Perspective communication technologies: trucks with data, Qudit and a network of cars

According to Cisco, by the beginning of 2017, 1.1 zettabytes (10 21 ) of data will be transmitted worldwide. By 2020, there will be 5.5 billion mobile subscribers in the world, and the volume of mobile data traffic alone will be 366.8 exabytes (10 18 ). Another 38.1 exabytes will add open Wi-Fi access points. Traffic does not always grow for "natural" reasons. Before the introduction of the law, Spring operators considered that in three years the amount of stored information on telephone conversations would reach a value of 1.35 exabytes and 156 exabytes of information about Internet traffic.
Cisco Systems calculated that from 2014 to 2020 the number of things connected to the Internet in the world will increase from 12.1 billion to 50 billion. By the way, such a rapid growth of the Internet of things causes a long-known problem: by the end of 2016, the transition to IPv6 in everything the world was just under 20%.
')
All data needs to be stored somewhere, but the real difficulties begin when it comes to the transfer of information. The existing communication technologies do not adequately transmit big data between a large number of sources “on the fly”. Obviously, standards and technologies are needed to solve key communication problems.
Very large data feeds

A source
Predicting the future is difficult and risky, especially in the IT industry, due to exponential changes in technology. However, now among technological leaders, there is agreement in understanding the basic trends of computerization for 5–7 years ahead. We understand that communication becomes seamless and ubiquitous, and the transfer of data from one device to another is inconspicuous and continuous. Communication of the future will work "on top" of any physical network, regardless of its device or location.
As traffic grows (and the number of connections between the exchanging data devices), the need to optimize existing communication channels and build new ones increases. In 2016, a consortium of 6 companies laid a 60 Tbit / s cable across the Pacific Ocean (for comparison, in 2015 the throughput of all international communication channels was 180 Tbit / s ). The cable is designed for 25 years and will be upgraded during the entire lifetime. And in 2017 it is planned to carry out the transatlantic cable MAREA - its capacity will be already 160 Tbit / s.
Taking into account the news about records on the transmission speed of information on optical fiber, trunk cables with high bandwidth become incredibly relevant. Back in 2009, by multiplexing 155 channels of 100 Gbit / s, it was possible to transmit a signal at a speed of 15.5 Tbit / s over a distance of 7000 kilometers, but the technology was difficult to implement in practice. Recently, Nokia Bell Labs and Alcatel-Lucent Submarine Networks (this is the world's largest submarine cable operator, which is now part of Nokia) said that they were able to achieve a record speed of 65 Tbit / s over single-mode fiber with a length of more than 6,600 km. They used the Probabilistic Constellation Shaping (PCS) modulation technology, which increases the range of data transmission, as well as the capacity of the channels in the already existing fiber-optic networks. PCS uses non-uniform signaling, reducing the number of high-power signals, which increases resistance to interference and allows better dynamic adaptation to variable transmission conditions.
The development of backbone communication channels and the new Nokia technology in the near future will help to cope with the main problems of increasing traffic volumes, but now they are trying to use other approaches, head-on. Amazon introduced the AWS Snowmobile truck to transport up to 100 petabytes (10 15 ) of data encrypted with a 256-bit key. It is capable of transmitting data at a speed of 1 Tbit / s via cable and high-speed switch. The advantages of the truck are obvious: to transfer one exabyte of data on the Internet will take more than 26 years when connected at a speed of 10 Gbit / s — one of the fastest wired connections. But even if you use the data channel at 100 Gbit / s, the trucks will still cope faster - they will pump the exabyte in about six months.
Distributed and secure blockchain
A source
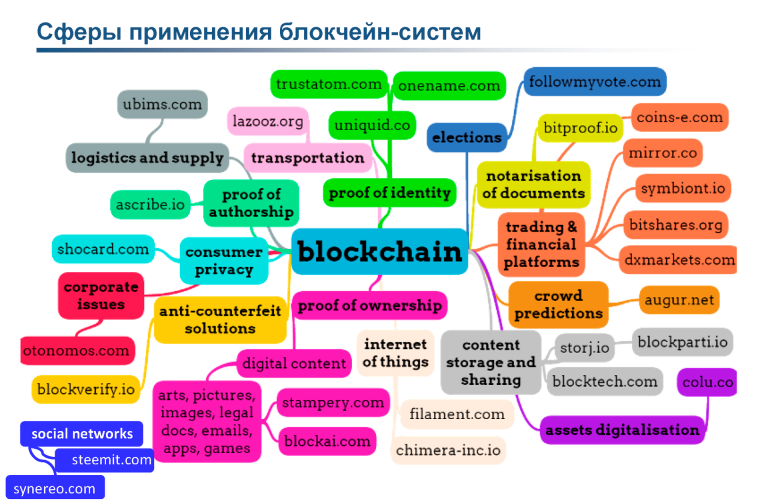
If it is not yet clear with Bitcoin, whether the currency will survive or die without coping with the peculiarities of its own architecture, the mechanisms of the blockchain are likely to become widespread. Decentralized databases, cryptographically guaranteeing the immutability of the information entered into them, will ensure the management of business transactions within the digital economy, but not only. Blockchain provides transparency of any transaction between the buyer and the seller, as well as a high level of security and the ability to track the status of product delivery in real time.
The idea of blockchain allows you to guarantee uninterrupted work in various spheres of life. Ukraine launched a voting system built on the blockchain technology - E-vox - to fight public sector corruption. Currently, the system is a prototype of a smart contract on the Ethereum network.
The Bittunes platform allows musicians without labels to sell songs to fans. Mediachain uses the blockchain to build a global base of copyright for photographers, allowing you to track the movement of images on the Internet. Social network Steemit on blockchain technology rewards (cryptocurrency) participants for generating content.
There are dozens of other ideas, as the blockchain can increase the speed of exchange of valuable information (eliminating intermediaries), while ensuring an adequate level of security, but not everything in the world can be solved with the help of blockchain projects.
Decentralized and encrypted

A source
When it comes to real security, not least the Tox is remembered. Tox is an information exchange protocol, the essence of which is similar to the work of BitTorrent Sync service. The Tox protocol allows you to exchange messages, files, make audio-video calls, and much more: Toxmail is used for the mail message, Toxscreen is used to access the remote desktop, and so on.
Tox has no dedicated servers, there is full end-to-end data encryption, all source code is open for review. For encryption, the NaCl cryptographic library is used. Security (or rather, the peer-to-peer information exchange itself) imposes certain restrictions on the interaction of Tox participants: there is no synchronization between different devices and there is no possibility to implement offline messages normally.
Obviously, the next step towards genuine security is the creation of alternative communication channels. Tor, I2P, Freenet, and other well-known methods of maintaining visible security work over the same communication channels that the providers provide us, while, for example, mesh networks can be generally isolated from the Internet. It is obvious that in the future the development of protocols will continue, which will allow users to exchange information in the conditions of blocking or complete collapse of existing systems.

A source
The topic is not new; a few years ago, the Serval Project company started developing tools that allow using mobile phones without connecting to a cellular network. In general, this can be done independently using Wi-Fi, but the company offered the Serval Mesh Extender device, which extends the range of open networks to 10 km. Serval Mesh uses the same phone numbers as regular cellular networks, so you can connect directly with other subscribers using the Serval Mesh program. In this case, voice communication, messages and files are transmitted in encrypted form.
To participate in the mesh-networks do not even need programming knowledge. Such devices as Mesh Potato allow you to raise your own mesh networks where traditional methods cannot do this. For the construction of managed mesh networks, various protocols are used: for example, BATMAN - stands for The Better Approach To Mobile Adhoc Networking.
New Quantum Protocols
A source
Quantum communications and quantum cryptography technologies, such as the quantum distribution of cryptographic keys, should provide the level of security that is impossible to achieve in industry-standard encryption algorithms. When it became aware of several variants of hacker attacks on protected lines, methods of counteraction began to be worked out.
MIT physicists have proposed a method similar in strength to the Varnam cipher (from a cryptographic point of view, it is impossible to come up with a system safer than the Varnam cipher) in which each new key is transmitted inside the main message using spatial light modulators (changing the intensity of the light beam).
To increase the number of bits transmitted in a single photon and allow multiple clients to receive information simultaneously and safely, researchers from the University of Vienna and the Autonomous University of Barcelona entangled three photons (instead of using the standard pairwise entanglement method). This type of asymmetric entanglement allows you to exchange data with a third party.
Triple entanglement allows you to move quantum information from standard qubit to Qudit (a unit of quantum information that can store more than two values in one bit: 3 - qutrit, 4 - kukvadrit, etc.), in which the transmitted information can be increased due to simultaneous coding spin states and particle motion in three dimensions. Qudit systems (multi-level quantum systems) can function as a complex of ordinary qubits. Some atomic-based Qudites make it easier to implement quantum teleportation, previously available only in three two-level qubit systems.
IoT and car protocols
A source
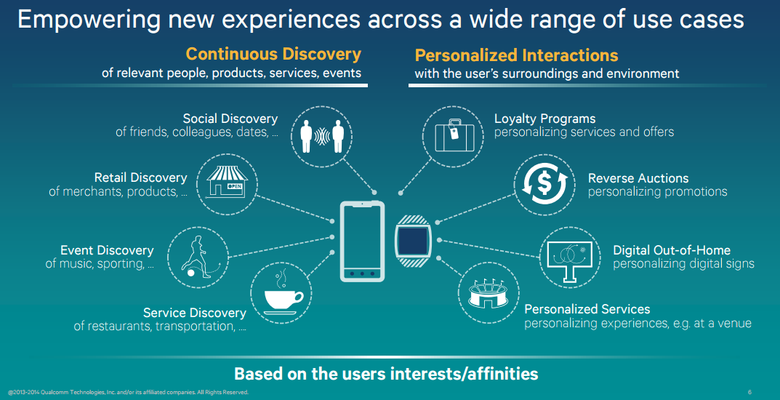
While smartphones seem to be stuck in development, communication standards continue to evolve. But if many already know about 5G, iBeacon, mesh networks (and many articles about them on Habré and Geektimes), then very few people have heard about Quecomm’s LTE Direct ( one article on Habré). Qualcomm suggested using an LTE module for direct communication (without base stations) with other devices (phones and sensors) for a distance of up to 500 meters. And no one bothers to build mesh networks.
To do this, the phone sends a data packet of 128 bits of information. Each device with LTE Direct support collects data from all surrounding similar devices and passes them through a filter configured by the user or a mobile application. For the system to work, it is necessary that the telecom operator allocates 1–2% of the LTE frequency spectrum available to it for it.
LTE Direct exceeds the range (and energy saving) of NFC, Bluetooth and Wi-Fi and can work where these networks do not work (do not exist). From March to May 2016 in Shanghai, Qualcomm conducted one of the most extensive technology tests. Over 9 weeks, 400 participants implemented 180,000 LTED interactions between devices.
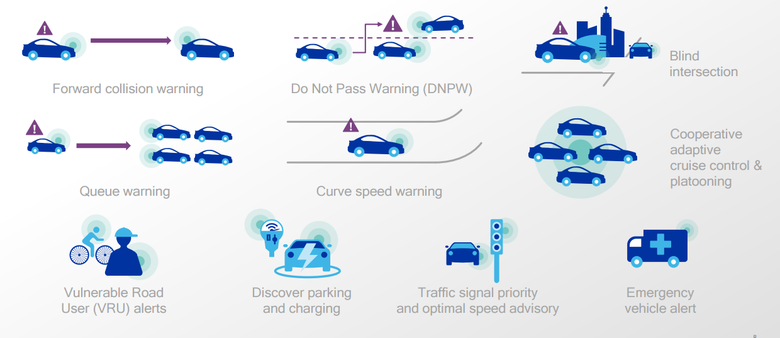
Experiments are ongoing. And although there are no real commercial solutions yet, there is a Cellular-V2X project, built on LTE Direct - a technology for connecting vehicles to each other (V2V, Vehicle-to-Vehicle), with pedestrians (V2P), with roadway infrastructure (V2i), with the network (V2N) and with everything taken together (V2X). V2X is one of the key technologies of the future, which will provide new opportunities for the driver:
- provides notification of possible hazards and 360 visibility in the absence of direct visibility, for example, at blind intersections;
- allows cars to travel at minimum distances from each other, optimizing road traffic;
- provides the ability to collect data on events of further road traffic when traffic stops or slows down.
A source
Connected cars will become part of the Internet of things, will communicate with other cars, share data, warn drivers about possible collisions. And, in addition, they will share information with your home, office, smart devices, acting as a digital assistant, who knows your entire daily routine.
Conclusion
We are still within exponential growth, within which forecasts are often wrong. But, as in any indicators that grow too fast, sooner or later a “wall” of a geometric progression will begin to appear when the factors that slow down growth start to work. The analogy can be cited by the example of high-speed transport: horses, first cars, trains, airplanes. And now you notice that you can not get to Amsterdam faster than flying a plane.
In the field of communications, there is already a clear tendency to change the “train” to “airplane”. The question is, will there be something outside of technologies that are now easily called promising?
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/399867/
All Articles