Wireless sound for home theater: the agony of choice - an abundance of formats, features and problems
Wireless data transmission standards quickly and everywhere win back the positions of traditionally cable segments. The sound was no exception, and every year an increasing share of the total market volume is cut off by wireless speakers, headphones, etc.
For owners of home theaters, wireless speakers provide a lot of new features, but at the same time make you seriously think about choosing a standard.

On the one hand, many users want to get rid of the “kilometers” of switching problems, acquire the ability to quickly move sources, on the other - no one is willing to sacrifice the quality of sound and image.
We can not keep silent about the fact that in this area another war of formats. As practice shows, the development of standards for wireless sound systems, commercial interests of manufacturers do not contribute to the unification and creation of a single or compatible standards. The result - users are doomed to choose receivers, speakers and panels that work according to the same specification, which largely deprives of freedom of choice.

')
The most common standards today are: Wireless Local Area Networks - WLAN, Wireless Wide Area Network - WWAN, Wireless Personal Area Networks - WPAN (Bluetooth), Wireless Metropolitan Area Networks - WMAN.
Most of the home wireless multimedia systems available today use WLAN with Wi-Fi technology or WPAN with Bluetooth technology. The next step in the evolution of wireless data transmission standards are Apple AirPlay, Miracast, Play-Fi, Qualcomm AllPlay, WiSA, AVB (Audio Video Bridging), WirelessHD, DLNA (wireless transmission) standards. An alternative to wireless transmission has become the HomePlug. Also known are their own corporate development of standards for wireless transmission of sound and images, which are conducted by such companies as Sonos, Bose, Denon, Samsung.
Most users are interested in a series of questions that manufacturers usually answer evasively. The following are especially common among them:
I will try to answer these and a number of other questions in this article. It should also be emphasized that everything stated in the article is valid for any wireless home audio systems, except for headphones and portable speakers.
First of all, it is worth noting that in the full sense of the wireless home multimedia systems at the moment is not created, because there is no technology that allows you to transmit power without wires. In cases with portable devices, this problem was solved using batteries. Probably with large stationary systems this would not be appropriate.
Signal power of the most advanced technologies such as Apple AirPlay, AVB (Audio Video Bridging) does not exceed 100 mW or 0.1 W - this clearly indicates that in the near future power will be provided using a standard home power network.
The above conclusion suggests that some of the advantages of wireless systems are offset by the lack of autonomous power, and the user will inevitably depend on the location of the sources (sockets). The logical solution may be the use of high-capacity batteries, however, statements of this kind have not yet been made by any of the manufacturers known to me.
Existing “wireless” standards other than HomePlug are based on data broadcast. Their differences can be divided into several groups:
One way or another, these differences in various degrees can affect quality, i.e. on the accuracy of audio and video signal transmission. I suppose you should not dwell on the fact that devices using different technologies will not work correctly with each other, even when using the same basic specification. Suppose WI-FI (a receiver using Qualcomm AllPlay is not compatible with the acoustics and the panel that use Miracast).
The following fact is essential for selection:
An example is the use of Wireless Fidelity (Wi-Fi) for transmitting sound and image over a 20 MHz channel in the 2.4 GHz band, when adjacent rooms use “non-overlapping” Wi-Fi channels adjacent to this band. In reality, the channel width will be larger, which in such a situation will inevitably lead to interference, which will significantly affect the quality of sound and image.

On the well-known fact that Wi-Fi, today the most common specification of network protocols for wireless networks (WLAN), does not make sense in detail. I note only that the practice has proved the high demand for Wi-Fi devices, which does not detract from some of the shortcomings of the standard.

Many experts note that with all the versatility and integrative capabilities of the standard, it is of little use for high-quality sound transmission. The latter is connected with the problem of the 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz band congestion, which facilitates the occurrence of interference (protocols IEEE 802.11b, IEEE 802.11a, IEEE 802.11g, IEEE 802.11n).
To eliminate the influence of third-party devices, the Wi-Fi Alliance has been developed and certified, various specification options that extend the capabilities of traditional Wi-Fi
Miracast is a version of Wi-Fi adapted to transmit sound and images in high quality. The basis of the updated data transfer format is the specification of the IEEE 802.11ac standard (Gigabit Wi-Fi) and the WiGig technology and the Multi-gigabit point-to-wireless wireless (IEEE 802.11ad standard) developed jointly with the Wireless Gigabit Alliance.
Miracast technology provides a radio channel operating in the 60 GHz band at speeds up to 7 Gbit / s, which allows streaming video in uncompressed HD quality and high-precision multi-channel audio signal. The disadvantages include the relatively low prevalence of the standard and, accordingly, not too wide choice devices.

Another option for upgrading the Wi-Fi connection for high-quality audio is Qualcomm AllPlay. This technology is based on Qualcomm chips and is actively used by companies such as Panasonic and Altec Lansing.
The main advantages of the standard are lossless transmission of the sound, as well as integration into the multiroom. In this case, the tests demonstrate that the quality of video transmission is inferior to technologies such as DLNA, Miracast WiSA, AVB and WirelessHD.

Everyone has long been aware that Bluetooth is the most common specification of Wireless Personal Area Networks network protocols - WPAN. Integration capabilities using this standard are one of its main advantages, including the transmission of sound.

If we take a closer look at the advantages of Bluetooth, we can single out the following:
In this application, Bluetooth also has a number of drawbacks, the main one being the reduction in sound quality. The problem is that when using Bluetooth to transfer audio data, they are converted from source codecs (MREG, MP3, AAC, etc.) to SBC, which assumes compression with loss of information. The effect of compression may not be noticeable when using lo-fi systems, however, with comparative blind tests on high-precision equipment, the problems of compression become tangible.
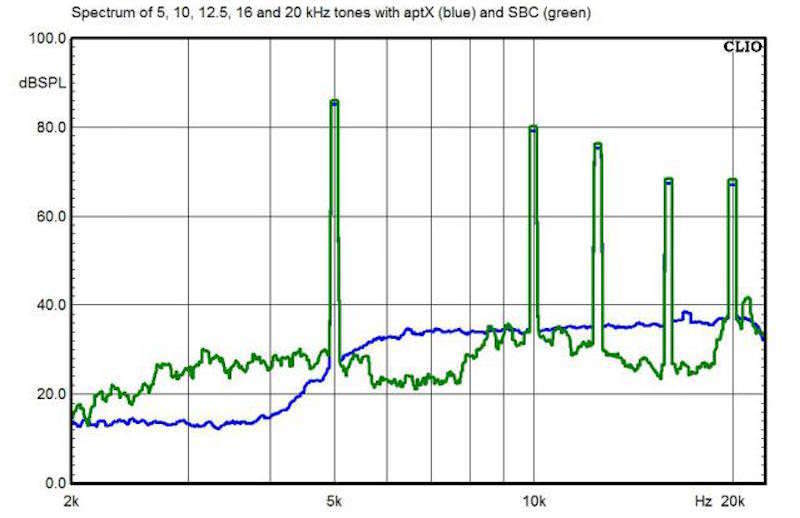
A comparison made by Brent Buttervut (by About.com) shows the difference in the noise that occurs when the tones are 5, 10, 12.5 and 20 kHz. The blue line is aptX, the green line is SBC (source)

This graph shows the spectra for a 1 kHz broadcast signal via aptX (blue) and SBC (green), and 4 kHz - aptX (magenta) and SBC (red) (source)
Another relative disadvantage of this standard is a relatively small range, not more than 9-10 meters.
Apple Inc. developed its own specification of wireless LAN network protocols. The standard naturally found application in the transmission of sound and images, and accordingly, can be used in home theater systems.

The main advantage of the specification from the “most ambitious company in the world” is sound compression without significant losses. With other things, it should be noted that the transmission of video signal using these protocols leaves much to be desired. As in the case of Qualcomm AllPlay, Apple's specification is inferior to a number of modern formats. So the standard does not allow to provide a level of quality that falls short of the requirements of panels with 2K and Ultra HD 4K resolution.
Another significant drawback of AirPlay is the calculation for a fairly narrow segment of the user audience, using products that only support Apple Inc. software (iPhone, iPad, Mac notebooks, iPod, iTunes, Apple Watch, etc.).
AVB - is a specification of industrial protocols of a wireless network of standards 802.11as, IEEE 802.1 Audio Video Bridging (AVB), IEEE 1722, IEEE 1733, developed by the AVnu Alliance.
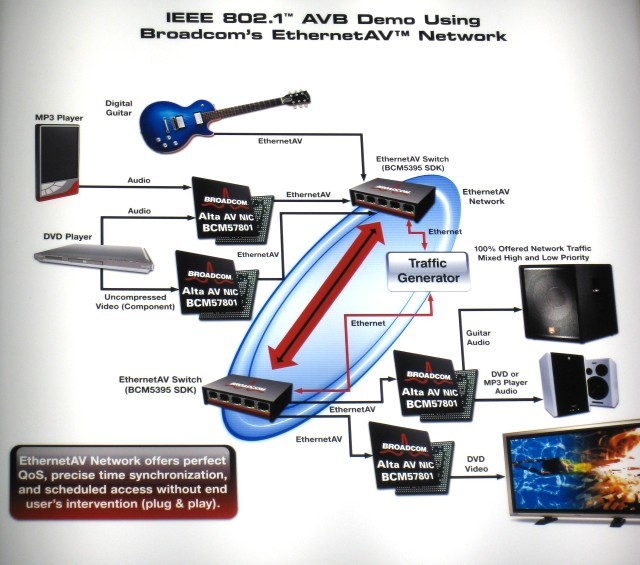
The wireless network, created by the technology of Audio Video Bridging, makes it possible to losslessly transmit audio in any audio format, broadcast streaming high-definition video. In addition to the described advantages, AVB can be integrated with any multimedia audio / video systems, home theater devices, and other equipment.

Significant disadvantages of the system include the high cost of equipment and software used to use the technology.
DLNA is a specification of network protocols that enable wired and wireless local area networks to be created and maintained by the Digital Living Network Alliance (DLNA). One of the distinguishing features of the technology is the ability to transmit data via cable or using radio.

Advantages of the standard:
Significant disadvantages of the standard include the lack of integration with Apple Inc. devices, as well as the limited range of signal transmission.
WiSA is a specification that was specifically created for home theaters by the Wireless Speaker and Audio Association.

The main advantages of the standard:
The most significant drawback of the standard is the need to integrate into each device a separate receiver and transmitter.
WirelessHD Technology is a technology that was jointly created by Intel, LG Electronics, Silicon Image, Panasonic, Philips, Samsung, Sony and Toshiba. The standard is specifically designed for use with multimedia systems and home theaters .

The technology provides wireless data transmission over the 60GHz band, while allowing lossless transmission of video data in DTV formats, including FullHD (1080p, 60 Hz). The standard also allows lossless audio transmission (including: 192 kHz stereo LPCM audio, 5: 1, 7: 1, 24-bit, 96 kHz LPCM audio, 13: 1, 24-bit, 192 kHz Dolby TrueHD or DTS-HD audio).
The disadvantages include the comparatively limited video transmission capabilities and the relatively high cost of equipment.
An interesting alternative to most existing standards was HomePlug technology. The developers decided to move away from the standard concepts of wireless transmission and decided to use the power network itself as a transmission link, thus reducing the number of switching lines.

High-frequency audio and video signals in systems with the HomePlug are transmitted via standard AC power in the form of encrypted data packets. Thus, this technology is inherently not truly wireless, but in no way inferior to existing Wireless standards.
Choosing the right standard from the existing variety is not easy, you should consider your own needs and capabilities of technology.

Personally, I sincerely hope that sooner or later there will be a unification in the field of wireless data transmission (and in particular sound). Otherwise, we risk getting into a situation that has recently been with mobile phone chargers.
For owners of home theaters, wireless speakers provide a lot of new features, but at the same time make you seriously think about choosing a standard.

On the one hand, many users want to get rid of the “kilometers” of switching problems, acquire the ability to quickly move sources, on the other - no one is willing to sacrifice the quality of sound and image.
We can not keep silent about the fact that in this area another war of formats. As practice shows, the development of standards for wireless sound systems, commercial interests of manufacturers do not contribute to the unification and creation of a single or compatible standards. The result - users are doomed to choose receivers, speakers and panels that work according to the same specification, which largely deprives of freedom of choice.

')
The most common standards today are: Wireless Local Area Networks - WLAN, Wireless Wide Area Network - WWAN, Wireless Personal Area Networks - WPAN (Bluetooth), Wireless Metropolitan Area Networks - WMAN.
Most of the home wireless multimedia systems available today use WLAN with Wi-Fi technology or WPAN with Bluetooth technology. The next step in the evolution of wireless data transmission standards are Apple AirPlay, Miracast, Play-Fi, Qualcomm AllPlay, WiSA, AVB (Audio Video Bridging), WirelessHD, DLNA (wireless transmission) standards. An alternative to wireless transmission has become the HomePlug. Also known are their own corporate development of standards for wireless transmission of sound and images, which are conducted by such companies as Sonos, Bose, Denon, Samsung.
Most users are interested in a series of questions that manufacturers usually answer evasively. The following are especially common among them:
- Does signal transmission via radio channels affect the sound quality noticeably?
- How autonomous are the modern wireless components of home theaters?
- What are the main technical advantages and disadvantages of the existing formats?
I will try to answer these and a number of other questions in this article. It should also be emphasized that everything stated in the article is valid for any wireless home audio systems, except for headphones and portable speakers.
Wireless technology with wires
First of all, it is worth noting that in the full sense of the wireless home multimedia systems at the moment is not created, because there is no technology that allows you to transmit power without wires. In cases with portable devices, this problem was solved using batteries. Probably with large stationary systems this would not be appropriate.
Signal power of the most advanced technologies such as Apple AirPlay, AVB (Audio Video Bridging) does not exceed 100 mW or 0.1 W - this clearly indicates that in the near future power will be provided using a standard home power network.
The above conclusion suggests that some of the advantages of wireless systems are offset by the lack of autonomous power, and the user will inevitably depend on the location of the sources (sockets). The logical solution may be the use of high-capacity batteries, however, statements of this kind have not yet been made by any of the manufacturers known to me.
Typical problems
Existing “wireless” standards other than HomePlug are based on data broadcast. Their differences can be divided into several groups:
- Used frequency bands;
- Transmission protocols;
- Speed and volume (channel capacity);
- Transmission range;
- Interference immunity;
One way or another, these differences in various degrees can affect quality, i.e. on the accuracy of audio and video signal transmission. I suppose you should not dwell on the fact that devices using different technologies will not work correctly with each other, even when using the same basic specification. Suppose WI-FI (a receiver using Qualcomm AllPlay is not compatible with the acoustics and the panel that use Miracast).
The following fact is essential for selection:
“The decisive condition for sound quality is not even the technology of wireless data transmission itself, but the level of interference, among others, arising from the interpenetration (layering) of radio channels from third-party sources. Interference reduces channel capacity, which can lead to significant problems. ”
An example is the use of Wireless Fidelity (Wi-Fi) for transmitting sound and image over a 20 MHz channel in the 2.4 GHz band, when adjacent rooms use “non-overlapping” Wi-Fi channels adjacent to this band. In reality, the channel width will be larger, which in such a situation will inevitably lead to interference, which will significantly affect the quality of sound and image.

Wi-Fi - the problem of the neighbor's router
On the well-known fact that Wi-Fi, today the most common specification of network protocols for wireless networks (WLAN), does not make sense in detail. I note only that the practice has proved the high demand for Wi-Fi devices, which does not detract from some of the shortcomings of the standard.

Many experts note that with all the versatility and integrative capabilities of the standard, it is of little use for high-quality sound transmission. The latter is connected with the problem of the 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz band congestion, which facilitates the occurrence of interference (protocols IEEE 802.11b, IEEE 802.11a, IEEE 802.11g, IEEE 802.11n).
To eliminate the influence of third-party devices, the Wi-Fi Alliance has been developed and certified, various specification options that extend the capabilities of traditional Wi-Fi
Kids Wi-Fi: Miracast and Qualcomm AllPlay
Miracast is a version of Wi-Fi adapted to transmit sound and images in high quality. The basis of the updated data transfer format is the specification of the IEEE 802.11ac standard (Gigabit Wi-Fi) and the WiGig technology and the Multi-gigabit point-to-wireless wireless (IEEE 802.11ad standard) developed jointly with the Wireless Gigabit Alliance.
Miracast technology provides a radio channel operating in the 60 GHz band at speeds up to 7 Gbit / s, which allows streaming video in uncompressed HD quality and high-precision multi-channel audio signal. The disadvantages include the relatively low prevalence of the standard and, accordingly, not too wide choice devices.

Another option for upgrading the Wi-Fi connection for high-quality audio is Qualcomm AllPlay. This technology is based on Qualcomm chips and is actively used by companies such as Panasonic and Altec Lansing.
The main advantages of the standard are lossless transmission of the sound, as well as integration into the multiroom. In this case, the tests demonstrate that the quality of video transmission is inferior to technologies such as DLNA, Miracast WiSA, AVB and WirelessHD.

Bluetooth - caries blue tooth
Everyone has long been aware that Bluetooth is the most common specification of Wireless Personal Area Networks network protocols - WPAN. Integration capabilities using this standard are one of its main advantages, including the transmission of sound.

If we take a closer look at the advantages of Bluetooth, we can single out the following:
- integration with most mobile devices, PCs, compatibility with all common OS, all video panels and speaker systems equipped with this technology;
- stable reliable connection;
- Connecting a large number of data channels, including multi-channel acoustics.
In this application, Bluetooth also has a number of drawbacks, the main one being the reduction in sound quality. The problem is that when using Bluetooth to transfer audio data, they are converted from source codecs (MREG, MP3, AAC, etc.) to SBC, which assumes compression with loss of information. The effect of compression may not be noticeable when using lo-fi systems, however, with comparative blind tests on high-precision equipment, the problems of compression become tangible.

A comparison made by Brent Buttervut (by About.com) shows the difference in the noise that occurs when the tones are 5, 10, 12.5 and 20 kHz. The blue line is aptX, the green line is SBC (source)

This graph shows the spectra for a 1 kHz broadcast signal via aptX (blue) and SBC (green), and 4 kHz - aptX (magenta) and SBC (red) (source)
Another relative disadvantage of this standard is a relatively small range, not more than 9-10 meters.
AirPlay Narrow Paths
Apple Inc. developed its own specification of wireless LAN network protocols. The standard naturally found application in the transmission of sound and images, and accordingly, can be used in home theater systems.

The main advantage of the specification from the “most ambitious company in the world” is sound compression without significant losses. With other things, it should be noted that the transmission of video signal using these protocols leaves much to be desired. As in the case of Qualcomm AllPlay, Apple's specification is inferior to a number of modern formats. So the standard does not allow to provide a level of quality that falls short of the requirements of panels with 2K and Ultra HD 4K resolution.
Another significant drawback of AirPlay is the calculation for a fairly narrow segment of the user audience, using products that only support Apple Inc. software (iPhone, iPad, Mac notebooks, iPod, iTunes, Apple Watch, etc.).
Audio Video Bridging (AVB) - the universal technology from the AVnu Alliance
AVB - is a specification of industrial protocols of a wireless network of standards 802.11as, IEEE 802.1 Audio Video Bridging (AVB), IEEE 1722, IEEE 1733, developed by the AVnu Alliance.

The wireless network, created by the technology of Audio Video Bridging, makes it possible to losslessly transmit audio in any audio format, broadcast streaming high-definition video. In addition to the described advantages, AVB can be integrated with any multimedia audio / video systems, home theater devices, and other equipment.

Significant disadvantages of the system include the high cost of equipment and software used to use the technology.
DLNA - with and without wire
DLNA is a specification of network protocols that enable wired and wireless local area networks to be created and maintained by the Digital Living Network Alliance (DLNA). One of the distinguishing features of the technology is the ability to transmit data via cable or using radio.

Advantages of the standard:
- integrates with any equipment of multimedia systems and home theaters (Blu-Ray-players, plasma and LCD panels, audio / video receivers, amplifiers, active speaker systems);
- the transfer of packets with audio content (all known formats) is lossless;
- provides video transmission with a quality level sufficient for full playback in Full HD, 2K in 2D and 3D formats;
- integration with Android OS devices is possible;
Significant disadvantages of the standard include the lack of integration with Apple Inc. devices, as well as the limited range of signal transmission.
WiSA - Home Cinema Standard
WiSA is a specification that was specifically created for home theaters by the Wireless Speaker and Audio Association.

The main advantages of the standard:
- the ability to work with all certified devices for home theaters;
- lossless audio transmission in any formats, in particular, multi-channel audio support (5: 1, 7: 1 systems);
- Adequate transmission of video data sufficient to fully reproduce 4K.
The most significant drawback of the standard is the need to integrate into each device a separate receiver and transmitter.
WirelessHD - collective creativity
WirelessHD Technology is a technology that was jointly created by Intel, LG Electronics, Silicon Image, Panasonic, Philips, Samsung, Sony and Toshiba. The standard is specifically designed for use with multimedia systems and home theaters .

The technology provides wireless data transmission over the 60GHz band, while allowing lossless transmission of video data in DTV formats, including FullHD (1080p, 60 Hz). The standard also allows lossless audio transmission (including: 192 kHz stereo LPCM audio, 5: 1, 7: 1, 24-bit, 96 kHz LPCM audio, 13: 1, 24-bit, 192 kHz Dolby TrueHD or DTS-HD audio).
The disadvantages include the comparatively limited video transmission capabilities and the relatively high cost of equipment.
HomePlug or Wired Wireless
An interesting alternative to most existing standards was HomePlug technology. The developers decided to move away from the standard concepts of wireless transmission and decided to use the power network itself as a transmission link, thus reducing the number of switching lines.

High-frequency audio and video signals in systems with the HomePlug are transmitted via standard AC power in the form of encrypted data packets. Thus, this technology is inherently not truly wireless, but in no way inferior to existing Wireless standards.
Total
Choosing the right standard from the existing variety is not easy, you should consider your own needs and capabilities of technology.

Personally, I sincerely hope that sooner or later there will be a unification in the field of wireless data transmission (and in particular sound). Otherwise, we risk getting into a situation that has recently been with mobile phone chargers.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/400439/
All Articles