Another giant project SpaceX, arithmetic and common sense

Last week, SpaceX made another sensation by submitting a request to the Federal Communications Commission (FCC) for permission to launch 4425 satellites. If you read the document carefully, it says “4425 satellites (plus up to two spare satellites per orbital plane)”, that is, the satellite constellation will have a maximum of 4591 satellites on 83 orbital planes. Such huge numbers have no analogues among existing satellite systems and raise reasonable doubts about the feasibility of the project. Let's try to figure it out.
general information
The SpaceX application is publicly available on the FCC website, anyone can download it entirely and become familiar. I will quote the most important points from there. The stages of creating a satellite constellation, orbital planes, the number of satellites, the height of the orbits and their inclinations are shown in the table:
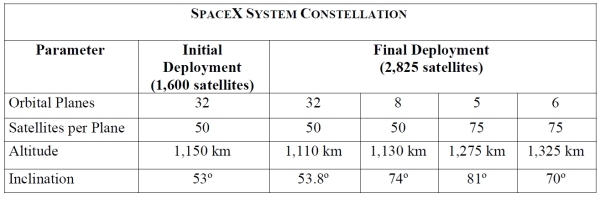
')
The dimensions and weight of the satellite are indicated in another table in the chapter devoted to the descent of satellites from orbit.
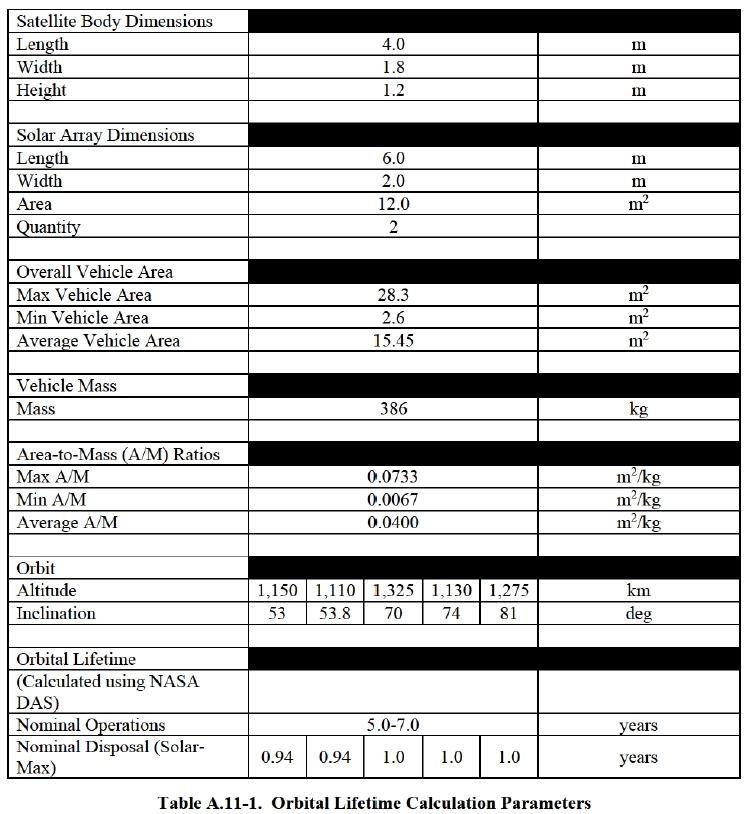
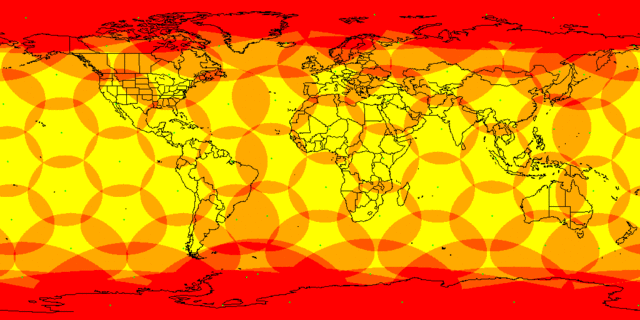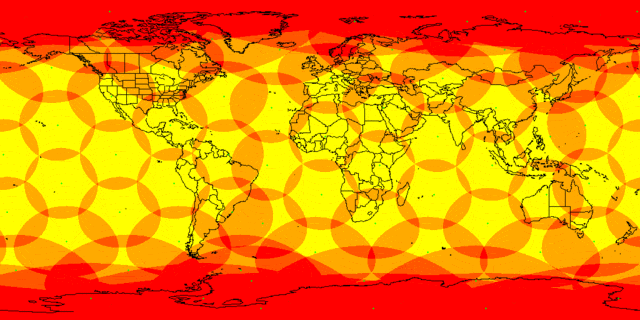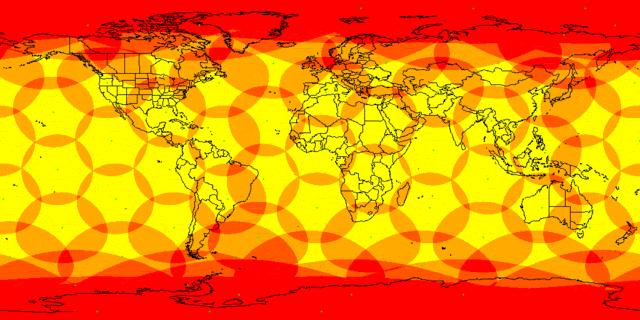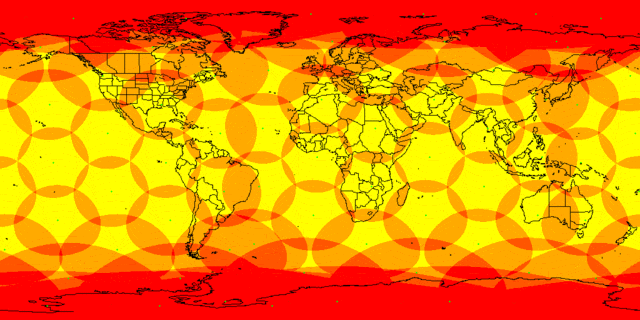
The satellites are designed so that land subscribers will only work with devices located above 40 ° above the horizon, and the radius of visibility of the satellite in this way will be 1060 km
Arithmetic
To understand the scale, now there are about four and a half thousand satellites in orbit, about one and a half thousand of them are operational. If the Mask project is fully implemented, the number of working satellites will increase fourfold.
The application indicates the duration of the active existence of one satellite from 5 to 7 years. Accordingly, the already deployed grouping will have to be replenished every year by from 632 to 885 satellites. We will try to convert this number into launches of Falcon 9 launch vehicles. But we cannot simply take and divide the official Falcon 9 carrying capacity into 22,800 kg by the satellite weight indicated in the application to 386 kg. First, such a carrying capacity is indicated for a low earth orbit with a height of 200 km. The working orbit of the SpaceX communications satellites ranges from 1,110 to 1,135 km, which requires additional fuel. Depending on the design of a solar synchronous orbit with a height of 600-800 km, the launch vehicles take from 1/2 to 3/4 of their payload to a low near-earth orbit. Secondly, a payload of 22,800 kg is indicated for the one-time first stage option. If you leave the supply of fuel for the landing of the first stage, then the mass of the payload will fall. The Falcon 9 did not have very heavy loads into low earth orbit (LEO), but for a mass output of almost five tons into a geo-transfer orbit, it is possible to estimate the maximum payload of 15 tons per LEO, and taking 2/3 as the average between 1/2 and 3/4, get about 10 tons per target communication satellite orbit. Our calculations are confirmed by the fact that it is planned to output 10 Iridium NEXT satellites with a mass of 900 kg each to a close polar orbit. Subtract from 10 tons, offhand, one ton per dispenser, which will satellites satellites in their orbit, and dividing 9 tons per mass of one satellite in 386 kg, we obtain the maximum theoretical carrying capacity of 23 satellites per launch Falcon 9 FT. Thus, to launch 632-885 satellites, we will need 28-39 launches per year. That is, in the best case, one rocket will have to start 2-4 times a month just so that the satellite system continues to work. But you and I did not take into account the size of the satellites at all - the fact is that 23 such satellites do not fit into the launch vehicle.
Open the instructions for the payload for the Falcon 9 rocket and on page 36 we see the size of the head fairing:
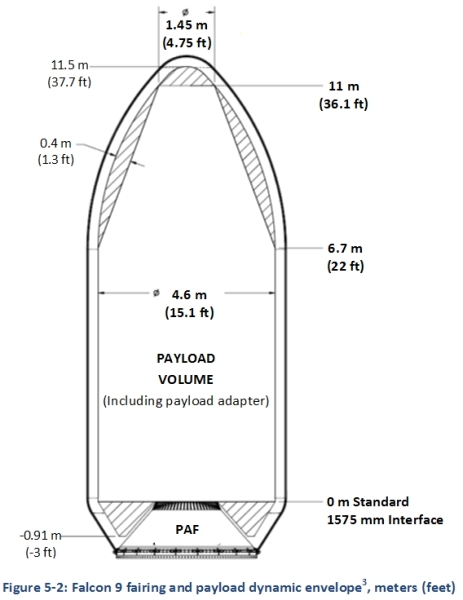
From the table above, we know the length, width and height of the satellite - 4.0x1.8x1.2 meters. And if we begin to lay them in the fairing, then in height you can not put more than two rows in height of 4 meters, and in the same row can not accommodate more than 4 satellites:
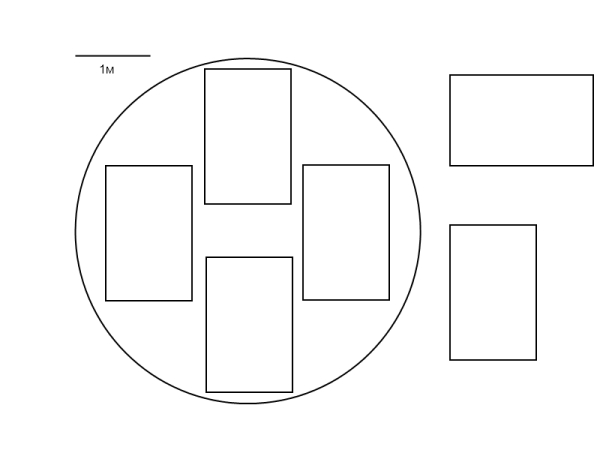
Thus, we cannot place more than 8 satellites on one rocket. And on 632-885 satellites per year to maintain the system in working condition, we will need 79-111 starts - one and a half to two starts per week. And in order to have something to launch, we will need factory capacities capable of producing 1.7-2.4 satellites per day.
If SpaceX wants to deploy at least the first phase of a system of 1600 satellites per year, then they will have to launch 4 rockets a week. Even if you deploy the first phase of 4 years, you will need to start one rocket per week and produce more than one satellite per day. Such intensity of production and launching operations is orders of magnitude greater than what we observed in a real space program.
Not fast, not mobile and not free
The US area without Alaska is placed in a rectangle of 5000x2500 km, and 6 satellites would be enough for its full coverage. But due to the fact that the satellites will be at an altitude of about a thousand kilometers, they will move quite quickly, and new ones should go to the place leaving the horizon. In principle, about 100-150 satellites would be enough for continuous coverage of the US territory (and, at the same time, other countries between 50 ° north latitude and 50 ° south latitude), obviously, the numbers 1600 of the first stage and 4425 full constellations assume that the satellites will work on the territory of an order of magnitude smaller, with a radius of around 100-300 km. But the irony is that in densely populated areas, even such an area will have a very large number of people. The more clients per satellite, the less speed each will receive, so gigabit speed can be achieved in principle only with a small number of users. The application states that the satellites will exchange information in the optical range between themselves. Today, this technology is at the level of individual experiments, and, although it promises greater speed than the radio band, will require the development and production of new and sophisticated equipment, so satellites will not be cheap. The application also states that 200 ground stations will be built for the first phase of the satellite system for receiving / transmitting data to the terrestrial Internet and 2 MCCs to control the satellite constellation. Investments in the satellites and ground equipment themselves will have to amount to tens of billions of dollars, so there is no real hope that such an Internet will be distributed free of charge. And finally, satellites will communicate with users in the Ku and Ka bands, and mobile antennas for this band are considered to be such as can be installed on a car.

Ka-band antenna

Ku-band antenna example
Given that the satellites are moving, the antennas will either have to accompany them, which requires expensive antennas with a guidance system, or have a taper pattern of an angle of 100 ° upwards, which will most likely make them even more cumbersome. If you recall satellite phones, they differed in large antennas, while working in a different range (L-band) and providing low speed (voice communication, SMS and low-speed Internet). And finally, you should not forget that even in the best case, when the signal from the user reaches the ground node through only one satellite, it will have to travel approximately 3000 km one way (1000 km to the satellite * sqr (2) * 2 ) and the same distance will have to go through the answer. This, of course, is better than 36,000 km in one direction to the geostationary orbit, but the delay in talking through a satellite phone is noticeable at the level of human perception, and, of course, the wired or cellular Internet will be noticeably faster. In general, if someone suddenly had time to rejoice that the SpaceX communication system will give free gigabit Internet to each smartphone, then this is a very strong delusion.
Already been
It is curious that similar news already existed. For example, in 2014, news agencies wrote that Musk wants, by launching 700 satellites weighing 100 kg, to provide everyone with Internet. As we can see, over the past two years, the mass and number of satellites have increased even more. It is even curious to wait another couple of years and see what news we will have to wait in the area of 2019, for which, on request, the deployment of the group is scheduled to begin.
But in reality
Of the existing systems in terms of the parameters of the orbit, the number of satellites and the purpose for the SpaceX project, the Iridium satellite communication system is most similar. In the early 1990s, the idea of 77 satellites appeared, which will be in polar orbits and provide a complete coverage of the entire surface of the Earth. Of the number 77, the name of the system was born - the chemical element iridium has atomic number 77. But already in the development process, the required number of satellites was reduced to 66. The ambitious program was supported by one of the then leaders of communication systems - Motorola. For the production of satellites, an innovative solution was used - a special multi-axis suspension, which allowed the satellite to be assembled in weeks rather than months and reduce its cost to “only” $ 5 million.
The first satellites were launched in 1997, and in 1998, US Vice President Al Gore had a historic first conversation. But, until the system was fully deployed, the connection was constantly interrupted. In addition, the cost of the conversation was high, satellite phones were expensive and cumbersome, and the management made mistakes. As a result, as early as August 1999, Iridium SSC filed for bankruptcy. In 2000, the staff of the company included only employees responsible for the descent of satellites from orbit. A brilliant dream worth around 7 billion dollars was nearing an inglorious end. The situation was saved by the US Department of Defense, which offered a contract to provide communications for $ 100 million a year, and a group of private investors who bought assets for $ 35 million. In 2001, "Iridium" was born again. To reach the break-even point required 60 thousand customers. By 2007, their number exceeded 160 thousand. At the moment, the original satellites are gradually failing due to old age, and the spare ones have already run out, and communication failures again begin in the system, especially in the equatorial area, where the distance between the satellites is maximal. In 2010, Iridium signed an agreement with SpaceX, which cost a record $ 492 million at the launch of 70 satellites of the new generation Iridium NEXT. Initially, the launch of the ten first satellites on a single Falcon 9 FT rocket was planned for 2015, but moved first to 2016, and now probably moved to 2017 due to the recent Falcon 9 accident.

The Iridium communication system provides voice communication at a speed of 2.2-3.8 kilobits per second (very strong compression is used) and a delay of 1.8 seconds on average. When transferring data, the speed is about 2.2 kilobits per second, but text or HTML can be transmitted at speeds up to 10 kbps. They promise that the data transfer rate of Iridium NEXT will be up to 1.5 megabits per second. Satellite communication is not cheap - a minute of conversation from an Iriduim phone is estimated at $ 0.75-1.5, and calls from a landline or mobile phone to satellite can cost up to $ 4 per minute. In addition, to call you need to leave the building - the phones can not break through the ceilings. But for those who work in places remote from civilization, these shortcomings are not fundamental - the opportunity in principle to contact the “big land” outweighs the inconvenience.
Conclusion
It makes little sense to speculate on the reasons for the emergence of such monstrous projects. Maybe Musk wants to divert attention from problems with the recent accident. Maybe he very seriously overestimates his capabilities. A more probable pragmatic version is that this is a trite PR to keep the whole world in admiration and waiting for new miracles. If we find out the reasons for the visible decisions, it will not be soon. But, as with the recent Mars project , the idea of supporting 4425 satellites in orbit can only be implemented in a very truncated version. In which, however, in contrast to the colonization of Mars, it may well be income from customers.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/399245/
All Articles