Close contact: what your smartphone is capable of with NFC
Hi, Geektimes! Although technologies are actively striving to the masses, you can often still notice the seller’s wide eyes at the checkout if you decide to pay for your purchase with a smartphone, or a puzzled colleague who saw you replenish your ticket for the subway without using a special terminal.

The name of this object of surprise is NFC, and today we'll figure out how this technology works and whether it is needed in your smartphone. By tradition, everyone who wishes is welcome under cat.
As many probably know, NFC is a high-frequency wireless technology with a small (a few centimeters, but not more than 10 cm) range. At the heart of Near Field Communication is short range radio frequency identification (RFID) - data that is stored in transponders is read and recorded using radio signals. Active and passive objects, in turn, are automatically identified.
')
But the standard definition is not enough here. The history of NFC is quite interesting: the technology originated more than 12 years ago - it was then that three technology giants (Nokia, Sony and NXP Semiconductor) decided to create an NFC forum to develop the interface of tangential interaction between devices. Despite the fact that the interface itself was far from fast (and remains so to this day), the idea of transferring small data with low power consumption still took its toll. RFID has earned a new way and received massive recognition. As a result, many manufacturers of smartphones, accessories and other devices now do not deprive NFC of any new product.
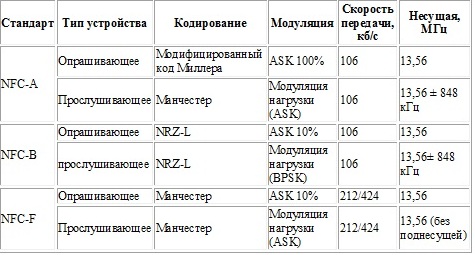
The operating frequency for NFC is 13.56 MHz, the maximum data exchange rate is barely more than 400 Kbps. However, in this case, the connection establishment time plays a huge role: it will take less than a tenth of a second to connect two devices using this technology.
The principle of operation of NFC is based on electromagnetic induction. The bottom line is that with the help of an antenna, the reader’s transmitter constantly radiates a sinusoidal signal at the aforementioned purity.

The sensor (or Listening Device) is also equipped with a frame antenna. When the sensor and the reader (Polling Device) are at a distance sufficient for NFC to work, both of them will form an air transformer. The magnetic field is generated by alternating current in the reader's coil, after which the current is created in the second coil - sensor. This energy is easily enough for the latter to work, so NFC is able to work with passive devices.
At this time, the antenna is shunted by one of the transistors of the transmitter device, from which the high-frequency signal is modulated. This signal and "catches" the reader. Mainly for NFC, Manchester coding is used (with an amplitude modulation factor of 10%). The modified Miller code is also used, although in this case the speed will barely exceed 100 Kbps.
In the passive mode, the reader creates an electromagnetic field, the NFC-tag modulates it and forms the answer. In other words, the label does not necessarily have to be connected to a power source or have a built-in battery, so its dimensions can be reduced to a minimum. If we have two devices with two active signals, everything is simpler here - they work, roughly speaking, “in turn”.
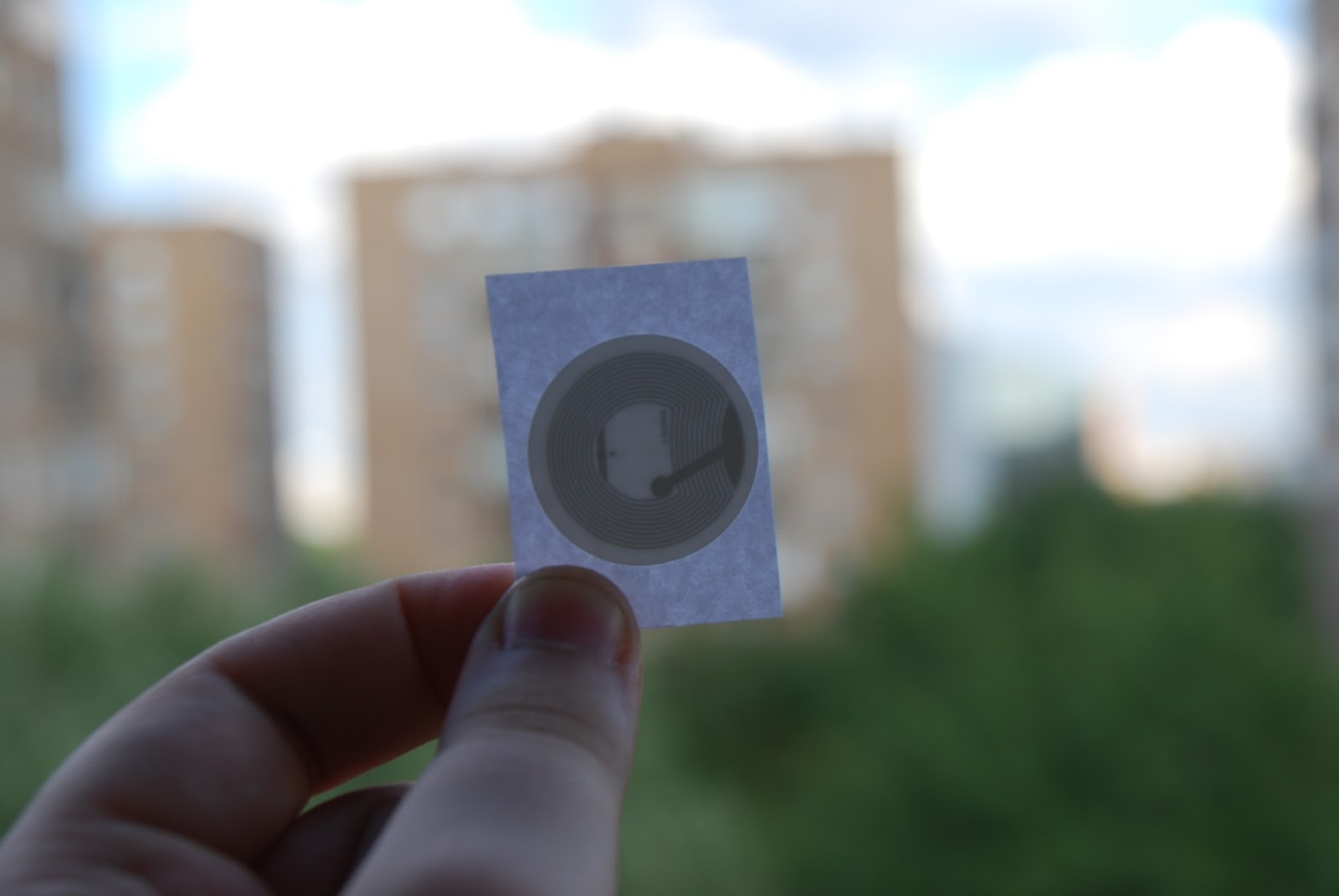
The passive NFC tag looks like this:
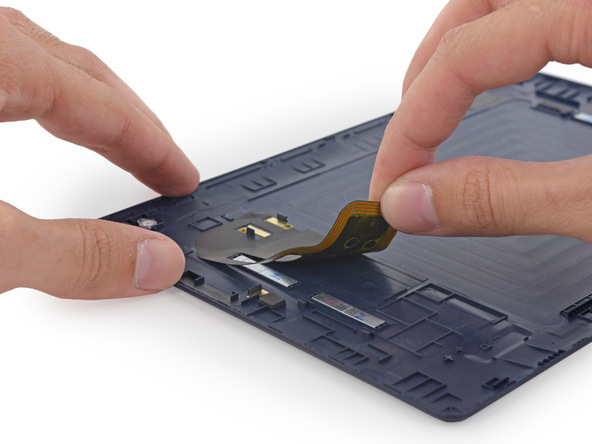
In smartphones, the NFC antenna is usually fixed under the back cover for a more stable signal.


After that, your smartphone is ready to act in several ways at once. It can become not only a means of payment and a key, but also a means of identifying the owner, a ticket or just a bonus card. Here are the main modes of operation of the smartphone with NFC on board.
Even in Android version 4.0, the Beam technology appeared, with the help of which devices can exchange files and folders: the exchange itself takes place using Bluetooth or Wi-Fi Direct, but NFC is used to identify smartphones. This reduces the time spent on connecting devices.
Cases of application NFC great variety. Among metro users, the ability to read information from a ticket using a smartphone is very popular. By installing special applications, you can not only find out the number of trips left and the validity of the ticket, but even replenish the Troika card without using terminals in the metro.


It is noteworthy that for this purpose you can use almost any smartphone with NFC - from Xiaomi Mi5s Plus to Lenovo X3 Lite .
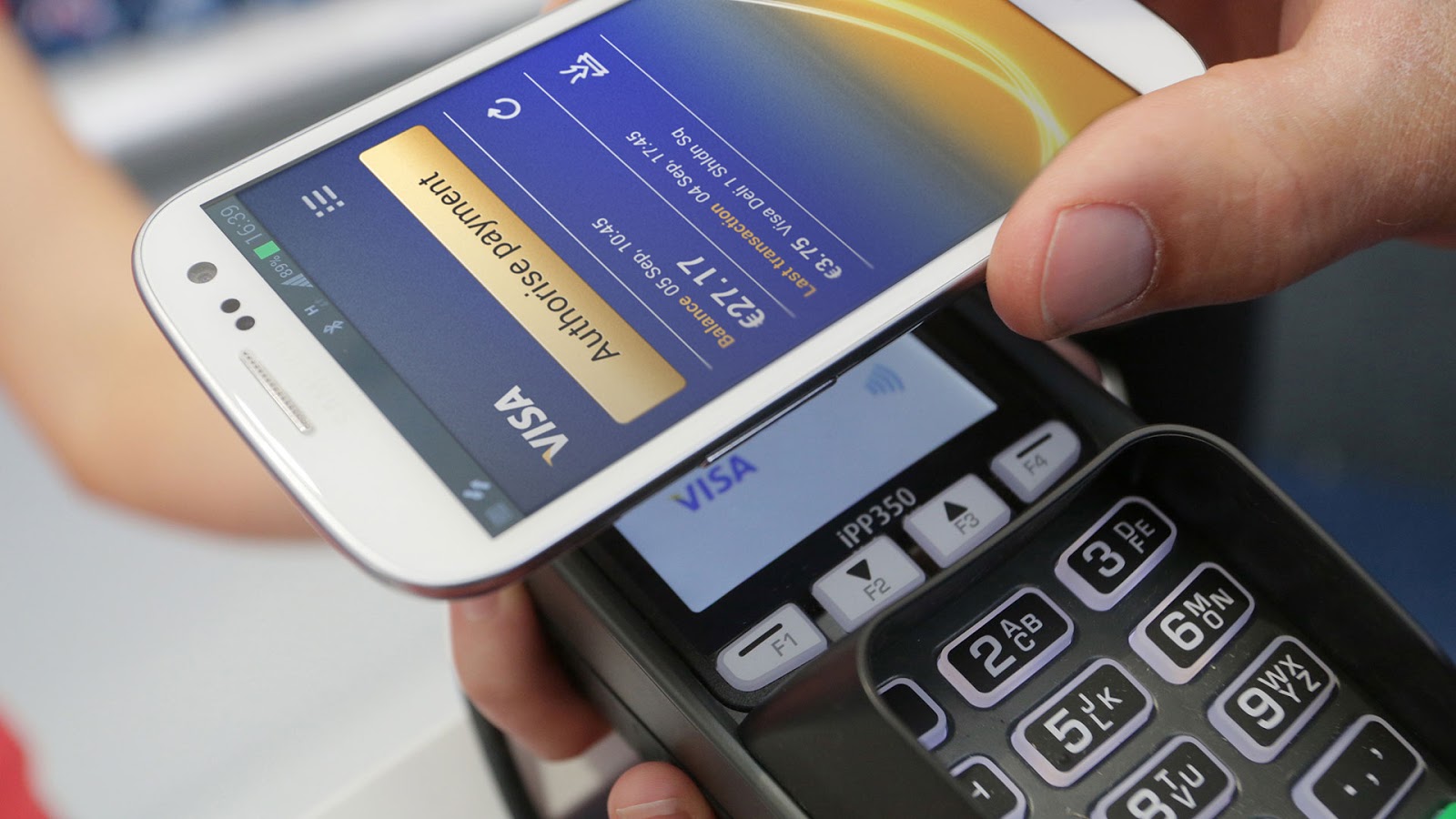
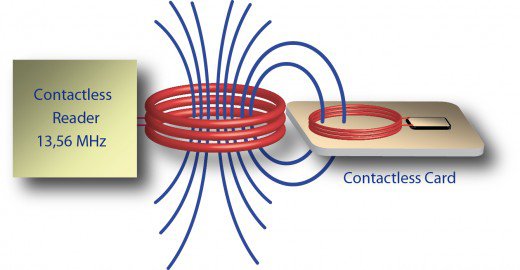
NFC is compatible with ISO 14443 and combines a variety of contactless cards, including credit cards that support MasterCard PayPass or VISA PayWave. The plastic card contains a microprocessor with an operating system and a payment application for interacting with the data of a specific customer. As soon as the card is inserted into the terminal or carried over it, it receives energy to start the operating system. In the case of contactless cards, power, as we have said, is obtained with the help of the electromagnetic field of the reader.
With the advent of contactless cards, the payment tool in fact can act not necessarily a card, but a smartphone, a watch, a key ring, and so on — not the form, but the availability of the required set of functions is important. After all, smartphones with NFC support, just like plastic cards, have a microprocessor. Starting with Android 4.4, payment applications can be used without Secure Element (with Host Card Emulation). You can record payment cards remotely, and it is really convenient.
To manage contactless applications remotely, smartphone makers and service providers connect to TSM, a service that provides access to secure data on NFC-enabled terminals. It remotely controls the Secure Element chips in smartphones, while the smartphone itself is a kind of modem that works through a secure communication channel. The user simply needs to connect the NFC payment option with his / her operator, and then pay for purchases in stores using mobile applications (usually banking).

When making purchases over 1000 rubles, you may be asked to enter a PIN code or put a signature on the check - everything here depends on the bank.
This is another common way to use NFC in a smartphone. NFC tags have gained great popularity in shopping and advertising areas: they are embedded in posters, billboards, placed on goods in stores. Usually these are small stickers, the cost of which does not exceed 50 rubles. The costs are minimal, but what an effect! From getting more information about a concert or product to a link to the trailer for a new movie.
You can create your own NFC tags, upgrade them and then use them in everyday life. As a rule, it uses third-party software like NFC TagWriter. The application is quite simple and allows you to write on the label many types of data - from contact and phone number to bookmark a web browser. You can even write down your contact information on the label, and then paste it on the business card - why is it not an original solution? Save on paper, however, if the interlocutor has a smartphone without NFC, it can be embarrassing.
In fact, NFC tags are a real gift when it comes to automation. For example, you can stick a label on a laptop and use the Trigger application to configure the access point to turn on by selecting Wireless and Local Area Networks as the action. The solution is simpler - write the Wi-Fi password to the tag, paste it on the router, and then, whenever guests ask for the password, send them to the NFC tag. Or again: set the label near the bed and make it so that when you touch it on the smartphone, the airplane mode will turn on (again using Trigger).
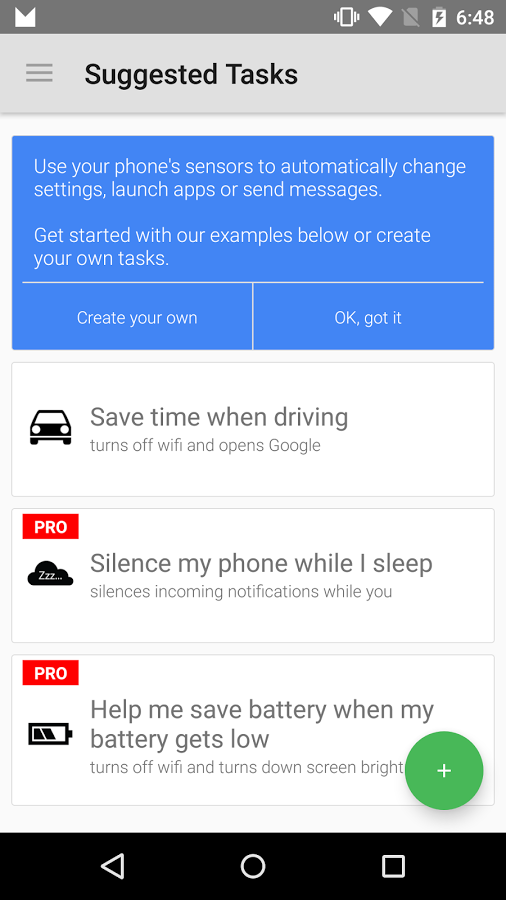
It will also be useful for motorists - they wrote down the algorithm for launching the navigator, pasted it on the holder for the smartphone, and whenever you install the device in this place, the navigator will start automatically.

And there are still very, very many such examples of using NFC tags. Often, the appearance of new cases is not limited at all by technology, but by the user's imagination.
Someone implements this at home, but mostly using NFC to identify and control the user is typical for businesses and organizations. Turnstiles and locks are configured in such a way that with the help of a label that is a pass, they decide whether to give its holder permission to enter or not.

With NFC, the smartphone really opens all the doors - if not in the literal sense, then in a figurative way. In fact, the user gets a universal tool, which, despite the speed limits, finds its application in a variety of situations. Here we are faced with another problem - the degree of prevalence of technology among service providers. The only thing that an ordinary user can do in this case is to use NFC as often as possible to show its relevance.
Perhaps the most pleasant thing about NFC is that this technology is available to a wide range of users. More and more manufacturers do not leave their smartphones without NFC, so it is in both devices like Xiaomi Mi5 (for $ 321.99 with Mi5SGBS code before December 31) and Nubia Z7 MAX , and in flagships like Xiaomi Mi Note 2 . Pleases also a variety of accessories with NFC support .
What about Apple and its iPhone 7, you ask? Alas, the manufacturing company limits the operation of the NFC chip in its smartphone, and it can only be used for the Apple Pay payment system. In the fall, however, it started in Russia, so at least some plus.
And how do you use NFC in everyday life? Share your experience with us in the comments.

The name of this object of surprise is NFC, and today we'll figure out how this technology works and whether it is needed in your smartphone. By tradition, everyone who wishes is welcome under cat.
What is NFC?
As many probably know, NFC is a high-frequency wireless technology with a small (a few centimeters, but not more than 10 cm) range. At the heart of Near Field Communication is short range radio frequency identification (RFID) - data that is stored in transponders is read and recorded using radio signals. Active and passive objects, in turn, are automatically identified.
')
But the standard definition is not enough here. The history of NFC is quite interesting: the technology originated more than 12 years ago - it was then that three technology giants (Nokia, Sony and NXP Semiconductor) decided to create an NFC forum to develop the interface of tangential interaction between devices. Despite the fact that the interface itself was far from fast (and remains so to this day), the idea of transferring small data with low power consumption still took its toll. RFID has earned a new way and received massive recognition. As a result, many manufacturers of smartphones, accessories and other devices now do not deprive NFC of any new product.
The operating frequency for NFC is 13.56 MHz, the maximum data exchange rate is barely more than 400 Kbps. However, in this case, the connection establishment time plays a huge role: it will take less than a tenth of a second to connect two devices using this technology.
The principle of operation of NFC is based on electromagnetic induction. The bottom line is that with the help of an antenna, the reader’s transmitter constantly radiates a sinusoidal signal at the aforementioned purity.

The sensor (or Listening Device) is also equipped with a frame antenna. When the sensor and the reader (Polling Device) are at a distance sufficient for NFC to work, both of them will form an air transformer. The magnetic field is generated by alternating current in the reader's coil, after which the current is created in the second coil - sensor. This energy is easily enough for the latter to work, so NFC is able to work with passive devices.
At this time, the antenna is shunted by one of the transistors of the transmitter device, from which the high-frequency signal is modulated. This signal and "catches" the reader. Mainly for NFC, Manchester coding is used (with an amplitude modulation factor of 10%). The modified Miller code is also used, although in this case the speed will barely exceed 100 Kbps.

In the passive mode, the reader creates an electromagnetic field, the NFC-tag modulates it and forms the answer. In other words, the label does not necessarily have to be connected to a power source or have a built-in battery, so its dimensions can be reduced to a minimum. If we have two devices with two active signals, everything is simpler here - they work, roughly speaking, “in turn”.
The passive NFC tag looks like this:
In smartphones, the NFC antenna is usually fixed under the back cover for a more stable signal.


After that, your smartphone is ready to act in several ways at once. It can become not only a means of payment and a key, but also a means of identifying the owner, a ticket or just a bonus card. Here are the main modes of operation of the smartphone with NFC on board.
- Peering - two active devices communicate with each other and exchange data. It can be both two smartphones, and a smartphone and a third-party accessory. For example, you can quickly establish a connection between your phone and an external speaker or headphones. The main thing is that the device has declared support for NFC: among such devices the KR is 8100 , Dacom Athlete , Bluedio R + Legend and others.
- Reading and writing - the smartphone reads codes from an NFC tag, and writes information to its memory.
- Card emulation - the smartphone becomes a full-fledged bank card. It is enough to bring it to the terminal to make a payment, and, for example, smart watches can also act as a card.
What is it for?
Even in Android version 4.0, the Beam technology appeared, with the help of which devices can exchange files and folders: the exchange itself takes place using Bluetooth or Wi-Fi Direct, but NFC is used to identify smartphones. This reduces the time spent on connecting devices.

Cases of application NFC great variety. Among metro users, the ability to read information from a ticket using a smartphone is very popular. By installing special applications, you can not only find out the number of trips left and the validity of the ticket, but even replenish the Troika card without using terminals in the metro.


It is noteworthy that for this purpose you can use almost any smartphone with NFC - from Xiaomi Mi5s Plus to Lenovo X3 Lite .
Smartphone as a payment method
NFC is compatible with ISO 14443 and combines a variety of contactless cards, including credit cards that support MasterCard PayPass or VISA PayWave. The plastic card contains a microprocessor with an operating system and a payment application for interacting with the data of a specific customer. As soon as the card is inserted into the terminal or carried over it, it receives energy to start the operating system. In the case of contactless cards, power, as we have said, is obtained with the help of the electromagnetic field of the reader.

With the advent of contactless cards, the payment tool in fact can act not necessarily a card, but a smartphone, a watch, a key ring, and so on — not the form, but the availability of the required set of functions is important. After all, smartphones with NFC support, just like plastic cards, have a microprocessor. Starting with Android 4.4, payment applications can be used without Secure Element (with Host Card Emulation). You can record payment cards remotely, and it is really convenient.
To manage contactless applications remotely, smartphone makers and service providers connect to TSM, a service that provides access to secure data on NFC-enabled terminals. It remotely controls the Secure Element chips in smartphones, while the smartphone itself is a kind of modem that works through a secure communication channel. The user simply needs to connect the NFC payment option with his / her operator, and then pay for purchases in stores using mobile applications (usually banking).

When making purchases over 1000 rubles, you may be asked to enter a PIN code or put a signature on the check - everything here depends on the bank.
NFC tags
This is another common way to use NFC in a smartphone. NFC tags have gained great popularity in shopping and advertising areas: they are embedded in posters, billboards, placed on goods in stores. Usually these are small stickers, the cost of which does not exceed 50 rubles. The costs are minimal, but what an effect! From getting more information about a concert or product to a link to the trailer for a new movie.
You can create your own NFC tags, upgrade them and then use them in everyday life. As a rule, it uses third-party software like NFC TagWriter. The application is quite simple and allows you to write on the label many types of data - from contact and phone number to bookmark a web browser. You can even write down your contact information on the label, and then paste it on the business card - why is it not an original solution? Save on paper, however, if the interlocutor has a smartphone without NFC, it can be embarrassing.

In fact, NFC tags are a real gift when it comes to automation. For example, you can stick a label on a laptop and use the Trigger application to configure the access point to turn on by selecting Wireless and Local Area Networks as the action. The solution is simpler - write the Wi-Fi password to the tag, paste it on the router, and then, whenever guests ask for the password, send them to the NFC tag. Or again: set the label near the bed and make it so that when you touch it on the smartphone, the airplane mode will turn on (again using Trigger).

It will also be useful for motorists - they wrote down the algorithm for launching the navigator, pasted it on the holder for the smartphone, and whenever you install the device in this place, the navigator will start automatically.

And there are still very, very many such examples of using NFC tags. Often, the appearance of new cases is not limited at all by technology, but by the user's imagination.
Open all the doors
Someone implements this at home, but mostly using NFC to identify and control the user is typical for businesses and organizations. Turnstiles and locks are configured in such a way that with the help of a label that is a pass, they decide whether to give its holder permission to enter or not.

With NFC, the smartphone really opens all the doors - if not in the literal sense, then in a figurative way. In fact, the user gets a universal tool, which, despite the speed limits, finds its application in a variety of situations. Here we are faced with another problem - the degree of prevalence of technology among service providers. The only thing that an ordinary user can do in this case is to use NFC as often as possible to show its relevance.
Instead of conclusion
Perhaps the most pleasant thing about NFC is that this technology is available to a wide range of users. More and more manufacturers do not leave their smartphones without NFC, so it is in both devices like Xiaomi Mi5 (for $ 321.99 with Mi5SGBS code before December 31) and Nubia Z7 MAX , and in flagships like Xiaomi Mi Note 2 . Pleases also a variety of accessories with NFC support .
What about Apple and its iPhone 7, you ask? Alas, the manufacturing company limits the operation of the NFC chip in its smartphone, and it can only be used for the Apple Pay payment system. In the fall, however, it started in Russia, so at least some plus.
And how do you use NFC in everyday life? Share your experience with us in the comments.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/399695/
All Articles