Coming soon: GMO bacteria in pills

E. coli (E. coli). Illustration: Chris Bickel / Science Magazine
American startup Synlogic , founded together with professors at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology, is ready to launch a new class of medical products on the market. It is called "synthetic bacteria" and "live therapy." Capsules for pre-oral use contain a colony of live bacteria. Getting into the intestines, they begin a useful activity. The task is to eliminate certain metabolic abnormalities that are the result of diseases and rare genetic disorders.
In the human body constantly live trillions of different bacteria that are in symbiosis with us. The number of microbes is more than an order of magnitude greater than the number of cells in the human body. The total mass of intestinal microflora is from 1 to 3 kg. Without these symbionts, we simply cannot survive.
All of them are collectively called microflora or human microbiota. Human gut microflora consists of more than 500 species, most of which are bacteria, for example, E. coli. Other representatives of microflora are microscopic fungi, in particular, yeast, as well as protozoa. One cubic centimeter of human saliva alone contains from ten million to a billion bacteria.
')
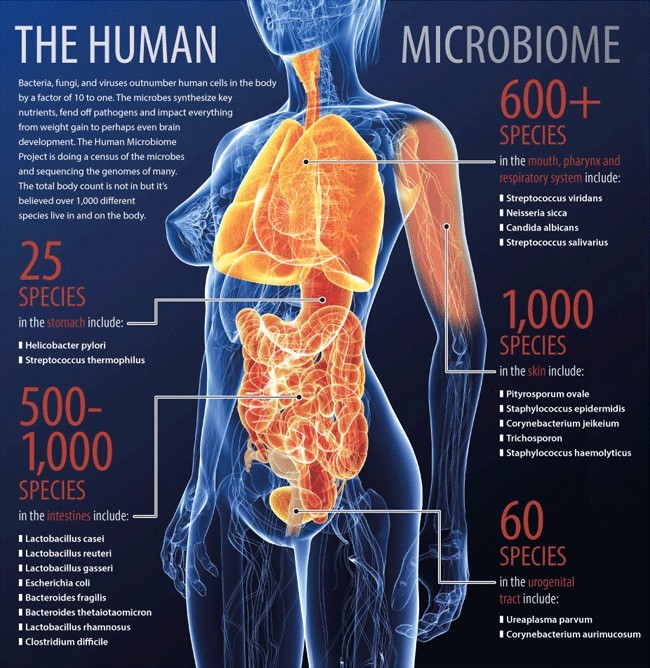
The study of intestinal microflora is one of the promising areas of modern science. In recent years, scientific studies have shown that the microbiota is a highly complex ecosystem that has a key impact on human health, including its physical and mental state. A person can be considered as a "superorganism". The microbial community controls the human body by programming the metabolism in the body with the help of enzymes that are encoded by the genome of bacteria.
Scientists are forced to admit that they are unable to give a complete qualitative and quantitative characterization of the microbiocenosis of the human body by traditional methods, much less analyze the population interactions of microorganisms, microbial "signaling systems" and determine other characteristics of microflora. This is due to the practical impossibility of cultivating more than 50% of human microflora representatives.
For the analysis of microbiota, fundamentally new directions and methods of microbiology have been developed, first of all molecular genetic methods using genetic platforms for metagenomic research.
The startup Synlogic works in this very innovative direction, studying the microflora and trying to influence it somehow to indirectly correct the human metabolism. For example, synthetic bacteria can eliminate excess ammonia in the body. The first clinical trials of the experimental drug Synlogic are scheduled for early 2017 .
Synthetic bacteria to eliminate the excess of ammonia - only the first trial ball in the new class of programmable bacteria that are designed to treat various diseases. Scientific research in this area has been going on for more than 15 years, and Synlogic bacteria in capsules is one of the first specific medical products that can be approved for medical use. Currently, there are 8 to 10 genetically modified microorganisms under consideration by the US Food and Drug Administration.
The basic idea is to genetically correct the bacterium E. coli, normal E. coli, which is present in large amounts in the body. Genetically modified bacterium has a special appetite for harmful ammonia, which is constantly formed in all tissues and organs of the body, and especially actively in the liver, intestines, muscles and nerve tissues. This is an extremely toxic compound that must be bound (neutralized) and removed from the body.
Usually, ammonia is excreted through the urine, but some people’s bodies are not able to bind and remove it quickly enough. Because of this, the body has a rather high and toxic level of ammonia. To the extent that a person becomes irritable, falls into delirium , and in newborns such a metabolic disorder can even cause death. Synthetic intestinal bacterium helps to convert ammonia to harmless arginine.
According to the recipe Synlogic, for a person to normalize the exchange of ammonia in the body it will be enough to take daily one capsule of the drug, which contains 100 billion bacteria of genetically modified E. coli.
The biotech start-up has already received about $ 70 million in venture financing. Independent experts believe that this is a very promising area of pharmacology. For example, another startup Ernest Pharmaceuticals is experimenting with the treatment of malignant tumors with genetically modified salmonella . This is a specific bacterium that tends to accumulate in cancer tumors. Scientists are trying to use this property of salmonella. An organism constructed by them should release an anticancer drug when it enters the cells of a malignant tumor.
Clinical trials should verify that GMO colibacillus bacteria are harmless to the body and do not exchange genes with normal human microflora bacteria. Engineers have made it so that the division of a synthetic organism requires the presence of a specific substance - thymidine , which is very small in the human intestine. This ensures that the GMO bacterium does not leave offspring.
Perhaps a few years later, on the shelves of pharmacies, we will see a lot of different bacteria with gene modifications. In general, such GMOs are used not only in medicine. For example, it has recently been reported that the development of microoranism, which synthesizes morphine from glucose , so that the future promises to be interesting.
According to expert estimates , the American pharmaceutical market of synthetic bacteria — drug pills and yogurts with live bacteria — is $ 3.5 billion.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/398953/
All Articles