City design based on data
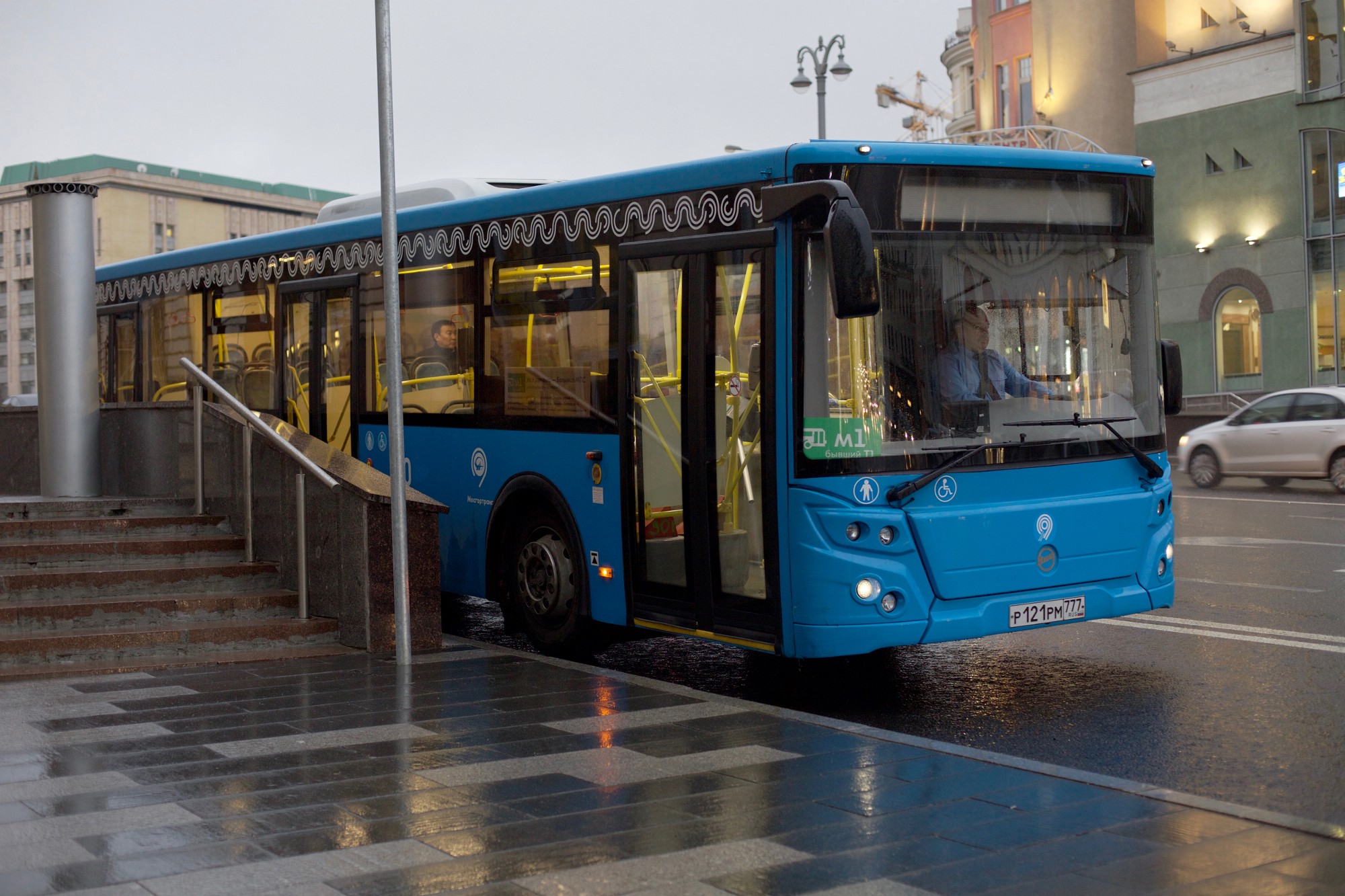

Quite recently, the Magistral land transport network has been launched in the center of Moscow. It is worth making a reservation right away - land transport was present in the central part of the city before, only the organization of the route network was inconvenient and inefficient. So the problem of land transport reform in the center of Moscow has been brewing for a long time.
In the summer of this year, the Moscow Department of Transportation gathered a working group that included many Russian and foreign experts, including well-known transport planner Jarrett Walker, who had already managed to redraw ground transportation in dozens of cities around the world, and Mobility in Chain. The Urbica team was able to participate in that part of the work related to the analysis and visualization of data.

')
The ultimate goal of the project, which later received the name "Magistral", was the planning of a new ground transportation network in the center of Moscow - inside the Garden Ring. However, before starting to design, there was a lot of research and intensive teamwork.
Among the data that we have at our disposal were arrays of information about the intervalence of traffic, passenger traffic, bus stops and the number of landings and landings on each of them, the speeds of buses, trolley buses and trams, population density and number of jobs in different areas, within walking distance and the presence of a variety of important objects in different parts of Moscow.
In order for the experts of the working group in general and the Department of Transport in particular to have the opportunity to compare, draw conclusions and impose different types of information for each other, we created a simple and convenient data research tool. The data that we had came from April 2016. At the very early stage of the work, it turned out that different data was stored in different places, in different formats and even in different institutions.
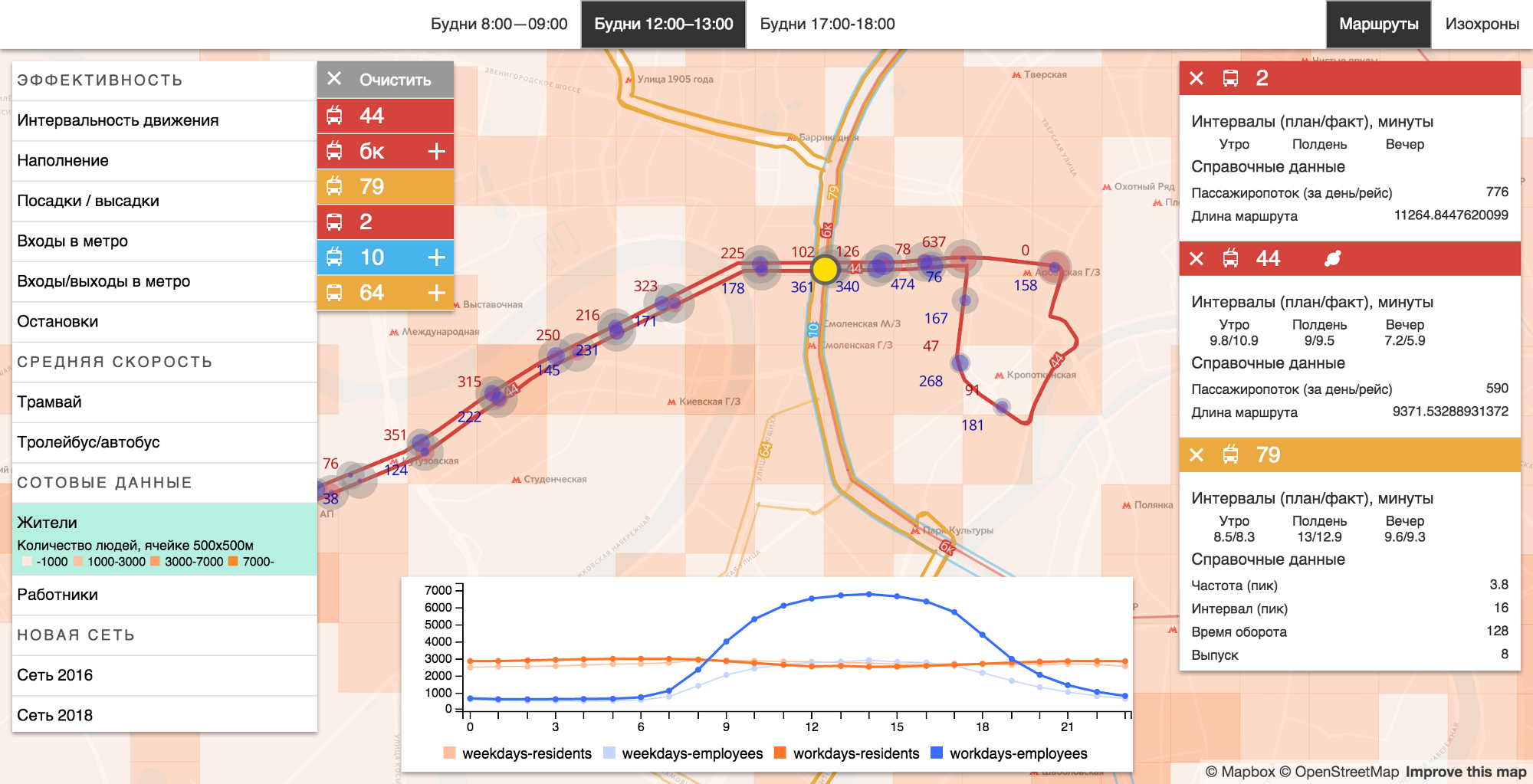
A data research tool created by us for transportation experts.
On July 11–13, the project’s working group gathered from all over the world to intensively reflect on the fate of the Moscow ground transportation. For three days, experts honed the ideas that formed the basis of the “Highway”. As a result, experts led by Jarrett Walker developed the main thing: the vision and concept of the new ground system.
The main principles on which the team worked on the project were high passenger traffic and density, on-foot accessibility, linearity and symmetry.
The main changes in the network have already occurred - the renaming of routes, the increase in traffic intensity, the opening of new lanes for public transport. Next year, the routes will become even simpler and more convenient, and the design principles of the “Highway” will be gradually applied throughout the city.

Immersion in the data
Like many other transport planning projects, in the “Highway” decisions are based on the analysis of statistical data. This is not to say that this approach is new, but few have previously tried to look at transport at the macro level, combining and comparing different data in a single analysis tool.
Creating a convenient and understandable interface for working with information, the lion's share of time is taken by the processing and structuring of data. There is never a lot of data, and when creating decision-making systems — namely, we created it for experts in this project — it is very important to understand which data is meaningful, which is secondary, and how this data is interrelated.
The quality of visualization depends on this: one can even say that these processes are interrelated. It is impossible to visualize data in a clear form, if they are not structured, but it is also impossible to understand the structure and nature of a large array of data without being able to visualize it. This process is helped by prototyping and short iterations: by obtaining a visual prototype, you can learn more about the data.
One of the most important criteria for the efficiency of public transport is passenger traffic: according to the data of landings and landings, it is possible to understand which routes are efficient and which are not, on which sections of the route land transport is overloaded, and where it carries air. The correlation between the cost of public transport and passenger traffic determines how efficient ground transportation is in an economic sense. We used the statistics of occupancy of land transport salons and statistics of congestion of the Moscow metro for each route, and the routes of transfers from one type of transport to another (for example, from the bus by subway) were determined by ticket numbers: the passenger must attach at the entrance to the subway ticket to validator. Thus, the basic patterns of movement of people around the city became clear.
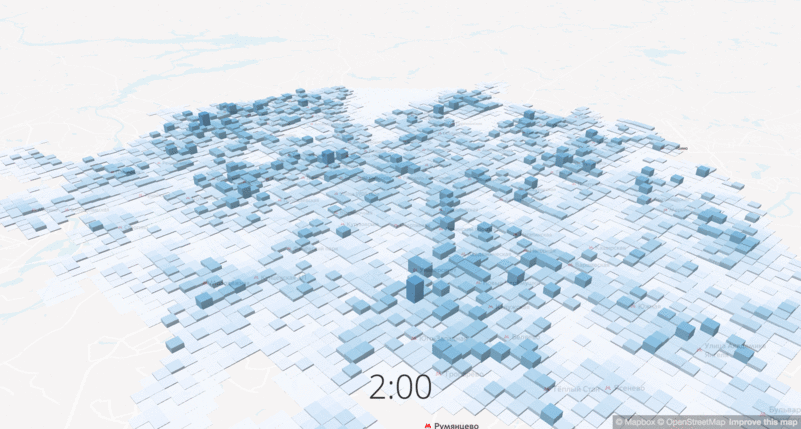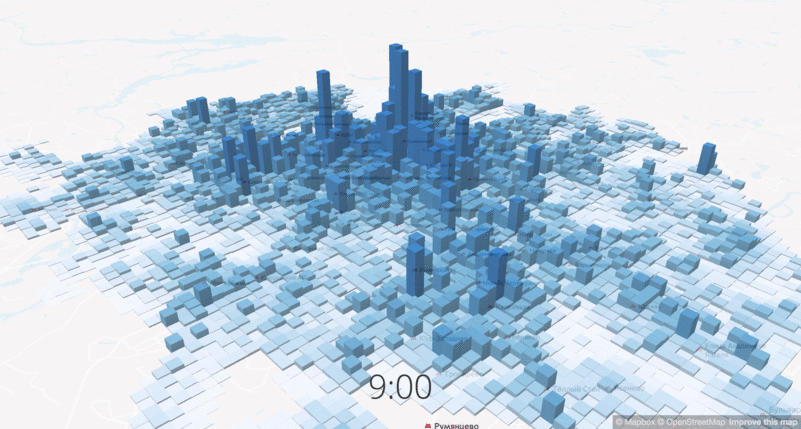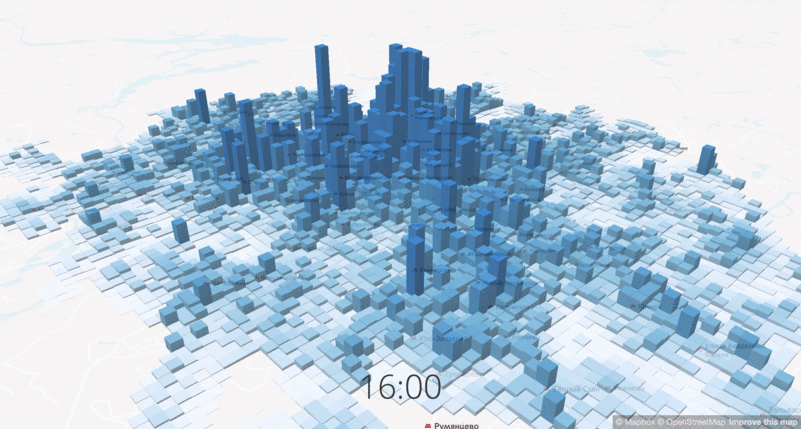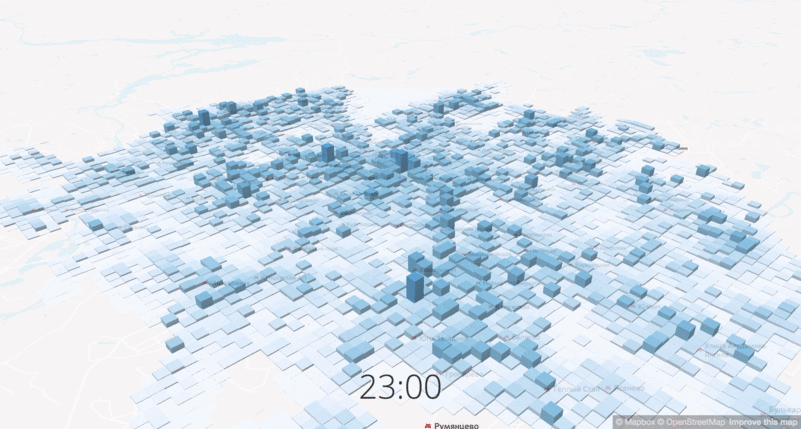
The change in the density of workers at different times of day
Another important data set is the population density, or rather, the change in population density at different times of the day. The project is focused on changing routes in the central part of the city, and in the central areas the density increases 10-12 times on weekdays, respectively, and the city should offer transport services for all of its residents. We used data from mobile operators to show the demand and concentration of potential passengers.
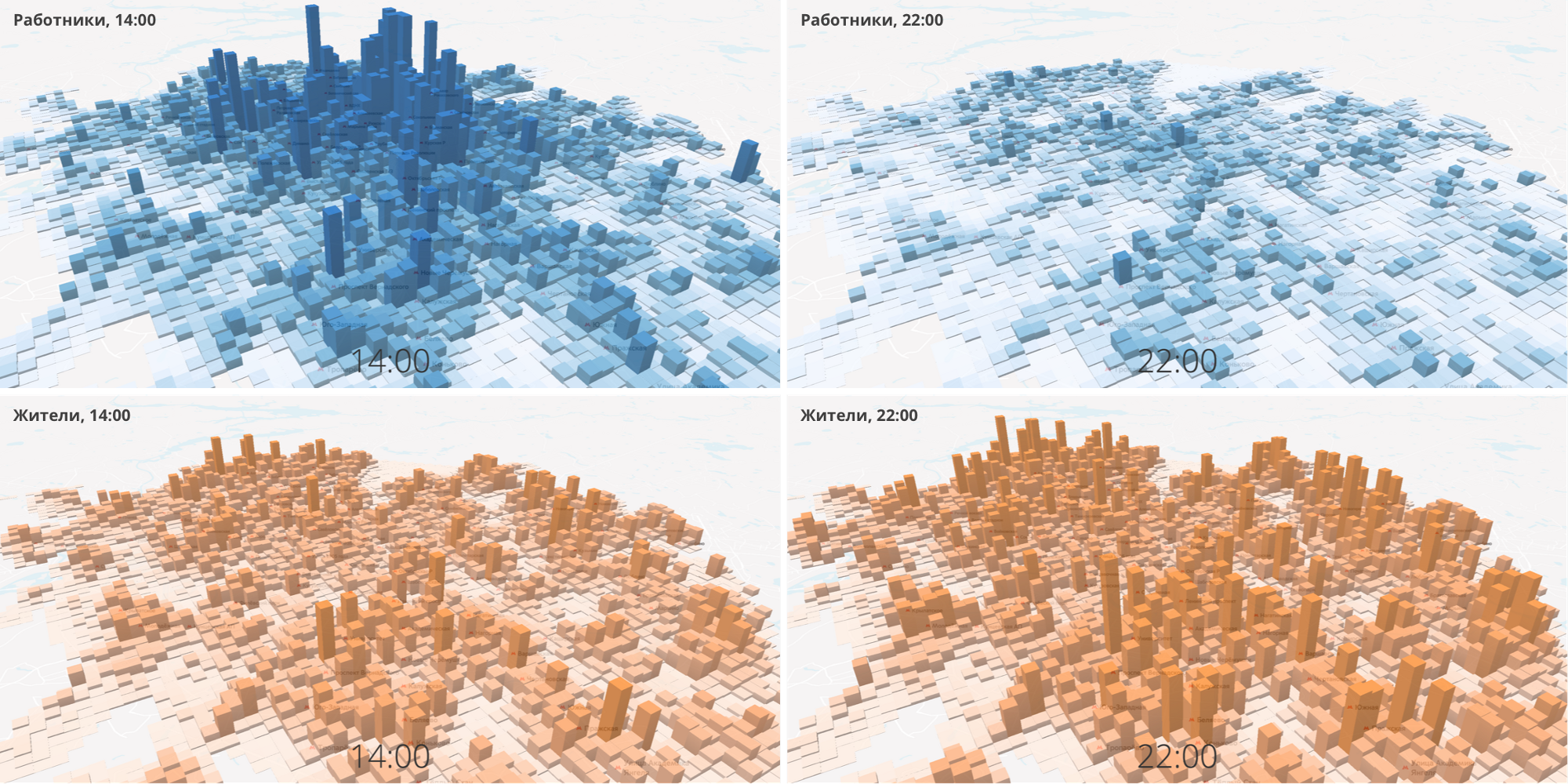
The density of residents and workers at different times of the day.
Labor migration (it is called “pendulum”) can also be seen from the statistics of the entrances and exits of the Moscow metro: in the morning, stations in residential areas operate mainly at the entrance, and in the evening at the exit; in the central areas where people work, the opposite is true.
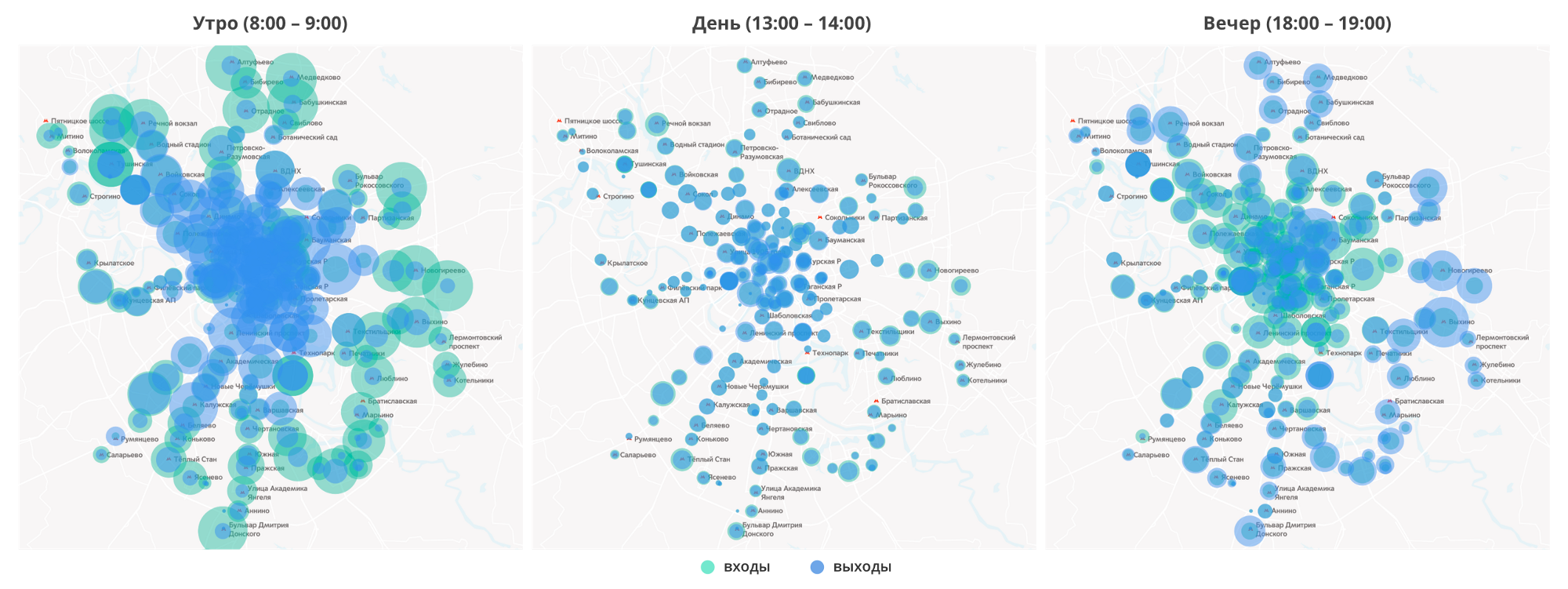
Statistics of entrances and exits of the Moscow metro at different times of the day (weekdays)
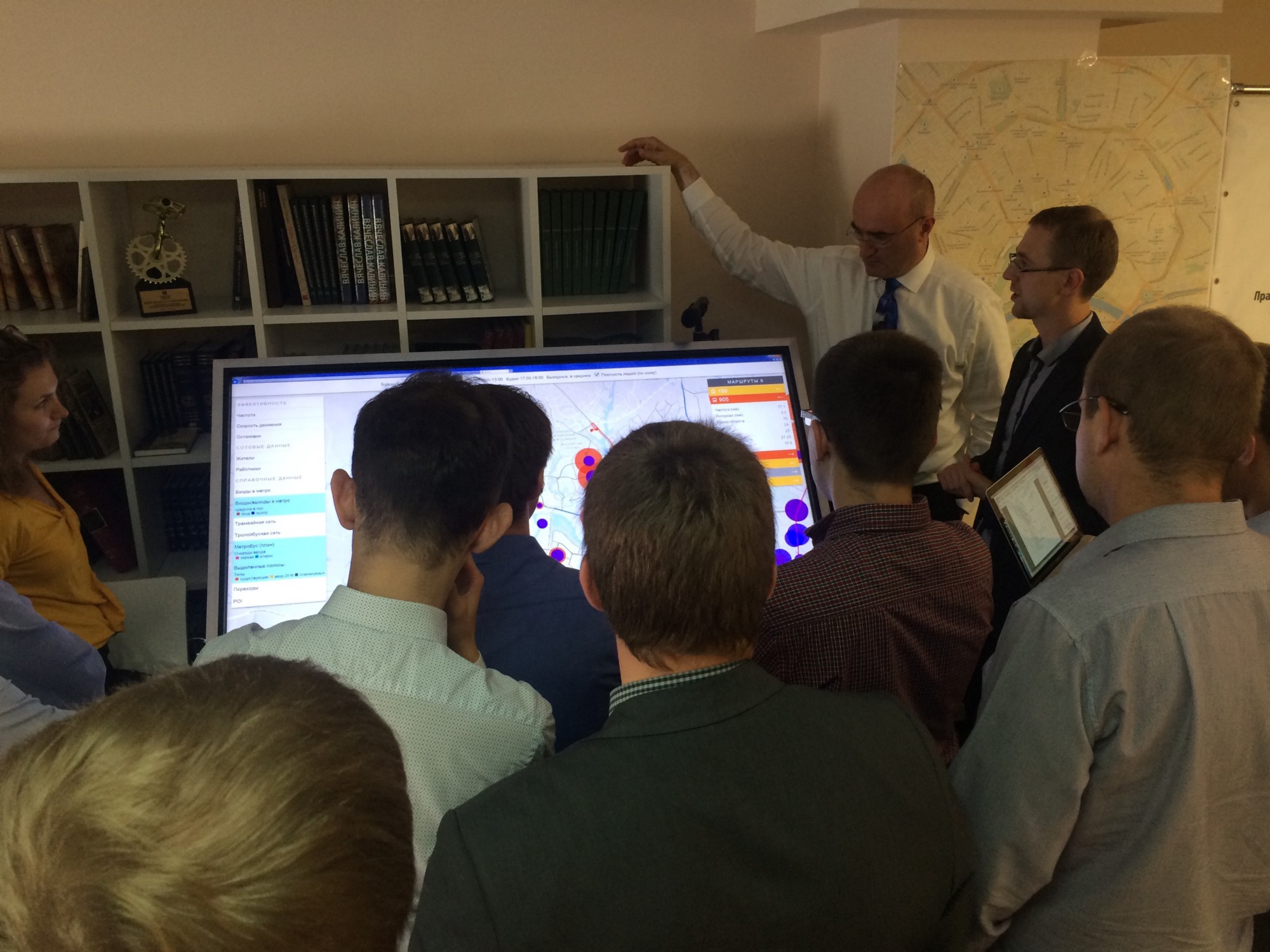
We processed the statistics of landings and landings, the frequency and speed of movement, the load on the roads and transfer nodes, data of cellular operators, data on the movement of each bus - in general, data from about 30 different sources - and brought them together in a single user interface with the ability to impose different layers at each other, so that the working group of experts can investigate what is happening in the city with transport.
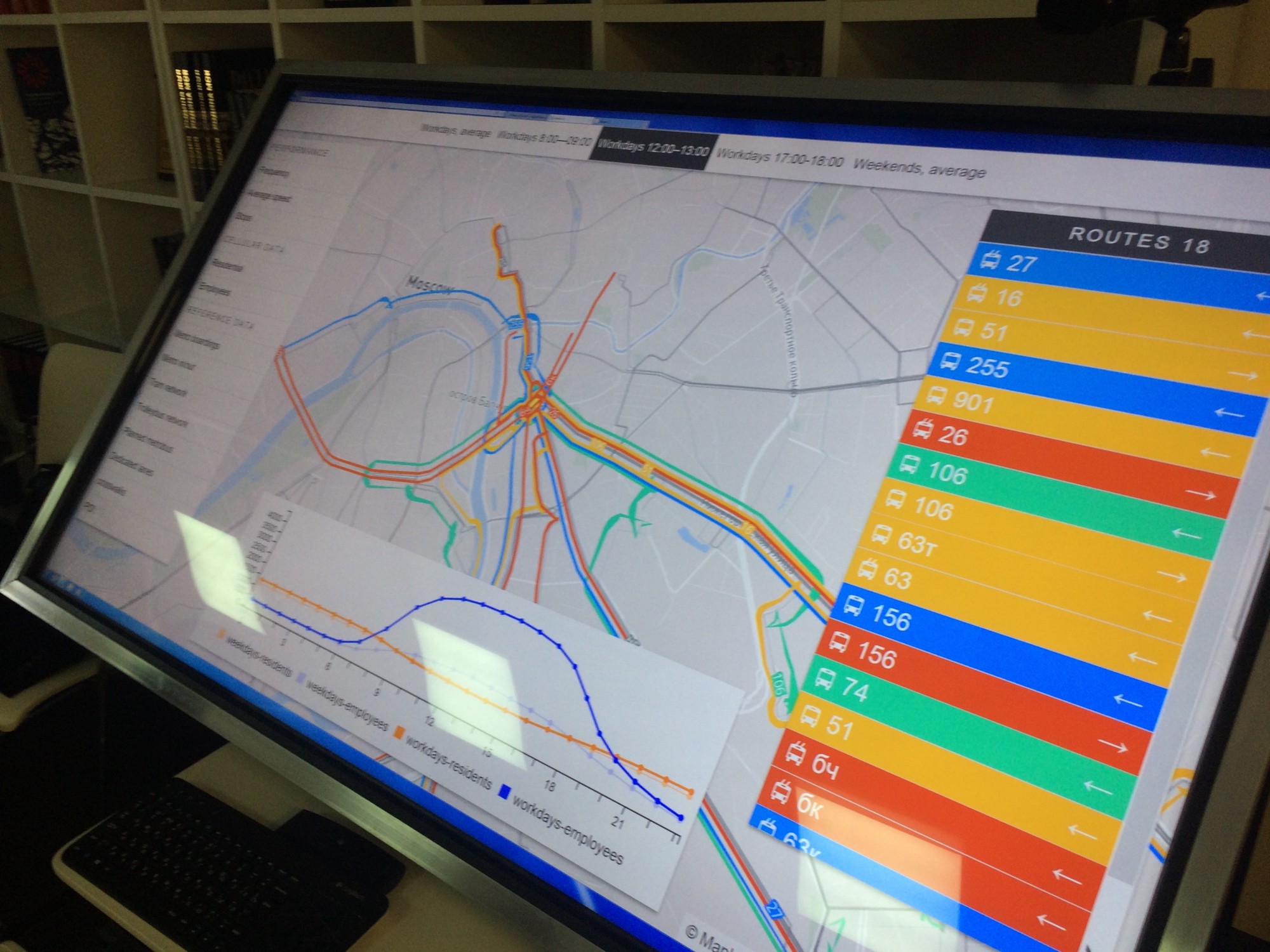
Data analysis system on a 60-inch multi-touch display at the time of the workshop
How to understand that design decisions will be effective?
In the work on the analysis tools for the Department, we just needed the isochron technology. For this project, we taught him to count accessibility zones on public transport (including both on-road and subway). Later, when the new network was already designed, we were able to compare the availability zones under the old and new modes of operation.
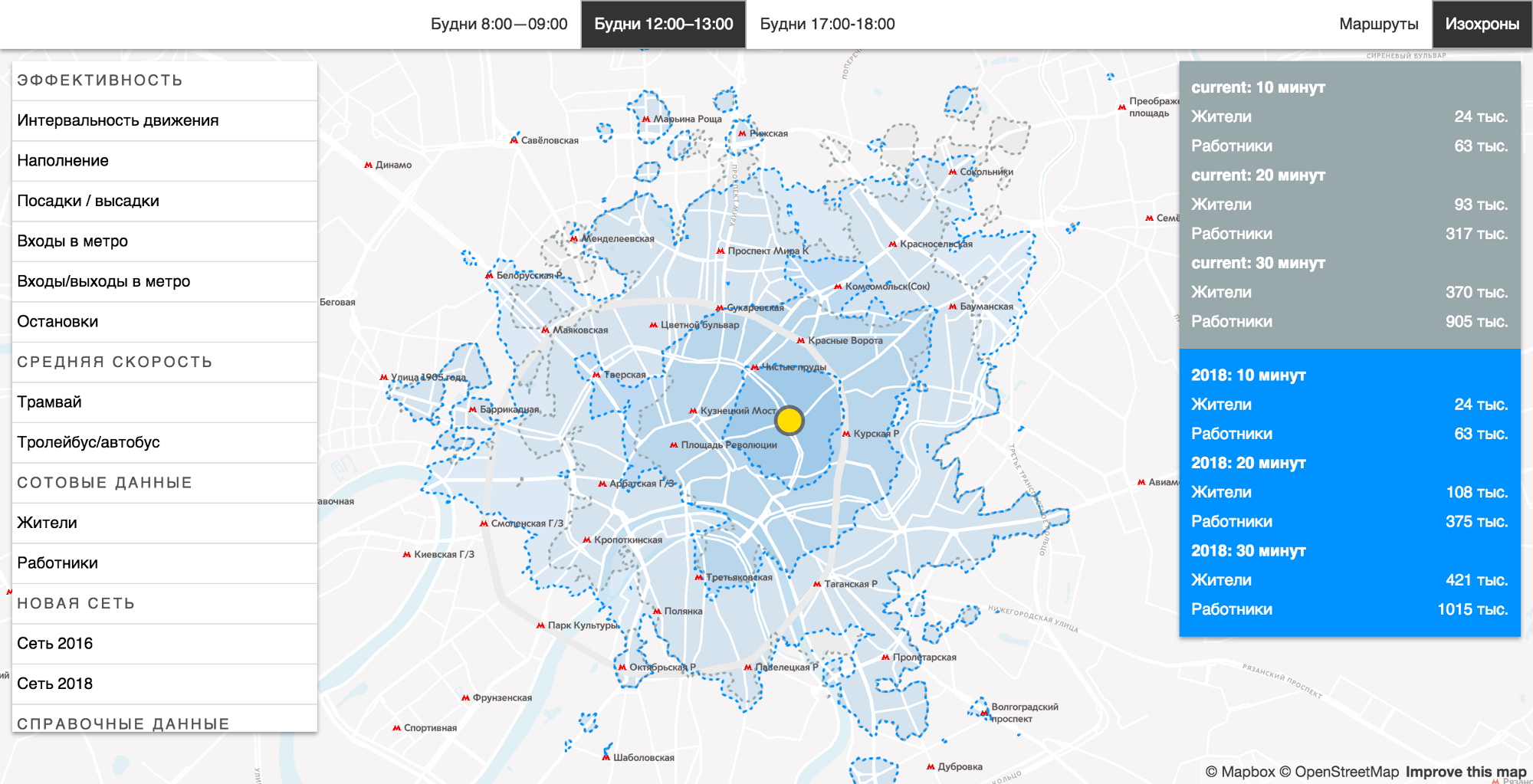
The availability zones tool allows you to compare existing and planned transport networks.
In early October, new routes started in the city - a new network of routes was called the “Magistral”. More information about the project can be read in the special project on the website of the Moscow City Hall . Now we are actively observing what happened: we are analyzing the statistics of the first two weeks of launch, identifying places that should be improved in the future.
We like to think of this project as something that has increased the level of freedom for the citizens. After all, convenient transportation means opportunities: the opportunity to go to school or to work, the opportunity to be at the right time at the right place, the opportunity to expand your horizons. And opportunity is freedom.

Jarrett Walker + Associates : Jarrett Walker and Partners has decades of experience in designing public transport networks. The company is engaged in both small projects, planning ready-to-implement transport concepts, and long-term development, developing the entire vision of the transport system in the city. Working in collaboration with clients and stakeholders, Jarrett Walker and his team develop plans that take into account the needs of local people and technical conditions, and this allows you to better understand the future of transport development.
Mobility in Chain - they are also MIC, this is a transport planning company. MIC is based in Milan, Moscow and New York. The company operates internationally, implementing projects in countries from the USA to Europe and China, from Russia to Turkey and Africa.
Urbica is a company engaged in the analysis and visualization of data about the urban environment. Urbica specializes in information design, interfaces and data analysis.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/398773/
All Articles