Galaxies moving at the speed of light
Time is needed only so that everything does not happen at the same time.
- Albert Einstein

We know the number of galaxies in our expanding Universe (at least 100 billion), but no less interesting is the question of how fast they can move. After all, as the Universe expands, the farther from us is the galaxy, the greater its escape rate.
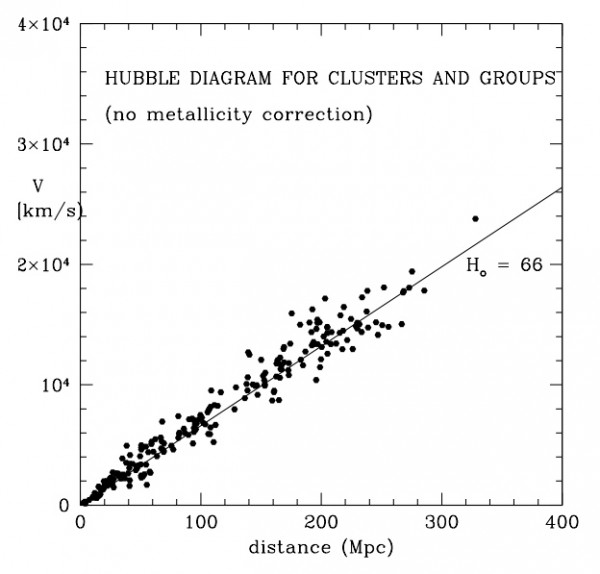
Moreover, since the expansion is also accelerating, the galaxies fly away faster and faster from us. Hence, it is not surprising that the light of the fleeing galaxies shifts to the red part of the spectrum.
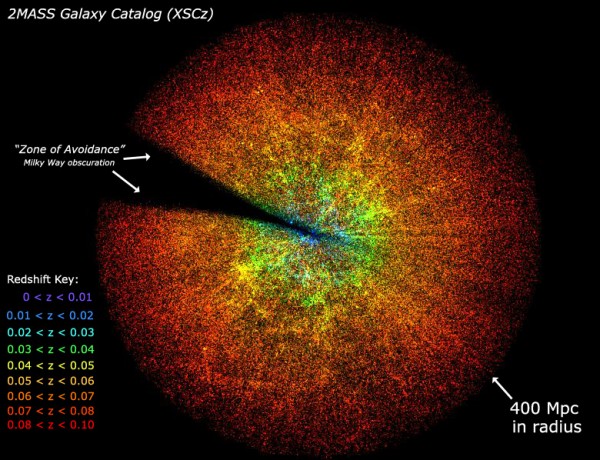
')
And there is nothing strange about it. If an object moves in your direction and emits light, its wave shrinks and the light appears bluer. If the object moves away from you, the wavelength increases and the light appears more red. And the faster the light source moves, the stronger the wavelength shift.
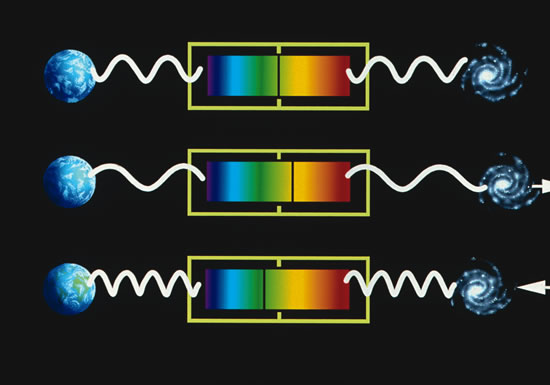
But think about it - if an object moves from you faster and faster, will we not see objects approaching the speed of light at some point?
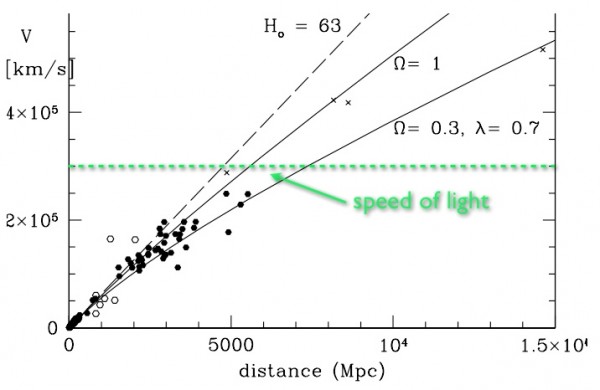
As you know, when approaching the speed of light, many things happen: and here are the two most counterintuitive phenomena related to the special theory of relativity.

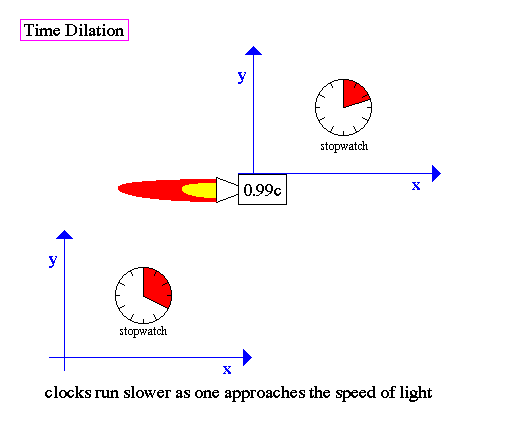
If you are resting, and the object is moving relative to you at a speed that is significant compared to light speed, you will notice two very strange effects: its length will decrease in the direction of its movement, and time will slow down. And, of course, you will immediately be interested in the question - are these effects observed in distant galaxies!

Length reduction cannot be measured, since we can measure length only in the direction perpendicular to the line of sight, and the expansion occurs parallel to it. What about time dilation? Is it or not? Let's think about what we can expect based on the predictions of the theory.
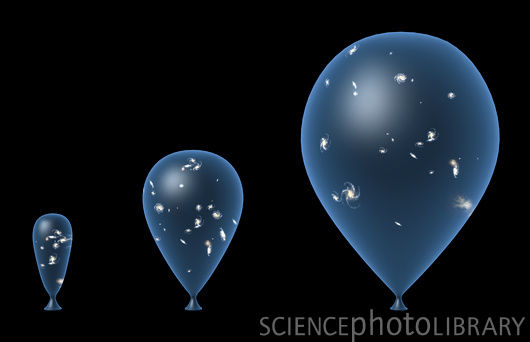
The studied galaxy does not move with relativistic velocities relative to objects located in its local spacetime. There is an expansion of the space between us and a distant galaxy. It is this expansion that increases the photon wavelengths, which makes the light look redder.
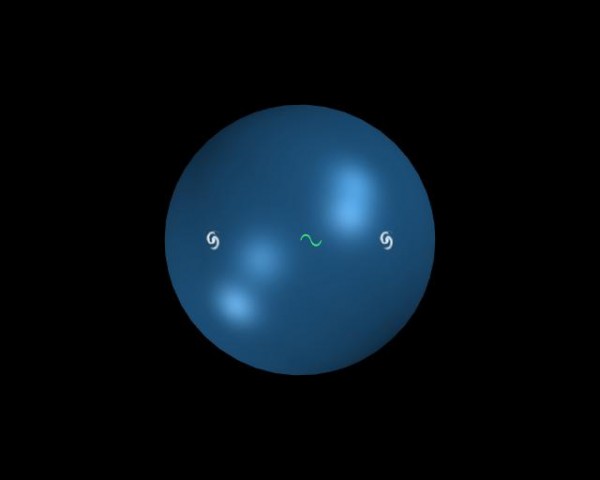
But when the light was emitted, the time from the peak to the peak of each wave was much less than the time that you can observe when these peaks reach you. So although the observed galaxy does not physically move at a relativistic speed, you should see a time dilation. So can you do it? What will you look for?

For example, it is known that spiral galaxies rotate. You may ask if it is possible to see a slowdown in their rotation. Unfortunately, in the past, the connection between the brightness of a galaxy and its rotational speed in the past was not the same as it is now, as spiral galaxies evolve with time .

You may decide to monitor the quasars, as these are very bright objects that can be clearly seen at long distances . However, the environment in which they are located, and the sources of variable characteristics (for example, gravitational microlensing ), differ in the distant and quasars closer to us.
Another candidate is gamma-ray bursts , they can be seen over long distances. But we would come up with a very well-studied class of objects with properties that do not change over time, which can be observed with a strong redshift. If we can measure the time dilation they have, this will be the final test of the theory!

Supernova type Ia ! These objects have a very well studied timeline, according to which they become brighter, fade out and disappear.
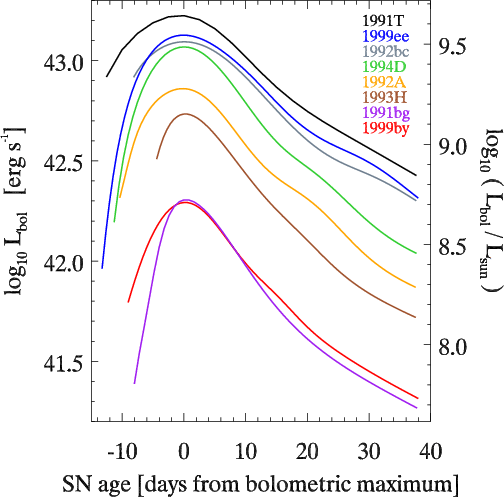
So, if we find a remote supernova with a strong redshift, its light curve should be stretched along the time scale. What happens in reality? Are there any such supernovae?
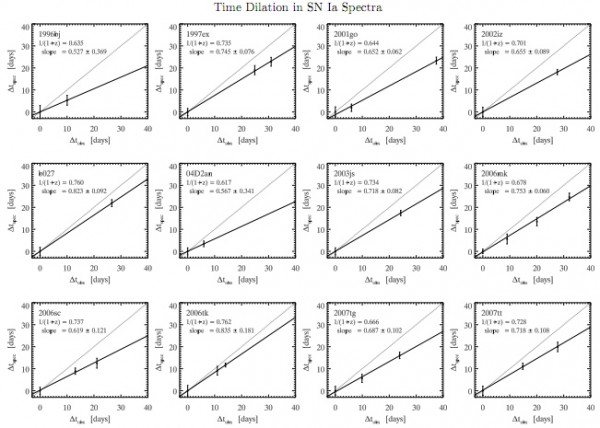
Believe it or not, believe it or not, but there are plenty of such people! The first - the supernova, moving away from us at a speed of almost 50% of the speed of light - appeared in 1996 ! Then another one , and another, and today we have a whole crowd of them , and we definitely see a time dilation in these distant galaxies!
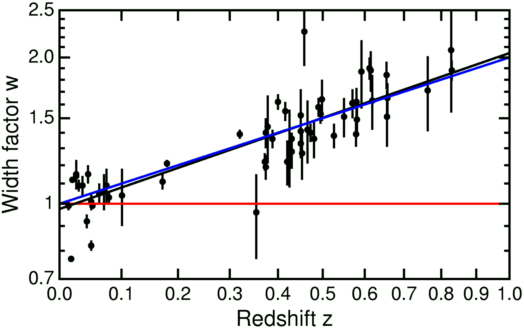
Red line - prediction without slowing down, blue line - with slowing down. So this is actually happening!
What is surprising is the presence of an observer in such a galaxy with a very powerful telescope capable of seeing us, we will already seem to him slowed down while they move at a normal speed for them!

So, watching very distant objects, you not only see them in the past, distant by billions of years, you see them in slow motion! And while you are thinking about it, know that someone in the billions of light years from us can see how you are thinking about it for much longer!
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/399605/
All Articles