ESA and Roskosmos published the first results of scientific observations "ExoMars-2016"
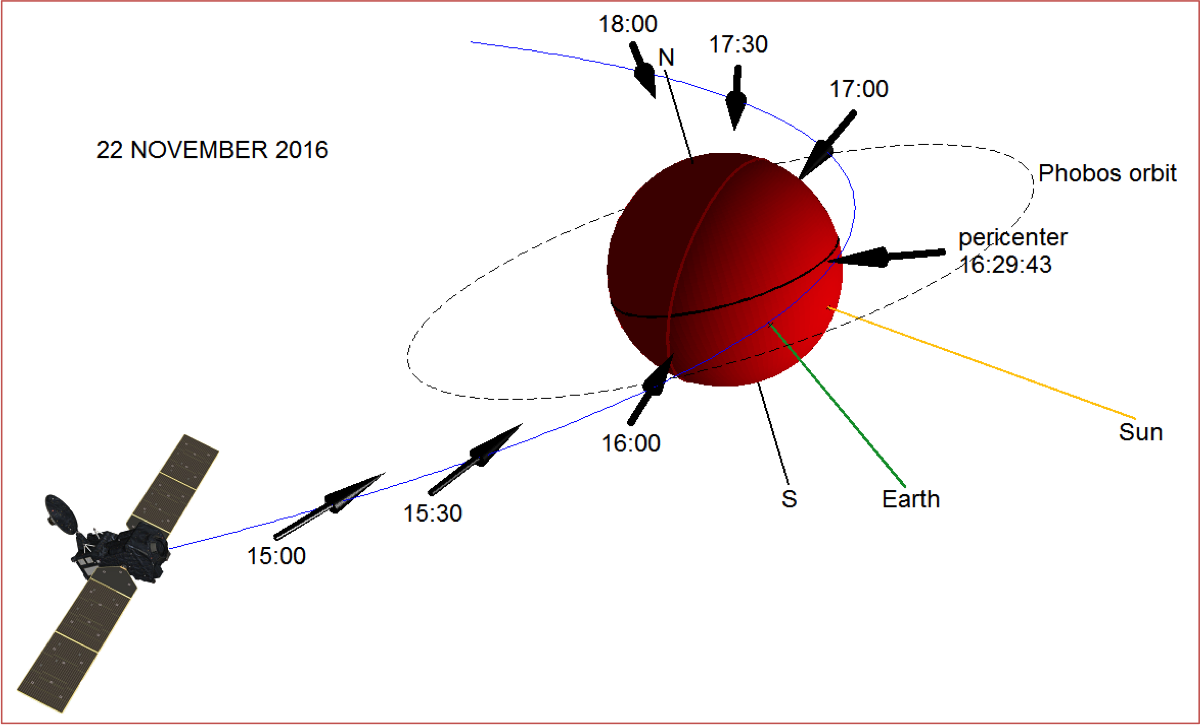
TGO span in high-elliptical orbit (blue line). The pericenter was passed on November 22, 2016 at 16:29:43, the green shows the direction to the Earth, the yellow shows the Sun. The dotted line indicates the orbit of Phobos, the arrows indicate the direction of the field of view of the instruments. (c) ROSKOSMOS / ESA / ExoMars / ACS / IKI
Despite the failure of the Schiaparelli descent module, the Exomarz mission was nevertheless recognized as successful. Largely due to the fact that the second part of the mission - the TGO ( Trace gas orbiter ) probe went into the calculated orbit, passed as it was intended. Currently, the probe is in the elliptical orbit of Mars, approaching during the motion to the surface of the planet at 230-300 km and moving away at 98,000 km. The circulation period is 4.2 days.
On November 20-28 of this year, scientific instruments onboard the module for the first time carried out verification measurements. The data collected over 8 days were sent to Earth, where scientists analyzed the information received. Telemetry allowed to calibrate the device, optimizing the mode of its operation. In eight days, almost all TGO scientific instruments were tested, no problems were identified.
One of the tools is the CaSSIS cameras (Color and Stereo Surface Imaging System). They photographed the surface of Mars from a height of 5300 km. The resolution was 60 meters per pixel.
')
“The first images we received are extremely spectacular - although this is just a test. We saw Hebes Chasma with a resolution of 2.8 meters per pixel. It’s just as if we were flying over Bern at a speed of 15,000 km / h and at the same time getting clear images of cars in Zurich, ”said Nicholas Thomas of the University of Bern.
In addition to cameras, the European scientific instrument NOMAD (Nadir and Occultation for Mars Discovery) also transmitted its data. With its help, scientists were able to obtain the first measurements of the Martian atmosphere. These measurements were carried out using two methods: the study of the flux of sunlight reflected by the surface of Mars and the observation of the scattered light in the atmosphere during the "sunset" of the Sun. Thanks to the dynamics of the spectrum of solar radiation, specialists can understand which substances and elements are contained in the atmosphere.
For the first time , two Russian devices were included . They were developed by the Space Research Institute of the Russian Academy of Sciences. The first device is a whole complex of spectrometers for studying the chemistry of the ASC atmosphere, the second is the neutron detector FRED.
The detector was turned on for the first time during the flight. FRAND monitored the radiation situation, collecting a whole array of data during the trip, which is necessary to compile a clear picture of the dynamics of the level of cosmic radiation when flying to Mars. After studying these data, it turned out that all this information correlates with data from other similar experiments. The analysis took into account the background radiation from the apparatus itself.
FRED was turned off on September 15 before braking, and 31, after the TGO entered Mars orbit, it was turned on again. During the month, the system conducted several observations of the neutron albedo of Mars. According to representatives of the project, these measurements are very important because they allow to calculate the dynamics of particle fluxes at a distance from the planet and when approaching it. In the future, it will help map the distribution of water or ice below the surface of the red planet.
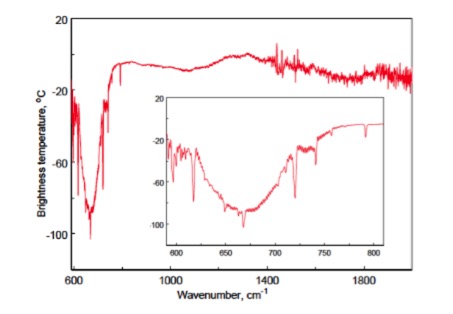
The spectrum of the Martian atmosphere obtained by the TIRVIM channel of the ACS spectrometric complex. Horizontal - wavelength, vertical - radiation intensity (brightness temperature in degrees Celsius) (c) ROSCOSMOS / ESA / ExoMars / ACS / IKI
As for the ACS complex, it consists of three infrared spectrometers at once. The main goal of the experiment is to search for those components of the atmosphere whose concentration is very low. Basically, the search is conducted methane - the main sign of biological activity on the planet. In the future, scientists plan to determine the location of the sources of this gas.
Also sent observation data Fourier spectrometer thermal infrared range TIRVIM. The task of this device is to search for aerosols in the atmosphere (dust and ice crystals), to compile temperature profiles and gas concentrations. The results of the first observation showed that in the observed area the surface temperature is about 0 degrees Celsius. Silicate dust has been found in the atmosphere, carbon dioxide absorption bands are visible.
“We are pleased and proud that all the tools work so well in Mars, this first impression is just a fantastic preview of what we get when we start collecting data at the end of next year,” said Håkan Svedhem , Chief Scientific Specialist of the TGO project.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/399685/
All Articles