Is something falling from the sky?
 A couple of years ago, I already briefly wrote about this development of one of the institutes of the Tomsk Scientific Center. Of course, the development of devices (especially environmental monitoring) is not always possible in the “fast” startup mode, but there are a number of explanations for this, which are often independent of the developers. I propose to analyze the situation and get acquainted with the development of interesting instruments for such a conservative field as meteorology. This article will discuss the optical precipitation meter , which, ultimately, should somehow replace the meteorological instrument used for these purposes - the bucket. Yes, yes, friends, it is a bucket. The Tretyakov bucket is a regular precipitation gauge, which Roshydromet has been using for decades. On the other hand, what could be safer than a bucket? Probably only the pelvis ... This is the exceptional conservatism of the field of meteorology. New means of measurement should not violate the long-term series of meteorological observations and in order to replace the Tretyakov bucket with new devices for recording precipitation, long-term comparative measurements are required. Is the first quarter of the 21st century enough for this? I suggest to discuss this under the cut!
A couple of years ago, I already briefly wrote about this development of one of the institutes of the Tomsk Scientific Center. Of course, the development of devices (especially environmental monitoring) is not always possible in the “fast” startup mode, but there are a number of explanations for this, which are often independent of the developers. I propose to analyze the situation and get acquainted with the development of interesting instruments for such a conservative field as meteorology. This article will discuss the optical precipitation meter , which, ultimately, should somehow replace the meteorological instrument used for these purposes - the bucket. Yes, yes, friends, it is a bucket. The Tretyakov bucket is a regular precipitation gauge, which Roshydromet has been using for decades. On the other hand, what could be safer than a bucket? Probably only the pelvis ... This is the exceptional conservatism of the field of meteorology. New means of measurement should not violate the long-term series of meteorological observations and in order to replace the Tretyakov bucket with new devices for recording precipitation, long-term comparative measurements are required. Is the first quarter of the 21st century enough for this? I suggest to discuss this under the cut!A little more about the Tretyakov bucket
Do not think that my sarcasm at the beginning of the article is somehow aimed at blackening the existing methods and instruments used for meteorological measurements. Not. At one time, such instruments and techniques were very advanced. The point is that the situation is changing, many interesting technologies make it possible to solve the problems of meteorology at a fundamentally new level and, most importantly, reduce the human factor. After all, the work on the removal of meteorological data at key meteorological posts is carried out by a meteorologist. These people are extremely responsible, but they are people. Of course, there are automatic stations for meteorological observations, but according to the rules, they are served by people with a certain frequency.
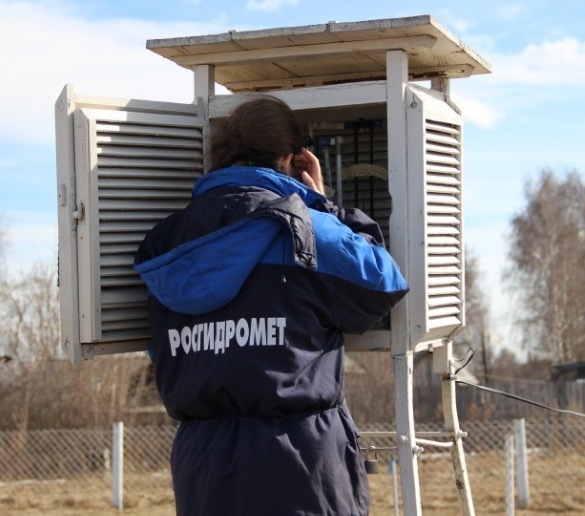

Returning to the Tretyakov bucket. This is a metal tank with wind dampers, such petals, which quench the wind influence when it rains obliquely. It looks like the device assembly.
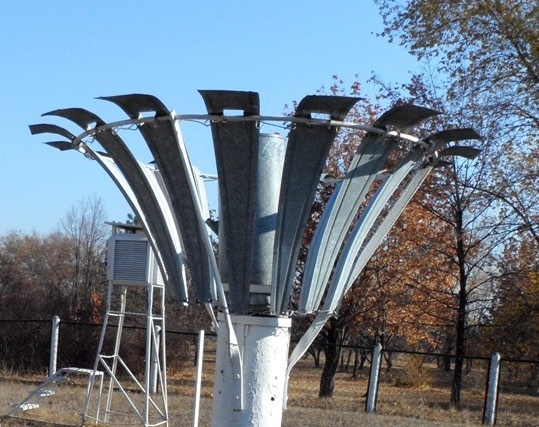

The Tretyakov bucket is installed at a certain height and, unfortunately, its maintenance does not do without a meteorologist. The specialist measures the amount of precipitation manually using a scale or ruler. After the measurements it is necessary to drain the water from the bucket. Of course, the device is not particularly suitable for determining solid precipitation.
')

By the way, the most common injury at the weather station is the fall of people from the stairs, because many devices are installed at a height of 2 meters. Imagine jumping every three hours on wet or icy metal stairs? Feet, hands take care!
Optical precipitation gauges
Of course, in most countries, such medieval precipitation recording technologies as a bucket have not been used for a long time. Most of them use optical precipitation gauges. Here, for example, devices of this type are used in Germany and the USA. As it is now customary to say - from "our partners."

Indeed, for such a task to use optical signal registration is the most reasonable. High accuracy, no need for special care, the devices are protected from freezing, there is no human factor. The developers of the Russian optical instrument for the registration of precipitations, the OPTIOS precipitation meter (OPTICAL Sediment Meter), went the same way.
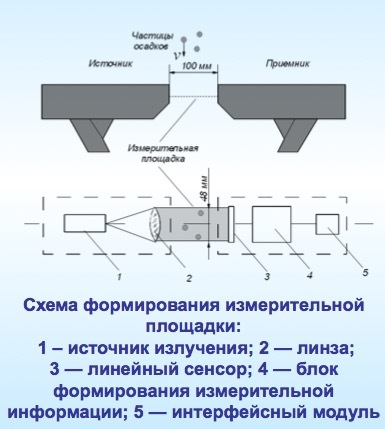
How do such devices work? The basis of the measurements is the continuous analysis of shadow images of droplets on the optical receiver during the passage of rain droplets through the measuring platform.
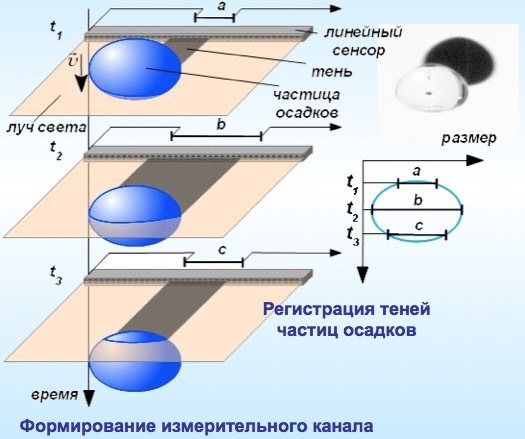
But the drops are not single? Yes, there are a lot of drops, but for this purpose, streaming image processing algorithms are used, and special extended high-speed matrices are used as an optical radiation detector. This allows not only to determine the integral (total) precipitation, but to determine the type of precipitation (rain, snow, hail), the rate of falling drops and the structure of precipitation. This provides additional interesting data that, in particular, can be used for scientific research. So, for example, it looks like the distribution of raindrops in size and, best of all, it is possible to record snowfall, which is difficult in the case of the Tretyakov bucket.
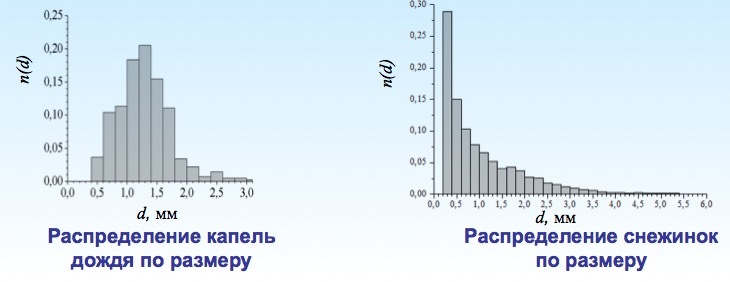
By the way, the drops are not spherical at all. They are somewhat elongated and almost everything near the surface of the Earth is broken into smaller ones, although at the height, of course, the drops are larger. The scattering of the drops is due to the fact that when flying to the surface of the Earth they gain a decent speed and even the largest drop at a certain speed inevitably scatters into small ones. The rate of droplets can also be estimated.
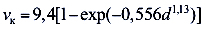
Most drops dare speed of not more than 9 m / s, and snowflakes fly with a maximum speed of no more than 1-2 m / s. Another thing hail. This is a more serious task, which the optical precipitometer also does well. Of course, we are talking about low-intensity hail. For example, such hail is not worth measuring. Better to just save yourself!

But this is rare. Most of the hail is much smaller. In 95 percent of cases, hailstones are no larger than 5 mm, but their speed is higher and can reach up to 50 m / s. This is how the shadow images of hailstones from the optical image receiver of the gauge look like.
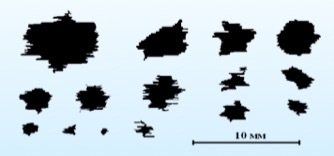
In general, the analysis of shadow images is very exciting. Indeed, the shapes and types of snow fall are surprising.

All this is only additional features provided by researchers. But the main task is solved by optical precipitation gages reliably. Automatically measure the amount, type and structure of precipitation, transmit data for analysis and can work even in the most severe conditions. One can only hope that they will come for the replacement of old instruments, but so far only the process of comparative tests, which can last a very long time, is underway. This is how it happens.

Instruments should stand together for many months and only comparative experiments can give a chance to a new instrument to appear in the arsenal of meteorologists. In general, this is essentially an absurd situation. Optical measurements more precisely, the precipitation gauge works better with snow and also determines the structure of precipitation. Of course, in the rain, convergence of results can probably be achieved, but what about the measurement errors? Human influence? Evaporation of water? These and other questions remain open ...
In general, the registration of precipitation is one of the most important tasks of meteorology, since the weather is determined, in particular, by the so-called world water container. Or more simply, the water cycle in nature. Therefore, the development of instruments for recording precipitation is an important technical task.
In general, meteorology is an extremely conservative field. Probably, this has its own explanations, but on the other hand, it is already difficult to explain traditions. Until now, the temperature at the weather station has to be measured by thermometers according to GOST 1968 (GOST 13646-68). I wonder what is so necessary? Mercury thermometers are also used to measure the temperature of the soil and water in reservoirs according to the requirements of GOST 112-78 1978. How many mercury thermometers are broken in the ground or drowned in rivers and lakes? Maybe this is the deep essence, but I do not understand it. If someone can explain - please leave a comment. And, of course, all the good weather and a nice day!
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/398823/
All Articles