Using the IBM Watson Analytics cognitive system to analyze data on the work of the heart
The heart is made of cloth,
which is very easily torn and
very easy to repair.
Alexander Dumas son
Gayane Harutyunyan, Business Analytics Architect, IBM Client Center in Moscow

')
This article is a practical attempt to understand how modern technologies can help modern science to move forward and solve problems related to public health more quickly.
Cardiovascular diseases (CVD) are among the most common in our country. According to Rosstat, the majority of deaths in January — June 2015 were caused by circulatory system diseases (almost 50%, or 493,385 thousand deaths). Young people died mainly from cardiovascular diseases (almost 30% of deaths).
At one of the conferences on medicine, I met a very interesting person, the founder of CardioQVARK. It turned out that our interests converge in the analysis of the work of the heart. He had a lot of factual material, impersonal data from patient examinations - cardiograms. I had the opportunity to analyze this data using IBM analytical tools. We are talking about the so-called cognitive, that is, intelligent analytics - the systems of the new generation for the study of large volumes of complex, unstructured data.
These include the IBM Watson family of products. It was the cloud service Watson Analytics that allowed to quickly analyze and visualize the series of cardiograms provided by CardioQVARK.
To conduct the experiment, additional resources and capacities were required at the IBM Client Center in Moscow, in which I and my colleagues conducted analysis.
The experiment itself consisted of three main stages: the preparation of information for the analysis, the actual analysis and visualization of the results, the interpretation of the results of the experiment.
We worked in close cooperation with CardioQVARK specialists, and our goal was quite ambitious to get meaningful results after processing large amounts of real medical data.
This task for large amounts of data is very difficult. Blaise Pascal was right when he said that the heart has its own laws, which "the mind does not know."
The fact is that a huge number of factors affect the work of the heart, and it is very difficult to understand which of them are the most important. Doctors are often guided by their personal experience, by intuition. We used the most advanced analytical systems that can see the connection between a variety of different factors and evaluate their impact.
The results of the analysis brought a lot of unexpected. To begin with, the specialists who have been working on this topic for a long time were surprised that the IT team was able to disassemble and classify the patients' condition with high speed and accuracy. After all, we are not experts in the field of medicine. However, cognitive systems are called this because they allow solving problems previously available only to experts in the usual way.
The results turned out to be impressive in the first place because it was possible to automatically identify a large number of important dependencies, isolate specific groups of patients, deviations from the norm, identify those who need urgent surgery, determine the effect of medications on the course of the disease and much more.
For example, it was possible to isolate and classify from the total mass:
• conditionally healthy patients and the nature of their cardiograms
• patients with impaired heart function.
• peak periods and heart loads
• patients who need heart surgery
• patients who have had heart surgery
• influence of drugs in the postoperative period
• nature of the heart in the recovery period
• returning the heart to normal operation
Moreover, the analytical tools of Watson Analytics allowed us to see interesting dependencies. So, it turned out that the phases of the moon affect the work of the patients' hearts, especially women. This very interesting relationship required a separate analysis, because the topic is already beyond the scope of traditional medicine and therefore requires a particularly careful approach.
Despite the fact that the influence of cosmic-scale phenomena - the Sun, the Moon, on living organisms has been studied for a long time, the great difficulty of identifying dependencies leaves this field of research quite problematic. The foundations of these studies were laid by the great Russian scientist A.L. Chizhevsky. In particular, he discovered the dependence of the blood structure on electric and magnetic fields, including the solar electromagnetic field. It is not by chance that the electromagnetic field of the heart is about five thousand times stronger than the field of the brain.
It is precisely because we were not medical specialists that a special technique was applied for the purity of the experiment and verification of the results.
We received anonymous cardiogram data from both healthy patients and patients. That is, in the analysis, our team did not know which cardiograms are related to sick patients, and which ones were taken from healthy people.
We discussed the results with a team of doctors. The interaction of the two teams was necessary because the CardioQVARK system collects a huge amount of factual information about the patient, and understanding many of these data requires special knowledge.
The statistics that were loaded into the IBM Watson system reflected the various characteristics of the work of the heart, such as the duration of cardiac cycles, their variations, arrhythmia, connection with the work of breathing, pulse rate, and so on.
Since the CardioQVARK system allows you to make a spectral analysis of the heart rate, that is, it determines the oscillations - the waves that occur when the heart muscles work. This data was also uploaded to the Watson Analytics analytical toolkit. In particular, these were parameters associated with respiratory waves, parameters of slow or medium waves associated with sympathetic activity or activity associated with heart rate, and much more.
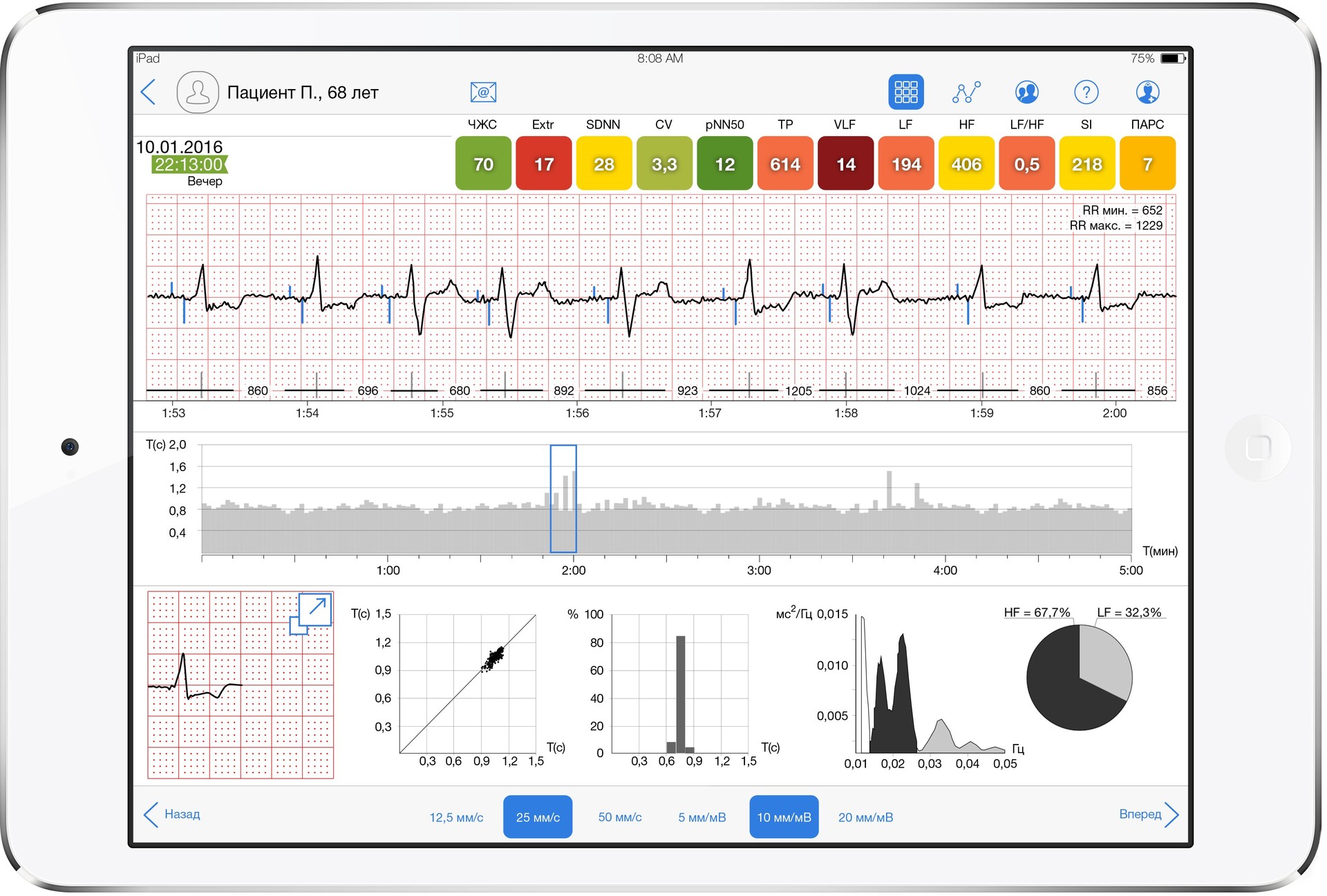
Fig. 1. Thanks to the application on the iPad, the doctor - the CardioQVARK user online monitors the patient's condition.
So, the analysis allowed us to identify a number of important indicators and dependencies:
• statistical values, that is, the average values for each of the indicators
• periods (cycles) of the heart
• building a weekly forecast for each of the parameters
• comparison of values with the lunar calendar
• determination of the degree of dependence between indicators during peak periods
The latter relationship is especially important, since peak periods are periods of critical heart function, and they may be the most dangerous for the patient's health.
Separately, it should be emphasized that the Watson Analytics toolkit allowed us to establish the degree of dependence of the heart’s work on the phases of the moon. This work requires continuation, and we hope for interest in it from the side of medicine.
Of course, most of the dependencies can be calculated manually, but the main thing in the work done is that similar results can be obtained instantly in automatic mode and with visual display. The doctor does not spend time on routine data analysis, but immediately sees a clear picture describing the patient's condition and can make decisions promptly.
After all, to evaluate and understand what happened with the patient will take only minutes. At the same time, a specialist doctor will be able to evaluate whole series of cardiograms, which will give a more accurate picture of the patient's heart work and will allow to take into account the characteristics of this patient and his personal history of the disease. In addition, it is possible to trace the patient's condition not only during his stay in the hospital, but also remotely. This will allow timely warning of possible deviations in health and time to take the necessary measures.
Our opinion is shared by colleagues in the experiment. CardioQVARK Deputy General Director Sergey Sadovsky commented on the results of the joint work: “In perspective, the use of analysis and machine learning based on smart, expert systems will allow the doctor to effectively sort patients according to the severity of their condition, to diagnose heart and some extracardiac pathologies, to track important parameters of the body. Already, this is confirmed at the laboratory level and during voluntary clinical trials. "
The experiment thus confirmed that the use of modern technology can significantly speed up and improve the accuracy of the patient's condition.
It is important to understand that the whole experiment took no more than one working week of pure time. This included the initial data preparation, statistical analysis and visualization with Watson Analytics, interpretation of the results, as well as consultation with medical specialists.
The use of cognitive systems in medicine can significantly reduce the cost of treating patients. After all, if the patient's condition is monitored all the time and the necessary measures are taken in time, the average recovery rates are much better. And what is even more important, you can get closer to the task of providing personalized assistance to those who need it. From standard mass treatment to individual treatment, taking into account all the characteristics of each patient - this is what the transition allows the use of cognitive analytics Watson Analytics.
which is very easily torn and
very easy to repair.
Alexander Dumas son
Gayane Harutyunyan, Business Analytics Architect, IBM Client Center in Moscow

')
This article is a practical attempt to understand how modern technologies can help modern science to move forward and solve problems related to public health more quickly.
Cardiovascular diseases (CVD) are among the most common in our country. According to Rosstat, the majority of deaths in January — June 2015 were caused by circulatory system diseases (almost 50%, or 493,385 thousand deaths). Young people died mainly from cardiovascular diseases (almost 30% of deaths).
At one of the conferences on medicine, I met a very interesting person, the founder of CardioQVARK. It turned out that our interests converge in the analysis of the work of the heart. He had a lot of factual material, impersonal data from patient examinations - cardiograms. I had the opportunity to analyze this data using IBM analytical tools. We are talking about the so-called cognitive, that is, intelligent analytics - the systems of the new generation for the study of large volumes of complex, unstructured data.
These include the IBM Watson family of products. It was the cloud service Watson Analytics that allowed to quickly analyze and visualize the series of cardiograms provided by CardioQVARK.
To conduct the experiment, additional resources and capacities were required at the IBM Client Center in Moscow, in which I and my colleagues conducted analysis.
The experiment itself consisted of three main stages: the preparation of information for the analysis, the actual analysis and visualization of the results, the interpretation of the results of the experiment.
We worked in close cooperation with CardioQVARK specialists, and our goal was quite ambitious to get meaningful results after processing large amounts of real medical data.
This task for large amounts of data is very difficult. Blaise Pascal was right when he said that the heart has its own laws, which "the mind does not know."
The fact is that a huge number of factors affect the work of the heart, and it is very difficult to understand which of them are the most important. Doctors are often guided by their personal experience, by intuition. We used the most advanced analytical systems that can see the connection between a variety of different factors and evaluate their impact.
The results of the analysis brought a lot of unexpected. To begin with, the specialists who have been working on this topic for a long time were surprised that the IT team was able to disassemble and classify the patients' condition with high speed and accuracy. After all, we are not experts in the field of medicine. However, cognitive systems are called this because they allow solving problems previously available only to experts in the usual way.
The results turned out to be impressive in the first place because it was possible to automatically identify a large number of important dependencies, isolate specific groups of patients, deviations from the norm, identify those who need urgent surgery, determine the effect of medications on the course of the disease and much more.
For example, it was possible to isolate and classify from the total mass:
• conditionally healthy patients and the nature of their cardiograms
• patients with impaired heart function.
• peak periods and heart loads
• patients who need heart surgery
• patients who have had heart surgery
• influence of drugs in the postoperative period
• nature of the heart in the recovery period
• returning the heart to normal operation
Moreover, the analytical tools of Watson Analytics allowed us to see interesting dependencies. So, it turned out that the phases of the moon affect the work of the patients' hearts, especially women. This very interesting relationship required a separate analysis, because the topic is already beyond the scope of traditional medicine and therefore requires a particularly careful approach.
Despite the fact that the influence of cosmic-scale phenomena - the Sun, the Moon, on living organisms has been studied for a long time, the great difficulty of identifying dependencies leaves this field of research quite problematic. The foundations of these studies were laid by the great Russian scientist A.L. Chizhevsky. In particular, he discovered the dependence of the blood structure on electric and magnetic fields, including the solar electromagnetic field. It is not by chance that the electromagnetic field of the heart is about five thousand times stronger than the field of the brain.
It is precisely because we were not medical specialists that a special technique was applied for the purity of the experiment and verification of the results.
We received anonymous cardiogram data from both healthy patients and patients. That is, in the analysis, our team did not know which cardiograms are related to sick patients, and which ones were taken from healthy people.
We discussed the results with a team of doctors. The interaction of the two teams was necessary because the CardioQVARK system collects a huge amount of factual information about the patient, and understanding many of these data requires special knowledge.
The statistics that were loaded into the IBM Watson system reflected the various characteristics of the work of the heart, such as the duration of cardiac cycles, their variations, arrhythmia, connection with the work of breathing, pulse rate, and so on.
Since the CardioQVARK system allows you to make a spectral analysis of the heart rate, that is, it determines the oscillations - the waves that occur when the heart muscles work. This data was also uploaded to the Watson Analytics analytical toolkit. In particular, these were parameters associated with respiratory waves, parameters of slow or medium waves associated with sympathetic activity or activity associated with heart rate, and much more.

Fig. 1. Thanks to the application on the iPad, the doctor - the CardioQVARK user online monitors the patient's condition.
So, the analysis allowed us to identify a number of important indicators and dependencies:
• statistical values, that is, the average values for each of the indicators
• periods (cycles) of the heart
• building a weekly forecast for each of the parameters
• comparison of values with the lunar calendar
• determination of the degree of dependence between indicators during peak periods
The latter relationship is especially important, since peak periods are periods of critical heart function, and they may be the most dangerous for the patient's health.
Separately, it should be emphasized that the Watson Analytics toolkit allowed us to establish the degree of dependence of the heart’s work on the phases of the moon. This work requires continuation, and we hope for interest in it from the side of medicine.
Of course, most of the dependencies can be calculated manually, but the main thing in the work done is that similar results can be obtained instantly in automatic mode and with visual display. The doctor does not spend time on routine data analysis, but immediately sees a clear picture describing the patient's condition and can make decisions promptly.
After all, to evaluate and understand what happened with the patient will take only minutes. At the same time, a specialist doctor will be able to evaluate whole series of cardiograms, which will give a more accurate picture of the patient's heart work and will allow to take into account the characteristics of this patient and his personal history of the disease. In addition, it is possible to trace the patient's condition not only during his stay in the hospital, but also remotely. This will allow timely warning of possible deviations in health and time to take the necessary measures.
Our opinion is shared by colleagues in the experiment. CardioQVARK Deputy General Director Sergey Sadovsky commented on the results of the joint work: “In perspective, the use of analysis and machine learning based on smart, expert systems will allow the doctor to effectively sort patients according to the severity of their condition, to diagnose heart and some extracardiac pathologies, to track important parameters of the body. Already, this is confirmed at the laboratory level and during voluntary clinical trials. "
The experiment thus confirmed that the use of modern technology can significantly speed up and improve the accuracy of the patient's condition.
It is important to understand that the whole experiment took no more than one working week of pure time. This included the initial data preparation, statistical analysis and visualization with Watson Analytics, interpretation of the results, as well as consultation with medical specialists.
The use of cognitive systems in medicine can significantly reduce the cost of treating patients. After all, if the patient's condition is monitored all the time and the necessary measures are taken in time, the average recovery rates are much better. And what is even more important, you can get closer to the task of providing personalized assistance to those who need it. From standard mass treatment to individual treatment, taking into account all the characteristics of each patient - this is what the transition allows the use of cognitive analytics Watson Analytics.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/400493/
All Articles