Answers to questions about surveyors "Lakhta Center"
Laser, optical, mechanical instruments for calculating even millimeter deviations from the target ...

- I need your clothes, helmet and electronic total station!
In the first part of our large geodesic review, we have already found out that this wealth is not from the arsenal of an extra-class sniper, but the “gentleman's set” of the surveyor “Lakhta Center”.
')
What was in the first part?
What will happen next?
Turn the tower vertically. Who and how leads her right course?
The construction process of the “Lakhta Center” is controlled by about 30 surveyors - quite a bit for the Petersburg “construction of the century”, where more than 3.5 thousand people replace every day.
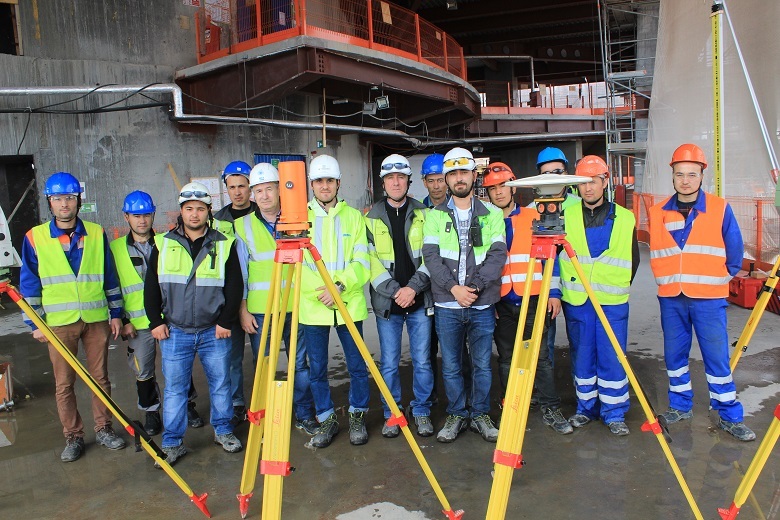

Surveyors "Lakhta Center"
The small size of the team clearly demonstrates the results of the scientific and technological revolution that has occurred in geodesy in the past 20 years: new technologies have allowed to drastically increase the productivity of the process, despite the fact that the tasks facing today's surveyors are becoming more complex in geometric progression.
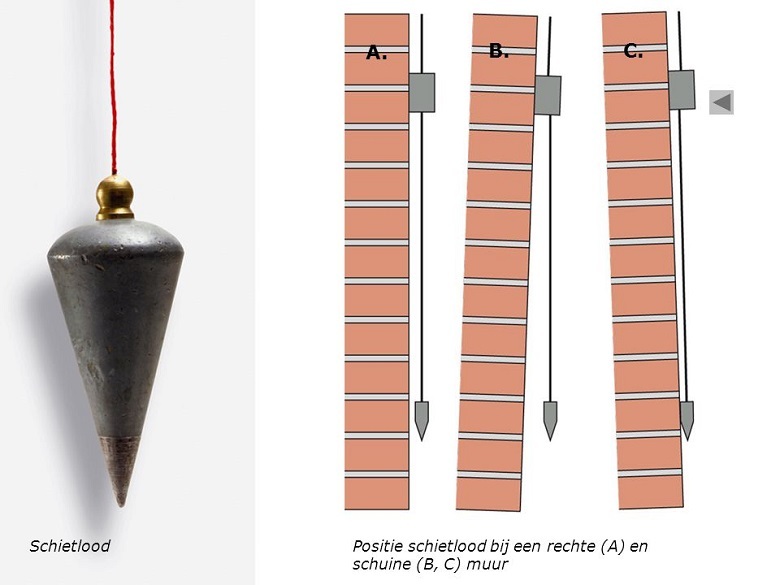
Once for construction enough and such a simple plumb line. But with the growth of buildings, everything changed.
The construction of the tower "Lakhta Center" uses several geodetic instruments and technologies that solve different tasks. Three of them are used for the first time in Russia, the rest have proven themselves in Dubai on the construction of Burzh Khalifa and Moscow (Federation complex, Renaissance Construction also acted as the general contractor).
So, the previously promised analysis of devices.
In the last publication, many were interested in the “miracle inclinometer”. We will once again admire the hero's photo:
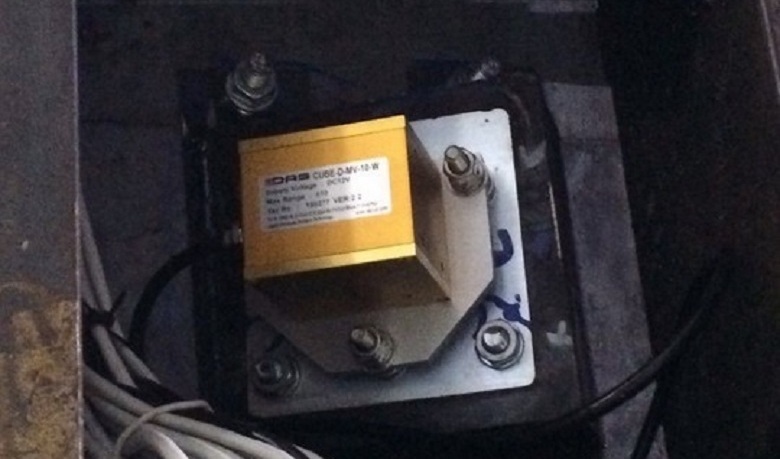

An inclinometer is a deflection sensor. It measures the angular displacements in space along perpendicular axes X and Y, transfers this data to the system. Further, with the help of special software, the delta of movement along each axis is calculated. The total deviation is the sum of the readings of all installed inclinometers. This final indicator is used as a correction for GNSS antennas, which will be discussed further.
Inclinometers are located on the inner walls of the tower’s core every 50–80 meters (12–20 floors). In order not to damage the sensors, they are hidden in metal protective boxes. You can find out more about inclinometers in the comments here .
Trimble GNSS:
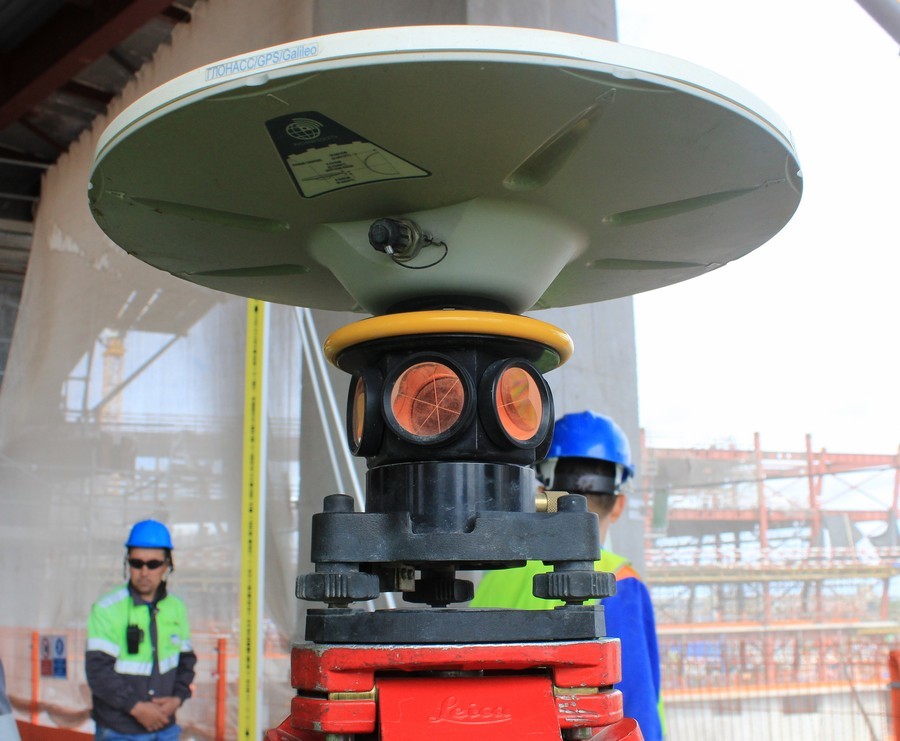

This is a flying saucer-like equipment — the antenna of the Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS), already familiar from the first part of the review. And she really has a connection with space. The system is used as a center base for formwork for the walls of the core.
The antennas are located at the highest point of the construction site - according to the diameter of the wind-proof shields of self-lifting formwork:

Geodetic satellite antennas on the formwork "Lakhta Center"
Decking (form for the walls of the core) takes steps - iterations:

After each such iteration, the current coordinates of the antennas are determined and compared with the design figures. If there is a delta exceeding the permissible error - the formwork is returned to the design smooth vertical axis.
Since the core of the tower is subject to wind oscillations - the higher, the stronger, and with it the antennas also oscillate, it is very important to have a stable point of reference. To this end, there are six additional ground stations located on the building site, from which data for correction is read when determining the exact location of the antennas on the core formwork. This readout occurs in real time.
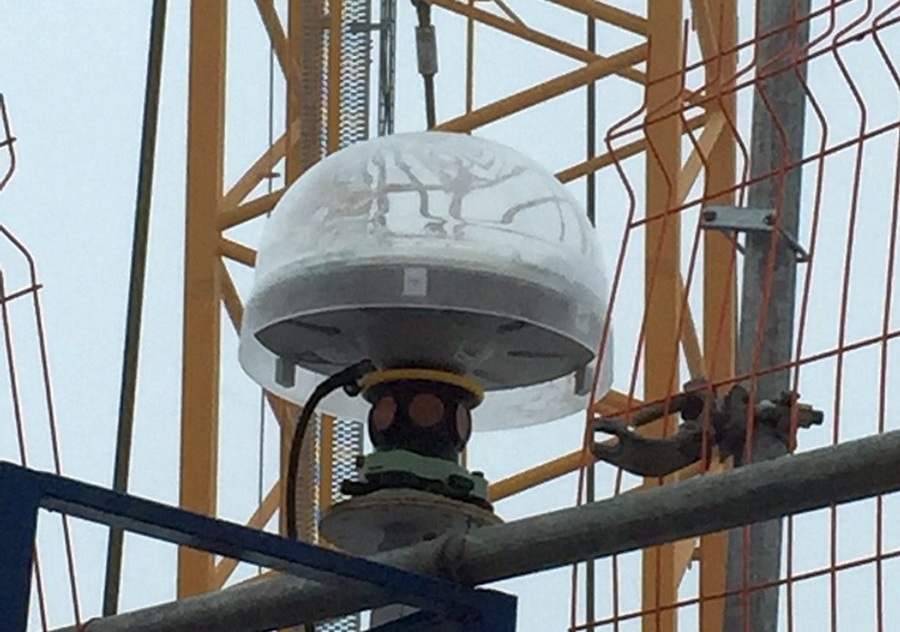

And one more station is located on the roof of the building of the general contractor, Renaissance Construction, on Chatelain Street. From the construction site to this point - almost 11 km. A distant station is needed to increase the leverage of triangulation.

The same roof
All antennas - at the core, terrestrial at the construction site and faraway at the roof of Renaissance work as one system, where the number of sensors and their location points reduce the error in the data obtained to the values allowed by the design documentation.
On the "plates" is located and another interesting device. Perhaps you have already paid attention to these prisms:

This is not a detail of the antennas, but a component of another system, with the help of which the most important thing is checked - the compliance of the actual center of the skyscraper with its design status.
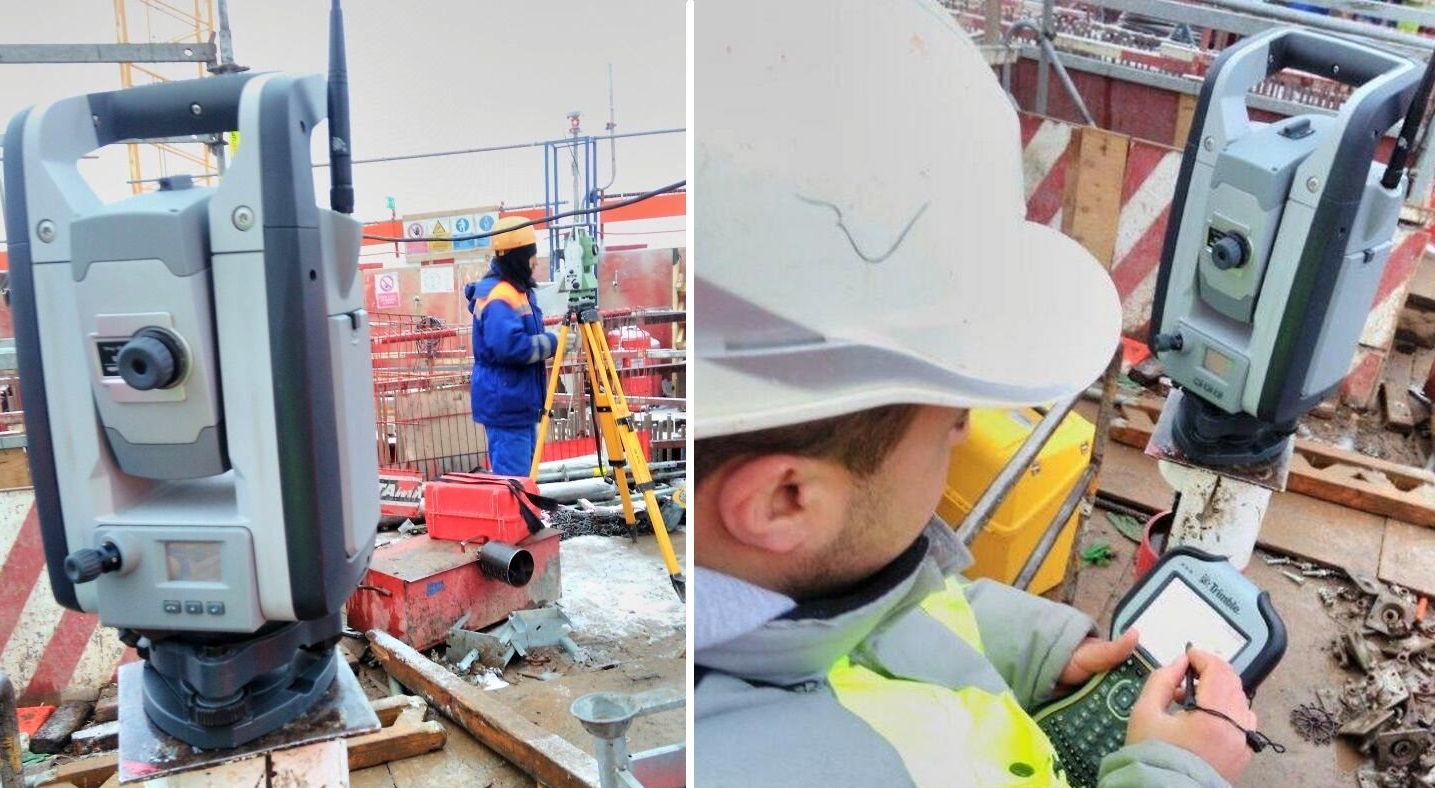
After the formwork has taken the next step and is ready to concreting the next floor, you need to check the correctness of the occupied position. The Trimble S6 robotic total station enters the scene:
The instrument collects data from prisms according to the formwork diameter. In addition to the constant prisms, additional ones are set to increase accuracy. Data is read and processed immediately.

The result is a clear picture of the points of the outer wall and the GNSS prisms, from which the coordinates of the center of the skyscraper's core are calculated.
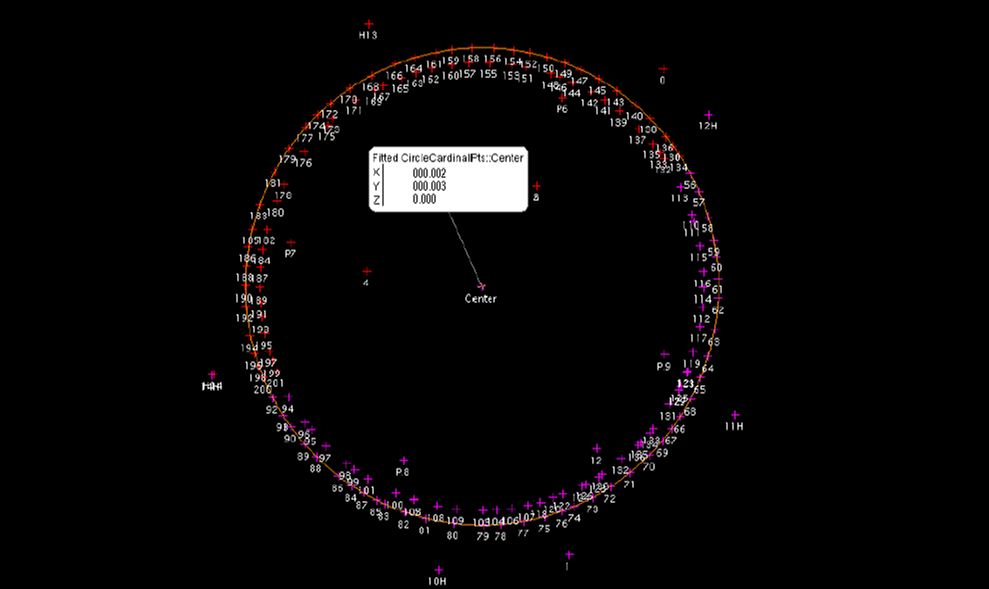
Deviation within the error (6mm). Correction of the formwork position for the next floor of the core is not required.
Device of vertical design FG-L100:
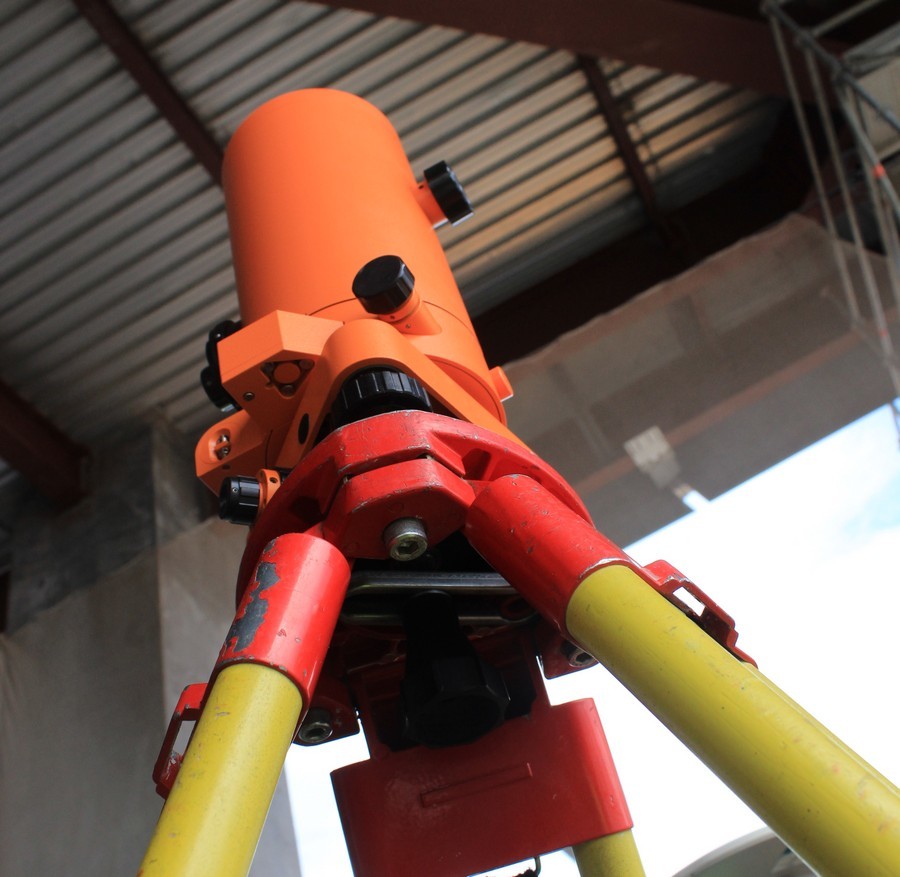

A bit like a coffee machine - a vertical laser. It is used to determine the presence of horizontal displacement on the tower.
It passes vertically up through technological holes, the position of the point above which it is centered. This is the most accurate equipment - the error per 100 meters - 1 mm (!). On the construction of the St. Petersburg tower, they use in conjunction with the GNSS system. This and some other instruments for measuring vertical displacement is a modern analogue of a construction plumb.
Leica ScanStation P20 is a pulse, high-speed 3D laser scanner with a dual-axis compensator. Its error on 50 meters is only 4 mm. At the same time, the maximum range, up to 120 m, is achieved even when scanning objects with weak reflectivity.

It is used as a control device. The result of the scan is the answer to an important question: whether the constructed one corresponds to the planned one and the actual one to the design BIM model.
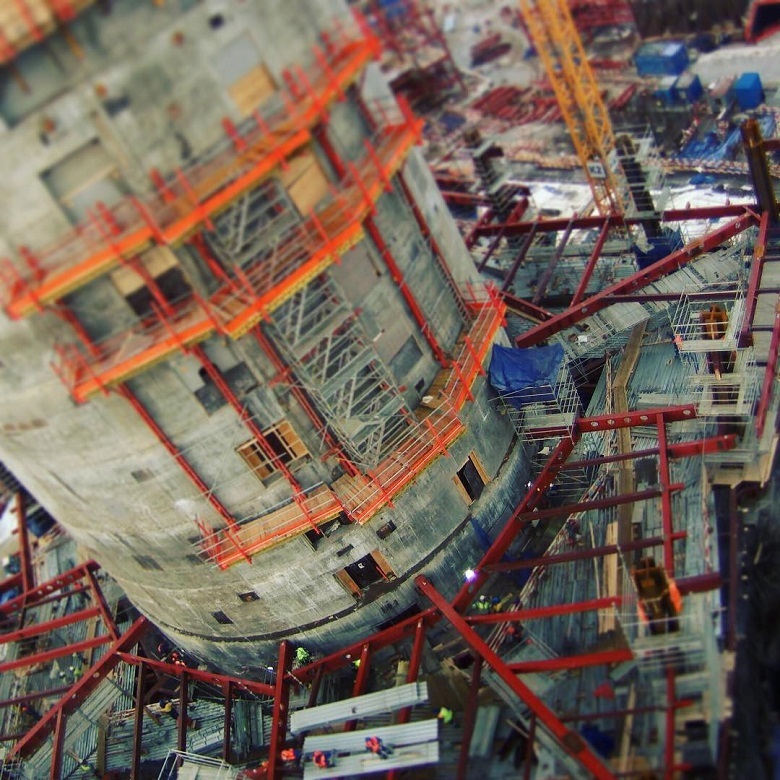

For example, it is important to confirm the position of the metal floor beams on which the floor is supported.
The scanner is installed on the points verified on the floor (by a technical gauge). The scanner placement points are strictly according to the plan.

The pattern of the positions of the scan points are designated as "P
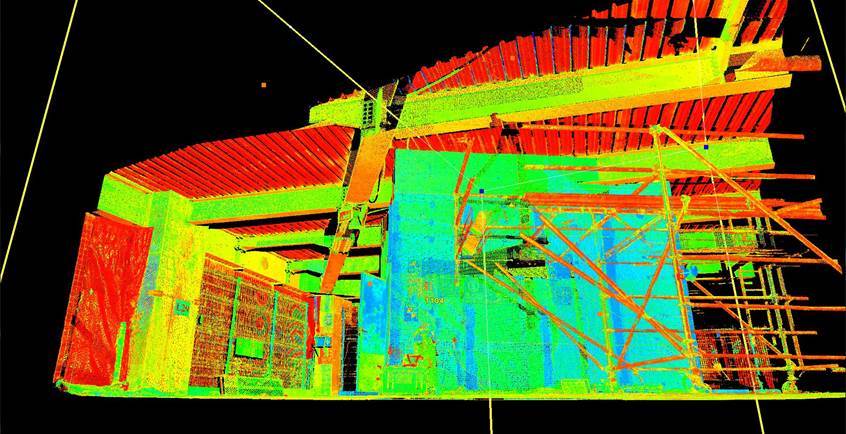
The scan results in a three-dimensional image:
After processing, it looks like this:
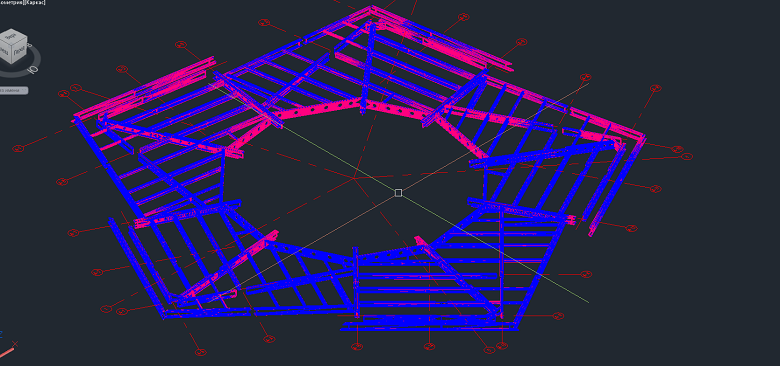
The data is then converted into a schema with accurate deviations:
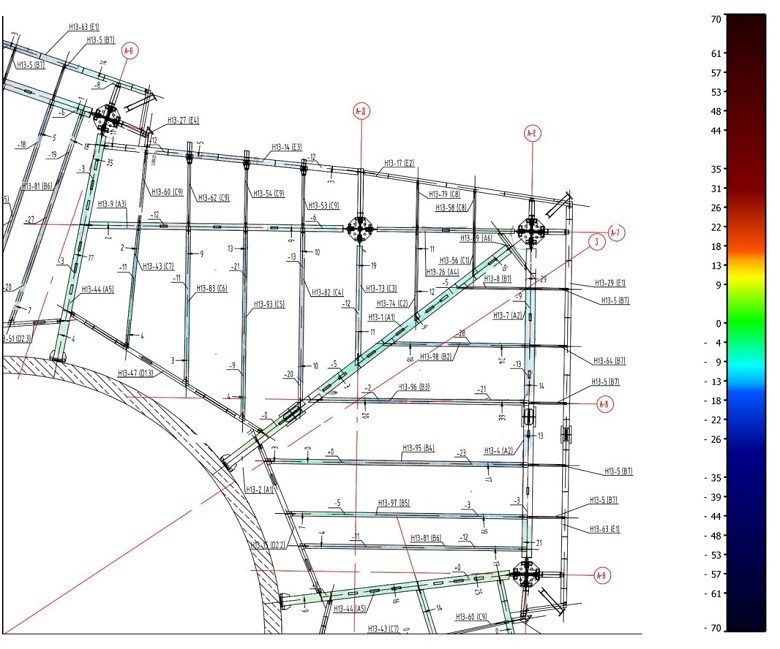
Going beyond the field of permissible error would mean both the analysis of the floor and the analysis of flights. So far there have been no such cases at the Petersburg construction site.
Conventional Leica Total Station:
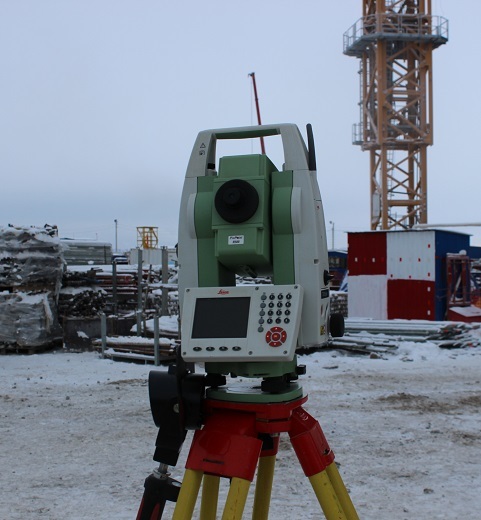

This is the surveyor’s workhorse. It has been used in construction for quite some time. This modification provides angular accuracy of 1 second and accuracy over a distance of 1.5 mm + 2 mm per 1 km. It is used to control the installation of equipment, creating a planned reference grid. They can also quickly and with high accuracy get a shot of a given area "in the plan" with a complete picture of the relief.
By the way, at the construction site it is especially important - here the “relief” is constantly changing, for example, due to construction equipment, changes in the height and configuration of buildings as they are erected.
Compare, for example:

Relief about a year ago, October 2015
And less than a year later, August 2016:

But back to the instruments - Electronic level Leica DNA03:

It is used for the program of monitoring the progress of construction in the following directions: sediment of the foundation, deformation of floors, shortening of columns. Measurements for control points in the core and columns, it performs with an accuracy of 0.2 mm.
And this is the optical version of the same level:

It is used to monitor steel structures. Its accuracy is 0.6 mm.
Laser tracker Leica. This laser tracker is remarkable in the first place - the range, and secondly - all-weather.
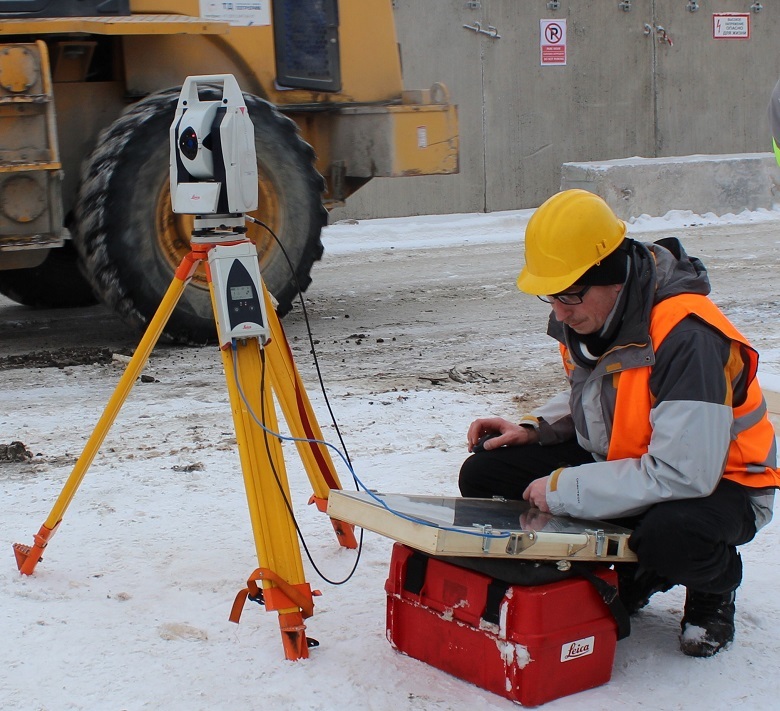

It can be used in the most severe conditions in the open air. Neither snow, nor rain, nor wind, nor building “precipitations” such as arc welding flashes or mounting dust will affect its sensors. It is applied at very large measuring distances - the range of the device is up to 320 m. It can rotate 360 degrees.
With the help of a laser tracker, surveyors check for deviations in the cores of the columns.
This is how it happens.
The columns of the tower (there are 15 of them, but before that we will reach in the following posts) have a steel “heart” in a shell made of concrete — the core:
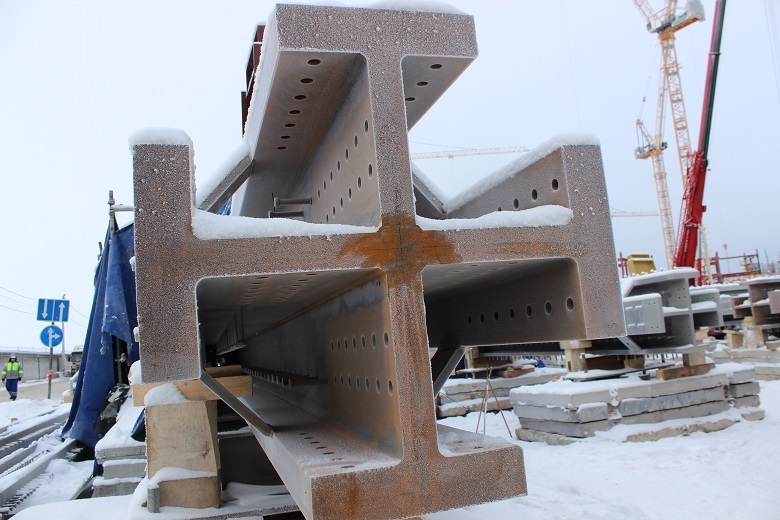

Before you send this, resembling a Maltese cross, the structure to a height, surveyors check it for "professional suitability" - the base should be exemplary even.
According to the plan, along the contour of the cross, the prism-reflector is installed alternately:

Reflector layout
Then, using a scan tracker, the points are scanned.

After processing the data by special software (enclosed in a “warm, lamp syncpad”, which was given much attention in the comments to the first part of the review) we get the following picture:
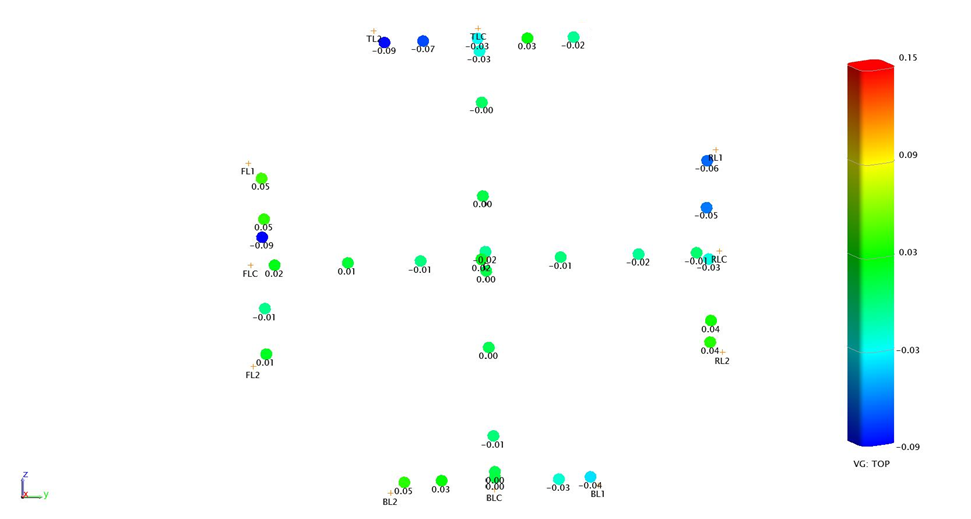
Green dots fix the ideal state of affairs, the rest - deviations, the degree and vector of which is indicated by color. If the column does not correspond to the ideal only within the limits of the allowed error, its path is up to a height. And if not, then to their homeland, to the manufacturer, to be melted down. To the credit of the latter, until the "home" no column returned.
The following should be added to the description of this geodesic splendor: although the measuring arsenal is really impressive, the instruments work only in the hands of the master. It is they who lead the tower upwards in the same way.
The engineers and surveyors Yury Gomzyakov, Petr Sokolov (MFC Lakhta Center JSC), Alper Cheken, Alp Ulusan (Renaissance Construction) helped them to work with the instruments.
* * *
After getting acquainted with the geodetic equipment, we moved down and saw how the Lakhta Center MFZ was being built. This is a complex of two futuristic buildings, from 22 to 85 meters high. The “filling” of the MFZ will be in keeping with the appearance - later a planetarium, an entertaining science center, laboratories and other interesting objects will be located here.
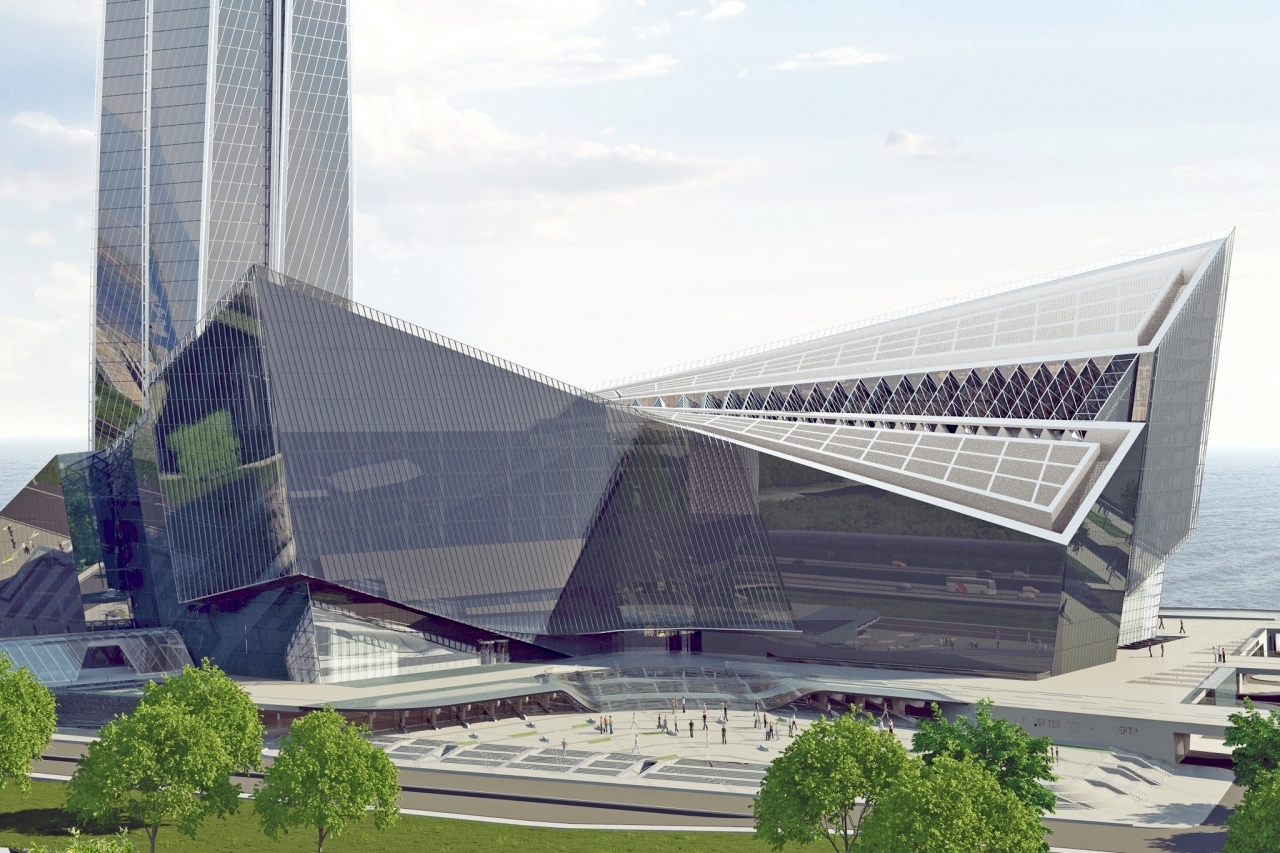

The MFZ is completely undeservedly "in the shadow of" the flagship building of the complex - the Lakhta Center tower. According to the chief surveyor of the Lakhta Center, Yury Gomzyakov, the architecture and constructive structure of the Moscow Physical Plant is more complicated than that of the Supertoll. Thus, the area of one floor is 2.2 hectares, which is more than that of the Winter Palace. The MFZ has the shape of a boomerang and is divided into two blocks that were not originally interconnected.
Subsequently, they will be united by a common translucent roof, which will be supported by reinforced concrete cores, it will be their whole burden. This will allow creating a giant atrium - this has not been built in Russia yet.
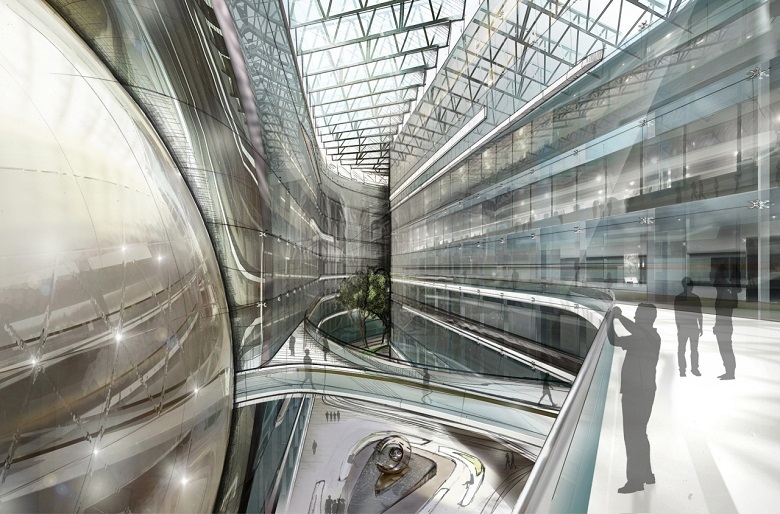

Design project atrium MFZ. The hemisphere on the left is a spherical planetarium.
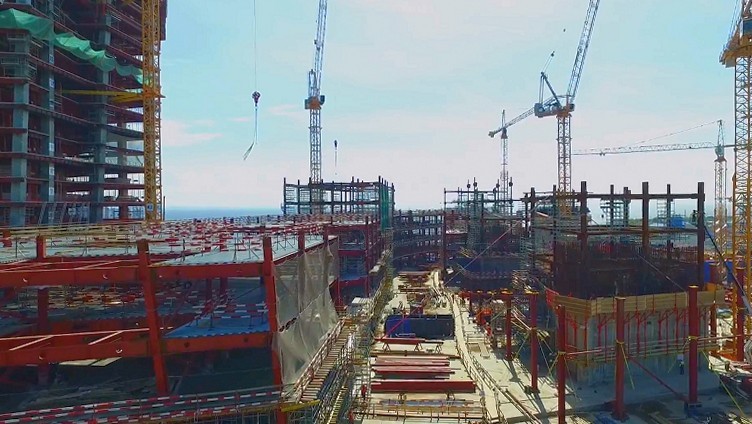

While the future atrium looks like this. On the left and on the right are metal structures of two buildings of the MFZ.
Here, too, there is a huge scope of work for surveyors. For example, for precise installation of huge 30-meter span farms. Or for the installation of facades - there are twenty-three views in the MFZ, due to the different levels of the building and its convex-concave shape. But that's another story.

- I need your clothes, helmet and electronic total station!
In the first part of our large geodesic review, we have already found out that this wealth is not from the arsenal of an extra-class sniper, but the “gentleman's set” of the surveyor “Lakhta Center”.
')
What was in the first part?
The task of geodzists is to ensure that all structures of the buildings being erected occupy the design position, and the Lakhta Center tower is strictly vertical. The allowed error is no more than 6 mm. throughout the half-kilometer journey to the top.
It would probably be less difficult to do with the tower "in a vacuum." But reality makes its own "oscillatory corrections": the building is always in motion. These fluctuations are the result of the behavior of the tower itself — its structures, materials, foundation soil, and the external environment — wind, sun, and construction work itself. Finding the right course "in this raging world" is the task of the surveyors of the Lakhta Center.
What will happen next?
In the final part of the review on the race for the vertical - analysis of instruments with answers to the questions: what, why, and how surveyors use Lakhta Center.
Turn the tower vertically. Who and how leads her right course?
BEFORE WHAT PROGRESS HAS REACHED
The construction process of the “Lakhta Center” is controlled by about 30 surveyors - quite a bit for the Petersburg “construction of the century”, where more than 3.5 thousand people replace every day.

Surveyors "Lakhta Center"
The small size of the team clearly demonstrates the results of the scientific and technological revolution that has occurred in geodesy in the past 20 years: new technologies have allowed to drastically increase the productivity of the process, despite the fact that the tasks facing today's surveyors are becoming more complex in geometric progression.

Once for construction enough and such a simple plumb line. But with the growth of buildings, everything changed.
The construction of the tower "Lakhta Center" uses several geodetic instruments and technologies that solve different tasks. Three of them are used for the first time in Russia, the rest have proven themselves in Dubai on the construction of Burzh Khalifa and Moscow (Federation complex, Renaissance Construction also acted as the general contractor).
So, the previously promised analysis of devices.
ANGULAR DISPLACEMENT OF THE TOWER KERNEL
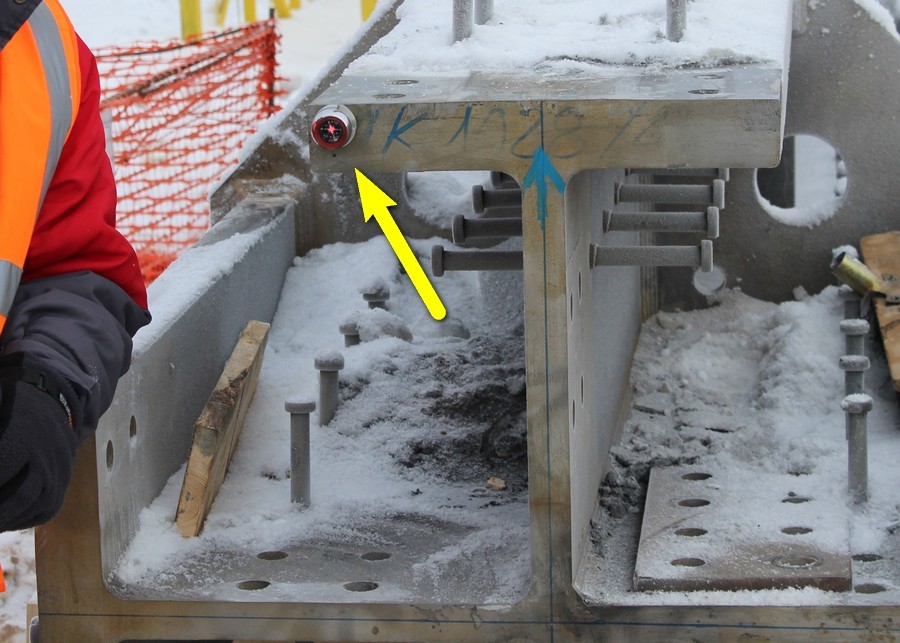
In the last publication, many were interested in the “miracle inclinometer”. We will once again admire the hero's photo:

An inclinometer is a deflection sensor. It measures the angular displacements in space along perpendicular axes X and Y, transfers this data to the system. Further, with the help of special software, the delta of movement along each axis is calculated. The total deviation is the sum of the readings of all installed inclinometers. This final indicator is used as a correction for GNSS antennas, which will be discussed further.
Inclinometers are located on the inner walls of the tower’s core every 50–80 meters (12–20 floors). In order not to damage the sensors, they are hidden in metal protective boxes. You can find out more about inclinometers in the comments here .
DISPLACEMENTS OF THE CLEAR CIRCLE HORIZONTAL
Trimble GNSS:

This is a flying saucer-like equipment — the antenna of the Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS), already familiar from the first part of the review. And she really has a connection with space. The system is used as a center base for formwork for the walls of the core.
The antennas are located at the highest point of the construction site - according to the diameter of the wind-proof shields of self-lifting formwork:

Geodetic satellite antennas on the formwork "Lakhta Center"
Decking (form for the walls of the core) takes steps - iterations:

After each such iteration, the current coordinates of the antennas are determined and compared with the design figures. If there is a delta exceeding the permissible error - the formwork is returned to the design smooth vertical axis.
Since the core of the tower is subject to wind oscillations - the higher, the stronger, and with it the antennas also oscillate, it is very important to have a stable point of reference. To this end, there are six additional ground stations located on the building site, from which data for correction is read when determining the exact location of the antennas on the core formwork. This readout occurs in real time.
And one more station is located on the roof of the building of the general contractor, Renaissance Construction, on Chatelain Street. From the construction site to this point - almost 11 km. A distant station is needed to increase the leverage of triangulation.

The same roof
All antennas - at the core, terrestrial at the construction site and faraway at the roof of Renaissance work as one system, where the number of sensors and their location points reduce the error in the data obtained to the values allowed by the design documentation.
For the first time, the technology was proposed by Leica for the construction of Burj Khalifa. After the successful debut, "space plates" began to actively use. For example, in Russia during the construction of the Federation tower (Moscow-City).
"The Plate" debuts at the core of Burj Khalifa. (Photo from here )
AXIS CHECK
On the "plates" is located and another interesting device. Perhaps you have already paid attention to these prisms:

This is not a detail of the antennas, but a component of another system, with the help of which the most important thing is checked - the compliance of the actual center of the skyscraper with its design status.
After the formwork has taken the next step and is ready to concreting the next floor, you need to check the correctness of the occupied position. The Trimble S6 robotic total station enters the scene:
The instrument collects data from prisms according to the formwork diameter. In addition to the constant prisms, additional ones are set to increase accuracy. Data is read and processed immediately.

The result is a clear picture of the points of the outer wall and the GNSS prisms, from which the coordinates of the center of the skyscraper's core are calculated.

Deviation within the error (6mm). Correction of the formwork position for the next floor of the core is not required.
VERTICAL NUCLEUS
Device of vertical design FG-L100:

A bit like a coffee machine - a vertical laser. It is used to determine the presence of horizontal displacement on the tower.
It passes vertically up through technological holes, the position of the point above which it is centered. This is the most accurate equipment - the error per 100 meters - 1 mm (!). On the construction of the St. Petersburg tower, they use in conjunction with the GNSS system. This and some other instruments for measuring vertical displacement is a modern analogue of a construction plumb.
CORRECT CONSTRUCTIONS, RELIEFS AND OTHER TASKS
3D SCANNING
Leica ScanStation P20 is a pulse, high-speed 3D laser scanner with a dual-axis compensator. Its error on 50 meters is only 4 mm. At the same time, the maximum range, up to 120 m, is achieved even when scanning objects with weak reflectivity.
It is used as a control device. The result of the scan is the answer to an important question: whether the constructed one corresponds to the planned one and the actual one to the design BIM model.

For example, it is important to confirm the position of the metal floor beams on which the floor is supported.
The scanner is installed on the points verified on the floor (by a technical gauge). The scanner placement points are strictly according to the plan.

The pattern of the positions of the scan points are designated as "P
The scan results in a three-dimensional image:

After processing, it looks like this:

The data is then converted into a schema with accurate deviations:

Going beyond the field of permissible error would mean both the analysis of the floor and the analysis of flights. So far there have been no such cases at the Petersburg construction site.
MULTIFUNCTIONAL TOTAL STATION
Conventional Leica Total Station:
This is the surveyor’s workhorse. It has been used in construction for quite some time. This modification provides angular accuracy of 1 second and accuracy over a distance of 1.5 mm + 2 mm per 1 km. It is used to control the installation of equipment, creating a planned reference grid. They can also quickly and with high accuracy get a shot of a given area "in the plan" with a complete picture of the relief.
By the way, at the construction site it is especially important - here the “relief” is constantly changing, for example, due to construction equipment, changes in the height and configuration of buildings as they are erected.
Compare, for example:

Relief about a year ago, October 2015
And less than a year later, August 2016:

LEVELING
But back to the instruments - Electronic level Leica DNA03:
It is used for the program of monitoring the progress of construction in the following directions: sediment of the foundation, deformation of floors, shortening of columns. Measurements for control points in the core and columns, it performs with an accuracy of 0.2 mm.
And this is the optical version of the same level:

It is used to monitor steel structures. Its accuracy is 0.6 mm.
LASER SCANNING
Laser tracker Leica. This laser tracker is remarkable in the first place - the range, and secondly - all-weather.

It can be used in the most severe conditions in the open air. Neither snow, nor rain, nor wind, nor building “precipitations” such as arc welding flashes or mounting dust will affect its sensors. It is applied at very large measuring distances - the range of the device is up to 320 m. It can rotate 360 degrees.
With the help of a laser tracker, surveyors check for deviations in the cores of the columns.
This is how it happens.
The columns of the tower (there are 15 of them, but before that we will reach in the following posts) have a steel “heart” in a shell made of concrete — the core:
Before you send this, resembling a Maltese cross, the structure to a height, surveyors check it for "professional suitability" - the base should be exemplary even.
According to the plan, along the contour of the cross, the prism-reflector is installed alternately:

Reflector layout

Then, using a scan tracker, the points are scanned.

After processing the data by special software (enclosed in a “warm, lamp syncpad”, which was given much attention in the comments to the first part of the review) we get the following picture:

Green dots fix the ideal state of affairs, the rest - deviations, the degree and vector of which is indicated by color. If the column does not correspond to the ideal only within the limits of the allowed error, its path is up to a height. And if not, then to their homeland, to the manufacturer, to be melted down. To the credit of the latter, until the "home" no column returned.
IN CONCLUSION
The following should be added to the description of this geodesic splendor: although the measuring arsenal is really impressive, the instruments work only in the hands of the master. It is they who lead the tower upwards in the same way.
A curious fact: in the most famous skyscraper in the world, the Burj Khalifa tower, the project-tolerated delta deviation during installation of structures and the construction of the core was up to 10 mm. In St. Petersburg "Lakhta Center" accuracy is almost twice as high - 5-6 mm in different areas of geodetic works.
The engineers and surveyors Yury Gomzyakov, Petr Sokolov (MFC Lakhta Center JSC), Alper Cheken, Alp Ulusan (Renaissance Construction) helped them to work with the instruments.
* * *
PS: HORIZONTAL SKY SCREEN
After getting acquainted with the geodetic equipment, we moved down and saw how the Lakhta Center MFZ was being built. This is a complex of two futuristic buildings, from 22 to 85 meters high. The “filling” of the MFZ will be in keeping with the appearance - later a planetarium, an entertaining science center, laboratories and other interesting objects will be located here.

The MFZ is completely undeservedly "in the shadow of" the flagship building of the complex - the Lakhta Center tower. According to the chief surveyor of the Lakhta Center, Yury Gomzyakov, the architecture and constructive structure of the Moscow Physical Plant is more complicated than that of the Supertoll. Thus, the area of one floor is 2.2 hectares, which is more than that of the Winter Palace. The MFZ has the shape of a boomerang and is divided into two blocks that were not originally interconnected.
Subsequently, they will be united by a common translucent roof, which will be supported by reinforced concrete cores, it will be their whole burden. This will allow creating a giant atrium - this has not been built in Russia yet.

Design project atrium MFZ. The hemisphere on the left is a spherical planetarium.

While the future atrium looks like this. On the left and on the right are metal structures of two buildings of the MFZ.
Here, too, there is a huge scope of work for surveyors. For example, for precise installation of huge 30-meter span farms. Or for the installation of facades - there are twenty-three views in the MFZ, due to the different levels of the building and its convex-concave shape. But that's another story.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/399503/
All Articles
