How our rockets lose weight

An interesting trend appeared in the domestic space program. Habitual us boosters begin to facilitate, removing one of the steps. Heavy "Proton" very soon will get a medium and light version, and recently there was news that the "Union" will have a new light version. How and why “lose weight” rocket?
"Proton-Light"
News about this project appeared in the summer. The Proton-M, which in its original form has, in fact, four stages (three stages of a launch vehicle and an upper stage), suggested that the second stage be removed. In this case, the mass of the rocket would have decreased by 168 tons, or approximately 20%. But they want to return part of the fuel by extending the first and third (became the second) stages. In an even lighter version of the Proton, they are going to remove two engines with side blocks in which fuel is stored. Since in the central unit of the first stage there is only an oxidizer, you will have to add a small fuel tank.
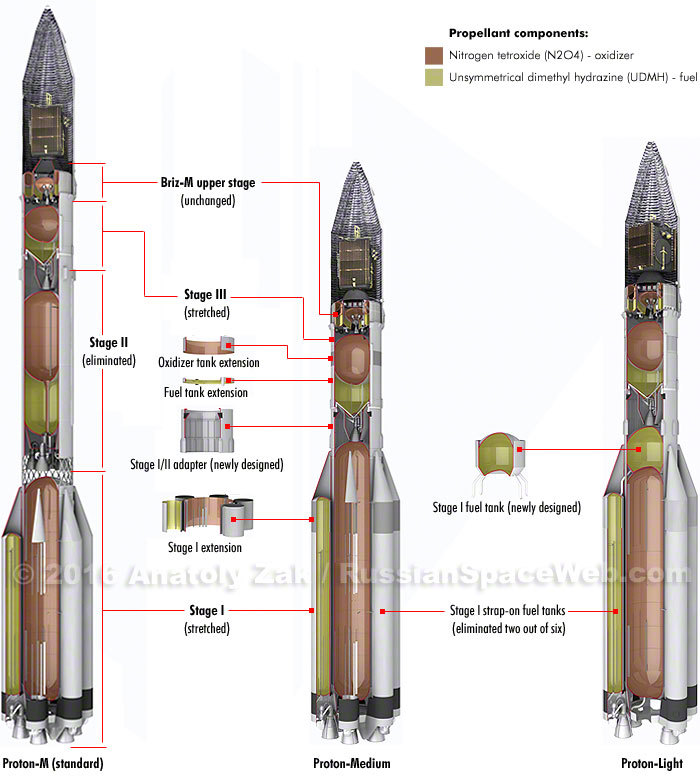
')
The resulting missiles are simpler and cheaper, but their payload capacity is enough for standard satellites to a geostationary orbit. It is there that most commercial telecommunications satellites live, which bring profit to their manufacturers and the creators of the rockets that derive them.
Some sources also write about the removal of the Briz-M upper stage with two satellites of the second (former third) stage and the idea of a soft landing for the first stage, but this information is probably not true. Both options would very seriously reduce the load capacity, which we do not observe.
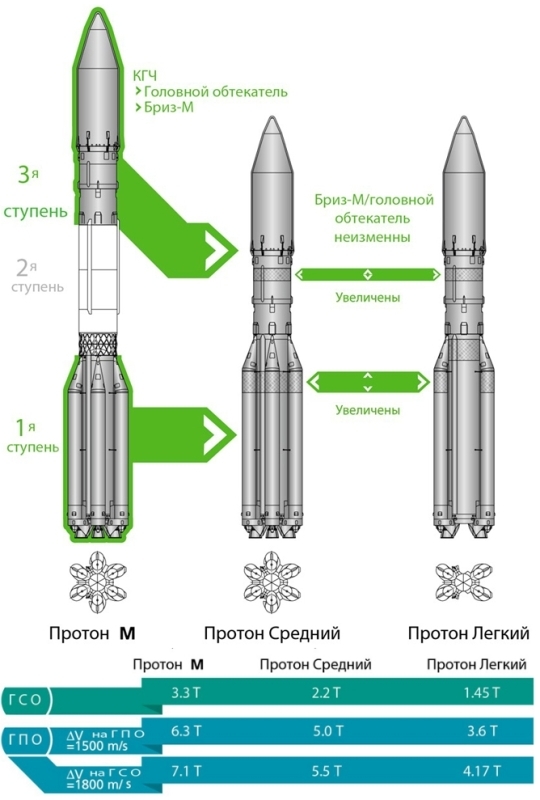
Please note that, in principle, the load is not indicated on the low-Earth orbit. The fact is that the Proton last time took out the modules of the ISS to it in 1998-2000, and since then it has worked exclusively for higher orbits.
The designations of the GPO 1800 and 1500 in the figure are a geo-transfer orbit from which the satellite itself will already go into geostationary orbit with its own engines. There are two standards in the world that have developed historically - GPO, from which it is necessary to accelerate to 1800 m / s, it is usually used by Americans, Chinese and Japanese, and GPO, from which it is necessary to accelerate to 1500 m / s, familiar to Europeans. “Proton”, starting from Baikonur, can go into orbits with other parameters, but from which the road to the geostationary orbit will occupy the same 1500 or 1800 m / s, for which the satellite is designed, that is, to compete with all countries. ILS, which sells the Proton launch services, has published a document with detailed load characteristics of various Proton variants, depending on the orbital parameters and how far it is necessary to accelerate to the geostationary orbit. For example, here is the table for the Proton Middle:
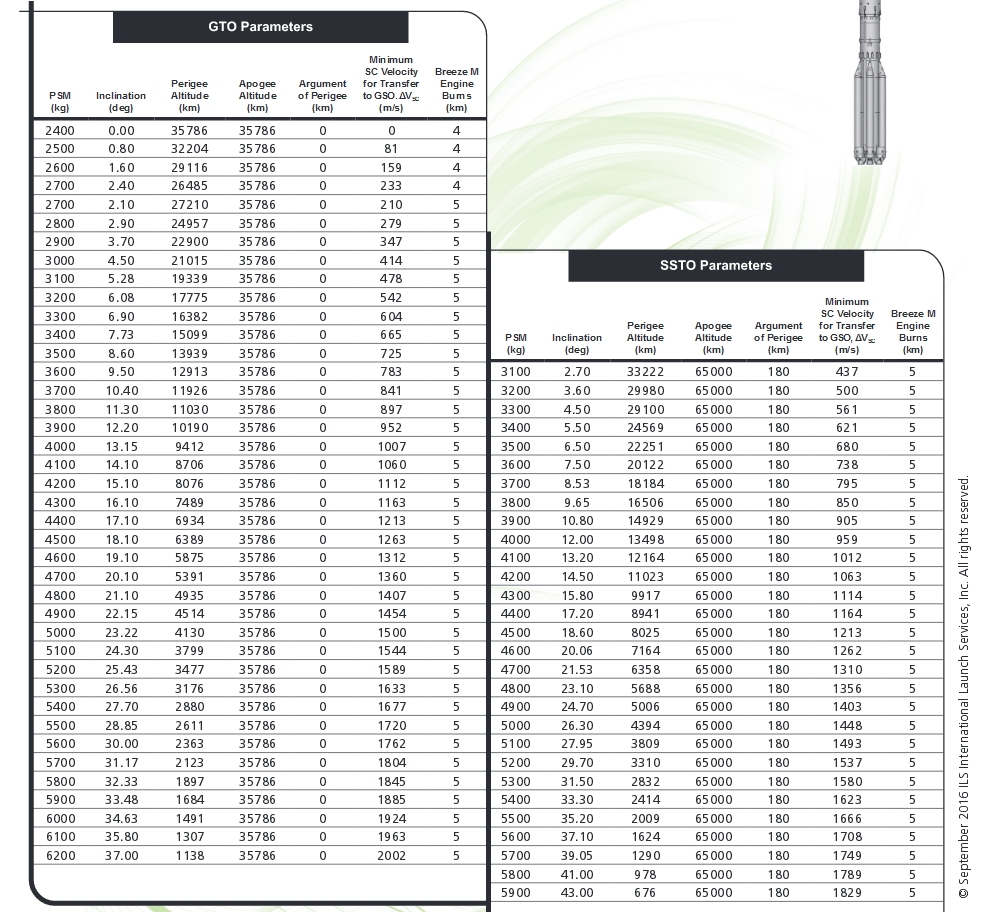
The publication of detailed characteristics for potential clients indicates that the project is being successfully implemented, and the first lightweight Protons have a real chance to fly in 2018 (medium) and 2019 (light) as planned. Moreover, Proton Middle has already concluded the first contract - according to ILS official information , 2019-2020 Proton Middle should be launched with an unnamed satellite in the interests of Eutelsat Communications, one of the largest satellite communications providers.
The reason for the appearance of the medium and light versions of the Proton is simple - competition in the launch services market. The exact value of satellite launch contracts is proprietary information. The cost of launching satellites with the heavy "Proton" various experts estimate in the region of $ 60-65 million, which is comparable with the estimated cost of launch services of the SpaceX company Ilona Mask. Previously, ILS had the advantage that the launch was not delayed and proceeded according to the plan, but in recent years, for various reasons, Proton had an accident about a year. The investigation into the causes of the accident and their elimination took months, and the launches were delayed. According to the Roskosmos General Designer for the Alexander Medvedev rocket complexes, the lightweight Proton will be a quarter cheaper, which will make it possible to compete successfully with SpaceX Falcon 9 from SpaceX.
Soyuz-2LK
More recent news - on the basis of the Soyuz-2 launch vehicle, it is proposed to make an easy modification of the Soyuz-2LK, removing the third step. Instead, there will be a “Frigate” upper stage, which in some modifications of the Soyuz is placed in the fourth stage.
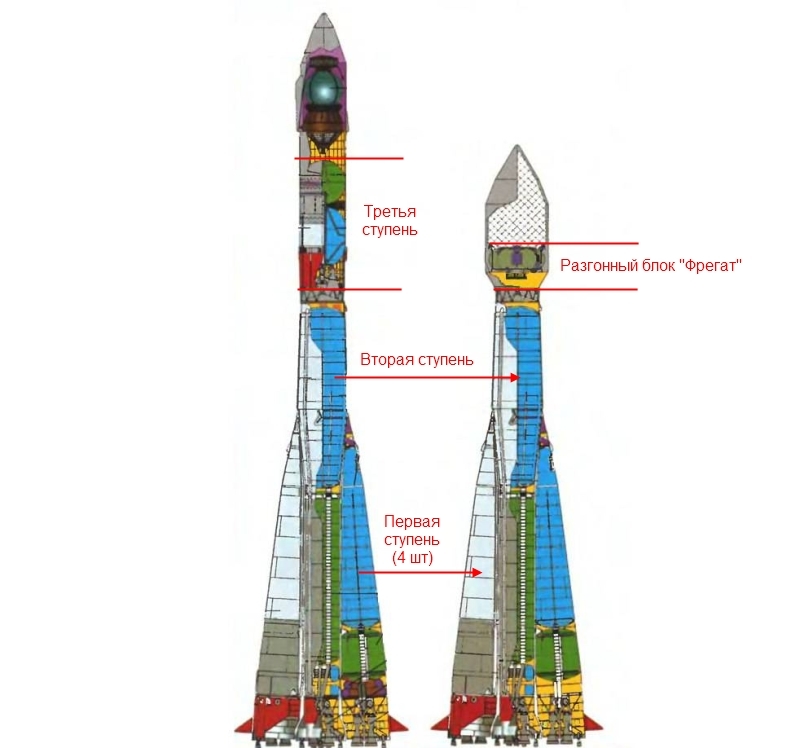
The resulting rocket will have a carrying capacity of 2-3.85 tons to a sun-synchronous orbit. This orbit is often used by Earth remote sensing, meteorology and cartography satellites because the satellite flies over different parts of the planet at the same local time. The acceleration unit "Frigate" can start the engine several times and therefore will be able to breed several satellites into different orbits. And without the third stage, on which the modern (and more expensive) engine stands, the cost is expected to be reduced by 25-40%. There are already four launch complexes in the world for the Soyuz launch vehicle (Baikonur, Plesetsk, Kuru, Vostochny), and the new rocket is compatible with them. True, Europeans are unlikely to buy “Soyuz-2LK” in Kuru, they already have an easier, but their own “Vega”.
It is also curious that the Soyuz already has a light modification, the Soyuz-2.1v , which has flown twice, in which the first stage was removed, the second stage engine was updated, and the Volga launch unit was also added.
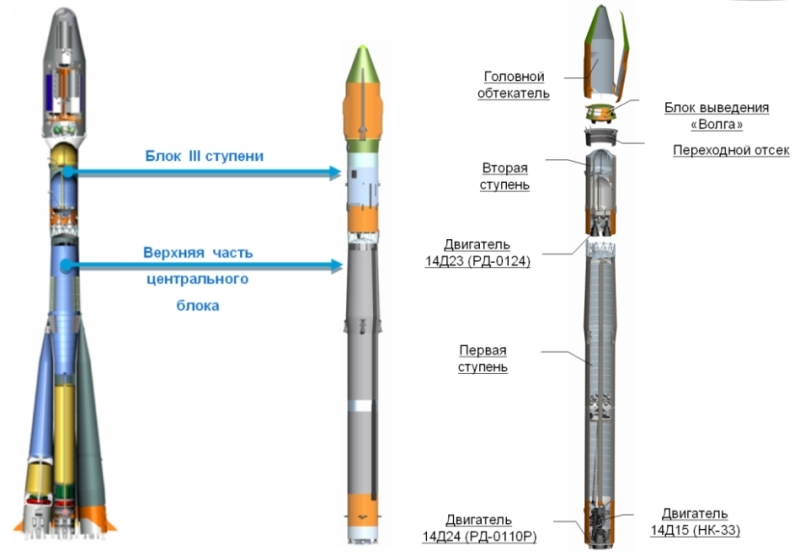
But the "Soyuz-2.1v" has more than two times less than the carrying capacity to the sun-synchronous orbit than the "Soyuz-2LK." Theoretically, they can solve different problems, option 2.1c will output single satellites for Roskosmos / the Ministry of Defense, and LC - several commercial satellites at once. Work on the project has not yet begun, but if funding begins to flow now, then Soyuz-2LK will be able to fly for the first time in 2019-2020.
Conclusion
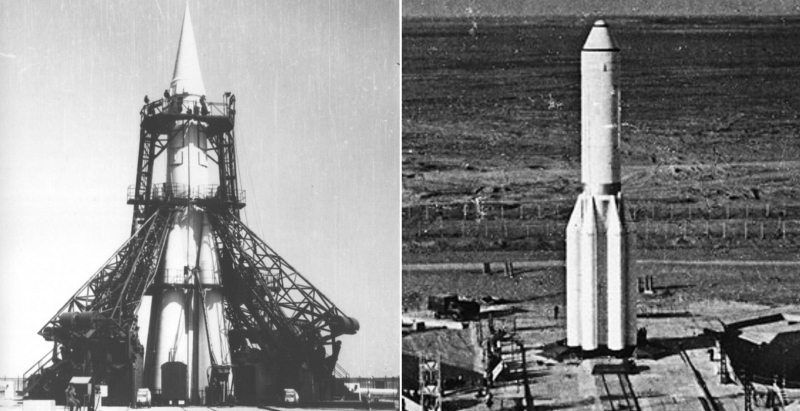
On the left, the R-7, from which the whole family has grown, including the Soyuz-2, on the right, the UR-500, the two-stage father of the Proton
It's funny, but both rockets, which are now “losing weight,” began their long and glorious career, being two-stage. Already then the number of steps rose first to three, then right up to four. And in that in the 21st century, for pragmatic reasons, they get lighter options, becoming similar to their ancestors, there is a kind of rocket dialectic. Well, if in very simple words, it is good that our rocket builders do not rest on their laurels and have not lost the opportunity to make new equipment, but try to meet the challenges of today.
See also:
» History of modifications of the family" R-7 "and" Soyuz-2.1v . "
» As previously removed steps and attempts to create a universal rocket.
» Related publications with different ways to facilitate access to space.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/399603/
All Articles