Google Neural Network arbitrarily styles images in real time
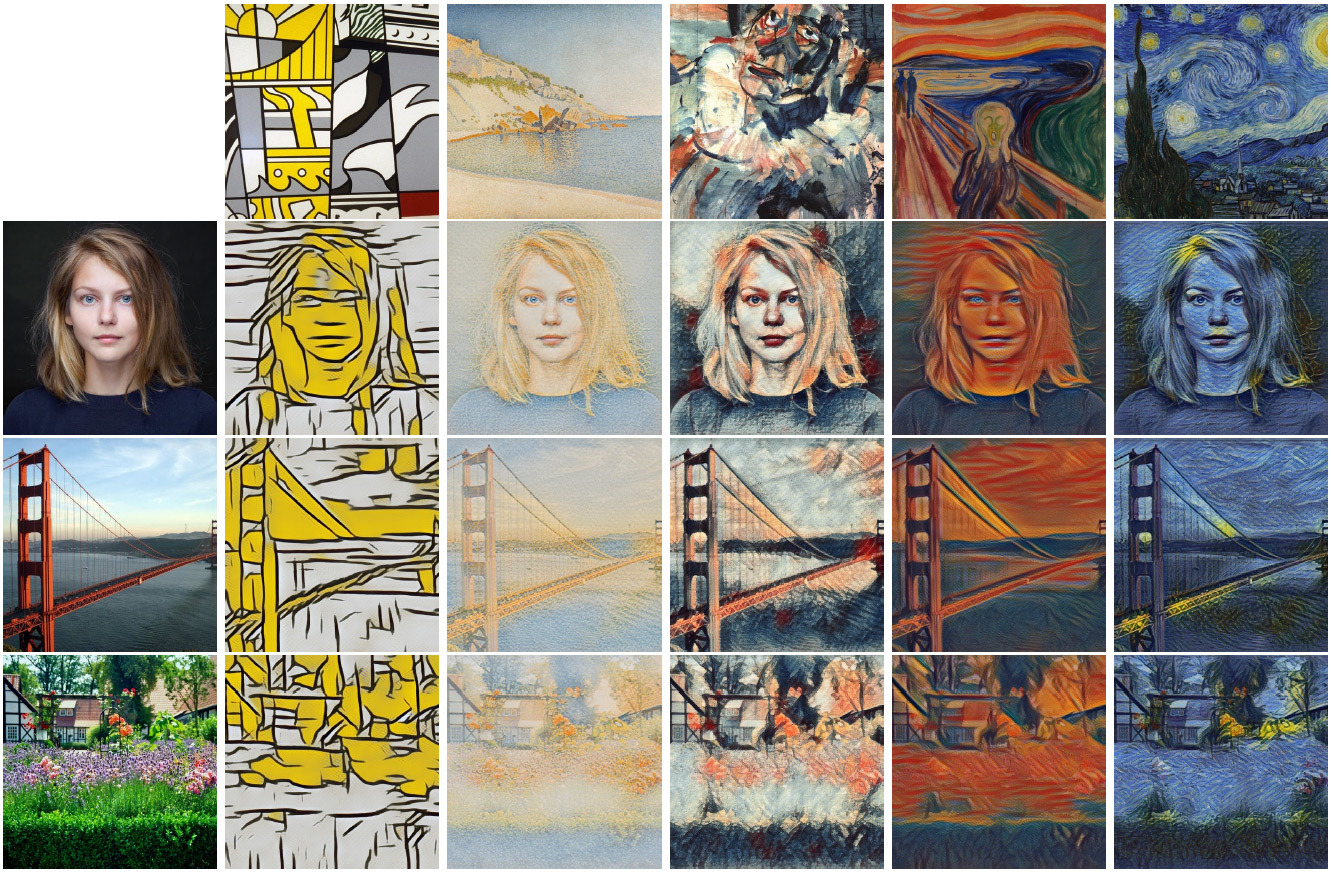

The neural network from Google imposes on the photo any of the 32 styles taught (five are shown here). The program is undemanding to the gland and memory. The code will be published soon
Synthesis of textures with transfer of style from one image to another is a well-known technique, which is 15 years old. It was first described in the article “ Analogies in Image ” by a group of researchers from Microsoft Research for the SIGGRAPH 2001 conference, as well as in the article “ Embedding an image for texture synthesis and transfer ” from Mitsubishi Electric Research and the University of California at Berkeley in the same 2001 Now it is difficult to say which one appeared earlier.
In 2015, the technique received a second life when neural networks connected to the synthesis of images with the transfer of style. This happened after the release of the scientific work " Neuroalgorithm of artistic style " Gatis, Ecker and Betge from Eberhard-Karl University in Tübingen, Germany ( article on Geektimes ). The work is so impressive that the described algorithm was soon implemented in several computer programs for the consumer market, including mobile applications like the Russian Prisma (June 2016).
The work of Gatis, Ecker and Betge is good because the authors taught the neural network on existing works of famous artists: Vincent Van Gogh, Pablo Picasso, Edvard Munch and others. In this case, the neural network can continue to train on other data sets, so it is a universal tool. Such a neural network works on the Prisma server and other companies that distribute mobile applications for styling user photos.
')
The Gatis, Ecker and Betge convolutional neural networks are based on the 19-layer Simonyan and Zisserman VGG neural networks , and the processing of the original image takes place in several stages. At each stage in the hierarchy, the number of filters increases. Styling for a specific style occurs in the first stages of downsampling (broad strokes, cubist patterns, etc.), and the last layers of the neural network process the original image so that the objects remain recognizable ( d and e in the diagram). The neural network starts working from a random position (or from the source image) until the result satisfies the specified requirements.
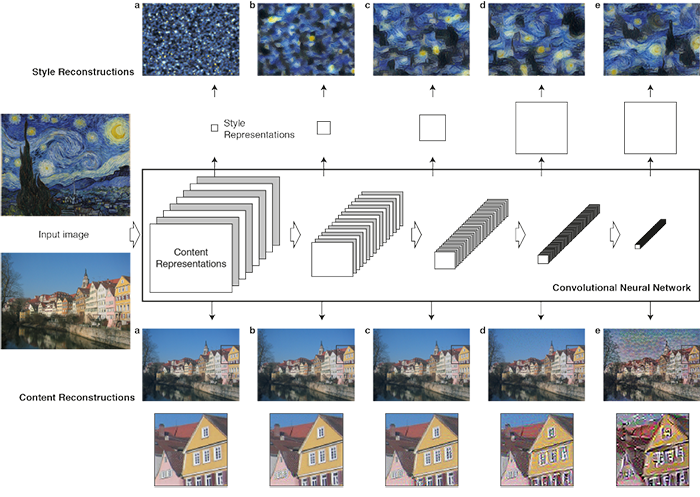
In a neural network, content and style representations are separated from each other. Thus, they can be controlled independently of each other. For example, to take content from one image, and style - from another.

Examples of image styling in the Gatis, Ecker and Betge neural networks
Original image: Old Town in Tübingen

Sample style: the painting "The head of a clown" (1907-1908), Georges Rouault, style: expressionism

The result of the neural network

This work is considered a fundamental breakthrough in depth learning technologies, because this is the first conceptual proof of the transfer of artistic style through a neural network. What was considered artistic vision, the author's style and genre of art, successfully succumbs to formalization and is assimilated by the neural network. Artificial intelligence first mastered the real creativity.
The idea of separating the style and content of the picture created a variety of neural networks, including for generating frightening images and for generating pornographic images .
Unfortunately, the Gatis, Ecker and Betge neural networks have a drawback: such a neural network is too demanding of computational resources. This became clear after the release of the first demo applications that were processed on the server for several minutes.
In subsequent works, including Russian specialists , the neural network was significantly optimized due to the limitation of functionality. As a result, optimization has reached such an extent that instead of a few minutes, the stylization of the photo began to occur almost instantly. So there was an opportunity to stylize even live video !
But similar styling has a reverse side of the coin. Ultra-fast styling is possible only if one image is taken as a sample. This is a limitation of the original algorithm, because it is not tied to one style. In other words, if you want to make a system capable of transmitting 100 different styles, then you will have to pre-train 100 different neural networks.
Now Google has contributed to this research. On October 24, 2016, Google Brain Team employees published an article describing an algorithm that works as fast as the previous ones, but at the same time in a single universal neural network that can superimpose any learned styles.
According to the developers, their algorithm is simple to implement and does not impose high requirements for RAM. Moreover, after training in several styles, he is able to combine several styles at the same time and works in real time. For example, here is a photo of the same Old Town in Tübingen, on which four styles are applied simultaneously .
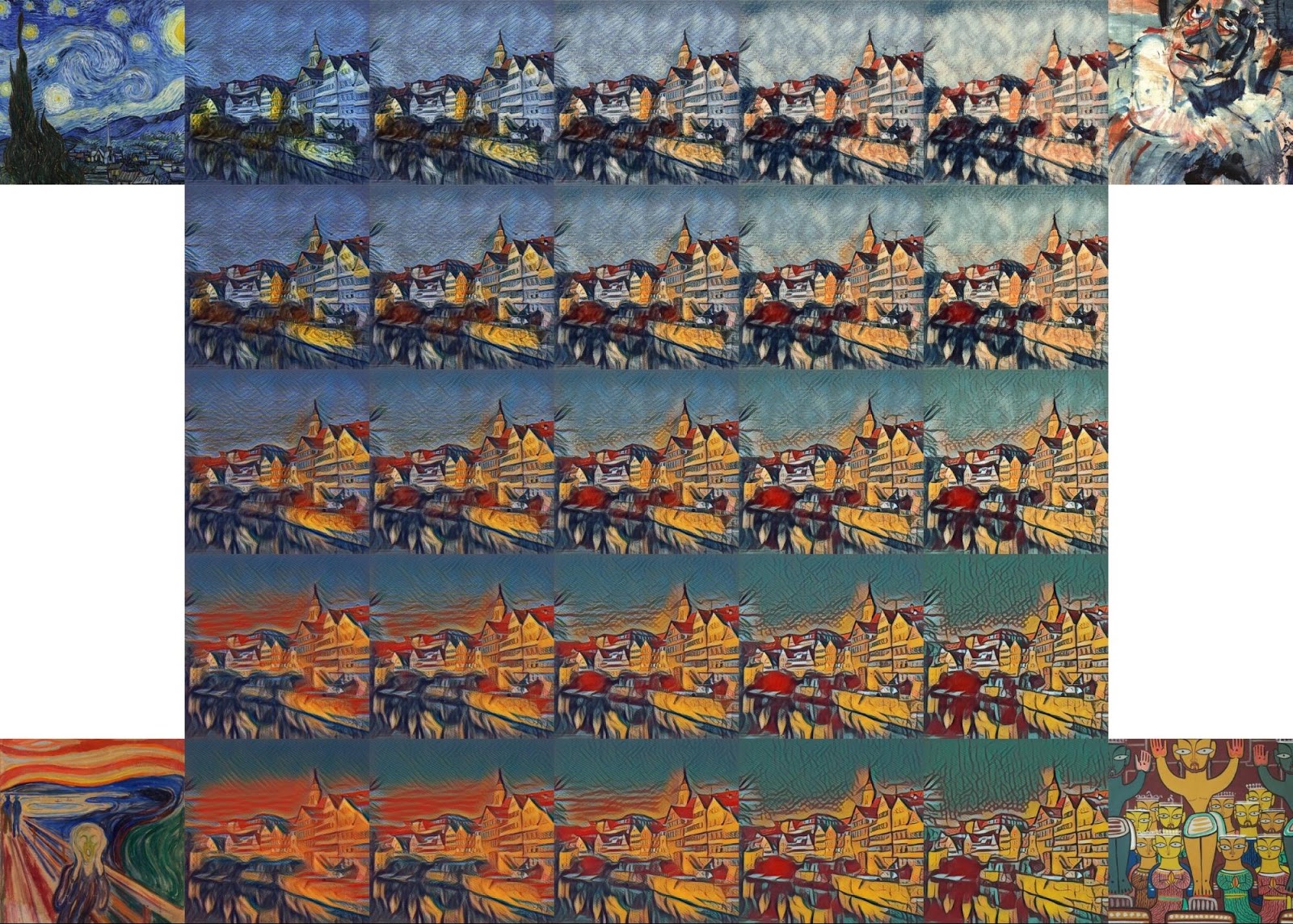

Researchers believe that their work opens up new opportunities for the creative use of neural network styling. In the near future on the Magenta blog, they promise to publish the source code of the program for TensorFlow, so that everyone can run the demo on their computer.
More information about the stylization of images in the neural network is described in the popular science video . It was recorded by two Nat and Lo employees in 20% of their working time, which Google allocates for projects of its choice.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/398703/
All Articles