Clouds slow global warming

Almost no one doubts that the average annual temperature on the whole Earth gradually rises. About global warming does not write just lazy. Most experts believe that the increase in temperature is largely due to the increase in the concentration of carbon dioxide, water vapor and other "greenhouse" gases in the atmosphere.
There are many reasons that lead to an increase in CO 2 concentration in the Earth’s atmosphere, but the main one is human activity. Not so long ago, a record of carbon dioxide concentration was made : 400 ppm. Climatologists say that CO 2 will not be less, the concentration of this gas will only increase. Scientists recently published a new study, the results of which indicate that some natural constraints are affecting global warming. It's all about the clouds.
It's all about the clouds . The faster it gets warmer, the more water evaporates, and the more water vapor enters the atmosphere. This water vapor affects the dynamics of cloud formation. Scientists usually say that carbon dioxide and water vapor are the two main factors of global warming. It is water vapor, experts say, that is responsible for approximately 36–70% of the greenhouse effect, excluding clouds.
')
A group of scientists from the Livermore National Laboratory. E. Lawrence, under the leadership of Chen Zhou, discovered that lately dense clouds have begun to actively form in the lower layers of the atmosphere, and now there are more of them than before. And these clouds reflect sunlight. The more clouds of this type are formed, the more sunlight is reflected. Perhaps it was the formation of cloud cover that caused global warming to slow down from 1998 to 2013.
Interestingly, at the beginning of the 21st century, most scientists, including the International Panel on Climate Change (IPCC), envisaged providing clouds with significant positive feedback that enhances the warming effect of an increase in atmospheric CO2. Dr. Roy Spencer of the University of Alabama in Huntsville showed that in fact this relationship is not positive, but negative. According to him, cause and effect are confused in most climate models, so scientists use the wrong direction of feedback. Here it is worthwhile to take into account the fact that clouds at high altitude transmit the sun's rays, but do not transmit the heat reflected by the Earth’s surface. Clouds that form directly above the surface of the planet reflect more sunlight and transmit the heat reflected by the Earth’s surface.
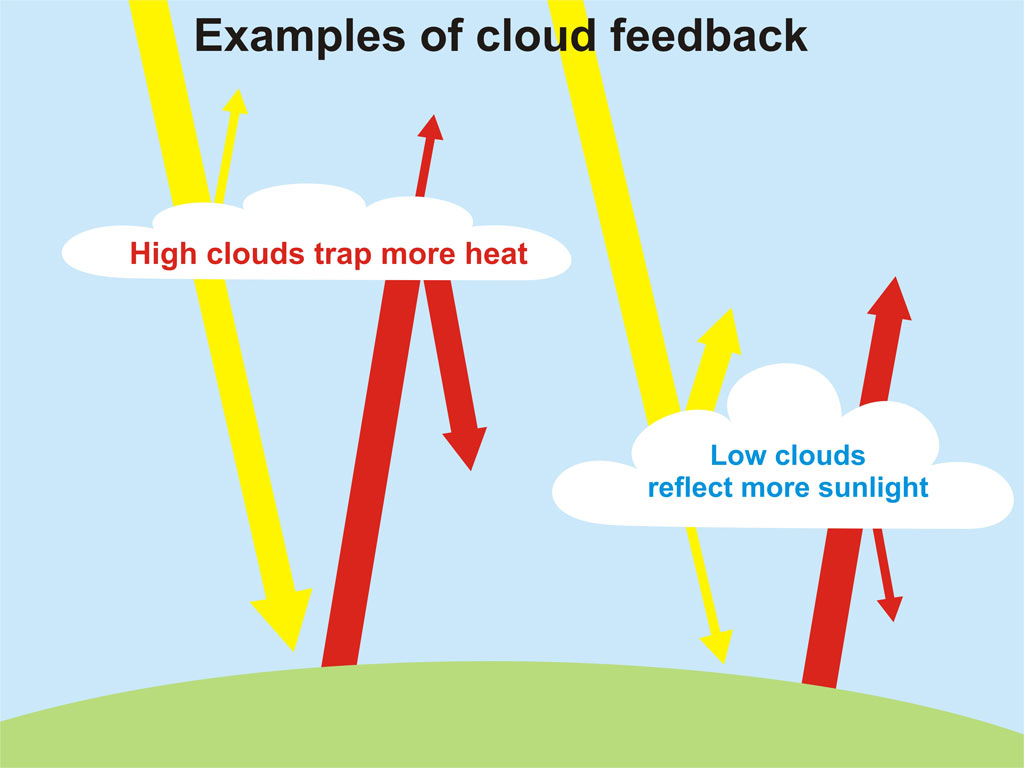
In 2010, it was shown that there is a possibility of a small negative feedback (cooling) under the influence of clouds at low altitude. These clouds are actively forming near the equator, in the tropics and subtropics.
Experts from the Livermore National Laboratory decided to test how climate models work, if we introduce such a factor as negative cloud feedback. Scientists decided to simulate climate change over the past 150 years, and compare the calculated data with real. As it turned out, these data correlate to a rather high degree. Therefore, scientists have concluded that the model created can be used to predict the dynamics of the Earth’s climate temperature in the future.
Interestingly, the model showed a period of time when clouds provided positive feedback for global warming, that is, increased warming. But as soon as there were more clouds forming at a low altitude, the positive feedback began to weaken a little and over time showed the opposite sign. The last few decades, this relationship is negative, that is, we can say that the cloud layer reduces the rate of global warming.
Now the warm eastern waters of the tropical regions of the Atlantic and Pacific Oceans heat up faster than the western regions. This situation has been traced since the 1980s. Heated air rises higher in warmer regions and decreases when moving to cool areas. The higher the temperature difference, the more clouds form in the lower layers of the atmosphere. Accordingly, the more they reflect light and heat energy, slightly reducing the rate of global warming. If the process of cloud formation slows down, the rate of global warming will increase. The influence of clouds on the climate of the planet has changed several times over the past decades; here everything depends on the formation and dynamics of warm and cold air masses in different regions of the world.
Experts say that slowing warming - only a temporary phenomenon. "In the future, heating the entire surface of the earth will probably reduce the influence of clouds on the temperature of the Earth ... The authors of the study showed us that so far we were lucky, because the clouds in the lower atmosphere became more and more, they reflected sunlight and heat energy back into space, slowing the heating of the planet. But you shouldn’t hope that the process will continue in the future, ”said climatologist Kate Marvel from NASA.
DOI: 10.1038 / NGEO2828
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/398743/
All Articles