As we began to take care of our fingers a little more.
Hi, Geektimes! The presence of a fingerprint scanner in a smartphone has recently become one of the main factors for many when choosing a device for purchase. Although this type of biometric security technology is not new, compact and cheap fingerprint scanners have learned to do relatively recently. But have you thought about what happens when you hold your finger to unlock the phone? We have now decided to understand and ask all those interested in the cat.

A fingerprint, as is well known, does not change over the course of a person’s entire life, which makes it possible to identify him at both 15 and 75 years of age. An imprint begins to form at the stage of fetal development, but even with identical twins, imprints are not identical. Therefore, it is one of the most common and safe (after the scanner of the retina and iris or DNA analysis) methods of human identification. Delete it as in the movie "Men in Black" will not work.

When viewed from the physiological point of view, a fingerprint is a specific set of protrusions with individual pores that are separated by depressions. And since it is associated with the thermal and electrical characteristics of the skin, you can use both heat, light, and capacitance (or all together) to obtain its image.
')
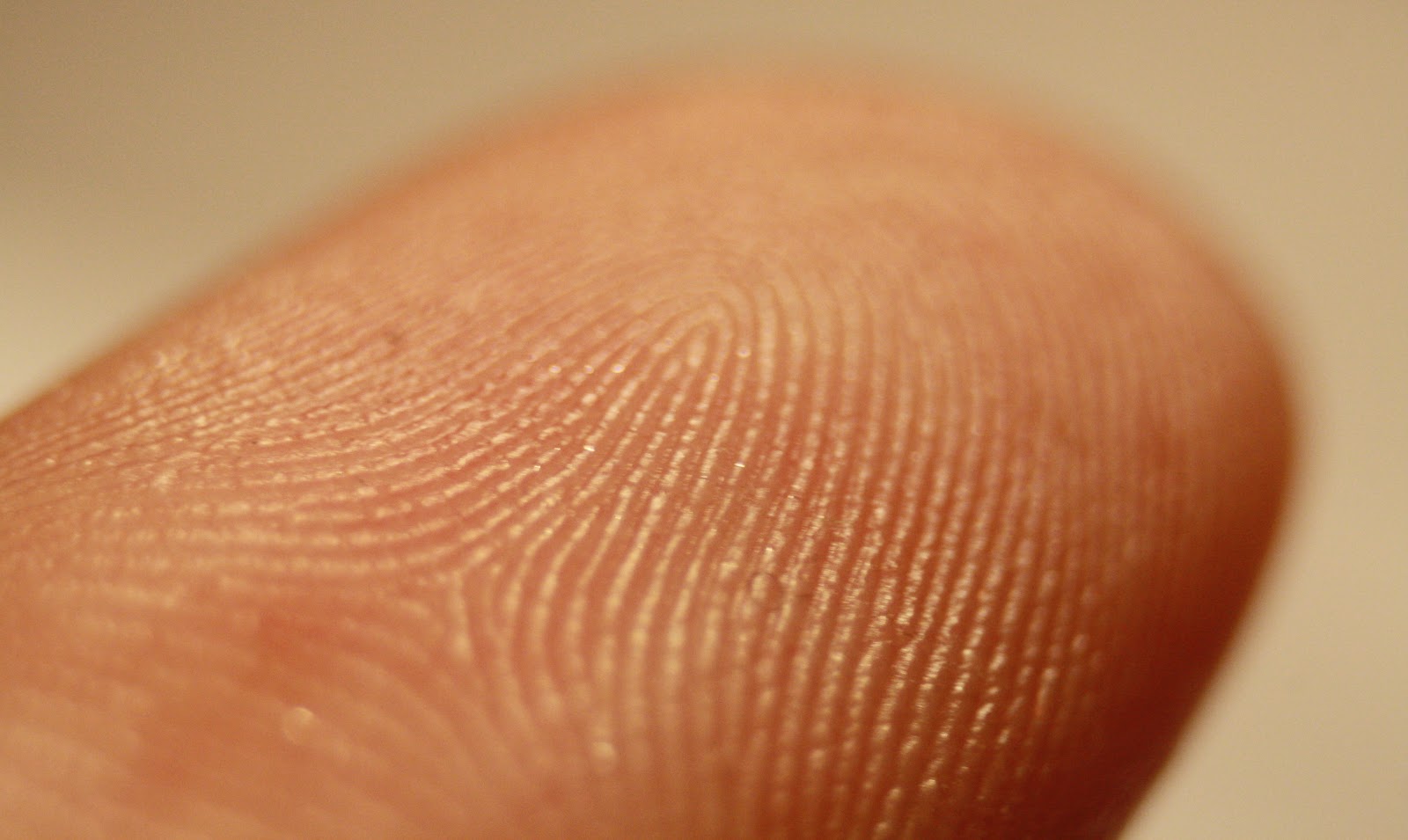

There are a number of varieties of fingerprint scanners - some are used on secret objects (along with gait analysis and other chips, of course), others have already come into the lives of modern smartphone owners as something ordinary. To summarize, we can distinguish three main groups of fingerprint scanners:
They, as the name implies, use optical methods for obtaining images of a print. This method is the oldest method for capturing fingerprints: a photo of a fingerprint is processed using special algorithms that detect unique crests and protrusions. The resulting image is compared with those in the system, after which a positive or negative response is sent to the user. Optical scanners are subdivided into FTIR scanners, fiber-optic, broaching, roller, electro-optical and non-contact.
FTIR scanners use the Frustrated Total Internal Reflection effect. In this case, the light falls on the interface between two media, after which one part of the light energy is reflected from the border, and the second penetrates through it into the second medium. How much energy will be reflected is determined by the angle of incidence: when it reaches a certain size, all light energy is reflected from the interface, which is called total internal reflection.
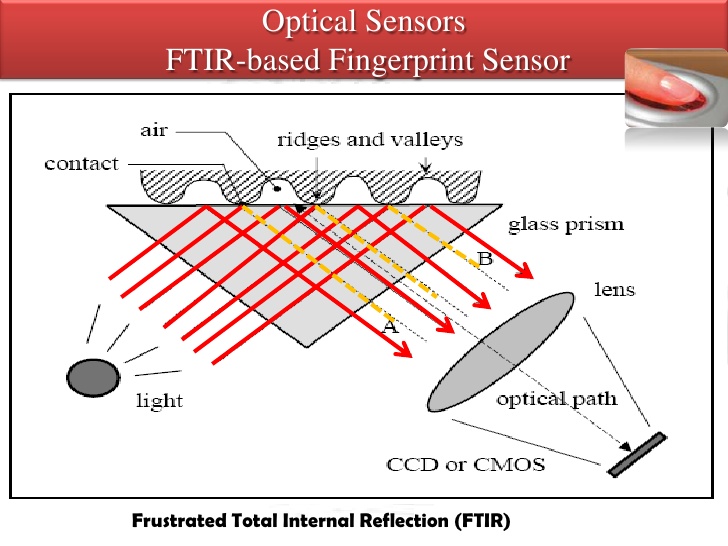
At the contact of a fingerprint (more dense medium) with a less dense beam of light passes through the border at the point of total internal reflection. So only those beams of light that fall into points to which the capillary pattern of the finger surface is not attached will be reflected. Then CCD or CMOS captures the final light image of the finger surface.
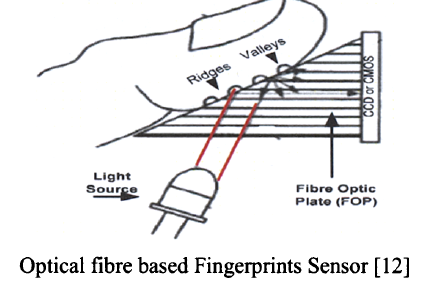
Fiber optic scanners work a little differently. In fact, we have a fiber-optic matrix, with each of its fibers ending with a photocell. Each photocell captures the residual light that has passed through the finger at the point where the fingerprint touches the surface of the scanner. Further, the data of all elements are aggregated and on their basis the image of a fingerprint is obtained.
Electro-optical scanners use a special polymer, which contains a light-emitting layer. It reflects the heterogeneity of the electric field of the finger at the surface of the scanner, after which a fingerprint is displayed. The rest of the work is done by photodiodes that convert everything into a digital form. Broaching scanners are one of the most interesting, because in this case the finger is not attached to the scanner surface, as we are used to, but is carried out on the reader, which is a narrow strip. The principle of their work is in many ways similar to the FTIR scanners mentioned earlier.
When using contactless scanners you don’t even have to contact the surface of the scanner. A finger is applied to a special hole, it is illuminated from below by several sources of light, the lens collects information, then the data are projected onto a CMOS, where they are converted into an image of a fingerprint.

Optical scanners are fairly easy to fool, since they capture only the 2D image — this is one of their main drawbacks. In our time, they have faded into the background, however, in many areas are still used. But certainly not on secret objects and not where they seriously care about security: for this they invented silicon (semiconductor) and ultrasound scanners.
The main difference between semiconductor scanners and optical scanners is that in this case, the image is obtained using the properties of semiconductors, which change at the points of contact of the fingerprint with the surface of the scanner. Semiconductor scanners are implemented in several ways, but the most common of them is capacitive.
In capacitive scanners, the effect of changing the capacitance of the pn junction of a semiconductor device is applied to obtain the image of a fingerprint when the crest of the fingerprint pattern is in contact with the semiconductor matrix. One of the modifications of the capacitive scanner is when the main module for scanning is a capacitor. That is, a traditional fingerprint image is not created: instead, data is collected using arrays of tiny capacitor chains. Because capacitors store an electric charge when the finger contacts the scanner, the charge will be changed where the comb touches the plate. Where on the hollow pattern, the charge will remain virtually unchanged.
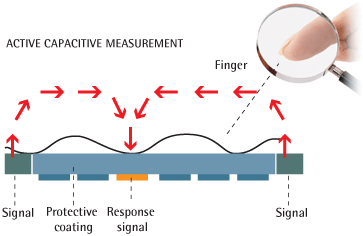
Changes in charge are monitored, thereby capturing fingerprint data. Then they are converted to digital, after which the search begins for distinctive and unique attributes of the fingerprint - they are compared with the fingerprints saved for comparison.
Capacitive scanners are now found recognition from manufacturers of smartphones due to the optimal ratio of price and quality. They have a low cost and a high degree of protection against dummies - of course, it is possible to deceive, but it will not be so easy. The first Xiaomi smartphone with a fingerprint scanner was Redmi Note 3 , which is also used in one of the company's new products, Xiaomi Mi Max . Does not refuse the capacitive scanner and OnePlus in its OnePlus 3 .

Of semiconductor scanners, pressure-sensitive and thermo-scanners are also actively used, but not in smartphones. In the first case, the image of the surface of the finger is obtained with the help of pressure, which the protrusions of the papillary pattern on the surface elements have, but the protection against dummies is rather low here. Thermo-scanners use a temperature map of the surface of the finger, which is converted into a digital image. To fake such a print is much more difficult.
The remaining types of semiconductor scanners are essentially a kind of capacitive, broaching or thermal scanners.
A few years ago, this type of fingerprint scanning was too expensive, but with the development of technology, it reached smartphones. The ultrasonic type is characterized by scanning the surface of the finger with the help of ultrasonic waves and measuring the distance between the source of the waves and the relief of the imprint along the reflected echo.
The ultrasonic pulse is transmitted to the finger in front of the scanner - part of it is absorbed, and the other part returns to the receiver. After that, it is recognized depending on the ridges, valleys and other unique elements of the print. The longer the scan takes, the better the additional fingerprint data is recognized - as a result, detailed 3D images are obtained.

The technology is, of course, very interesting - Le Max 2 from LeEco was one of the first smartphones with an ultrasonic fingerprint scanner. Other manufacturers are still looking in this direction with caution, yet the ultrasound scanner in smartphones is not yet “run-in”, and the implementation is more expensive, which may increase the final cost of the smartphone for buyers. Therefore, in Mi5 , for example, Xiaomi did not use an ultrasound scanner and made a choice in favor of a capacitive one.
At CES 2016, Qualcomm introduced Sense ID technology, an advanced 3D scanner sensor that collects much more individual information. Ultrasound penetrates metal surfaces, glass and some plastics and receives not a two-dimensional, but a detailed three-dimensional fingerprint card.
Qualcomm Sense ID - Ultrasound Fingerprint Scanner
Of course, any fingerprint scanner can be fooled. Capacitive scanners of the old model were not well perceived by wet or cold fingers, in modern smartphones (the same Redmi Pro ) this problem is almost solved and the scanner works very quickly. In a certain way, ultrasound scanners are safer, but this trend is likely to reach the market only after a couple of years. Making a fingerprint is difficult, even harder to use it to unlock a modern smartphone.

The vulnerability of fingerprint scanners in the first place lies in the implementation of technology by manufacturers of smartphones. A vivid example - Samsung and HTC in their Galaxy S5 and One Max smartphones stored images with users' fingerprints in the general section of the file system. It was a simple, unprotected .bmp file — in other words, a plain image. Now this is almost never the case, since manufacturers use either a special chip or a separate area in the chipset to store information about prints: Qualcomm has Snapdragon Mobile Security, ARM has TrustZone, and Apple has Secure Enclave. TrustZone actively uses Huawei : the technology analyzes fingerprints in a separate operating system on a dedicated virtual processor, which even the main system cannot reach. This means that third-party applications will not be able to access fingerprint scans.
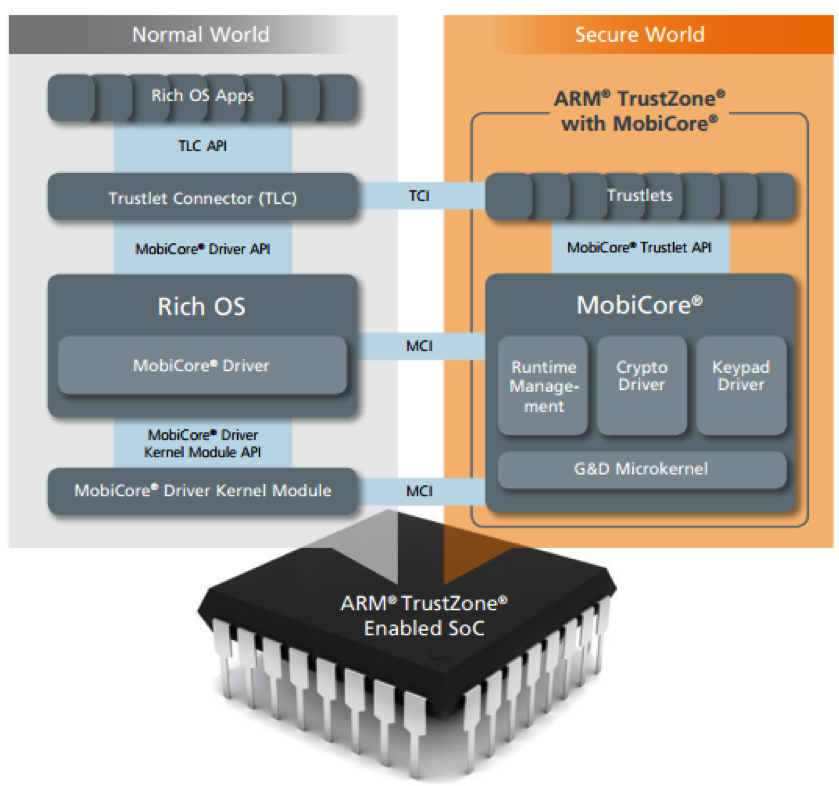
Very interesting is implemented in the Secure Enclave area of Apple. In essence, this is a coprocessor that uses encrypted memory and includes a hardware random number generator. In the manufacture of each such co-processor has its own unique identifier - it is unknown to other components of the system, or Apple itself (at least, so they say in the company). Secure Enclave processes data from the Touch ID sensor: the processor cannot read the fingerprint information and immediately redirects it to the coprocessor. Data is encrypted using the AES algorithm.
Notice that the iPhone asks for a password every time after rebooting? The password is the key to decrypt the fingerprints - it is activated under any circumstances that indicate extraneous interference: adding a new fingerprint, turning off the smartphone, five incorrect attempts to unlock, and so on. By the way, including, therefore, the button with the Touch ID must be protected - if it breaks and you change it to a non-original one, then the fingerprint scannerwill turn into a pumpkin will not work. What do you want? Security.
Nevertheless, Apple and everything is not so perfect, though here it is worth blaming the blame on the application developers. If someone sees the password of the owner of the iPhone, he will be able to unlock the smartphone, add his fingerprint, and then log in to all applications with Touch ID (messengers, banking, etc.), even if their passwords are different from the system one. Starting with iOS 9.0, developers can install a check (this was recently posted on Geektimes) about the appearance of new fingerprints at the time of launching the application, however, many, as a rule, do not use this recommendation.
The answer is simple and obvious - to use! Fingerprint scanners have already entered our lives as a safe alternative to remembering usernames and passwords, and owners of smartphones with the appropriate functionality do not complain about anything. You can hack everything, however, now the security level of scanners is really high, besides, the technology does not stand still and is developing - ultrasonic scanners in smartphones are proof of that.
If we have made a mistake somewhere in the text - correct us in the comments.

A fingerprint, as is well known, does not change over the course of a person’s entire life, which makes it possible to identify him at both 15 and 75 years of age. An imprint begins to form at the stage of fetal development, but even with identical twins, imprints are not identical. Therefore, it is one of the most common and safe (after the scanner of the retina and iris or DNA analysis) methods of human identification. Delete it as in the movie "Men in Black" will not work.

When viewed from the physiological point of view, a fingerprint is a specific set of protrusions with individual pores that are separated by depressions. And since it is associated with the thermal and electrical characteristics of the skin, you can use both heat, light, and capacitance (or all together) to obtain its image.
')

There are a number of varieties of fingerprint scanners - some are used on secret objects (along with gait analysis and other chips, of course), others have already come into the lives of modern smartphone owners as something ordinary. To summarize, we can distinguish three main groups of fingerprint scanners:
- Optical
- Semiconductor (silicon)
- Ultrasound
Optical scanners
They, as the name implies, use optical methods for obtaining images of a print. This method is the oldest method for capturing fingerprints: a photo of a fingerprint is processed using special algorithms that detect unique crests and protrusions. The resulting image is compared with those in the system, after which a positive or negative response is sent to the user. Optical scanners are subdivided into FTIR scanners, fiber-optic, broaching, roller, electro-optical and non-contact.
FTIR scanners use the Frustrated Total Internal Reflection effect. In this case, the light falls on the interface between two media, after which one part of the light energy is reflected from the border, and the second penetrates through it into the second medium. How much energy will be reflected is determined by the angle of incidence: when it reaches a certain size, all light energy is reflected from the interface, which is called total internal reflection.

At the contact of a fingerprint (more dense medium) with a less dense beam of light passes through the border at the point of total internal reflection. So only those beams of light that fall into points to which the capillary pattern of the finger surface is not attached will be reflected. Then CCD or CMOS captures the final light image of the finger surface.
Fiber optic scanners work a little differently. In fact, we have a fiber-optic matrix, with each of its fibers ending with a photocell. Each photocell captures the residual light that has passed through the finger at the point where the fingerprint touches the surface of the scanner. Further, the data of all elements are aggregated and on their basis the image of a fingerprint is obtained.

Electro-optical scanners use a special polymer, which contains a light-emitting layer. It reflects the heterogeneity of the electric field of the finger at the surface of the scanner, after which a fingerprint is displayed. The rest of the work is done by photodiodes that convert everything into a digital form. Broaching scanners are one of the most interesting, because in this case the finger is not attached to the scanner surface, as we are used to, but is carried out on the reader, which is a narrow strip. The principle of their work is in many ways similar to the FTIR scanners mentioned earlier.
When using contactless scanners you don’t even have to contact the surface of the scanner. A finger is applied to a special hole, it is illuminated from below by several sources of light, the lens collects information, then the data are projected onto a CMOS, where they are converted into an image of a fingerprint.

Optical scanners are fairly easy to fool, since they capture only the 2D image — this is one of their main drawbacks. In our time, they have faded into the background, however, in many areas are still used. But certainly not on secret objects and not where they seriously care about security: for this they invented silicon (semiconductor) and ultrasound scanners.
Silicon (semiconductor) scanners
The main difference between semiconductor scanners and optical scanners is that in this case, the image is obtained using the properties of semiconductors, which change at the points of contact of the fingerprint with the surface of the scanner. Semiconductor scanners are implemented in several ways, but the most common of them is capacitive.
In capacitive scanners, the effect of changing the capacitance of the pn junction of a semiconductor device is applied to obtain the image of a fingerprint when the crest of the fingerprint pattern is in contact with the semiconductor matrix. One of the modifications of the capacitive scanner is when the main module for scanning is a capacitor. That is, a traditional fingerprint image is not created: instead, data is collected using arrays of tiny capacitor chains. Because capacitors store an electric charge when the finger contacts the scanner, the charge will be changed where the comb touches the plate. Where on the hollow pattern, the charge will remain virtually unchanged.

Changes in charge are monitored, thereby capturing fingerprint data. Then they are converted to digital, after which the search begins for distinctive and unique attributes of the fingerprint - they are compared with the fingerprints saved for comparison.
Capacitive scanners are now found recognition from manufacturers of smartphones due to the optimal ratio of price and quality. They have a low cost and a high degree of protection against dummies - of course, it is possible to deceive, but it will not be so easy. The first Xiaomi smartphone with a fingerprint scanner was Redmi Note 3 , which is also used in one of the company's new products, Xiaomi Mi Max . Does not refuse the capacitive scanner and OnePlus in its OnePlus 3 .

Of semiconductor scanners, pressure-sensitive and thermo-scanners are also actively used, but not in smartphones. In the first case, the image of the surface of the finger is obtained with the help of pressure, which the protrusions of the papillary pattern on the surface elements have, but the protection against dummies is rather low here. Thermo-scanners use a temperature map of the surface of the finger, which is converted into a digital image. To fake such a print is much more difficult.
The remaining types of semiconductor scanners are essentially a kind of capacitive, broaching or thermal scanners.
Ultrasound scanners
A few years ago, this type of fingerprint scanning was too expensive, but with the development of technology, it reached smartphones. The ultrasonic type is characterized by scanning the surface of the finger with the help of ultrasonic waves and measuring the distance between the source of the waves and the relief of the imprint along the reflected echo.
The ultrasonic pulse is transmitted to the finger in front of the scanner - part of it is absorbed, and the other part returns to the receiver. After that, it is recognized depending on the ridges, valleys and other unique elements of the print. The longer the scan takes, the better the additional fingerprint data is recognized - as a result, detailed 3D images are obtained.

The technology is, of course, very interesting - Le Max 2 from LeEco was one of the first smartphones with an ultrasonic fingerprint scanner. Other manufacturers are still looking in this direction with caution, yet the ultrasound scanner in smartphones is not yet “run-in”, and the implementation is more expensive, which may increase the final cost of the smartphone for buyers. Therefore, in Mi5 , for example, Xiaomi did not use an ultrasound scanner and made a choice in favor of a capacitive one.
At CES 2016, Qualcomm introduced Sense ID technology, an advanced 3D scanner sensor that collects much more individual information. Ultrasound penetrates metal surfaces, glass and some plastics and receives not a two-dimensional, but a detailed three-dimensional fingerprint card.

Qualcomm Sense ID - Ultrasound Fingerprint Scanner
And what, is it really safe?
Of course, any fingerprint scanner can be fooled. Capacitive scanners of the old model were not well perceived by wet or cold fingers, in modern smartphones (the same Redmi Pro ) this problem is almost solved and the scanner works very quickly. In a certain way, ultrasound scanners are safer, but this trend is likely to reach the market only after a couple of years. Making a fingerprint is difficult, even harder to use it to unlock a modern smartphone.

The vulnerability of fingerprint scanners in the first place lies in the implementation of technology by manufacturers of smartphones. A vivid example - Samsung and HTC in their Galaxy S5 and One Max smartphones stored images with users' fingerprints in the general section of the file system. It was a simple, unprotected .bmp file — in other words, a plain image. Now this is almost never the case, since manufacturers use either a special chip or a separate area in the chipset to store information about prints: Qualcomm has Snapdragon Mobile Security, ARM has TrustZone, and Apple has Secure Enclave. TrustZone actively uses Huawei : the technology analyzes fingerprints in a separate operating system on a dedicated virtual processor, which even the main system cannot reach. This means that third-party applications will not be able to access fingerprint scans.

Very interesting is implemented in the Secure Enclave area of Apple. In essence, this is a coprocessor that uses encrypted memory and includes a hardware random number generator. In the manufacture of each such co-processor has its own unique identifier - it is unknown to other components of the system, or Apple itself (at least, so they say in the company). Secure Enclave processes data from the Touch ID sensor: the processor cannot read the fingerprint information and immediately redirects it to the coprocessor. Data is encrypted using the AES algorithm.
Notice that the iPhone asks for a password every time after rebooting? The password is the key to decrypt the fingerprints - it is activated under any circumstances that indicate extraneous interference: adding a new fingerprint, turning off the smartphone, five incorrect attempts to unlock, and so on. By the way, including, therefore, the button with the Touch ID must be protected - if it breaks and you change it to a non-original one, then the fingerprint scanner
Nevertheless, Apple and everything is not so perfect, though here it is worth blaming the blame on the application developers. If someone sees the password of the owner of the iPhone, he will be able to unlock the smartphone, add his fingerprint, and then log in to all applications with Touch ID (messengers, banking, etc.), even if their passwords are different from the system one. Starting with iOS 9.0, developers can install a check (this was recently posted on Geektimes) about the appearance of new fingerprints at the time of launching the application, however, many, as a rule, do not use this recommendation.
So what to do?
The answer is simple and obvious - to use! Fingerprint scanners have already entered our lives as a safe alternative to remembering usernames and passwords, and owners of smartphones with the appropriate functionality do not complain about anything. You can hack everything, however, now the security level of scanners is really high, besides, the technology does not stand still and is developing - ultrasonic scanners in smartphones are proof of that.
If you decided to buy one of the mentioned smartphones, then here’s a discount
1. Xiaomi Mi Max 16GB ROM 4G Phablet for $ 169.99 for the MIMAXS coupon (until December 31st)
2. OnePlus 3 4G Smartphone for $ 445.99 for the GBOPlus coupon (until December 31st)
3. XiaoMi Mi5 5.15 inch 64GB 4G Smartphone for $ 356.99 for coupon Mi5gb (until December 31st)
4. LeTV Leeco Le Max 2 4G Phablet for $ 219.99 for the coupon LeTVGBS (until December 31st)
5. Xiaomi Redmi Pro MIUI 8 4G Phablet for $ 255.99 for coupon MIUI8 (until December 31st)
2. OnePlus 3 4G Smartphone for $ 445.99 for the GBOPlus coupon (until December 31st)
3. XiaoMi Mi5 5.15 inch 64GB 4G Smartphone for $ 356.99 for coupon Mi5gb (until December 31st)
4. LeTV Leeco Le Max 2 4G Phablet for $ 219.99 for the coupon LeTVGBS (until December 31st)
5. Xiaomi Redmi Pro MIUI 8 4G Phablet for $ 255.99 for coupon MIUI8 (until December 31st)
If we have made a mistake somewhere in the text - correct us in the comments.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/399601/
All Articles