The Intel 4004 chip is 45 years old. A bit of IT history
Without modern electronics, human life is hard to imagine. Of course, there are many places where modern technologies have not yet been heard, not to use. But nevertheless the overwhelming part of the population of the Earth is somehow connected with electronics, which has become an integral part of our life and work.
Since ancient times, man has used various devices in order to make some production processes more efficient or to make his own existence more comfortable. The real breakthrough happened in the late 40s of the 20th century, when transistors were invented. The first were bipolar transistors , used so far. They were followed by MOSFETs (metal-oxide-semiconductor).
The first transistors of this type were more expensive and less reliable than their bipolar "relatives". But, beginning in 1964, integrated circuits began to be used in electronics, which were based on MOS transistors. This subsequently made it possible to reduce the cost of manufacturing electronic devices and significantly reduce the size of gadgets and systems while reducing energy consumption. Over time, the microcircuits became more and more complex and sophisticated, replacing large blocks of transistors, which made it possible to reduce the size of electronic devices.
')
By the end of the 60s, microchips with a rather large number of logic gates (large for that time) began to spread: 100 or more. This allowed the use of new elements to create computers. Developers of electronic computers relatively quickly recognized that increasing the density of transistors in the chip will eventually allow you to create a computer processor in the form of a single chip. Initially, integrated circuits with MOS transistors were used to create terminals, calculators, they began to be used by the developers of onboard systems of passenger and military vehicles.
Key moment
Today, most electronics experts admit that the start of a qualitatively new stage in the development of electronics began in 1971, when a 4-bit processor 4004 from Intel appeared, later replaced by an 8-bit chip 8008. It appeared after a small Japanese company named Nippon Calculating Machine, Ltd. (later Busicom Corp.) ordered only 12 chips from Intel. Companies needed these chips for their calculators, and the logical design of the chips was developed by an employee of the customer company. At that time, for each device, a new chipset was developed, which served highly specialized functions.
When fulfilling the order, Marshian Edward Hoff proposed to reduce the number of chips for a new device of a Japanese company by introducing the use of a central processor. It was he who, as conceived by the engineer, was to become a data processing center and perform arithmetic and logical functions. The processor had to replace a few chips at once. The management of both companies approved this idea. In the autumn of 1969, Hoff, with the help of Stanley Maizor, proposed a new microchip architecture, the number of which was reduced to just 4. Some of the proposed elements are a 4-bit central processor, ROM and RAM.
The processor itself was able to develop Federico Fadzhin, a physicist from Italy, who became the chief designer of the MCS-4 family at Intel. It was he who, thanks to the knowledge of technology MOP was able to create a processor, implementing the idea of Hoff. By the way, the world's first commercial microcircuit, where silicon gate technology was used, was also developed by him. She bore the name Fairchild 3708.
Fadzhin, being an employee of Intel, was able to create a new method for designing arbitrary logic systems. He was assisted in his work by Masatoshi Sima, who worked at that time as an engineer at Busicom. Fadzhin and Sima subsequently developed the Zilog Z80 microprocessor, which, by the way, is being manufactured now.
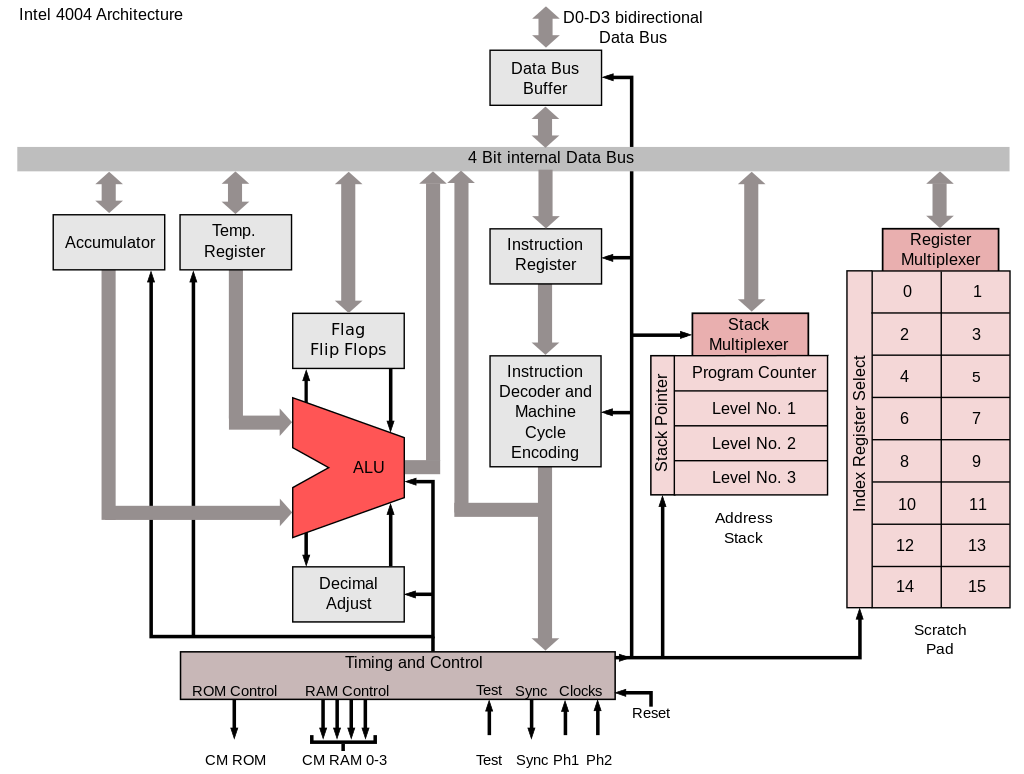
Intel 4004 processor architecture
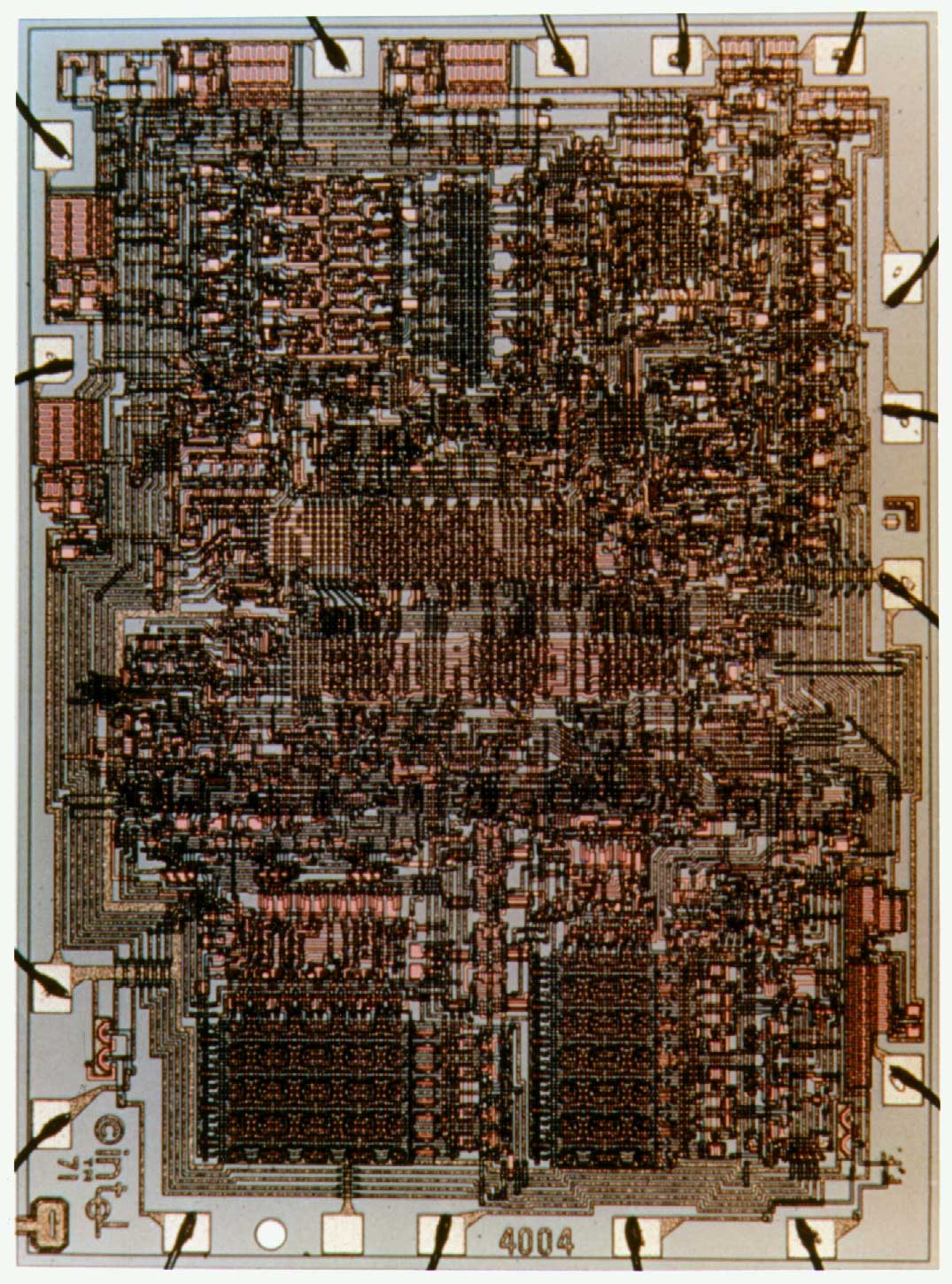
But the main thing happened on November 15, 1971. This is the date of the appearance of the first microprocessor from Intel, chip 4004 . Its cost at that time was 200 dollars. A total of almost all the functions of the mainframe processor were implemented on a single chip. He was announced in November 1971 in the magazine Electronic News.
Processor Specifications:
- Date of appearance: November 15, 1971
- Number of transistors: 2300
- Crystal area: 12 mm²
- Manufacturing process: 10 µm (P-channel silicon pie MOS technology)
- Clock frequency: 740 kHz (specifically from 500 to 740.740 ... kHz, since the clock period is 2..1,35 μs (or 92.6 kHz?)
- Digit register: 4 bits
- Number of registers: 16 (16 four-bit can be used as 8 eight-bit)
- Number of ports: 16 four-bit input and 16 four-bit output
- Data bus width: 4 bits
- Address bus width: 12 bits
- Harvard architecture
- Stack: internal 3-tier
- Memory of commands (ROM / ROM): 4 kilobytes (32768 bits)
- Addressable Memory (RAM / RAM): 640 bytes (5120 bits)
- Number of instructions: 46 (of which 41 are 8-bit and 5 are 16-bit)
- Instruction cycle: 10.8 microseconds
- Power supply: −15 V (pMOS)
- Operating temperature: 0 to + 70C
- Storage and operation conditions: from -40 to + 85C
- Connector: DIP16 (the microcircuit was directly soldered to the printed circuit board or installed in a special slot)
- Case: 16-pin DIP (1 type of plastic or 3 types of ceramic, for example, C4004 (white ceramics with gray stripes), C4004 (white ceramics), D4004 (black and gray ceramics), P4004 (black plastic))
- Type of delivery: separately and in sets of MCS-4 (ROM, RAM, I / O, CPU)
Per second, this processor ran from 60,000 to 93,000 instructions. At the same time, one of the first electronic computers, ENIAC , could execute only 5,000 instructions per second. At the same time, ENIAC occupied 280 square meters, weighed 27 tons and consumed 174 kW of energy.
4004 processor did not become too popular. The 8080th chip, which can be called the "great-grandson" of the 4004th, has become widely used.
Calculators and computers
In 1971, Intel had competitors. For example, Mostek, a company that developed semiconductor elements and devices based on them, created the world's first “calculator on a chip”, MK6010 .
Pico Electronics and General Instrument also had a working version of a “calculator on a chip”, which was called the G250. Within six months, Texas Instruments introduced a working version of its own “calculator on a chip,” <a href= en www.datamath.org/Story/Datamath.htm#The \\> TMS 1802. This was the first model in the top-notch 0100 line. at the same time, these systems could work perfectly as calculators, but they could not do anything else. But 4004 worked with instructions that were stored in external memory. And it allowed to use this particular chip when creating a computer.
At that time everything changed very quickly. Busicom started a period of financial problems, so this company sold exclusive rights to the 4004 processor. Soon, new devices began to work on the basis of this and other more powerful processors. These included a word processor, gaming machines (pinball) and other systems.
4-bit processor, as mentioned above, quickly replaced the 8-bit microprocessors, which became popular. By the way, the first 8-bit processor was not 8008 at all, but TMX 1795 from Texas Instruments.
The “window” in modern electronics was “cut through” by the D200 computer on integrated circuits, created in 1967 by Autonetics . This compact 24-bit computer was created for use in aviation, marine and other fields. His weight was only a few kilograms. It was used to control the Poseidon rocket, it was also used to control the fuel consumption in military aircraft.
The Central Air Data Computer is the “heir” of the D200. It was created by the company Garrett AiResearch (now part of Honeywell). The computer was created for the aircraft F-14, it contained 28 chips.
In 1969, the "programmable terminal" Datapoint 2200 was created. It was developed by employees of Computer Terminal Corp. (CTC) from Texas. It was no longer a terminal, but a real computer with an 8-bit processor, which initially included 100 bipolar chips.
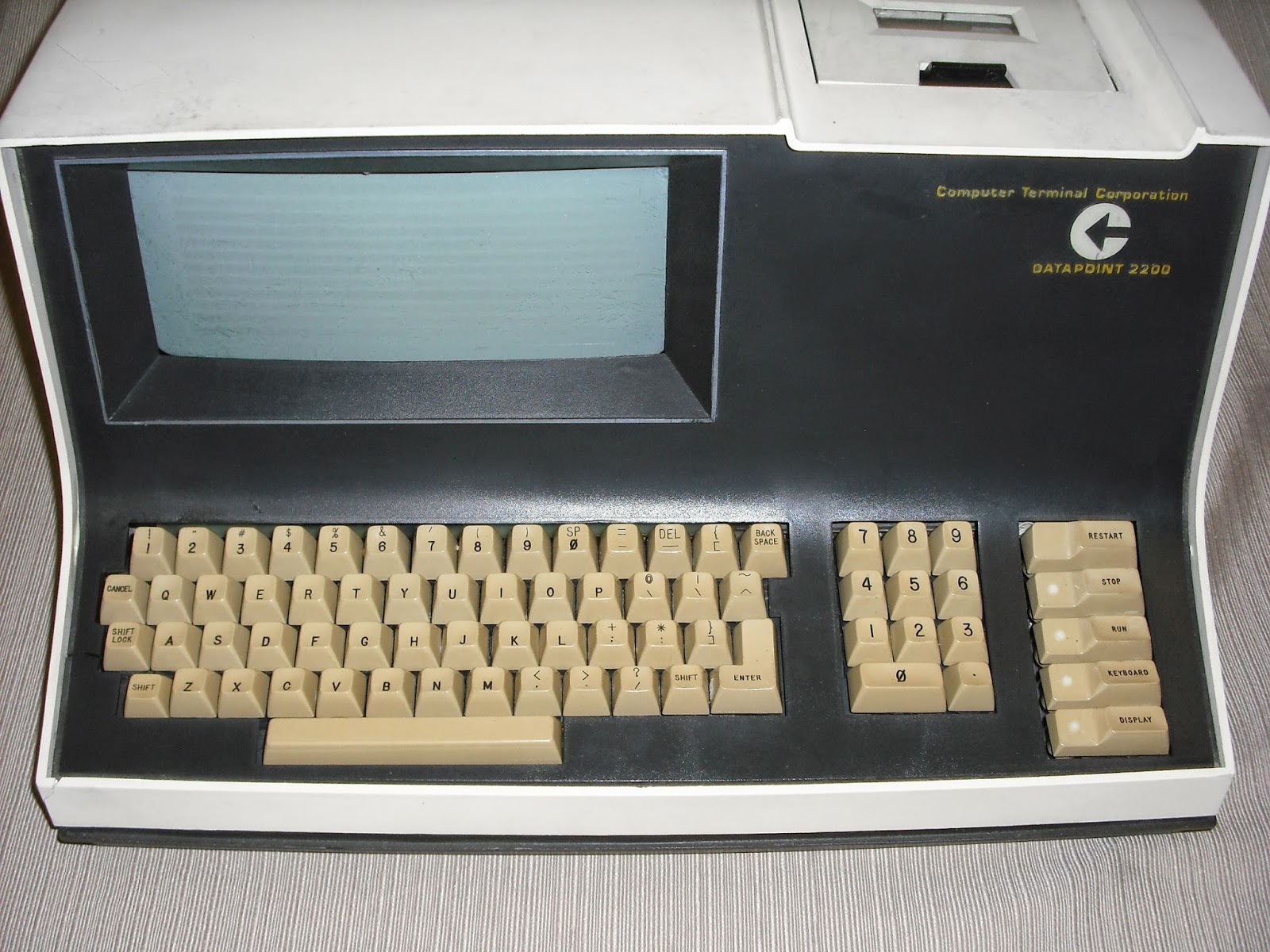

A year later, ITS turned to Intel with a request to develop a new processor for the D2200. Intel employees did the job by releasing specifications for this chip. The logical design developed at that time became the basis of the Intel 8008. In 1970, when Intel began working on the 8008th processor, it was a relatively small company with 100 employees.
ITS has requested to develop a processor based on specifications created in Intel and in Texas Instruments. At that time, this company employed 45,000 people. TI proposed a variant consisting of three chips, but the JTS was asked to develop only one chip for all the specified tasks. Intel continued to work on creating a similar chip. TI has developed a prototype, called TMX 1795 .
In June 1971, Texas Instruments launched a media campaign dedicated to the benefits of its processor. At that time, the TMX 1795-based Datapoint 2200 was described as “a powerful computer superior to the original version”, which meant that the capabilities of the Datapoint 2200 based on the TMX 1795 were significantly superior to those of the Datapoint 2200 based on bipolar transistors. But STS, after checking the operation of the new chip, rejected it, continuing to use bipolar chips. Intel was still working on its own processor.
After some time, TI, convinced of the lack of demand for TMH 1795 (later - TMC 1795), completed the media campaign and ceased production of the system. But this particular chip went down in history as the first 8-bit processor.
In 1971, STS lost interest in a single processor for its systems, transferring all rights to the new Intel chip. The company did not give up this opportunity, and continued to develop the 8008 chip , successfully offering it to a number of other companies. In April 1972, she was able to deliver hundreds of thousands of such processors. Two years later, the 8008 processor was replaced with a new 8080, after which the 8086 came and the era of systems on the x86 architecture began. Now, working on a powerful PC or laptop, it is worth remembering that the architecture of such a system was developed many years ago for the Datapoint 2200 programmable terminal.
Intel then used more advanced technology, which provided the advantage of its processors. They were fast and relatively economical in terms of energy consumption. Plus, in Intel chips, the transistor density was higher than on a TI chip, which made it possible to reduce the size of processors. Plus, marketing played an important role, in this area Intel also took a number of successful steps, which ensured the company's development.
Whatever it was, the situation with the primacy in the development of the first processors is not so straightforward as is commonly believed. There were several pioneers here, but the development of only one of them became popular later. Actually, with the modernized "descendants" of this technology, we are all dealing today, in the 21st century.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/399473/
All Articles