US military testing electrical brain stimulation to improve multitasking
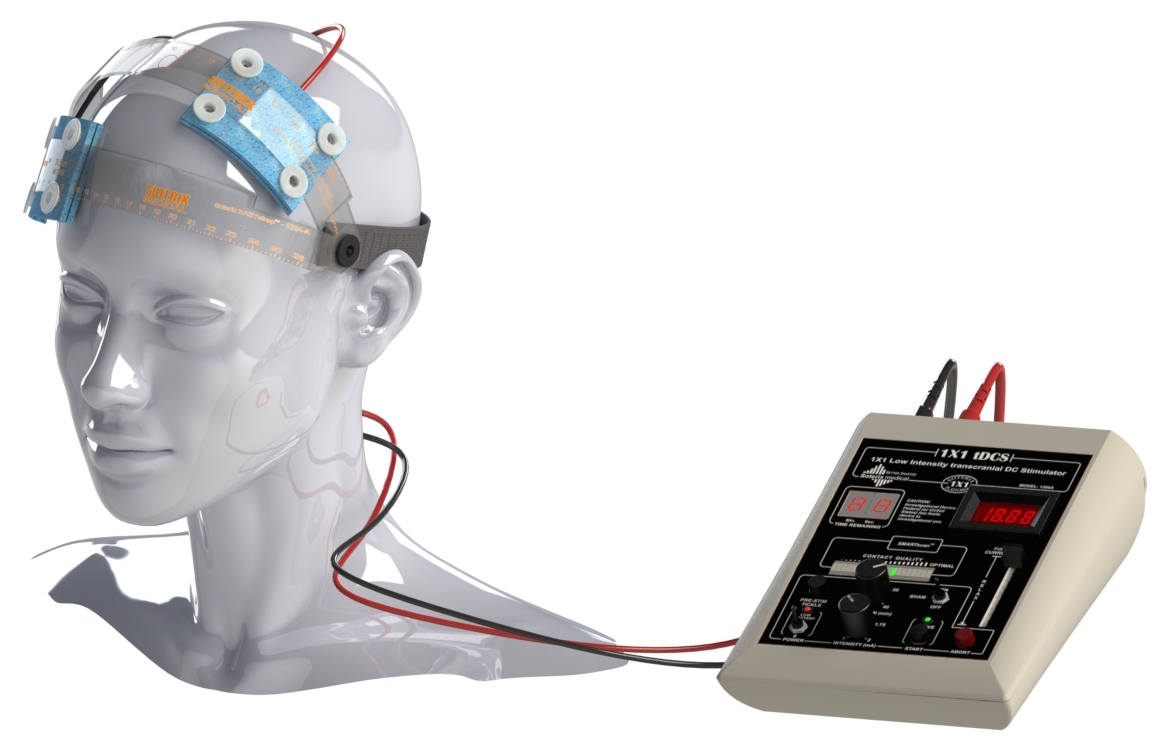
The US Army began testing a new way to improve the mental abilities of people with the help of brain electrical stimulation. The category of specialties that will be offered this technique includes the Air Force, drones and other military operators who need to respond quickly to problems in stressful situations. According to the experts who developed the technique, electrical stimulation, among other effects, reduces the time of human response to external stimuli. This is the so-called “transcranial micropolarization” (tDCS).
The hardware part of the system includes five electrodes that send a weak electrical discharge through the skull to certain areas of the cerebral cortex. Previous studies have shown that it helps to improve the work of certain groups of neurons, which in turn improves the cognitive abilities of the person himself.
This technology is seen as a safer alternative to medicines such as modafinil and Ritalin. Both are used as brain stimulants, including in the US Army. Issued these drugs, if necessary, only by prescription.
')

A person’s cognitive abilities may deteriorate if the loads become too intense. Research by scientists shows that brain stimulation using electrical signals can improve brain function and keep it at a certain level for a certain time.
The developers of brain electrostimulation technology are confident that there are no harmful side effects. At the same time, some experts believe that in order to assert that the technology is completely harmless, it is necessary to monitor volunteers who experience electrostimulation for a long time.
One of the reasons for concern is the fact that in this area there are still no standards describing the scope of the technology and the quantitative parameters of work (current strength, placement of electrodes, operating time, etc.). Therefore, in the near future it is necessary to develop these standards in order for the technology to become regulated. The fact that micro-stimulation improves concentration, said the authors of the 2015 study . The US military, as far as can be understood, only repeated this study, deciding to use it in practice.
So far, electrostimulation is tested on a limited number of volunteers at the Air Force Base named. Wright-Patterson in Ohio, USA. According to scientists who are working on the project, the cognitive abilities of the tired military increase after the brain of people is stimulated with electricity.
“The Air Force often conducts air operations with the use of remote control of aircraft, when the human operator monitors the operation of the device and responds to external factors for a long period of time. Due to the monotony of the operations performed, the efficiency of the operators may fall shortly after the start of the operation, ”the experimenters said in a statement.
Researchers have found that stimulating the brain with electricity improves a variety of human capabilities, including multitasking and speed of reaction. Scientists, they say, work with micropolarization (transcranial direct current stimulation (tDCS)), which has a significant effect on humans.
During the experiments, scientists selected several volunteers and asked them to take a test developed by NASA. This test checks the ability of a particular person to perform multiple tasks at the same time. As part of the test, a volunteer needs to track an object inside a moving circle on a computer screen. At the same time, the subject must observe the other three tasks and respond to emerging requests on the screen.
Volunteers were divided into two teams . Representatives of the first part put electrodes on their heads, which gave a current of 2 milliamperes for 36 minutes. The second group of volunteers also received stimulation, but only for 30 seconds.
The authors of the project claim that the representatives of the first group passed the multitasking test much better than the representatives of the second group. The difference in the execution time of the test tasks was four minutes. “The results showed that micro-stimulation improves a person’s capabilities, in particular, his ability to perform several tasks at the same time,” the developers point out. Scientists are now working on a larger-scale test of the effectiveness of brain electrical stimulation. In particular, they want to find out for how long the cognitive abilities of a person improve after the completion of electrical stimulation.
The results of scientists from the air base in Ohio confirm the results of previous studies, which were conducted by other specialists. Last year, scientists showed that microstimulation works better than caffeine. Snipers were also subjected to electrical stimulation, testing the effect in training programs of virtual reality.
The military is now analyzing the results of research, assessing the possibility of using electrical stimulation for other groups of soldiers, not only pilots and snipers. Nevertheless, a number of specialists require additional studies proving the safety of the method in the long term. “Even for those specialties where a person’s attention is extremely critical, we must be convinced that all this is safe before we begin active implementation,” said Neil Levy, deputy director of the Oxford Center for Neuroethics.
Frame from the movie "Love and Doves"
The problem is that almost anyone can create equipment for electrical stimulation - it is not too difficult. For example, on the Internet you can buy a kit for electrical stimulation and work with it for an arbitrarily long time - all this is not regulated at all. Young people, whose nervous system is still in the formative stage, may experience electrostimulation, and no one knows how this will affect their bodies. In addition, the use of high currents can cause brain damage - this is also necessary to be aware of.
And in 2014, a scientist from Oxford, Roy Cohen Kadosh (Roi Cohen Kadosh) warned that electrical stimulation improves part of a person’s abilities, this is true. But at the same time, other abilities are deteriorating . For example, in one study, the subjects well memorized the system of characters with numerical matches (for example, chicken = 2, egg = 7), but using this data in another, related task, volunteers with microstimulation got worse than the control group.
At the same time, this year a group of scientists from Harvard, Oxford and Tubingen University found that tDCS accelerates learning and improves verbal memory by more than 20%. At the same time, the effect was long-term and lasted for 2 months. Here, electrical stimulation was performed using a current of 1 milliamper for half an hour a day for two days in a row.
Another group of scientists found that microstimulation reduces sleep time, and the quality of sleep does not decrease: there is no fatigue or drowsiness after waking up. The ratio of the phases of sleep also does not change.
Why and how does electrostimulation work?
There is no doubt that it really has an effect on the nervous tissue. Scientists have conducted several studies on this topic. Conclusion - micro-stimulation causes the so-called long-term potentiation and long-term depression of synapses. All these are the processes that underlie the formation of memory and learning. As for the first term, it describes the process of rebuilding the connections between individual neurons, which enhances the “connectivity” of individual areas of the brain. The second term describes the process of reducing "connectivity."
Mainly, electrical stimulation changes the membrane potential of neurons. That is, there is a change in the physiological state of the cells of the nervous tissue, which makes them either more active, prone to agitation, or less.
And what else?
There are other effects. This year, another research team found that microstimulation affects neuroplasticity through the activation of glial cells, which can be called auxiliary cells of the nervous tissue. In addition, another study showed the possibility of altering the epigenetic regulation of the BDNF gene as a result of the influence of microcurrents on the nervous tissue. This gene is responsible for the formation of long-term memory. BDNF refers to neurotrophins, substances that stimulate and support the development of neurons.

The US military uses the characteristic configuration of electrodes to stimulate areas of the brain responsible for increasing concentration and resistance to "nervous fatigue" from performing monotonous actions.
A different configuration of electrodes can lead to other effects, for example, an improvement in “motor learning”. In this case, the anode must be placed above the primary motor cortex. Microstimulation is also used to treat depression , including its severe forms. According to experts, the effect of the action of microcurrents is probably similar to the action of antidepressant drugs, as a result of which the brain begins to actively produce endorphin and serotonin, the so-called “hormones of happiness”. And the side effects inherent in the medical treatment of depression, there is practically no.
In general, more than 12 thousand articles have already been published on the subject of microstimulation of the brain, and in most of them the authors come to the conclusion that there are no serious side effects. In some cases, itching at the point of attachment of electrodes or headache is noted, but this rarely happens.
Now, many experts are confident that electrical stimulation is good. In the US, Europe and Russia, start-ups began to appear, offering their own kits for electrical stimulation in the home or office. Moreover, there are systems for athletes as well as for people who lead a sedentary lifestyle and for whom clarity of thought and concentration are important.
As already mentioned, so far there is no information about the negative effects of the use of electrical stimulation. Perhaps they really do not exist, or perhaps they simply did not conduct research aimed at studying the long-term effect of using small currents to activate the brain.
Society, in general, perceives electrostimulation positively. Among those users who worked with different tDCS systems, the majority (about 50%) rate the effect as “strong positive”. About 40% speak about “average positive effect”. Other users claim that the experience with tDCS was unsuccessful.
As for the military, they intend to continue their experiments.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/399147/
All Articles