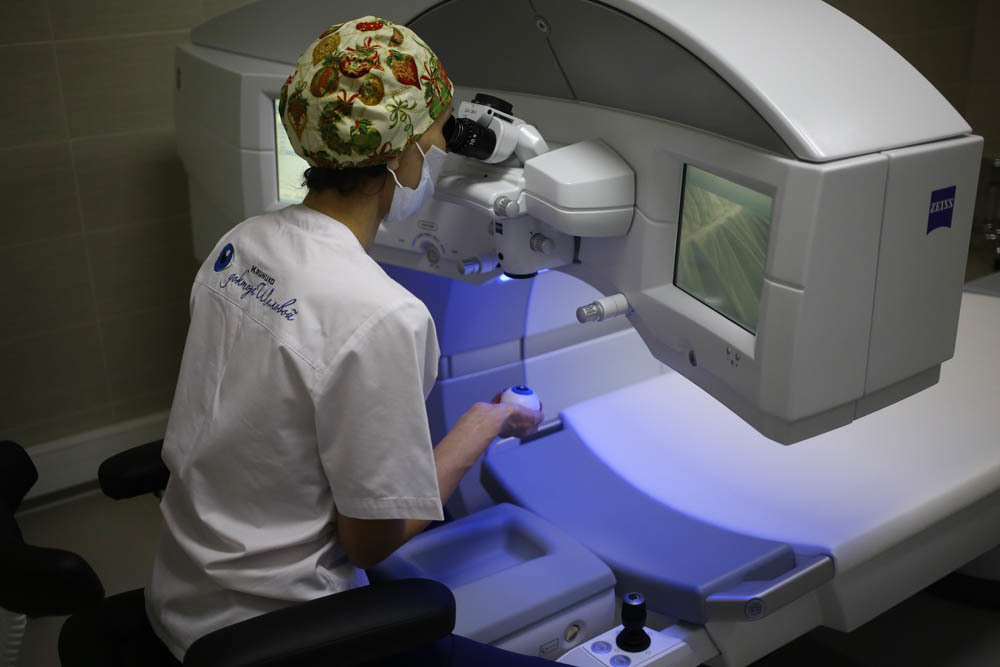
Pay attention to how everything is at hand.
As for the human factor, there are a couple of important points for successful surgery:
- The surgeon must have stereoscopic, that is, three-dimensional vision, since it is important to see three-dimensional here - the cut is curvilinear, it has depth.
- It is necessary to focus on the sound and light indication - each mode of the laser and each situation has its own indication.
- This is the type of surgery, when at the moment of surgery the surgeon is left alone with the patient - at this moment only he controls his behavior.
Further - about the software. The interfaces of VisuMax are slightly newer than on excimer, but still on “ATM” Windows.
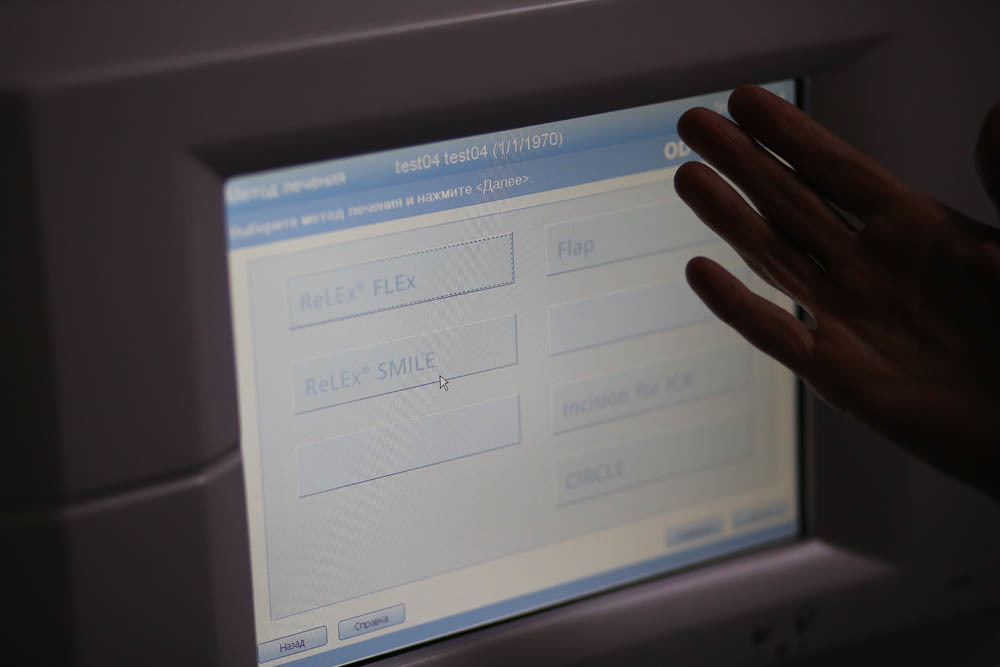

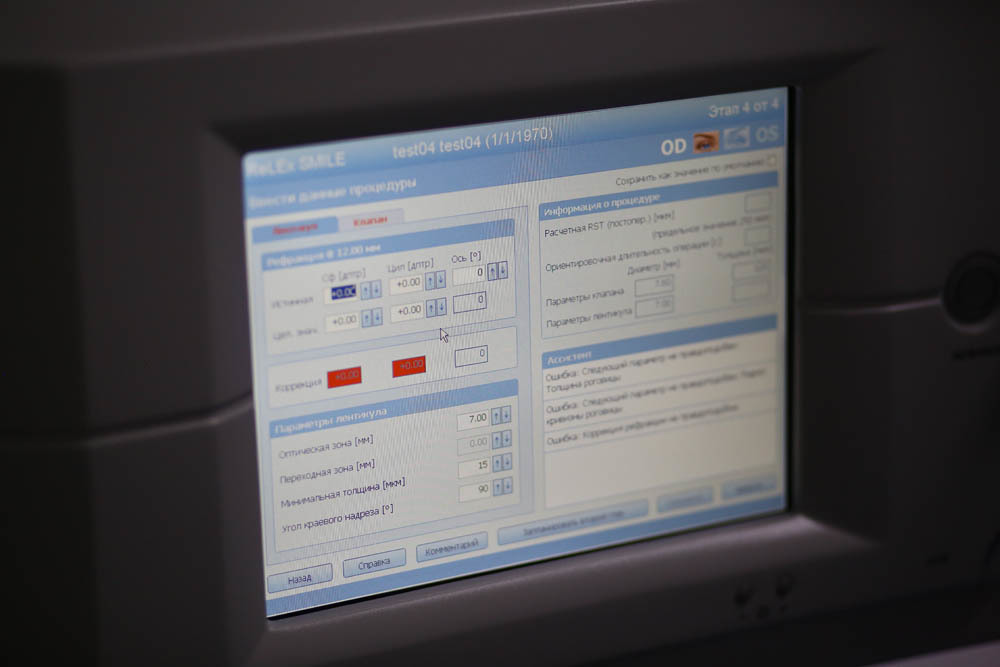
During the adjustment, an animation of how the cuts will be placed in the cornea and their geometry will be displayed on the left of the screen.
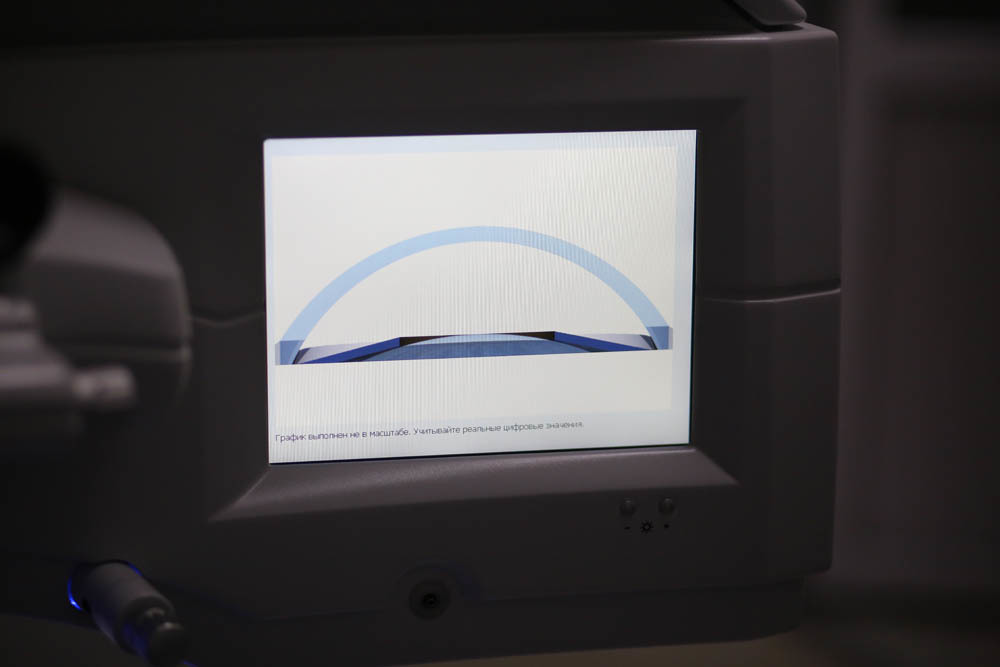

The laser insures against errors: if something in the aggregate of parameters falls out of best practice, warnings are issued. And yes, of course, the last 100 operations are written in the “black box” with all the telemetry and video.
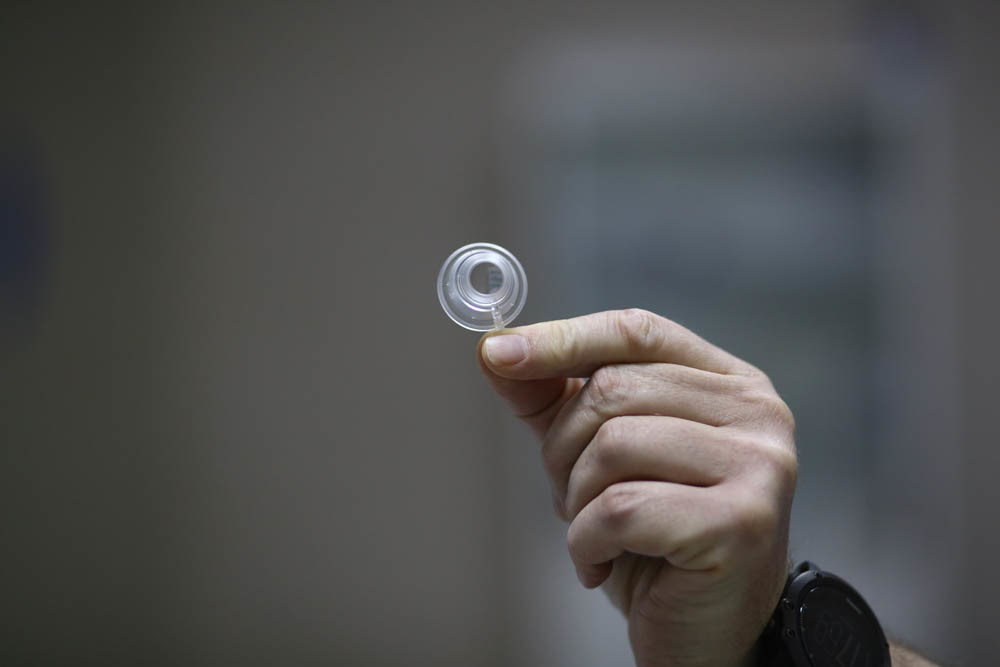
And here is the cone that comes with the license (this is the replacement part adjacent to the eye):

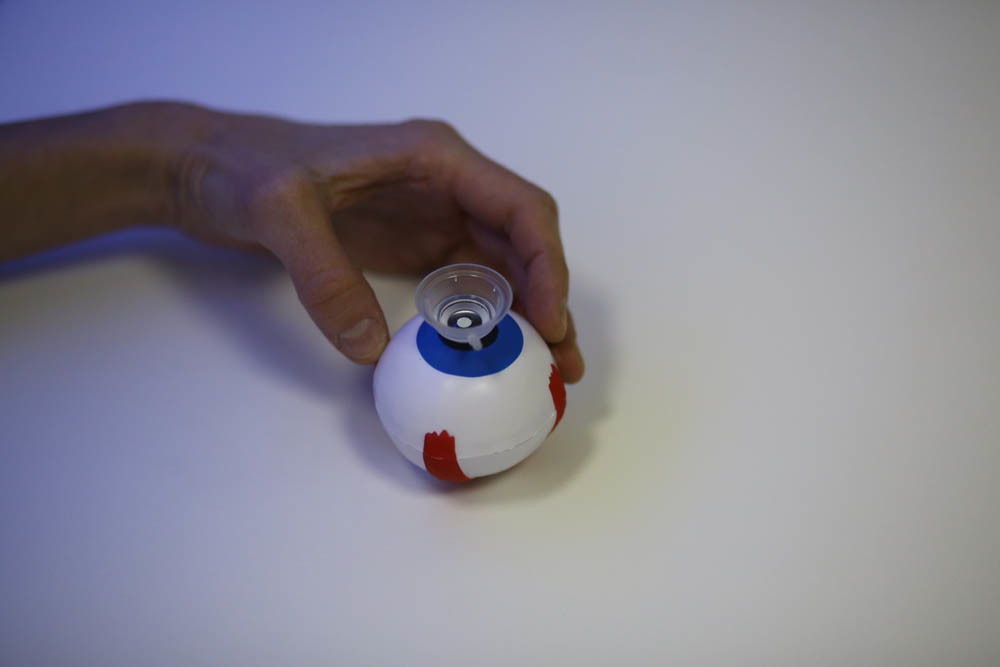
This is how he gets on the eye during the operation (by the way, this is a soft toy, which we give to the patient in hand to divert motor skills):

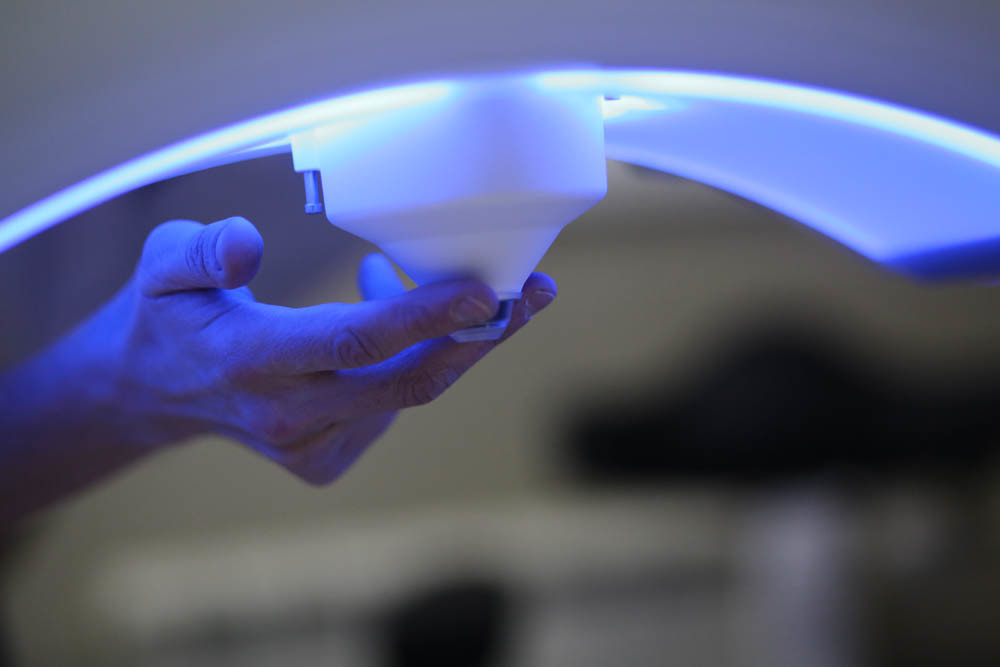
Here the cone is located on the laser:

For now. In the first post, you can read about how the ReLEx SMILE femtosecond laser works at the physical level and how the cut is done inside the cornea, in the second - look at the telemetry of the real operation , in the third - what are the operations , in the fourth - different issues about vibration protection, what will happen if you shake your head and so on, the fifth is specifically the FAQ about ReLEx SMILE in Russia, and the sixth about side effects and diagnostics . This is the seventh, I hope you now have a holistic view of how it all looks. Then we will talk about other methods of correction (in particular, about intraocular lenses), comparison of contact lenses and correction, and a little later I will tell about other eye diseases.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/400529/
All Articles