MIT developed a millimeter-wave wave reflector to ensure the wireless operation of VR helmets
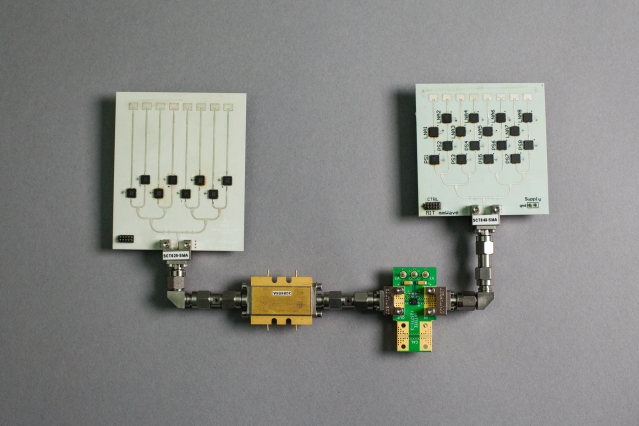
MoVR Prototype
The presence of wires and, as a result, the constraint of movement when using virtual reality helmets has become a stumbling block in the development of technology. While startups and manufacturers are trying to adapt not the fastest (attached to BP helmets) and reliable, but mass technology like Wi-Fi, MIT engineers have proposed using millimeter waves to transmit data to BP helmets, as stated in the corresponding published work , as well as in a press release on the website of the Institute. Back in January 2016, researchers presented a prototype of this device, which they called the “MoVR”.
At the end of the last millennium, some manufacturers promised to extend the millimeter technology in the field of cellular communication (the millimeter range corresponds to a wavelength from 1 to 10 mm or from 30 to 300 GHz). Cellular GSM, for example, operates in the megahertz frequency range from 850 to 1900 MHz.
')
However, this technology has a significant disadvantage. Due to the short wavelength, the signal is subject to serious attenuation at a distance when propagating in the atmosphere due to resonant absorption of oscillations by gases (this is the 57-64 GHz band in which the wave enters into resonance with oxygen molecules). For this and a number of other reasons, the millimeter range for communication is more often used in the “point-to-point” format within the line of sight and broadcast through narrow-band antennas with high signal gain.
At the same time, the millimeter range allows you to make antennas of a much smaller size. Now, at these wavelengths, short-range radio communication (up to several kilometers) works, the quality of which, among other things, is strongly dependent on weather conditions and terrain relief. Weather forecasters are located on the range of 37-64 GHz, since the data on the attenuation rate of the signal make it possible to obtain data on the state of the atmosphere. In addition, the millimeter range is actively used by the military both in radar and detection devices, and in some types of weapons.
As you can understand, the millimeter range is not suitable for mass long-distance communication systems, however, it shows itself perfectly at short distances in controlled climatic conditions (for example, in a room where it cannot rain). Modern ordinary Wi-Fi routers, which are now in the apartments of ordinary users, and working under the standards 802.11b and 802.11g in the 2.4 GHz band, provide a real channel up to 20 Mbit / s or 2.5 MB / s wide (not to be confused with declared 100 Mbit / s or more professional and expensive equipment models). The most common reason for this behavior is the low signal routing speed between the LAN and WAN interfaces.
For a stable broadcast of two FullHD video streams in real time, this bandwidth is not enough. VR helmets from leading manufacturers in FullHD mode require a channel width of 6 Gb / s (6000 Mb / s) or 750 MB / s . So far, only a wired HDMI connection specification 2.0 can provide such a channel.
In their work, researchers use an analogue of the IEEE 802.11ad standard , with the introduction of which, due to its nature, serious problems arise. Previously, for millimeter waves, home use was not found due to their inability to overcome walls and barriers, even if they ensured the speed of wireless transmission of information at the level of 7 to 10 Gbit / s. Also, they initially refused to use the millimeter waves, since the player in the VR-helmet is in constant motion, which prevents the constant reception of a stable signal in the line of sight.
In fact, MIT engineers propose to return to the previously rejected technology and data transfer on a “point-to-point” basis, when the player (receiver) is in the line of sight of the millimeter router signal regardless of its orientation relative to the device itself.
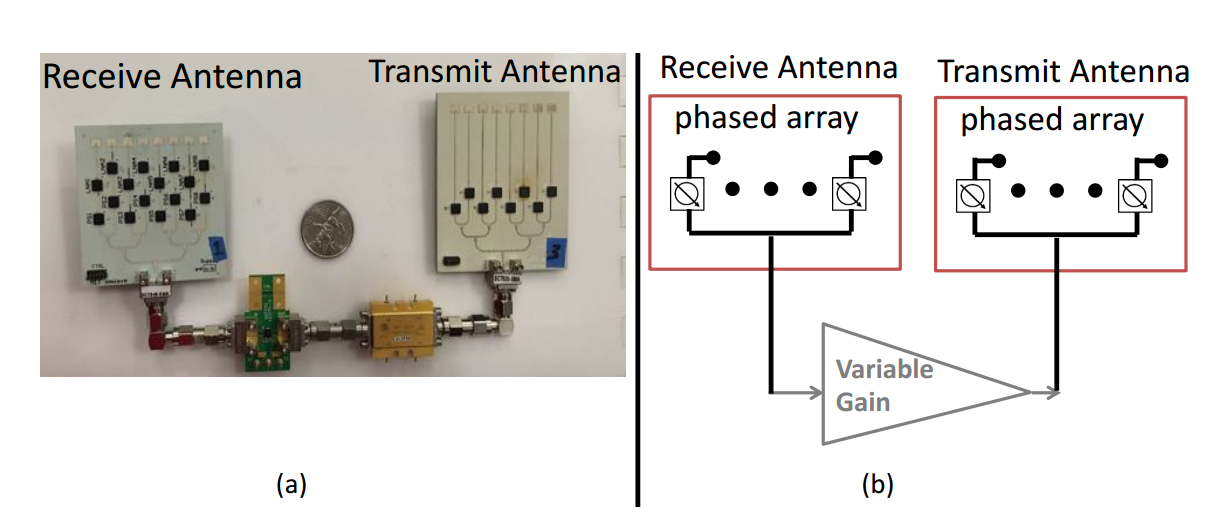
MoVR Reflector Prototype Scheme
The MoVR reflector uses two millimeter- shaped mirror antennas , which will allow to collect the signal from the router into a narrow beam and redirect it to the receiver antenna on the helmet. To ensure the performance of the design during the game, the mirrors are equipped with an automatic signal orientation system. Thus, engineers propose to use an adapted and previously known point-to-point millimeter communication system, which works exclusively in visibility conditions, but provides a stable and wide channel.
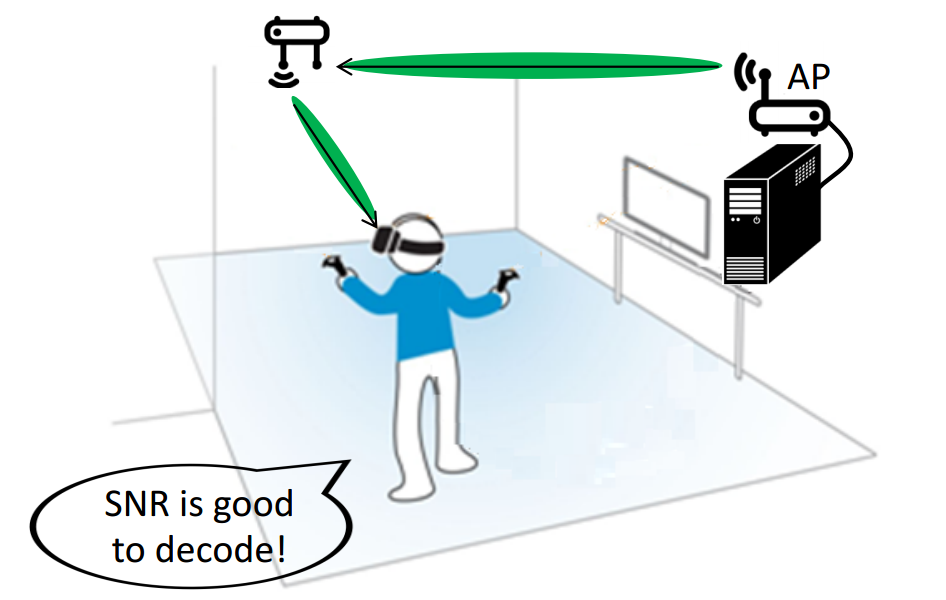
So engineers schematically show the principle of operation of MoVR (in the upper left corner of the room)
It is argued that this approach can ensure the stable operation of several devices at once in the same room without overlapping the signal and creating interference.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/399117/
All Articles