Iron cryptography: Enigma, phone calls and quantum intricacy
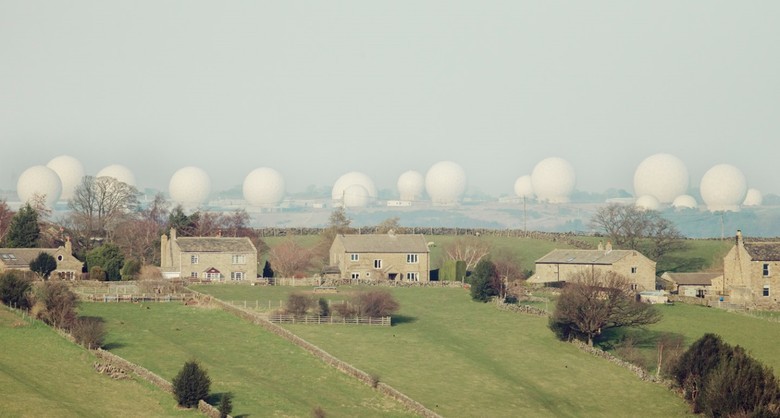

This is not an exhibition of giant golf balls, but a Menwith Hill base in North Yorkshire. What is the connection with cryptography? This will tell under the cut
When it comes to cryptography, they usually talk about intangible objects: mathematical algorithms, hash functions, programs, probability theory. This is the real, but not the only basis for encryption methods. In addition to mathematics, there are extremely interesting objects in the world of cryptology. Some of them (but not all) involved in the decomposition of integers into prime factors, the search for discrete logarithms, the generation of random numbers are called crypto machines. Others have a significant, but indirect relationship to cryptography - quantum computers. And finally, the third is a mystery in its purest form.
It's time to talk about crypto objects that you can touch. But not everyone.
')
We wanted to write a big post about cryptography since we started encrypting video calls all over the world in ICQ. End-to-end encryption in ICQ means that the keys used for encryption and decryption are generated and stored only on the end of the send-receive devices — the server side does not participate in the creation of keys and does not have access to them. ICQ encryption is based on the open protocol ZRTP.
Voice-over Transport Protocol (RTP) (Real-time Transport Protocol), which works at the application level, appeared in the distant 1996. Ten years later, the already-secure cryptographic protocol ZRTP was created, which was proposed as a method for negotiating encryption keys using the Diffie-Hellman method through the same media stream in which the RTP connection was established.
 The name of the protocol is a reference to the creator name of Phil Zimmermann (Phil Zimmermann): Zimmermann + RTP = ZRTP. Zimmerman has created another secure system — the most popular encryption method in the world for Pretty Good Privacy (PGP) emails and documents.
The name of the protocol is a reference to the creator name of Phil Zimmermann (Phil Zimmermann): Zimmermann + RTP = ZRTP. Zimmerman has created another secure system — the most popular encryption method in the world for Pretty Good Privacy (PGP) emails and documents.The Diffie-Hellman method used in ZRTP is in fact also called the cryptographic protocol (this is how the “matryoshka” turns out). In general, it describes the possibility of obtaining a secret key over unsecured communication channels using symmetric encryption.
ZRTP is able to detect the presence of a “man in the middle” attack, and indeed it is generally considered very reliable, which was confirmed by the documents of Snowden, in which ZRTP is mentioned in relation to the activities of the NSA. It is known for certain that several years ago a bundle from Tor, an additional anonymization service, instant messaging system CSpace and ZRTP was considered absolutely unbreakable. At the same time, Tor's vulnerability in this chain was not the strongest link. By the way, PGP is also considered an unsolvable task for the NSA.
Thus, modern cryptography has shown resilience in the fight against the most powerful resource in the history of cryptographic wars ... But is this really so?
There is one interesting crypto history showing that it is not always worth believing well-known facts.
NSA can keep secrets
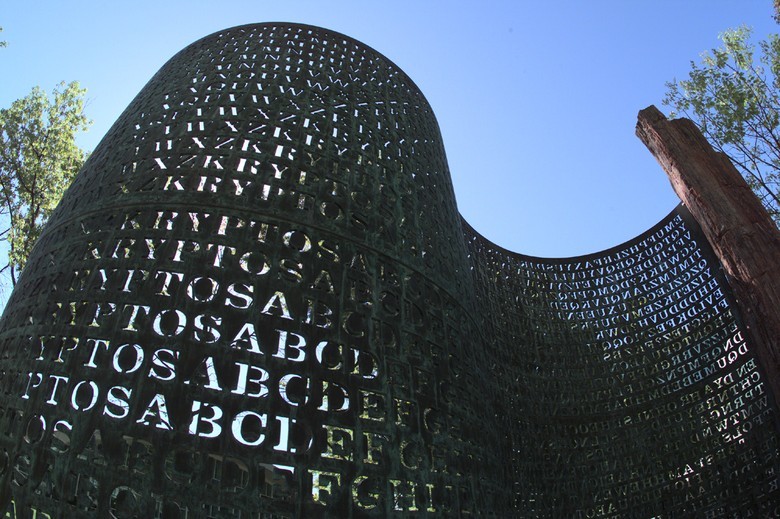

A source
About the Agency and its secrets are legendary, but one of the most amusing cases associated with the main monument of modern cryptography (and its reliability) - Kryptos sculpture. A huge metal panel with many letters appeared on the order of the CIA in front of the office in Langley on November 3, 1990, and since then has become a real symbol of mysteries and secrets.
The creator of Kryptos, James Sanborn, approached the matter creatively and decided that sculpture in the inner courtyard of one of the most closed organizations in the world cannot be banal. Although the CIA’s original plan did not provide for the construction of anything remarkable, Sanborn himself suggested creating a metal allusion to the secrecy, secrecy and mystery of people who would see it from the windows of their offices.
The sculptor did not know anything about encryption methods, so for 4 months he studied cryptographic techniques from the end of the 19th century to the Second World War, and the former head of the Langley cryptographic center Edward Steidt helped him. James Sanborn deliberately did not study the modern at that time methods, and the plan of the sculpture did pencil on paper - machine methods would only complicate and confuse his work. Without operating with complex mathematical algorithms and without doing calculations on computers, he encrypted his message to the world in four parts (segments) of sculpture.
You may have heard that the fourth, the last, part of the puzzle has not been solved yet. But now this is not interesting, but the history of the solution of the previous three sections. Sanborn himself believed that it would take several days (and several months to decrypt the last difficult part), but only in 1999, the crop-analyst James Gillogly, using his own program, provided the solution.
However, after that, the CIA published documents from which it became known that intelligence officer David Stein, having spent 400 hours of his personal time, decided all the same three sections 16 months before Gillogly. Here one would be surprised by the waiting tactics of the CIA, but wait. In 2013, the NSA officially announced (with supporting facts ) that it had coped with the task five years earlier than the CIA. Three Agency staffers deciphered the three sections of Kryptos for several months in 1992–93. Regarding the fourth section, it was concluded that decoding it would take too much valuable staff time.
So, the NSA was silent about the success of 10 years, of which for 5 years the answer to the riddle was known all over the world. It is now officially considered that the fourth part of the Cryptos is not deciphered. Given the patience and endurance of the NSA, it will not be strange to think that they already know the answer (or know that the answer does not exist). And this concerns not only the solution of the mystery of the sculpture, but also many other cryptographic secrets. You will read more about this further, and the topic with Kryptos will end with a mention of another important project of its author.
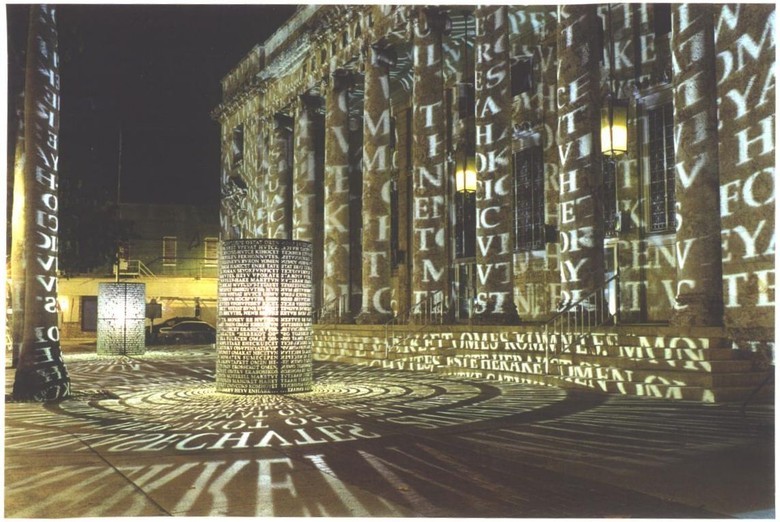

A source
Sanborn was clearly impressed with the attention received during the years of the existence of Kryptos, and made several more projects at the intersection of cryptography and the arts. The Monument "Antipodes" combines fragments of texts in Latin from Cryptos and Cyrillic from the project "Cyrillic Projector". The projector, endowed with a light source, was a three-meter hollow cylinder, the entire surface of which is covered with cut-through letters of the Russian alphabet, in which the secret messages of the KGB are encrypted. The Cyrillic part, unlike Kryptos, was solved.
All for the sake of hacking
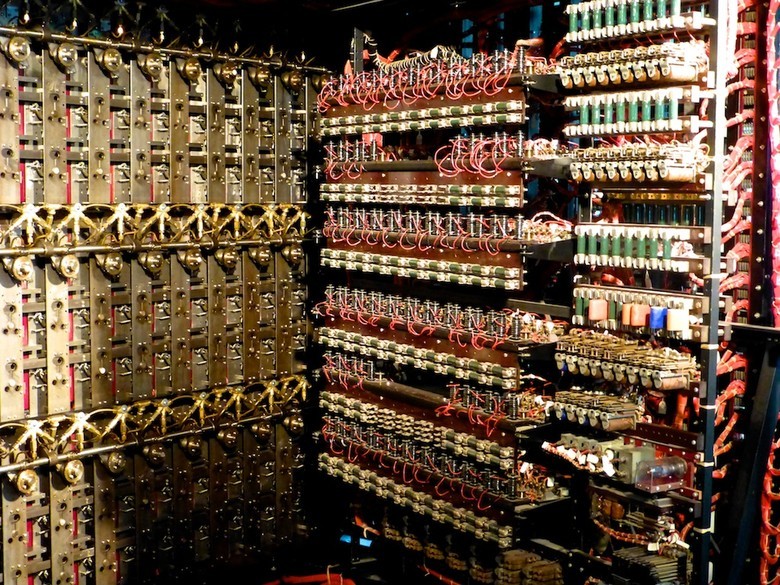

Modern reconstruction of the Colossus, the first "supercomputer" used to crack ciphers
A source
The history of cryptography has about 4 thousand years, but until the beginning of the 20th century most of the ciphers, with rare exceptions, did not constitute a serious mathematical challenge to human abilities. In the end, you could always catch the coder, crucify and get valuable information. Everything changed before the beginning of the Second World War, when electromechanical encryption devices appeared in the world, the result of which was considered not openable (and the rack did not always help). Began the era of cars, which has not ended so far.
Yes, it is believed that in the field of decryption we are at a dead end of technological capabilities, and the struggle is in the field of learning algorithms. However, one should not discount the effect of Moore’s law and the inevitable appearance of quantum computers. Decryption machines were not always the most productive, as can be clearly seen in the example of Turing Bombe, which participated in the hacking of the famous Enigma, but all cryptomachines always remained at the height of technological progress.
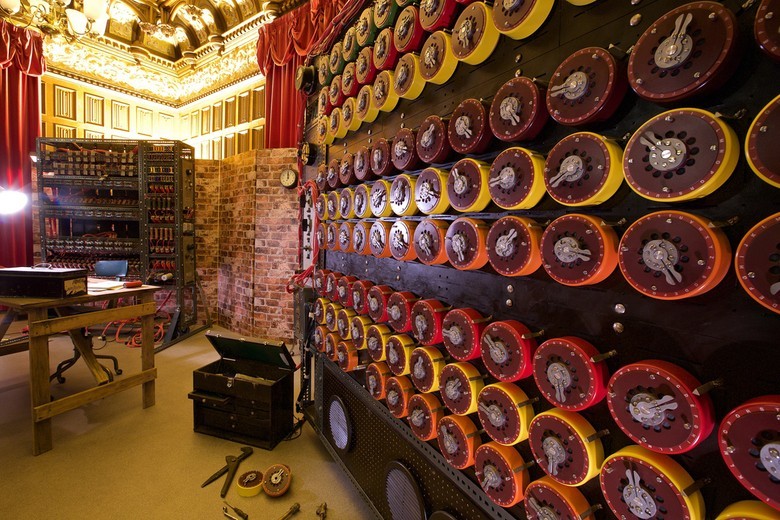

"Killer" "Enigma." Modern reconstruction (all models for the purpose of secrecy were destroyed after the war)
Turing Bombe is an electronic-mechanical decryption machine created during World War II with the participation of Alan Turing. The principle of operation was to search for possible options for the cipher key and text decryption attempts using the known structure of the decrypted message. One Bombe machine simultaneously emulated the actions of several dozen Enigma machines. 212 such machines decrypted up to 3 thousand messages per day.
Later, computers were used to decrypt messages. The largest in the world - at the time of construction - the computer "Koloss" was used to crack the encryption machine "Lorenz", which served to communicate the highest German command.
Rosetta stone, cuneiform, Navajo, the most complicated German ciphers - it turned out that everything can be cracked using computer technology. Since the creation of Hepburn's disk encoder, attempts to create a real cipher machine have not ceased, but every time any stable cipher was vulnerable.
Cryptogadgets
Cryptomachines always differed in a certain difficulty in use, while the user most often needed a magic wand, one stroke of which would be enough to hide important information from a curious third party.
Such a magic wand could be a cryptophone, which “on the fly” encrypts the transmission of a voice signal. In 1978, for decades before the calls to ICQ were encrypted, the Phaserphone appeared, allowing you to encrypt your voice. It was assumed that the device can be launched into a free commercial sale for $ 100. However, under pressure from the NSA, the project was classified.
From the end of the 70s, the NSA began producing phones for secret government communications - STU. These were not the first phones, at least known about the KY-3 (TSEC / KY-3) models from the 60s, but they became the most popular and reliable. According to some, STU-3, produced in 1987, was used until 2009, after which they were replaced with Secure Terminal Equipment and other more advanced equipment.

A source
STU-III looked the same as regular office phones, connected to a standard telephone jack, and calls from them could be made to any ordinary telephone (but such calls did not receive special protection). However, when calling from one STU-III to another, when you press a special button, protected communication mode is activated. There were both portable and military versions of such phones. Most of them had an internal modem and an RS-232 port for data and fax transmissions. Telephones were produced by telecommunications companies AT & T, RCA (L-3 Communications) and Motorola.
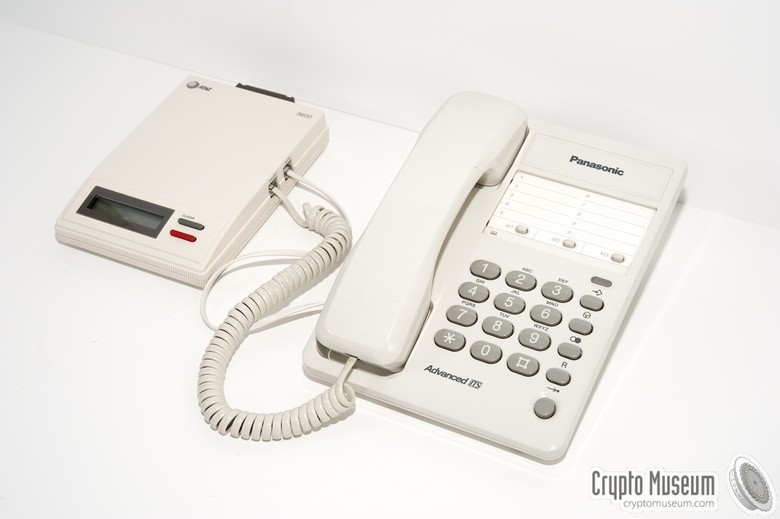

A source
In 1993, AT & T developed the TSD-3600, the first cryptophone that used the Clipper Chip. The chip used the Skipjack encryption algorithm developed by the NSA to transfer information. The NSA itself, of course, had a decoding key that made it possible to read messages encrypted using Clipper.
In the future, the NSA launched a separate project, the SME-PED (Secure Mobile Environment Portable Electronic Device), in which it continued experiments on the creation of phones designed for top-secret communication.
The phone in the screenshot above is one of the most expensive in the world. In 2009, it cost $ 4,750 - and this is only "hardware", excluding the cost of software and licenses. It does not have rhino skin, diamonds or any kind of jewelry, it’s just a highly functional Sectéra Edge device designed for top-level secure communications.
The secure voice part is only a small part of modern cryptography. To learn more, you need to go to the place of registration of the organization that has done a lot for cryptology: both good and bad.
Cryptographic Headquarters
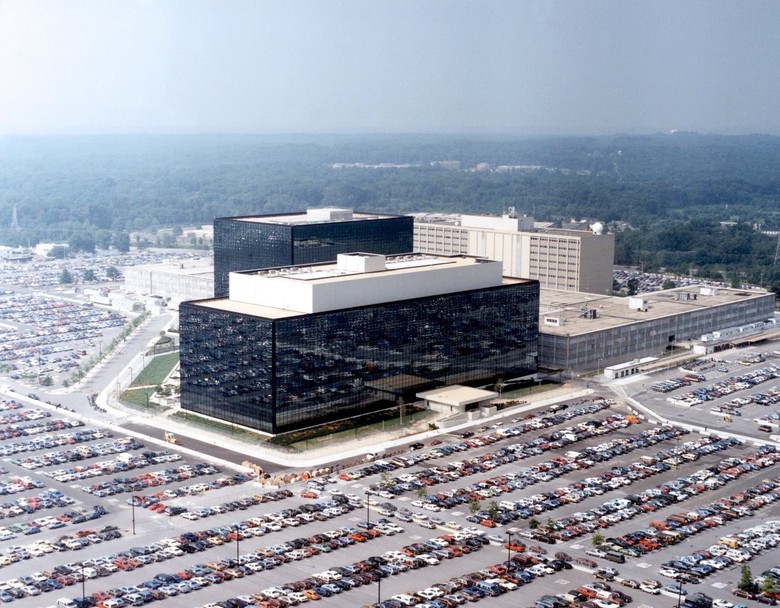

The most famous image of the NSA office, made and distributed by the NSA itself sometime in the 1970s. However, since then the territory of the complex has been significantly increased and built up
In the picture above - the main center of world cryptography, the headquarters of the US National Security Agency. What exactly is located in this office, except for the command center, is not precisely known. Yes, the headquarters itself is currently building a supercomputer worth $ 896 million. It also houses an analytical center that has access to the NSA's cloud storage in several data centers located in the US and the UK. But there are no guided tours here and you cannot get close to the territory of the complex.
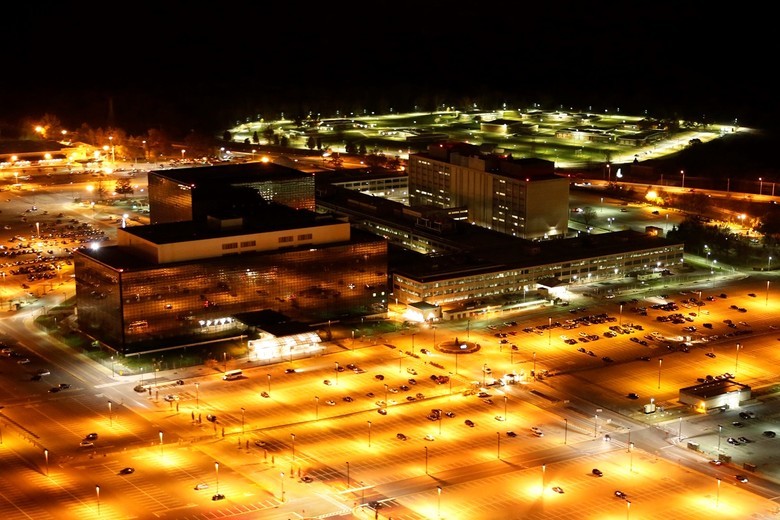

Photo office, made in 2013. Find the 10 differences between shots.
Around the 26-storey complex there is the largest in the world car parking for 18,000 places for agency employees. The whole complex is surrounded by a fence with barbed wire and is protected by 400 people with a variety of weapons: from fighting dogs to armored personnel carriers. But literally two steps away from the office, the National Museum of Cryptography, open to the public since 1993, contains thousands of exhibits displaying the history of American cryptography from the times of the war of independence to the present. The territory of the NSA is not limited to the museum and the central office. We know exactly about dozens of objects around the world associated with the activities of the Agency.
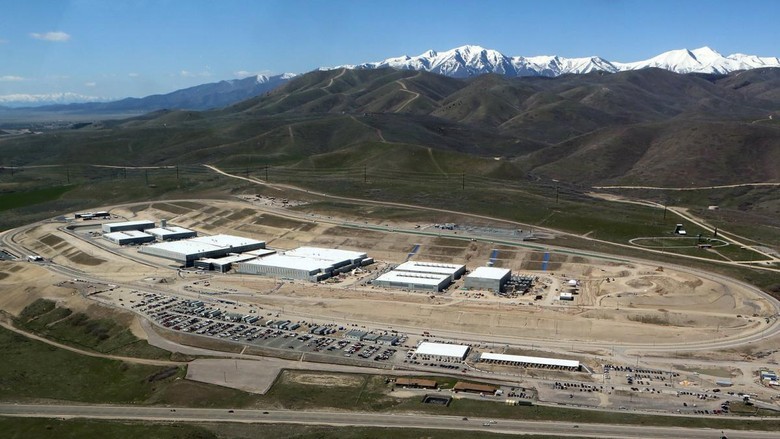

In the picture above - the largest data center of the NSA (and the third in size among all data centers in the world), the construction of which began in 2012 in Utah. Four rooms with a total area of 9290 m 2 were allocated for servers, the area of all administrative and technical buildings is 83 613 m 2 . The center is designed to crack coded data: first of all, all information in deepnet, and then financial information, operations with securities, commercial transactions, foreign military and diplomatic secrets, legal documents, confidential personal information. The potential amount of information that can be placed in this data center is staggering. According to experts , the center is being built to process in the future yottabayt (!) Data. Another opinion was expressed by the Internet Archive engineer Paul Vixie: the total capacity of data carriers in the data center at the first stage of development will take 3–12 exabytes.
Another reason for the construction of this data center is AES (Advanced Encryption Standard), a symmetric block encryption algorithm (block size 128 bits, key 128/192/256 bits), adopted as the encryption standard by the US government. Most experts said that a brute force attack to unlock this cipher would take longer than the age of the Universe. Hacking AES for the NSA is a modern Manhattan project. For these purposes, R. Kotter's supercomputer center was built, where computers were specially modified to perform cryptanalysis against certain algorithms, such as AES.
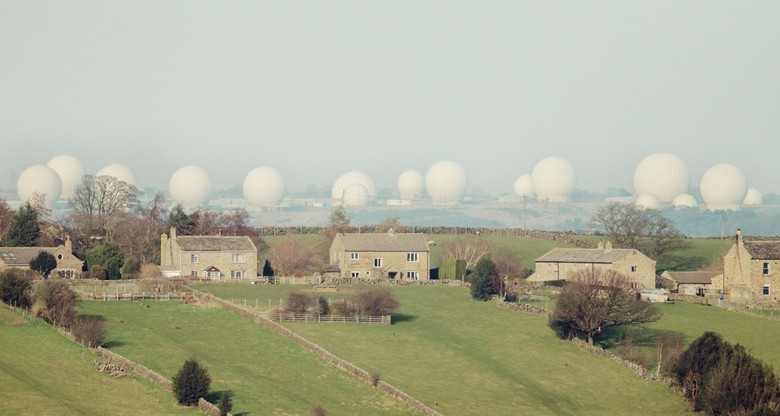

Menwith Hill , the main brain of the NSA outside the US and the source of the most important encrypted information
If the information cannot be cracked right now, then it can be deciphered in the future - for example, using quantum computers or artificial intelligence forces. But for this you need to fulfill a number of conditions. First, the information needs to be stored somewhere and for this purpose new data centers are built (at least those we know about). Then you need to configure the method of obtaining information. And in this, Menwith Hill, a secret base built in the middle of the 20th century to monitor the USSR, plays a significant role. Now the main task of the station is to intercept telephone conversations and other communications from Europeans, Russia and the Middle East. According to documents promulgated by the former NSA employee Edward Snowden, more than 300 million phone calls, calls from instant messengers and electronic messages are processed daily at the base.
The massive white “golf balls” that you see on the horizon are 30 powerful antennas of the FORNSAT (Foreign Satellite interception) project designed to intercept signals from foreign communication satellites. The site also has other facilities and antennas that use US government satellites to monitor wireless communications on the ground - including mobile calls and Wi-Fi traffic. Menwith Hill also allows you to control almost all small satellite earth stations, that is, terminals with a small antenna (VSAT, Very Small Aperture Terminal) used in satellite communications since the early 90s.
In addition to its own group of satellites and communication stations scattered across hidden and obvious bases around the world (through which, in all likelihood, all world traffic is filtered), the NSA has its own IAD (Information Assurance Directorate) management specializing in the development of cryptoalgorithms and information protection . They also sponsor various scientific research in the field of the theory of quantum-cryptographic attacks.
Recall that by quantum cryptography is meant primarily the quantum distribution of keys, based on the laws of physics. All classic key distribution methods are insecure from the outset, since nothing prevents a third party from simply copying the key during the distribution process. However, the laws of quantum physics prohibit copying of an unknown quantum state. Quantum entanglement allows you to accurately determine when someone third wants to connect to the communication channel.
These phenomena are well known, and the quantum key distribution is now present in selected commercial products for the banking sector. But quantum cryptography is also algorithms, those classical algorithms, which, when adapted to the probabilistic result of the work, provide an amazing time gain on quantum computers. Most of them require a full-fledged quantum computer for their implementation, but nothing prevents to develop such algorithms in theory. In 1994, the creation of a quantum algorithm for efficient factorization made it possible to crack standard encryption schemes, including RSA.
It was believed that before creating full-fledged quantum computers, we still needed at least ten years, but thanks to the Information Assurance Directorate, it became known that modern quantum cryptography is already outdated, and it is necessary to develop post-quantum security standards quantum computers). Last year, the NSA openly announced the need to develop new standards for the post-quantum era - and this happened a few months before the announcement of open access to the IBM cloud computing quantum service.
IBM Quantum Experience
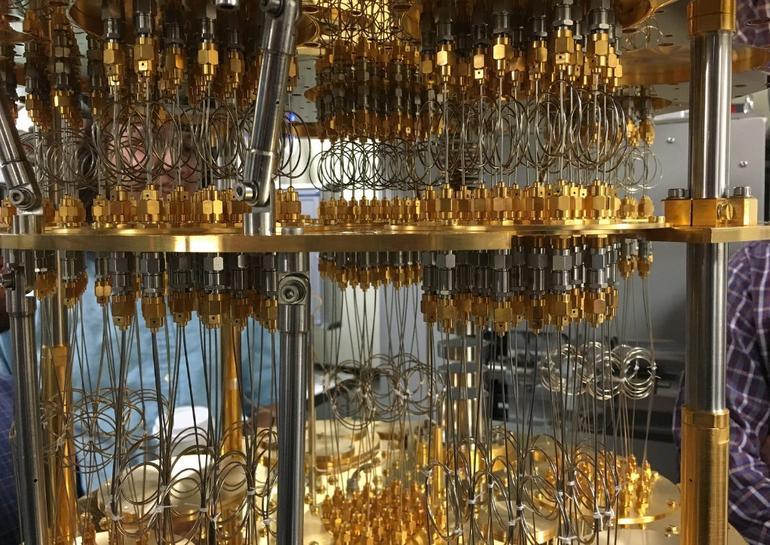

" Quantum iron " - part of the cooling system of a quantum computer, which lowers the temperature of qubits to -272 °
There are three points of view why the NSA is forcing research in the field of post-quantum cryptography:
- Prepare a sleigh in summer. The absence of a real quantum computer did not prevent us from building theoretical models of the operation of such machines, based on the principles of quantum mechanics, known to us for decades. With pure mathematics (and some physics), we managed to find out that a quantum computer would destroy most of the traditional algorithms before the advent of these computers. Thus, it is better to be ready now, than in 5–10 years to be left without any encryption at all.
- Quantum computer has already been created. The NSA itself or some scientific / commercial enterprise could theoretically build a quantum computer that breaks asymmetric cryptosystems based on elliptic curves like protein nuts. The problem is that we can not verify it. It is precisely known that Snowden’s published documents do not say a word about such a system in the US intelligence services, and it’s impossible to build it from scratch for several years. Dialectic suggests that Snowden might not have access to such information. But it is still a big doubt that the fact of the operation of a real quantum system can be hidden.
- It is possible that the study of quantum algorithms in certain scientific circles controlled by the NSA prompted researchers to the path to significantly more powerful attacks using traditional classical computers. That is, if we have a method of theoretical attack with the participation of a quantum computer, then it can be so good that it is reproduced on a “normal” supercomputer. This statement again has one drawback - it is extremely difficult to verify in practice.
So, of all the options right now, you can check only one - by looking at the list of quantum computers in the world and assessing their capabilities. The list is short, as of 2016, only limited options are built in several laboratories, or specific ones (D-Wave), which solve an extremely limited subclass of tasks. From time to time, simple quantum algorithms are run on simple multi-qubit registers and simple problems are solved. But science does not stand still, and there is a movement towards the quantum era.
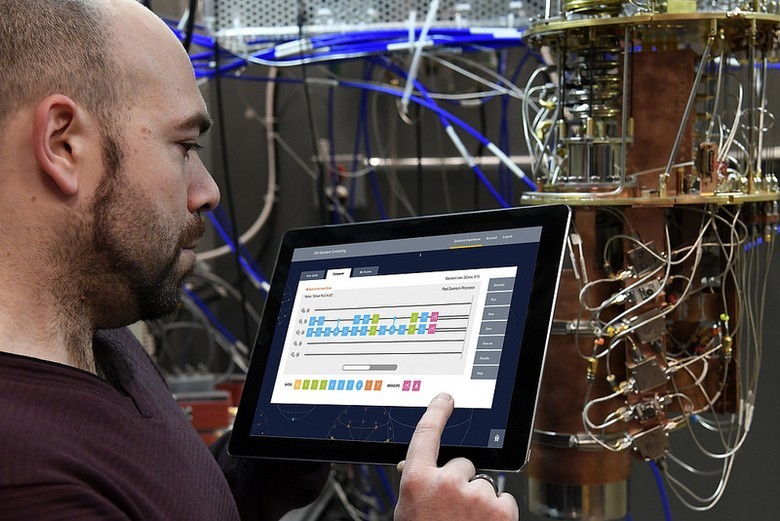

"Quantum programming"
This year, IBM launched its own cloud computing service based on a five-bit quantum computer, free for researchers. IBM Quantum Experience , sponsored by DARPA, allows, for example, to estimate the speed of the quantum algorithm for solving the enumeration problem ( Grover’s algorithm ), and it will be higher than the speed of a classical computer. With cloud access to qubits, more people will start learning quantum computer programming. And this means that the world will have more opportunities to study attacks that can destroy some asymmetric cryptoalgorithms.
Future: now, then, then

FPGA-based Bitcoin Mining Farm
A source
In the case of cryptography, it is impossible to determine exactly what is the future and the next step of development. It may well be that we already live in the past, and the future in certain secret places has long come (and managed to grow old).
Obviously, there are several areas in which cryptography will evolve rapidly. Alas, these are not phone calls. The blockchain, based on modern cryptography, is one of the most promising growth points. Bitcoin itself uses the digital signature algorithm of elliptic curves (ECDSA) for signing transactions and the hash function SHA-256 and RIPEMD160. A quantum computer would be able to crack ECDSA, however, SHA-256 and RIPEMD160 at the moment are not broken even theoretically. However, this does not mean that in a year or two another way will not appear. For a world in which billions of dollars have been spent on computer chips that do nothing but SHA-256 calculations, this will be a heavy blow.
Secure communication channels for banks on the basis of quantum entanglement are already at serious risk. Several ways to access the keys have been published. They are difficult to implement, but possible. Perhaps the next step in the field of data protection will be neural networks. Yes, everyone is already fed up with news about neural networks that are once again drawing something, but researchers from Google Brain brought in many ways unusual news: two neural networks " agreed " to exchange encrypted messages with each other so that the third grid could not crack them and decrypt.
The first call that the world is waiting for thousands of new Cryptos - not iron, but neuro-cryptography.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/399557/
All Articles