Operation "U". How to make a facade of a skyscraper
Glazing of the first Petersburg skyscraper is a unique operation. There are at least two reasons for this. The first is the scope of work. The glazing area of the Lakhta Center Tower is 72,500 m². These are almost three Red Squares in Moscow, or ten football fields or fifteen platforms for landing the first stage of the FalX 9 mission of SpaceX ...
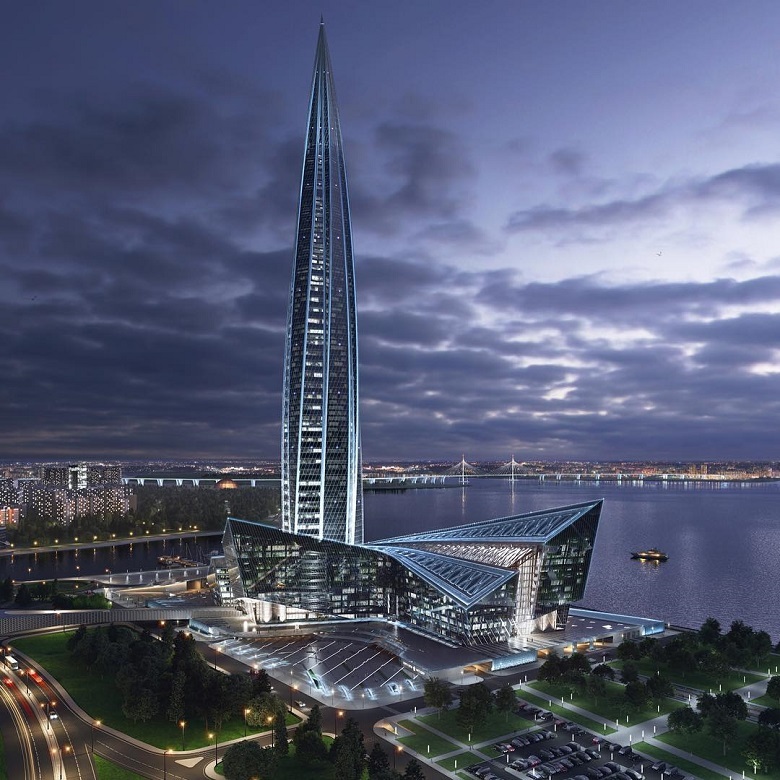

In total, the glass part of the facades of the complex (tower + MFZ) reaches 130 thousand square meters. meters Claims world record.
')
The second reason is that in addition to the impressive square, the unique shape of the tower makes it difficult. It changes on each floor - it expands, narrows and twists - every floor 0.82 degrees relative to the central axis.

This difficult geometry has given many tasks not only to designers, but also to those who directly glaze the tower. Because of the shape, most of the glass packs are slightly different from each other - it means that each has its own place.
We will learn how this glass puzzle consists of 16,505 elements + a premiere video showing how it will be washed.
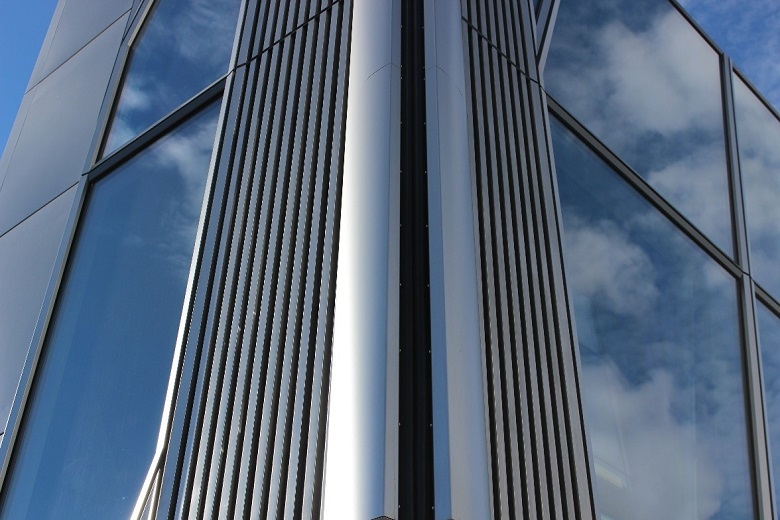
The parallelogram of the bent form acts as a facade element:
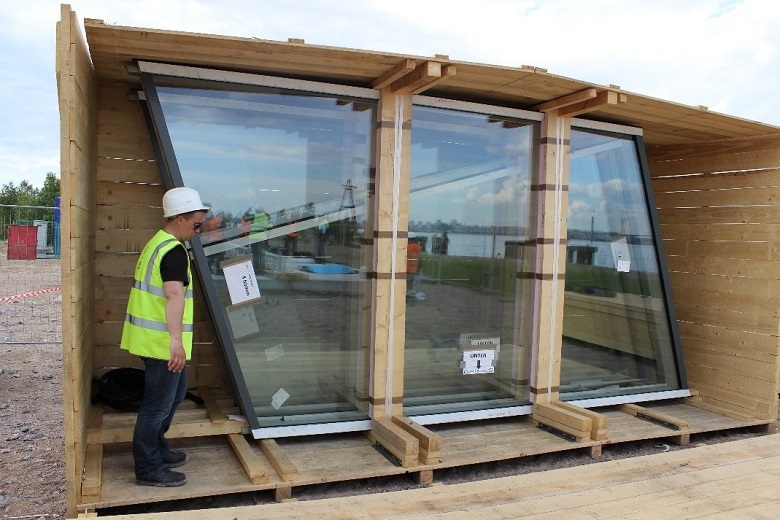

The curvature of the glass unit is needed to achieve the spiral shape of the building - the facade, as it were, flows around the tower around its axis. Simple flat glazing will give in this case the effect of "faceted glass." Cold-bent version implies a smooth monolithic surface:

A laminated bag measuring 2.8 mx 4.2 m is placed in an aluminum frame lying in a horizontal position. Under its own weight (about 780 kg), the glass packet is deformed, bending under the frame shape. Thermal effect is absent - this is the technology of "cold bending". The maximum deformation of one corner of the glass from a plane is about 40 mm.
To begin with, in Russia cold-formed glasses make. If we talk about purely Russian brands, for the time being, this is a couple of relatively small productions that do not yet have the capacity to develop a volume of 72 thousand square meters. meters But we think that they have everything ahead.
For the tower "Lakhta Center" windows are produced by Josef Gartner GmbH, for the MFZ - 4 companies at once.
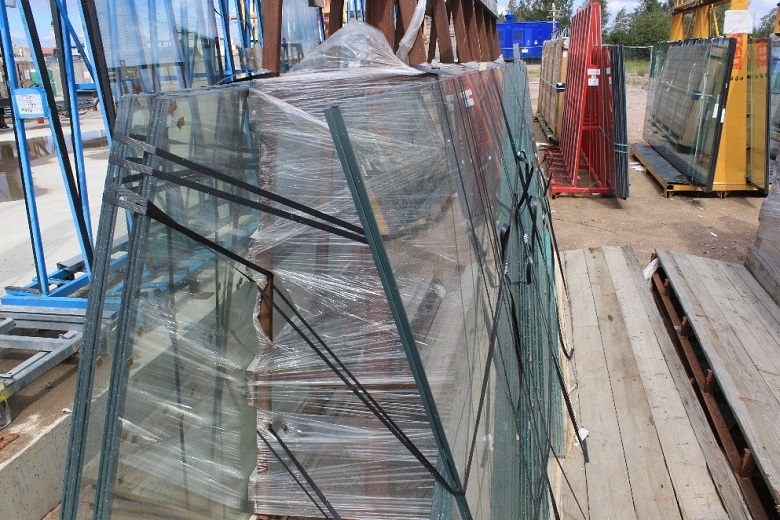

Glass samples of all four manufacturers of facades MFZ, exhibited at the site for full-scale modeling. Lakhta, Petersburg, 2016
Gartner operates in Russia - specifically for the project, the Germans opened production in Levashovo, 20 kilometers from the site. This solution is from the field of logistics: to deliver oversized and very heavy double-glazed windows from Germany is, of course, not German - non-pragmatic.
The incorrect behavior of glass in the facade means that a person somewhere made a mistake - in the calculation, or in the manufacture, or in transportation, or in the installation. Therefore, all four stages are controlled - before arrival at the site by the manufacturer, and then - by the builders. So we meet the newly arrived party of double-glazed windows not with a loaf, but with special means.
Inspectors on special technological instructions look at each glass unit - each of those tens of thousands who will be in the whole complex of Lakhta Center. A weekly report is made of the negative nuances found, if any. When the glass is redone, this is a subtle manufacturing defect, but internal bubbles or defects due to poor transportation will help to establish attentiveness and meticulousness of specialists.
The process itself looks like this:
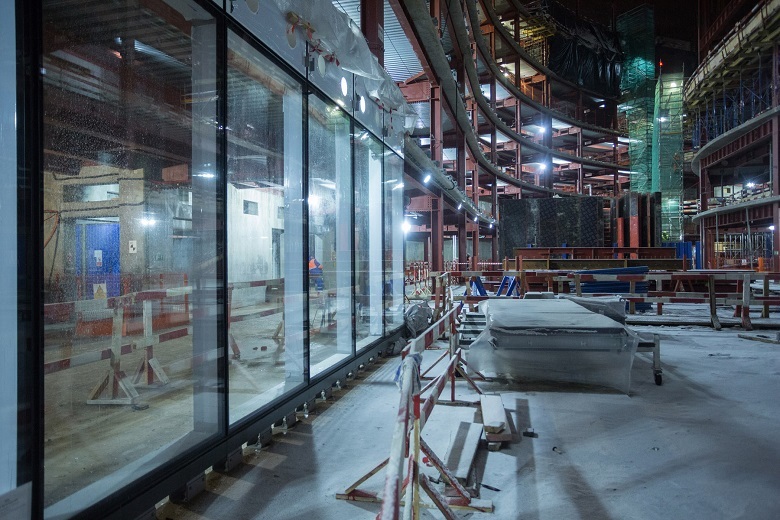
Front fastening system - mounted. Front panels (double-glazed windows in frames) are hung on brackets, and are not fixed rigidly to the bearing frame of the building.
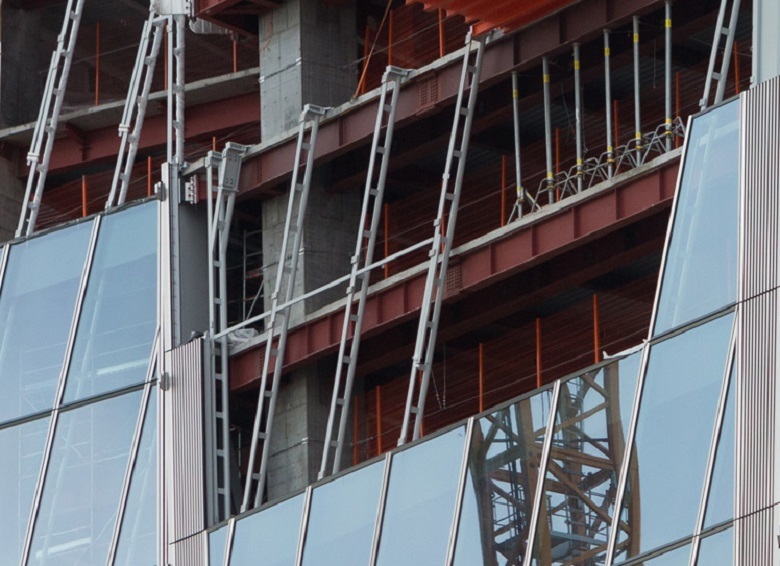

In the finished form from the inside:
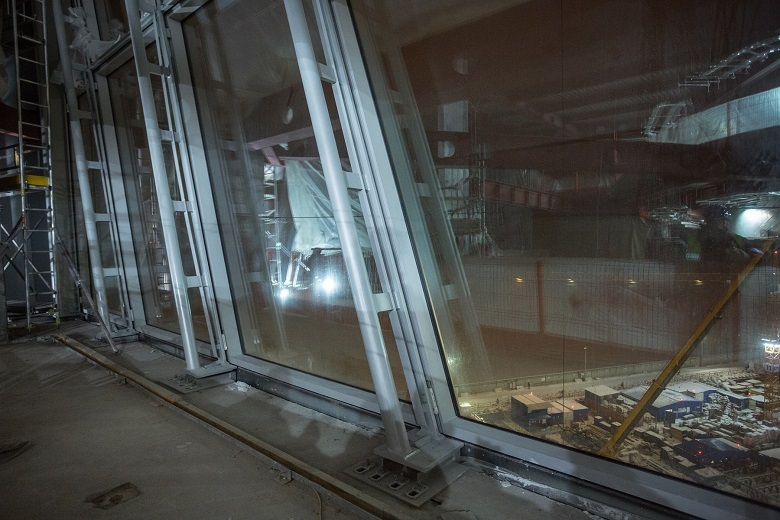

View of staples for hanging glass in the neighboring MFZ:

Row in finished form, ibid:

Due to the hinged system, it turns out that the glass envelope fits the design, but is not built into the building, while remaining somewhat independent.
The reason for choosing such an option is that the tower will be movable due to precipitation and shrinkage during construction and after the completion of all monolithic work, the impact of external facts such as wind and sun. The hinged system and the decision on the joints between the double-glazed windows give a compensating effect, making the facade independent of the vibrations of the building and the efforts arising in its structures.
Another reason is that the facade panels themselves are also moving - due to temperature differences: in the summer they expand, and in the winter they contract. The same, but less pronounced process occurs during the day. Of course, these factors required consideration in the design of the glass unit and the fastening system of the facade.
It turns out that between the joints of the glass is formed some space? And there is. Each panel around the perimeter has seals that prevent the influence of external factors on the internal climate of the building. The facade system is sealed.

There is also a space between the facade and the interfloor overlap - it is closed during subsequent works.
Glazing - "closing" type of work on the construction of the tower. Glazed levels allow you to see what the skyscraper will look like in its completed look.

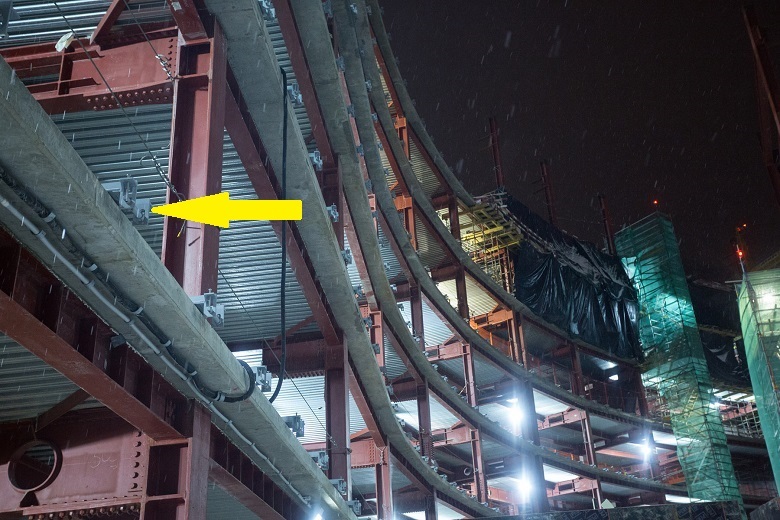
The technological gap between the glazing and the construction of a composite structure around the core of the tower is due to the convenience of placing equipment for lifting and installing double-glazed windows and the required safe distance. Protective grids are installed under the floors to be erected to prevent the fall of construction tools and materials.
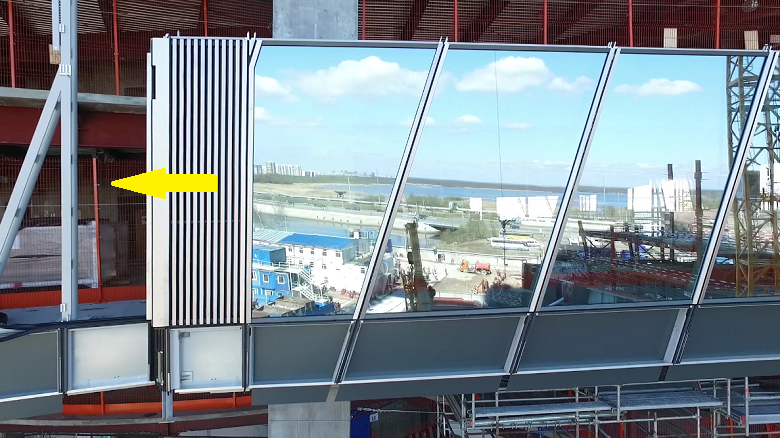
The height of the glass, as we recall, 4.2 meters. This is equivalent to the height of one floor. Front elements are hung around the perimeter of the floor. After that, the installation process goes to a higher level.
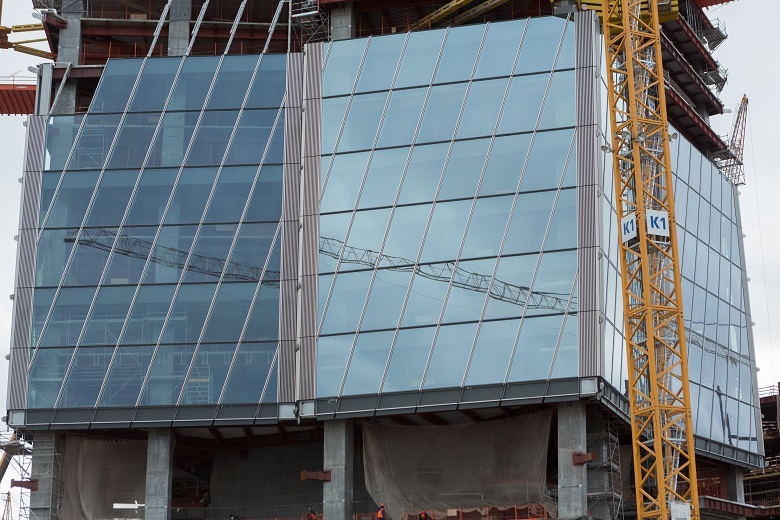

The building in horizontal section consists of five petals. In the corners, between the edges of the petals, there are double facades. The space between the "threads" of the facades - buffer zones.
Buffer zones are peculiar glazed loggias with the help of which natural ventilation is possible: on the “loggias” there are provided “air vents” - technical valves that will automatically open under certain conditions.
Buffer zones occupy two floors at a height, so the front panels are not hung on the floor slab, but on the guide frames:

Two-story buffer zone, inside view:
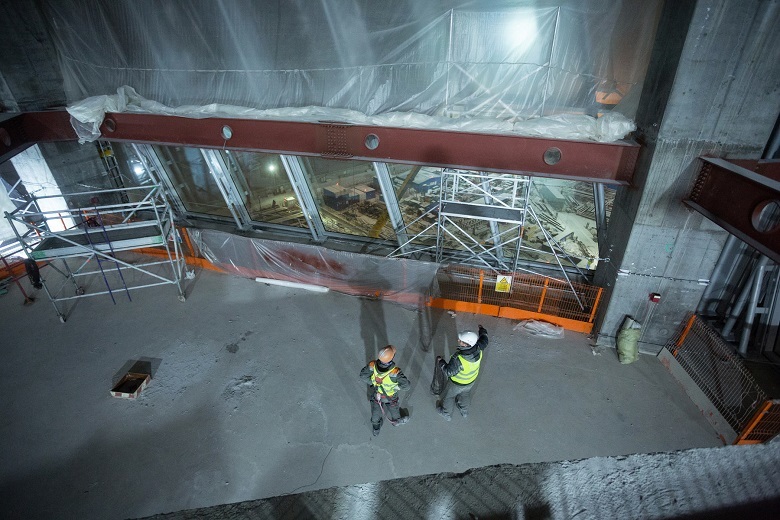

And a view of the "loggia" from the side:
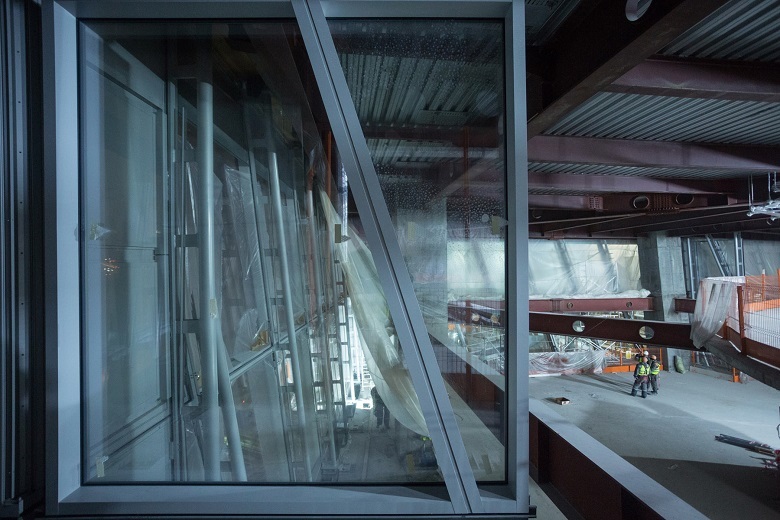

All structural elements and engineering systems of a modern building are interconnected. The facade is no exception. To clean the facade of the Lakhta Center from pollution or to replace damaged glass, use a special lift. In the ribs of the tower between the front panels, grooves are provided, and in the cradle itself - clamps with rods, which are fixed in the slots of the facade.

This mounting system allows you to completely eliminate swinging cradles at height.
This is called "SOF", a facade maintenance system. SOF was developed specifically for the tower - because of the spiral shape, there were no ready-made solutions. On the SOF, we will tell in one of the posts. For now - a video about this system. By the way, this is the premiere.
The first glass facade as an architectural element of the building appeared in Germany in 1926. Fully translucent facades for the first time in the world began to be used in the Soviet Union. The first building with facade glazing was the House of the Central European Union, built in Moscow in 1936 by the famous architect Charles Edouard Le Corbusier.

Photo of the CentroSoyuz building from the site “Moscow walks”
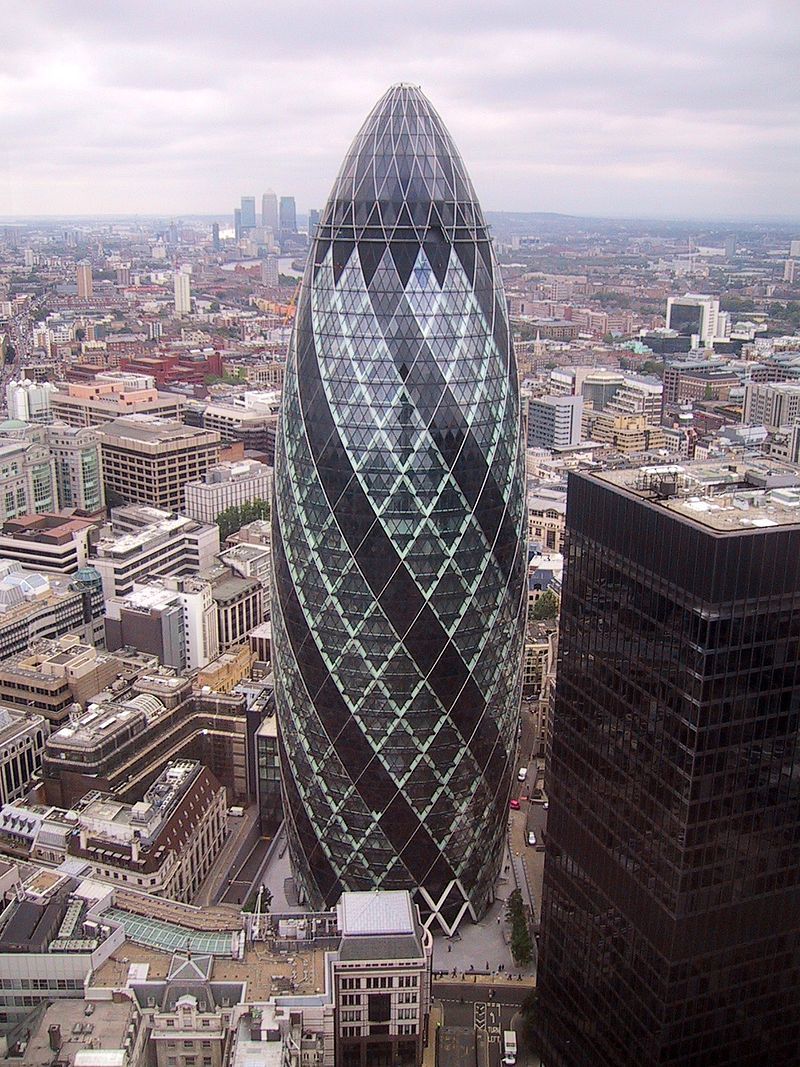
Soon this architectural innovation became very popular. At first, the mirror facades were just straight. Then, in the 1940s, curved architectural glass appeared in Western Europe. At the heart of the bending - bending process - heating the glass to a temperature of - 600 ° C, then - bending with a mold and slow cooling. From the glass made the top of the skyscraper 30 St Mary Ax - London Cucumber.

In the early 1990s, cold-rolled glass was invented. Canadian Rick Silas has managed to bend tempered glass at room temperature, while maintaining its structural integrity. Invented way Cold Bent Shattered Glass allows you to bend glass and laminated glass around virtually any existing structures.
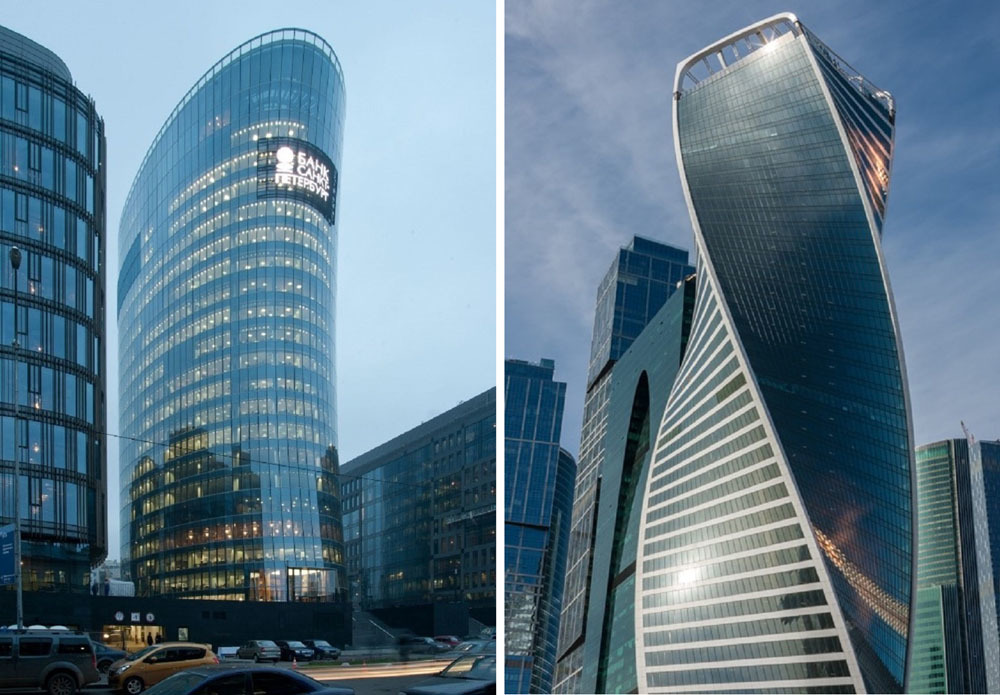
The first object from cold-formed glass in Russia was the St. Petersburg headquarters of the Bank St. Petersburg, the glass area is 20,000 m². The second is the 255-meter tower "Evolution" in Moscow City:

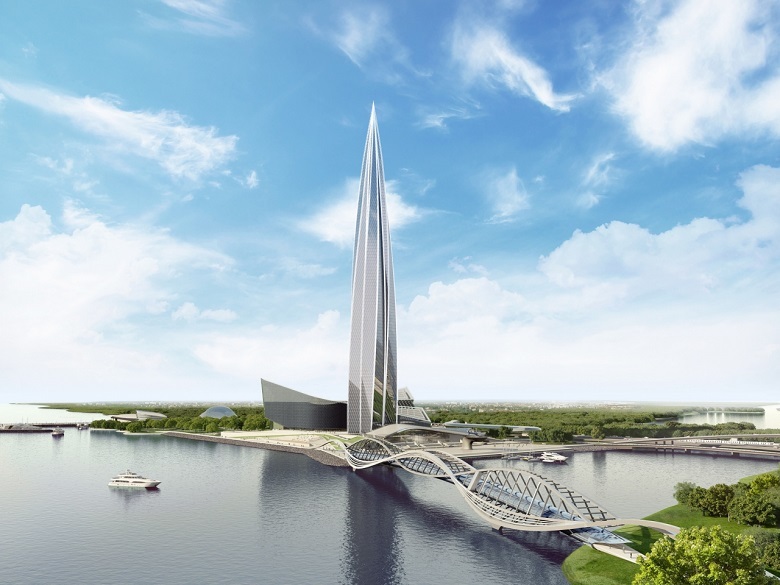
The next object is the 462-meter “Lakhta Center”, where the area of cold-formed glazing reaches up to 85% of the entire front surface of the Supertoll.


In total, the glass part of the facades of the complex (tower + MFZ) reaches 130 thousand square meters. meters Claims world record.
')
The second reason is that in addition to the impressive square, the unique shape of the tower makes it difficult. It changes on each floor - it expands, narrows and twists - every floor 0.82 degrees relative to the central axis.

This difficult geometry has given many tasks not only to designers, but also to those who directly glaze the tower. Because of the shape, most of the glass packs are slightly different from each other - it means that each has its own place.
We will learn how this glass puzzle consists of 16,505 elements + a premiere video showing how it will be washed.
Main element
The parallelogram of the bent form acts as a facade element:

The curvature of the glass unit is needed to achieve the spiral shape of the building - the facade, as it were, flows around the tower around its axis. Simple flat glazing will give in this case the effect of "faceted glass." Cold-bent version implies a smooth monolithic surface:

How to bend the glass in a "cold" way
A laminated bag measuring 2.8 mx 4.2 m is placed in an aluminum frame lying in a horizontal position. Under its own weight (about 780 kg), the glass packet is deformed, bending under the frame shape. Thermal effect is absent - this is the technology of "cold bending". The maximum deformation of one corner of the glass from a plane is about 40 mm.
Where do such glasses
To begin with, in Russia cold-formed glasses make. If we talk about purely Russian brands, for the time being, this is a couple of relatively small productions that do not yet have the capacity to develop a volume of 72 thousand square meters. meters But we think that they have everything ahead.
For the tower "Lakhta Center" windows are produced by Josef Gartner GmbH, for the MFZ - 4 companies at once.

Glass samples of all four manufacturers of facades MFZ, exhibited at the site for full-scale modeling. Lakhta, Petersburg, 2016
Gartner operates in Russia - specifically for the project, the Germans opened production in Levashovo, 20 kilometers from the site. This solution is from the field of logistics: to deliver oversized and very heavy double-glazed windows from Germany is, of course, not German - non-pragmatic.
The plant in Levashovo is the 12th, owned by the group and the first high-grade production company in Russia.
Total control
The incorrect behavior of glass in the facade means that a person somewhere made a mistake - in the calculation, or in the manufacture, or in transportation, or in the installation. Therefore, all four stages are controlled - before arrival at the site by the manufacturer, and then - by the builders. So we meet the newly arrived party of double-glazed windows not with a loaf, but with special means.
Inspectors on special technological instructions look at each glass unit - each of those tens of thousands who will be in the whole complex of Lakhta Center. A weekly report is made of the negative nuances found, if any. When the glass is redone, this is a subtle manufacturing defect, but internal bubbles or defects due to poor transportation will help to establish attentiveness and meticulousness of specialists.
Anchoring process
The process itself looks like this:
Front fastening system - mounted. Front panels (double-glazed windows in frames) are hung on brackets, and are not fixed rigidly to the bearing frame of the building.

In the finished form from the inside:

View of staples for hanging glass in the neighboring MFZ:

Row in finished form, ibid:

Due to the hinged system, it turns out that the glass envelope fits the design, but is not built into the building, while remaining somewhat independent.
The reason for choosing such an option is that the tower will be movable due to precipitation and shrinkage during construction and after the completion of all monolithic work, the impact of external facts such as wind and sun. The hinged system and the decision on the joints between the double-glazed windows give a compensating effect, making the facade independent of the vibrations of the building and the efforts arising in its structures.
Another reason is that the facade panels themselves are also moving - due to temperature differences: in the summer they expand, and in the winter they contract. The same, but less pronounced process occurs during the day. Of course, these factors required consideration in the design of the glass unit and the fastening system of the facade.
An interesting example of a building that was glazed without proper consideration of temperature fluctuations led Igor_O to discussions on the previous article. The result is sad - the glass has crumbled, even if not immediately.
It turns out that between the joints of the glass is formed some space? And there is. Each panel around the perimeter has seals that prevent the influence of external factors on the internal climate of the building. The facade system is sealed.

There is also a space between the facade and the interfloor overlap - it is closed during subsequent works.
Why not immediately glass
Glazing - "closing" type of work on the construction of the tower. Glazed levels allow you to see what the skyscraper will look like in its completed look.

The technological gap between the glazing and the construction of a composite structure around the core of the tower is due to the convenience of placing equipment for lifting and installing double-glazed windows and the required safe distance. Protective grids are installed under the floors to be erected to prevent the fall of construction tools and materials.

The height of the glass, as we recall, 4.2 meters. This is equivalent to the height of one floor. Front elements are hung around the perimeter of the floor. After that, the installation process goes to a higher level.

Buffer zones
The building in horizontal section consists of five petals. In the corners, between the edges of the petals, there are double facades. The space between the "threads" of the facades - buffer zones.

Buffer zones are peculiar glazed loggias with the help of which natural ventilation is possible: on the “loggias” there are provided “air vents” - technical valves that will automatically open under certain conditions.
Buffer zones occupy two floors at a height, so the front panels are not hung on the floor slab, but on the guide frames:

Two-story buffer zone, inside view:

And a view of the "loggia" from the side:

SOF
All structural elements and engineering systems of a modern building are interconnected. The facade is no exception. To clean the facade of the Lakhta Center from pollution or to replace damaged glass, use a special lift. In the ribs of the tower between the front panels, grooves are provided, and in the cradle itself - clamps with rods, which are fixed in the slots of the facade.

This mounting system allows you to completely eliminate swinging cradles at height.
This is called "SOF", a facade maintenance system. SOF was developed specifically for the tower - because of the spiral shape, there were no ready-made solutions. On the SOF, we will tell in one of the posts. For now - a video about this system. By the way, this is the premiere.
Glass Innovations
The first glass facade as an architectural element of the building appeared in Germany in 1926. Fully translucent facades for the first time in the world began to be used in the Soviet Union. The first building with facade glazing was the House of the Central European Union, built in Moscow in 1936 by the famous architect Charles Edouard Le Corbusier.

Photo of the CentroSoyuz building from the site “Moscow walks”
Soon this architectural innovation became very popular. At first, the mirror facades were just straight. Then, in the 1940s, curved architectural glass appeared in Western Europe. At the heart of the bending - bending process - heating the glass to a temperature of - 600 ° C, then - bending with a mold and slow cooling. From the glass made the top of the skyscraper 30 St Mary Ax - London Cucumber.
In the early 1990s, cold-rolled glass was invented. Canadian Rick Silas has managed to bend tempered glass at room temperature, while maintaining its structural integrity. Invented way Cold Bent Shattered Glass allows you to bend glass and laminated glass around virtually any existing structures.
The first object from cold-formed glass in Russia was the St. Petersburg headquarters of the Bank St. Petersburg, the glass area is 20,000 m². The second is the 255-meter tower "Evolution" in Moscow City:

The next object is the 462-meter “Lakhta Center”, where the area of cold-formed glazing reaches up to 85% of the entire front surface of the Supertoll.

Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/400345/
All Articles