Elektroovtsy ate people: the possible consequences of the development of AI for the labor market

In his next lecture in our office, the author of one of the strongest Russian chess programs, a specialist in machine learning methods and the founder of the 22century.ru portal , Sergey oulenspiegel Markov, spoke about the immediate and remote prospects of automation in various areas of the economy. And we, in turn, as always prepared a post based on the speech.
What technologies create the prerequisites for replacing people in certain professions? What specific projects of recent years are important milestones on the path to the full automation of various types of work? ConvNet, LSTM, DNC, what next? Where exactly do we run faster? Is the bionic approach alive? Hodgkin, Huxley, the giant axons of the squid - how will it be a brave new world? ..
What history teaches us: is it possible to extract some practical benefit from the search for historical analogies for the current situation? What professions are under threat now? Who is supposed to be replaced by a car in 5, 10, 20 years? What new jobs and new professions does the development of machine learning technologies create? Possible solutions to emerging problems: can this help new technologies?
')
The title of my lecture is very pretentious: the electricians ate people. Who are the electricians, you probably know. According to Philip Dick 's iconic work “Do Electrons Do Androids?” , The film “Blade Runner” was shot with Harrison Ford in the title role. It is difficult for me to assess the real significance of this work, but it was the first association that I had with the famous "sheep that ate people."
“Oh sheep, so tame and unpretentious in food. They become so greedy and rampant that they devour people, devastate and make fields, houses and cities deserted ”(Thomas More.“ Utopia ”)
In England of the 15th — 16th centuries, because of the development of weaving, sheep breeding, which supplied raw materials for the developing industry, began to bring in special profit. In order to expand the area of pastures, the landlords drove the peasants off the land, eliminating agricultural communities, and this led to very serious social problems - many people were left without means of subsistence. The government struggled with this rather inhumane, but consistent with the spirit of the time, methods. Flashing uprisings (for example, Thomas Ket’s uprising) were suppressed, punishments tightened, laws were passed against vagrants. For example, in 1495, the English Parliament adopted a statute ordering the authorities to “grab all such vagrants, loafers and suspicious people and chain them into pads, and keep them for three days and three nights on bread and water; and after these three days and three nights they set them free, ordering that they no longer appear in the city. ” The result of these measures was the reduction of the population by some estimates by 30%. For comparison, the USSR lost 15% of its population in World War II. One can imagine the scale of the catastrophe that was caused by a change in the technological structure.
It is clear that people driven from the ground joined the ranks of industrial workers in the cities. But industry did not develop quickly enough to eat up this released labor force. Therefore, about this story remained quite heavy historical memories.
At the beginning of the lecture, I picked up 24 professions, in which on the horizon of 10-20 years a noticeable reduction in the number of jobs is expected due to the arrival of modern machines using AI technologies and the latest engineering achievements. We will go over these 24 professions, and for each I will show several examples of projects aimed at reducing the need for human labor. In fact, it is worthwhile to touch upon such a topic, and you understand that there are no such professions at all 24 or even 124. For each of them, you need to make more than one slide, but at least 7-8, in order to tell more or less that going on in this area. Nevertheless, I think that after our short run you can create an impression about the scale of the processes taking place.
Accountant
Let's start alphabetically, the first letter “B” is an accountant. I don’t know whether you were thinking or not, but before the invention of electronic computers in the era of the triumphal march of the industrial revolution, there was a rather serious need for calculations. There were large companies, monopolies, trusts, which organized mass industrial production. Warships, locomotives, or airplanes that left the assembly lines of factories in the first half of the 20th century were technologically quite complex products, each of which often consisted of several thousand, or even tens of thousands of parts. Accounting and control operations were carried out inside the corporation, and quite nontrivial calculations were carried out in large volumes.
It is clear that at the beginning of the century automation came in the form of mechanical, electromechanical counting devices, tabulators (in general, mechanical devices were used for calculations before, for example, the famous Pascalina, but only at the turn of the 19th and 20th centuries they began to be used massively). But the basis of all accounting and the basis of mass computing were human teams.

On the right is a picture of people engaged in streaming calculations. At the time of the creation of the first atomic weapon models in the USSR and the USA, large working groups and complex computing technologies used in organizing the work of such groups were formed. Such people were literally called human calculators or human computers. In the book by David Alan Greer, the cover of which is on the left, you can learn more about the people-calculators and counting technologies of the time. The book is called "When the counters (computers) were people."
Often for calculations the whole conveyor was organized. Some girls who performed some kind of operation on mechanical typewriters transferred the results to the next row of girls, where the next routine calculation was carried out, and so on. Such a team was able to perform fairly complex matrix calculations. It is clear that with the advent of computers, all these people have lost their jobs. Mechanization and automation displace not the most primitive types of labor. The girls involved in computing were representatives of the educated sections of society. Despite the fact that it was quite intellectual work for its time, it fell among the first victims of computers that came to replace people.
This is happening now as the methods of collecting and processing information are improved in the same production. As paperless technologies slowly make their way, the number of accountants and other office clerks decreases. If today you are an accountant and do not have high qualifications, and perform routine operations, then, probably, somewhere in the depths of any startup, a system is already being developed, designed to replace you.
Driver
Everyone knows about these stories well enough. Top left Google Car, lower left Tesla Model S, equipped with autopilot function. On the right, a slightly less well-known story: Daimler received a license to conduct tests of automated trucks, which then with great fanfare drove a fairly long route along the roads of Nevada.

Cars move one after another at a very small distance, because the autopilot cannot fall asleep at the wheel. Due to this, a direct economic effect is immediately achieved. It turns out that when trucks follow at such a short distance, the air resistance decreases and the fuel consumption over a sufficiently large interval of the route becomes significantly lower. If this technology will find mass application, it will mean the almost complete disappearance of the driver's profession.
Captain of the ship
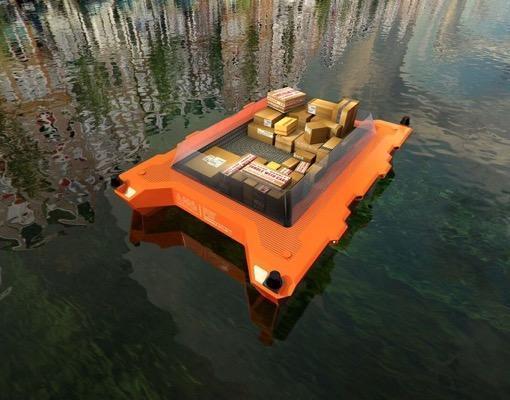

Here I am surprised only by the fact that this did not happen earlier. Technologically and technically, driving a ship is a simpler task than driving a car, due to less intensive traffic and lower speeds. Perhaps the problem was a lack of investment. There are not many cities in the world that use waterways as the main thoroughfares.
As for ocean-going dry-cargo ships, tankers and other large ships, even now the level of automation of their management is impressive. People perform supervisory functions and sometimes participate in maneuvers in the event of heavy water traffic in ports. If we compare two roughly the same size and displacement of warships - the American concept of the missile carrier of the project Arsenal (1996) and the Japanese battleship Yamato, founded in 1937, it turns out that the second team is 50 times more (2500 against 50).
A five-year program has been opened in Amsterdam, within the framework of which the possibility of creating a transport network based on automated floating facilities is being considered. To save money on a naming project, they simply called Roboat, and the saved 25 million euros decided to spend on getting a working prototype of such a boat by 2017. In a word, drivers will be replaced not only in land transport, but also in water transport.
Storekeeper
I do not know if you have heard about the practice of Amazon in this area, but this corporation is successfully introducing the eighth generation of robotic warehouses. People who are interested in warehouse technologies are well aware that there are many companies in the world that are ready to build a robotic warehouse for your needs. Even in Russia there are at least a few such companies. Amazon has one of the world's largest robotic warehouses (if not the largest at all), it employs 15,000 robots.

These are small carts with a height of only 30 cm, but capable of carrying more than 300 kg of cargo. The coordinated movement of carts is controlled by a centralized system - logistic artificial intelligence, which seeks to optimize all transport transactions inside the warehouse.
Judging by the fact that this is already the eighth generation of robotic warehouses, the technology is completely viable. The solution from Amazon is based on the startup Kiva Systems, acquired by the transnational giant for $ 775 million. However, Amazon is not enough, and now the company is actively negotiating with the government to get permission to use drones to deliver small loads over short distances. The main subject of bargaining is that, in the opinion of the government, this technology can be implemented only if the number of jobs is maintained. The sticking point is precisely the social consequences of such automation.
Cosmonaut
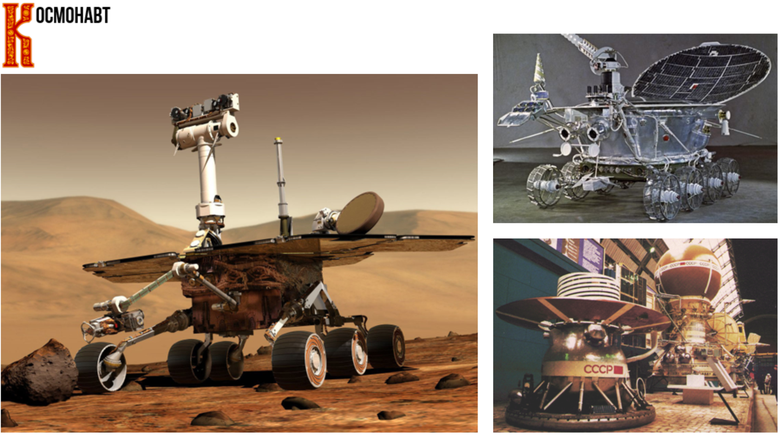
It is clear that space from the very beginning belonged to the machines, due to the complexity of working conditions in outer space, which include hard radiation, high / ultra low temperatures, lack of air and a lot of other problems. On top of that, people are not able to tolerate high overloads, which greatly limits the pace of space exploration. If you look at the statistics of manned flights, then their number has greatly decreased compared to the 70-80 years. At the moment, many experts and scientists are of the opinion that people do not need to fly into space - this is too dangerous and not too effective. From man there is little use in space in the case of a number of long reconnaissance missions.
On November 29, TASS, citing the Advanced Research Foundation, said that Russia plans to use robots in the construction and operation of planetary bases, in particular on the Moon. And in the first flight on the ship "Federation" in 2021, the robot "Fedor" will go. I think that in time, Matroskin and Sharik robots will have to join it.
Courier
When we talked about Amazon, we already mentioned the possibility of using drones for cargo delivery. Of the vivid media stories on this topic, I also recall the PR campaign of the company Dodo Pizza, during which this company demonstrated pizza delivery with the help of copters. However, Gosavinadzor quickly pointed out zealous start-ups to the wintering grounds of the river crustaceans, and the ugliness was successfully stopped. However, as you understand, this is not the only such startup in the world.

The technology of drones finds more and more wide application in many respects owing to growth of capacity of accumulators. In many Moscow hypermarkets, today it is already possible to purchase a fully functional drone with a camera for 6-7 thousand rubles. And if not a big pizza, then he definitely can lift a few pies.
DHL, like Amazon, does not want to stay in the wagon train of progress. This company already has a rather scary cart that carries parcels. More conservative Germans decided not to mess with the drones and trust the old proven wheels.
Pilot

Uber has announced a serious program to create aerotaks VTOL. This is a vertical take-off device, in fact, a load-lifting drone. It is curious that the car is completely unmanned, and it is not entirely clear what will happen to pilots who are engaged in passenger transportation over short distances.
Health worker

I like this picture very much, at least because Japanese designers always have a chance to subtly roll. However, despite the humorous performance, the project is designed to solve a rather important for Japan problem associated with an acute shortage of nurses. The creators of RoBear set themselves the task of creating a special robot that will help care for partially or fully immobilized patients. The car was taught to carefully carry a person on mechanical arms, including the stairs. The robot is equipped with a variety of sensors that help ensure the careful treatment of patients. With the release of each new model, the robot becomes lighter, the last model weighs 140 kg (the weight of the previous one was about 200). In the coming years, such mechanical assistants will be used where there is a shortage of medical personnel, but as technology improves and becomes cheaper, they are likely to find wider application. Robots do not ask to eat, do not arrange strikes, do not talk too much: in short, from a business point of view, they have many advantages over humans.
Call center operator

I must confess that one of the working groups working under my command is developing such a system. The first pilot projects in this direction will be launched as early as the beginning of 2017, and by the middle of 2018 we expect AI to be able to achieve work efficiency comparable to the average operator of a highly specialized banking call center. Of course, this does not mean that half of the operators will immediately replace the machines, but definitely the focus of personnel policy will shift from hiring low-skilled operators, essentially performing mechanical work, to hiring intellectual employees who are able to operate effectively in non-standard situations.
At the moment, the entire technology stack already exists in the industry to replace the operator of a specialized contact center, I’ll tell you about them a little later, so that it is clearer why we are seriously considering a project to create such a system and do not believe that any significant technological risks.
Cook
Today in the world there are quite a lot of fun projects to automate the work of a cook. The picture below shows an anthropomorphic machine, but more often such projects are limited to a set of robot hoovers, like, say, in the project “Automated Kitchen” by Moley Robotics. Using the rail system to move various elements of the automated kitchen complex, you can also replace the waiters, as is done in the Baggers restaurant (Nuremberg, Germany). In the next 10–20 years, robots, apparently, robots will be able to replace people when performing virtually any routine operations in the kitchen, completely displacing people from this area.
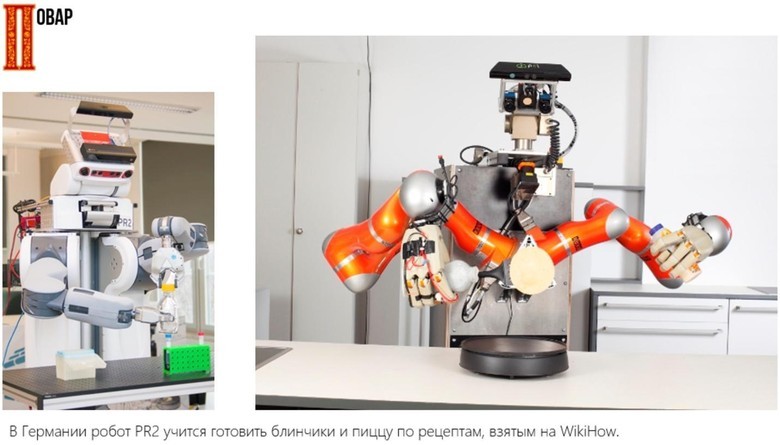

Because of the expensive labor, Japan is one of the pioneers in this field of automation. In 1977, Minoru Ikishima (Minoru Ikishima), the owner of a network of sushi bars, began a project to create the world's first sushi robot - machines for automating sushi production. Created three years later, the working prototype created a real sensation. The number of people willing to buy sushi-robot in only one region of Japan was in the hundreds. This prompted the enterprising Japanese to think about opening a separate business for the production and supply of equipment for sushi bars and sushi restaurants. Currently, Japan accounts for about 70-80% of sushi-robots sales. Such devices are used in Russia.
The advantages of automatic chefs are obvious: strict adherence to recipes and technology, guaranteed the absence of direct contact with human hands, increased productivity, the possibility of combining the cooking process with automated packaging and delivery processes.
Politician
Is it possible to automate the work of the policy? I think that it is possible, only politicians are likely to resist the longest. In one of the latest episodes of the Black Mirror, a dystopic world was drawn, in which money was replaced by evaluations that people put to each other, and on the basis of which a certain rating is formed, determining the level of human access to public goods. If you want to rent a car - a good car for rent only for those who have a rating of more than 4. If you have a low rating, they give you a wreck with an outdated charging interface.

A terrible world in its own way, in which, however, the possibilities of a democratic system for collecting feedback from the population are brought to its logical absolute. Already, direct democracy in society is technically feasible, it has all the necessary tools: interfaces, data storage and transmission systems, cryptographic schemes that allow you to organize an honest vote.
And then a quite logical question arises: why is this not being implemented? The fears of the power elites, in my opinion, in this case lie in the fact that if democracy really works as it is described by the ideal model from a school textbook, then it will not seem to anyone: what solutions can be made by people who have not got access to quality education, not having sufficient completeness and quality of information, brought up by poverty and the street? What we now consider democracy, in terms of its formal characteristics, is rather an oligarchy: the media are controlled by big business, and political processes are influenced by lobbying certain laws. The overwhelming majority of members of society in democratic countries participate nominally in the voting procedure, but in reality people's opinions are largely determined by the parameters of the information flows coming to them, which are not determined by democratic means. Moreover, if in the sphere of politics, decision-making in developed countries is at least nominally carried out as a result of democratic procedures, then in the sphere of economic decisions they represent poorly controlled arbitrariness of owners of large companies, most of whom have been granted the right to make such decisions based on the right of inheritance.
“There are many truths, but only one truth:
Stamped recognized truth.
She's getting ready
From dirty linen
Under the watchful eye of the state
For all needs
And tastes and brains.
It is usually served with coffee.
Printed on fresh sheets,
She is swallowed hastily in trams
And every shot in the morning
For the whole day has convictions
And political views:
Can argue
Make noise in the gathering and vote. "
Maximilian Voloshin. "Ways of Cain"
Representatives of technical intelligentsia who are skeptical about both the competence of business owners and the ability of large sections of the population to make really smart decisions often support the idea of meritocracy. Why not test people for the knowledge they need to make qualified decisions? Let us assume that we will assume that the voice of an uneducated person has less weight during voting than the voice of an educated person. Or we will make it so that experts in some field will have more weight when making decisions in their field, and so on. Behind such schemes there are always various fears that a sufficiently educated person cannot be voiced out loud, because democracy is one of the fundamental declared values of the first world. In my opinion, the root of the problem with democracy is precisely how access to knowledge and education in the world is organized. How much does our society spend on the upbringing and education of the younger generation? Why, instead of schools and institutions, we prefer to spend resources on a huge military, police and ideological suppression apparatus, designed to deal with the consequences of hunger, darkness and illiteracy? Many modern researchers believe that the problems described can be completely overcome using the resources of direct democracy. Researchers such as Paul Kokshott and Allyn Cottrell from the University of Glasgow in the early 1990s in their book Towards New Socialism examined the possibilities of changing our society based on the opportunities offered by the progress of new information technologies.
Seller
With auto sales, I think everyone has already encountered. In addition to the vending machines installed now on almost every corner, many fully automated supermarkets have been launched. Such stores have long ceased to be a wonder in Europe, where there are already quite a few of them, the first such trading enterprises are opening in Russia. For example, Auchan opened the first automated supermarket in Kaluga back in 2009.

There are several possible automation models of the supermarket. This is also a simple self-checkout when you pay for purchases at the exit using a special terminal. It is clear that with such a scheme, a staff of warders-guards is still needed. Their number largely depends on the level of social responsibility of the population. In the end, in our Soviet past, there were already “automatic conductors”, simple devices that allow a passenger to unwind tickets on their own, then putting the appropriate amount of money into the money receiver. I think that such a scheme in retail looks too fantastic at the moment, but equipped with some reasonable combination of automated and manual control may well give rise to working business models. The Amazon Go experimental store in Seattle performs automatic tracking of goods using QR tags - placing the goods in the cart, returning it to the shelf, exit for payment in the cash zone. Replication of the project is scheduled to begin in four years.
There is another scheme - a self-moving trolley for the buyer, equipped with a payment terminal. An ordinary online store is also, in fact, a type of trading automation, the share of online purchases has increased significantly over the past decade.
Industrial worker
I have an interesting video on this subject: this is how KIA cars are already doing today.
There are a lot of commercials on Youtube with different industrial automations, their number is infinite. You can google, robotic lathe, all sorts of robotic lathe-milling machines - these are very beautiful machines that do absolutely unimaginable things. In the manufacturing sector, machines have long and confidently crowded people, leaving them only the functions of development, adjustment and maintenance.
Service worker

As long as we still need people in the factories, we will need robots that can safely work alongside these people, so-called collaborative robots. The most famous example of such a robot today is Baxter, created by Rethink Robotics. Now the new company Tend.ai has developed a roboruku, to which you can attach a regular webcam. It is assumed that roboruka facilitate the process of working with many 3D-printers. « », 3D- . Tend.ai — , «» , . , , , , .
, . , , . , , , — .

- , , , , , 10 . , « , », .
-
, , . , , . , , , , , . , .

Roxy 2010 . . 2010 - 4000 . , . . , , , . , - , .
1 . .
Soldier
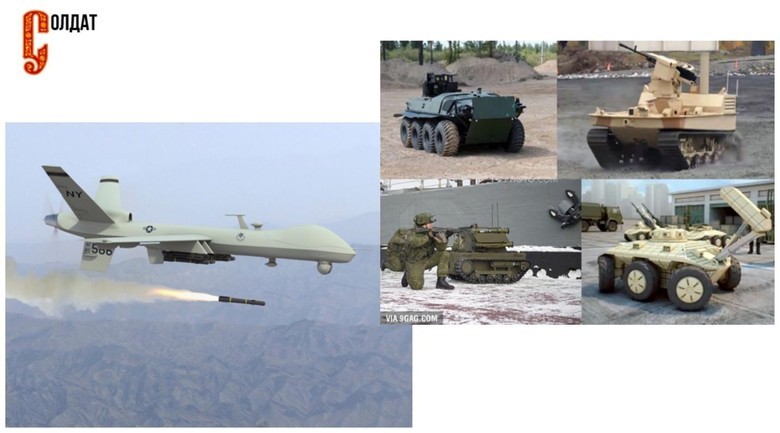

, . , , (, ). — «-9», . YouTube:
:
, , . . 1929 , . , - — , , . ? - , , . . . , , , , , . , . .
, , . , .
Youtube. Doom, . .
, , :
SMM
, . , , , . , , - - , , - . , , , , . , , , - , .
. : - , LSTM-. , , , , . 90% , - .
, , , . , , -SMM-, -, - , .
Sportsman
. , , , . , , . , , 10—20 , . 2—3 , , , , . , . , - 30—40 , , . , , , , , .
, . , c 1993 RoboCup — -. RoboCup — , . «Robot Soccer World Cup» ( ). , , , , .. :
2000- , . , Dog Fight, — .

, ( ), , . , , — . , — , , . , ? , . , 10—20% ? ? ?
Building

, , — outdoor-. 2014 , WinSun , 24 . : 2016 Beijing HuaShang Tengda Industry and Trade. : 3D- 400 ² 45 .
Beijing HuaShang Tengda Industry and Trade , WinSun, 3D- . WinSun , , .
HuaShang Tengda 3D-. , ( ) (. ).
If you look at the structure of the employment market in Moscow, then the share of people employed in the area designated in official statistics as “real estate transactions, rent and provision of services” amounts to about 18% of the economically active population in 2000–2014, second only to people engaged in retail. In the intermediary economy of 1990–2000s, very long trade chains were built between the manufacturer of a commodity (or the builder, the importer) and its consumer. In some transactions, this figure reached 4-5, or even 6 links.

Those who are not involved in the trade sphere rarely think that online trading has revolutionized the world over. There were large aggregator platforms, which removed a significant part of intermediaries from trade chains. If 15 years ago you went to a real estate agency so that you could find a housing option, now almost every web user is accessing the services of relevant online services. The Internet has largely eliminated informational fragmentation in the retail and rental of real estate, which is currently putting enormous pressure on the labor market in these areas.
Cleaner
When Michio Kaku spoke in Russia in 2012, he said, among other things, that if you are a garbage man, then your work machine is not too threatened. Because this is a job that is difficult to automate, and not too highly paid, so robots will not come there very soon.
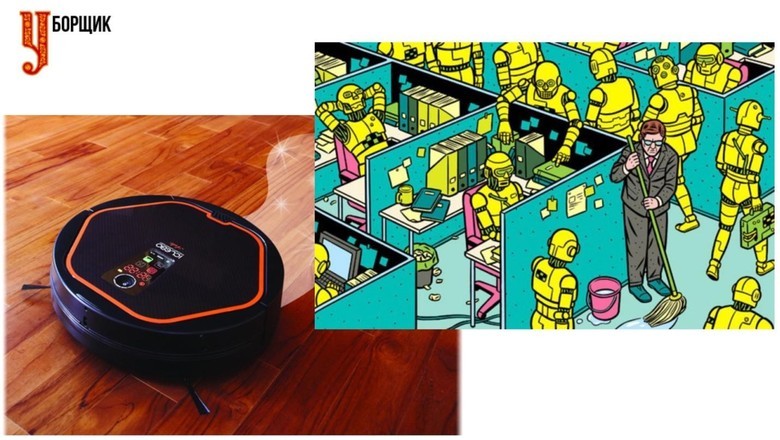

This is true if we are talking about scavengers who clean objects that are nontrivially configured in space. But there is a huge amount of routine operations that can be automated now. All the same there will be people who will clear any difficult designs. But if earlier cleaning of the office required 20 cleaners, now there will be enough 10 or 15 due to the fact that floor-cleaning machines and vacuum cleaning robots can take over.
Teacher
In the autumn of 2016, a robot teacher (mobirobot), developed at Tomsk Polytechnic University, entered the “pedagogical practice”. The first platform for practical tests of the robot was the lyceum at the university.
During the tests, young scientists and educators will appreciate how the robot fits into the learning process, whether the students will be interested in his lessons and whether the teachers understand the interface of the electronic assistant. Regarding the latter, the developers are calm: previously, teachers from Tomsk schools helped them in adapting the management system for people of different ages and levels of training, and the methods of conducting lessons with the help of a robot were fully developed by teachers of the Lyceum at TPU.
It is planned that mobirobot will read theoretical courses in lessons, as well as conduct online testing and substantive practice.
In training, they traditionally try to use some kind of automation or telepresence tools. But if you think about it, then, say, Coursera and other online learning systems are much more powerful tools for automation. If at the end of the 90s the projects of individual universities for remote education were peculiar curiosities, now we all use online courses. Now one specialist can train a much larger number of people than he could, teaching in the institute classroom, even in a large one. And despite the fact that some innovative technologies come to the learning process in schools and universities throughout the world, online learning is the most serious threat to the labor market in this area.
Of course, the needs of our society for educated specialists are much higher than the current education system provides, but many states are striving at all costs to reduce budget expenditures on education, reducing the number of free places in universities, saving teachers ’salaries and other expenses on the educational process, therefore pressure on the labor market from online education cannot be underestimated.

Surgeon
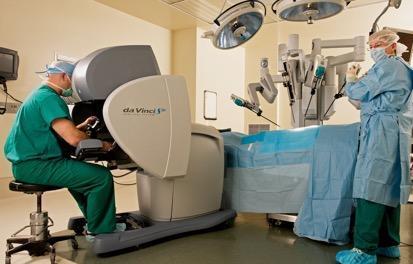
This is the da Vinci robot. More precisely, not quite a robot, but a robot-assisted surgical system “da Vinci” - an apparatus for performing surgical operations. Produced in series by Intuitive Surgical. Used in several hundred clinics around the world.
The mass of the device is half a ton. It consists of two blocks, the first is intended for the surgeon-operator, and the second - the four-armed robotic arm - is the actuating device. In 2012, the global number of operations performed using the da Vinci system was about 200 thousand. The US clinics as of July 2014 had 2,153 “da Vinci” systems, in Russia twenty-five similar surgical systems were installed.
Initially, “da Vinci” was developed for the needs of the army, and then came to the civilian sector. The accuracy of some system manipulations comes to single cell layers. To date, the removal of a cancerous tumor (not too neglected) on Da Vinci is as follows: the machine cuts off one layer of cells, immediately performs a biopsy, and if there are no cancer cells in the sample, then it cuts off a couple more layers for reliability. Even in the case of a fairly complex tumor, the robot very precisely draws the line between the affected tissue and the healthy one. Naturally, this greatly increased the survival rate for some types of cancer.
The introduction of robotic systems in surgery is unlikely to lead to the displacement of skilled surgeons. It is rather an effective tool that needs a qualified operator. While only some of the operations are robotic. But if earlier, 7-8 surgeon assistants were needed to carry out operations, then with the help of such a machine, two people cope with a rather complicated operation.
To a greater extent, the labor market in the medical field is threatened by automated diagnostic systems. According to analyst consulting company Frost & Sullivan Singh Buttar (Singh Buttar) "By 2025, the system of artificial intelligence penetrated into all areas of health care, until the creation of digital assistants, answering all questions of patients and independently engaged in their treatment."
The market of highly intelligent medical solutions today amounts to about $ 1 billion. In accordance with the data of Frost & Sullivan experts, by 2021 these figures are expected to reach $ 6 billion with an annual growth of about 40%. It is separately noted that with each passing year the role of artificial intelligence in medicine will only increase.
The main supplier of intelligent diagnostic medicine solutions today is IBM, the creator of the Watson supercomputer expert system. Considering that more than 700,000 scientific articles are published in the world every year, the effective development of diagnostics without the use of AI becomes simply impossible.
In 2015, Watson IBM acquired about 30 billion different medical images for training. Also, the training array is likely to add about 50 million anonymous electronic medical records that IBM received after purchasing startup Explorys.
One of Watson’s most famous medical applications is the Watson for Oncology project. According to such an indicator as the accuracy of optimal treatment in diagnosed lung cancer, Watson with a value of 90% has long bypassed the average level for US medicine by 50%. In this case, the treatment method can be adjusted in real time. Having introduced the information on the patient's condition change from a mobile device, the doctor will receive from Watson a refined diagnosis with an updated course of treatment within 30 seconds.
A bit of healthy humor and self-irony
Some of the technologies mentioned above so far resemble this small fragment from the magnificent movie “New Times” with Charlie Chaplin in the lead role. Many modern IT and technology startups are not far from the shown machine for feeding workers without interrupting production. And yet, technology is rapidly changing our world, despite our, perhaps, sometimes a little over-enthusiasm for them.
Technology
What technologies are at the heart of this movement? What happened in the technological world that moves these processes forward? Here is a small list of innovations claiming to make a significant contribution to the development of technology over the past two years.
American engineers have equipped the robot with a new type of touch sensor - thanks to it, the machine was able to grab the USB cable that hung in the air and insert it into the USB port, according to the Massachusetts Institute of Technology website. The new sensor was demonstrated at the International Conference on Smart Robots and Systems, which was held September 14-18, 2014 in Chicago.
Engineers from the Massachusetts Institute of Technology announced the commercialization of a project to create a lithium-metal battery, the energy density of which is twice that of the lithium-ion battery. This is reported on the website of the institution. In fact, this means that on a single battery charge, electric cars of the near future will be able to travel a distance exceeding the mileage from one refueling of almost any modern car with an internal combustion engine. You should also expect the emergence of automated electric aircraft for transporting people and goods of medium weight.
In October 2016, the Microsoft Artificial Intelligence and Research team at Microsoft announced the creation of a speech recognition system that makes the same or even fewer mistakes than people who professionally do this work. Researchers reported that the word error rate (word error rate) decreased to 5.9% compared with 6.3%, the result reported last month. In fact, advances in specialized neural network architectures, such as, for example, LSTM, convolutional neural networks, have significantly enhanced the ability of machines to understand and process both human speech and a wide range of visual images. Another progressive model that emerged at the border of neural networks and conventional computational methods is the neural Turing machine (NTM), a machine learning algorithm capable of reconstructing the transformation algorithm based on the analysis of input and output data. The development of this model by a division of Google - the company DeepMind - was named the Differential Neural Computer (DNC). The demonstration of the work of DNC was a small project, during which the model’s ability to independently learn how to use the London Underground routes effectively was shown.
Google has completely translated the Google Translate service into deep learning. According to Google's preliminary estimates, the neural network provides much better translation quality than conventional statistical methods. It has already been tested in the most difficult language pair - Chinese, and the neural network immediately reduced the number of translation errors by 60%. In short, in the field of machine learning and neural networks, small revolutions occur almost every month, and so far this area of technology is at the stage of exponential growth.

What does all this lead to? What are the estimates that give experts? After 30 years, robots will be able to do practically everything that humans can do, such a prediction was given by Moshe Vardi, a professor of computational engineering and director of the Institute of Information Technology Ken Kennedy Kennedy Institute for Information Technology at William Marsh Rice University). This will lead to the fact that more than 50% of the inhabitants of the Earth will become unemployed.
“We are approaching the time when cars will surpass people in almost any business,” said Vardi. - I believe that society needs to face this problem before it rises to its full height. If the machines will be able to do almost everything that people can do, what will they have to do? ”
Vardi made this statement at the annual meeting of the American Association for the Advancement of Science, presenting the report "Smart Robots and Their Impact on Society."
What social consequences will lead to so many significant changes in the labor market? At the time, Jonathan Swift, having listened to the speeches of his contemporary elite, wrote a very caustic essay, which was called “A Modest Proposal” (completely: “A modest sentence, designed to prevent poor children in Ireland from being their parents or their homeland, and on the contrary, to make them useful to society. ") A very trolly pamphlet explained in detail how to use the children of the poor for the benefit of society.
“One very educated American whom I met in London assured me that a small healthy one-year-old baby, for whom there was proper care, was a highly delicious, nutritious and healthy food, regardless of whether it was cooked in stew , fried, baked or boiled. I have no doubt that it will also perfectly suit fricassee or stew. ”
In a word, the author proposes to sell the children of the poor as a delicacy for the table of representatives of the class to which the author belongs. The following are recipes for preparing babies for food and costing, proving the economic benefits of implementing such a proposal. As a negative side effect, the author foresees the elimination of Ireland, but rejects other options for solving the problem on the run because of their inefficiency.
Indeed, are there any real alternatives? First, if you look closely at our economy, and you always need to look at it to a certain extent as the murder story, then you need to ask the same question that the detective who is investigating the crime always asks: qui prodest? Who benefits? Who is the main beneficiary of all this technological history? The main beneficiaries are large technological corporations, because it is their profits that grow thanks to these processes. And the position taken by the left is such that these super-profits must at least partially be withdrawn and spent on compensation for the negative social consequences that accompany the development of technology in our society. As one of the possibilities, the introduction of unconditional basic income is considered, when each member of society is paid some fixed amount of money, regardless of whether the person has a job or what his level of income is. The first pan-European survey conducted in April 2016 showed that 64% of EU residents would support the introduction of unconditional basic income, 35% are aware of the concept itself, 23% say they fully understand the essence and objectives of this program, a quarter have heard of it, 17 % do not know anything about it. Only 4% of citizens after the introduction of unconditional basic income refuse to work. The most convincing advantages of this model are people who believe that such social payments “reduce anxiety about basic financial needs” (40%) and help ensure equal opportunities for people (31%). Interestingly, the idea of unconditional income was born about Swift’s time in the works of Thomas Paine and the Marquis de Condrose.
However, for obvious mathematical reasons, unconditional income cannot stop the property stratification in society. It is extremely difficult to achieve a balance between the situation when taxes collected from corporations for making payments will not be large enough to prevent uncontrolled growth of corporate wealth and power, and a situation where too high a level of taxation will suppress corporations from any opportunity to develop and implement innovations.
With the development of technology, the question is generally not very simple, their development is based on the progress of fundamental science, and it is not corporations that do basic science. Corporations are mainly engaged in the industrial implementation of what was invented in an academic environment. Most of the fundamental innovations are being made today in the non-profit sector, be it state science or, for example, if you look at the USA (the largest universities in the Ivy League), non-profit organizations.
Corporations, no matter how large they are, simply do not have enough “long” money for the development of some technologies. The development of new technological areas is a very serious venture with extremely high risks and a long payback period. Classic example: space exploration. What the state space program did in the USSR and the USA in the late 50s - early 60s is still an unattainable bar for private corporations, despite the enormous technological progress that has occurred over the past half century. And the reasons here are mostly purely financial.
, , , , . , , . , , , , . , . , , .
. , , . . , , . 4—5 , , . , .
— , . , , , , , , . . , , , . , , — ! — , 90- , . , 10 .
Conclusion
, . , , . . , .
? , , . , Deus Ex, . () , , , , , … , . , , , , , , . .
, , - , ? ? ? , ? , , , , , ? , , , . . , , , , , .
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/399899/
All Articles