He who has “ears”, hears - the criteria for selecting headphones
Today, headphones use almost everything. The choice of a particular model, design, principle of operation of headphones is largely due to the scope of their application. In this article, we described what should be considered in the first place when choosing headphones. Intentionally distancing from headsets and highly specialized devices, we focused on those headphones that are used to listen to music, watch videos, and also talked about some professional devices for recording studios and live performances.
Due to the fact that the topic is very extensive and the factors that influence the choice are enough for 10 articles, in this material we decided to give general information about the design and technical features of headphones of various types and purposes. In the future, each of the issues raised in this article will be the reason for a separate publication.

')
I will note that for people who approach the quality of the transmitted sound from the “if only the sound was” position, only a part of this material will be useful. I also emphasize right away that any references to brands and models will be minimized, are for informational purposes only. This article will not answer the question "which headphones are better?". The material was created only in order to facilitate the selection, to tell in detail about the existing technologies and principles.
Type of construction
When purchasing headphones, first of all decide on the type of their design, as the scope of application depends on it. It is well known that the following are currently being produced and widely used:
Plugin
In 1991, Etymotic Research came to the market as a household gadget. Due to the relatively low cost, today liners are included in the basic configuration of most mobile devices. Their main advantage can be considered a compact size. Among the drawbacks is the low ergonomics - you have to choose the right size for your ears.
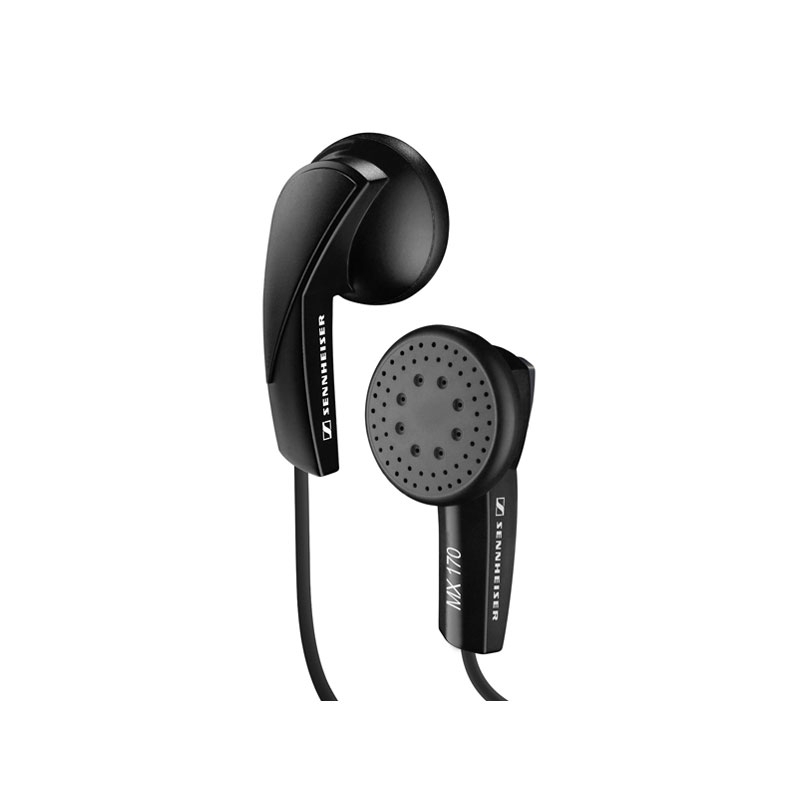

In some cases, the disadvantage is a mediocre sound. The latter is not mandatory, but more than 80% of the range does not reach the hi-fi class. Previously, this type was very common, and in the lines of several well-known brands can be distinguished worthy liners. But the market situation is doing its job, and manufacturers are increasingly leaning towards the intra-channel samples when developing flagship models.
Intra channel
" Gags " - one of the most common types of portable headphones today. Principle: the driver is outside, tubes with latex or foam ear cushions are placed in the external auditory canal. Many people mistakenly believe that the intrachannel design appeared later plug-in, but it is not. On the market, “gags” began to appear as concert monitors as early as the 70s, from which they later migrated to less specific segments, but the first mention of such a design dates back to 1895, in which Thomas Edison equipped his kinetophone with the first in-ear headphones.
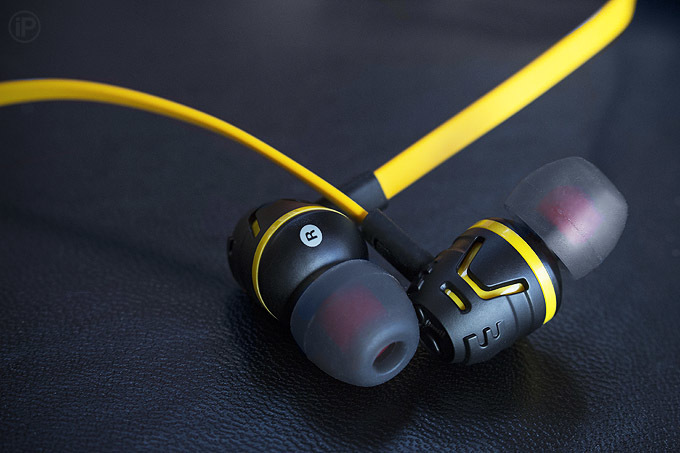

The main advantages of the design:
• mobility (smaller or equal plug-in in size);
• well suited to lovers of pronounced, dynamic bass (acoustic properties of the structure often distort the frequency response to the bottom);
• Fit well in the ear, which makes them comfortable in sports.

Disadvantages: distortions, often arising in connection with the design features and size, high probability of influence on hearing (intensity of sound pressure + location in the external auditory canal). In most cases, do not have a headband. As before, decently sounding intra-channel systems are used as concert and studio monitors.
Overhead
This type is widely used as a peripheral for the PC, as well as headphones for players. The relatively small size and weight made this type the most popular in offices. Tangible design flaws are:

Many models are equipped with a microphone and a functional unit with a volume control that hints at stationary use and use as a headset. A number of overhead models are created for listening to music, some of them are designed for outdoor use. Some experts believe that the overlay design is a priori less prone to distort the sound than liners and channel samples. Another trend of overhead systems is office, workplace, PC.

Full size
As the name implies, this type cannot boast of compactness. That does not detract from its merits. Large dimensions and often the mass of such devices have a positive effect on the acoustic properties of the structure. This is the case when size matters.
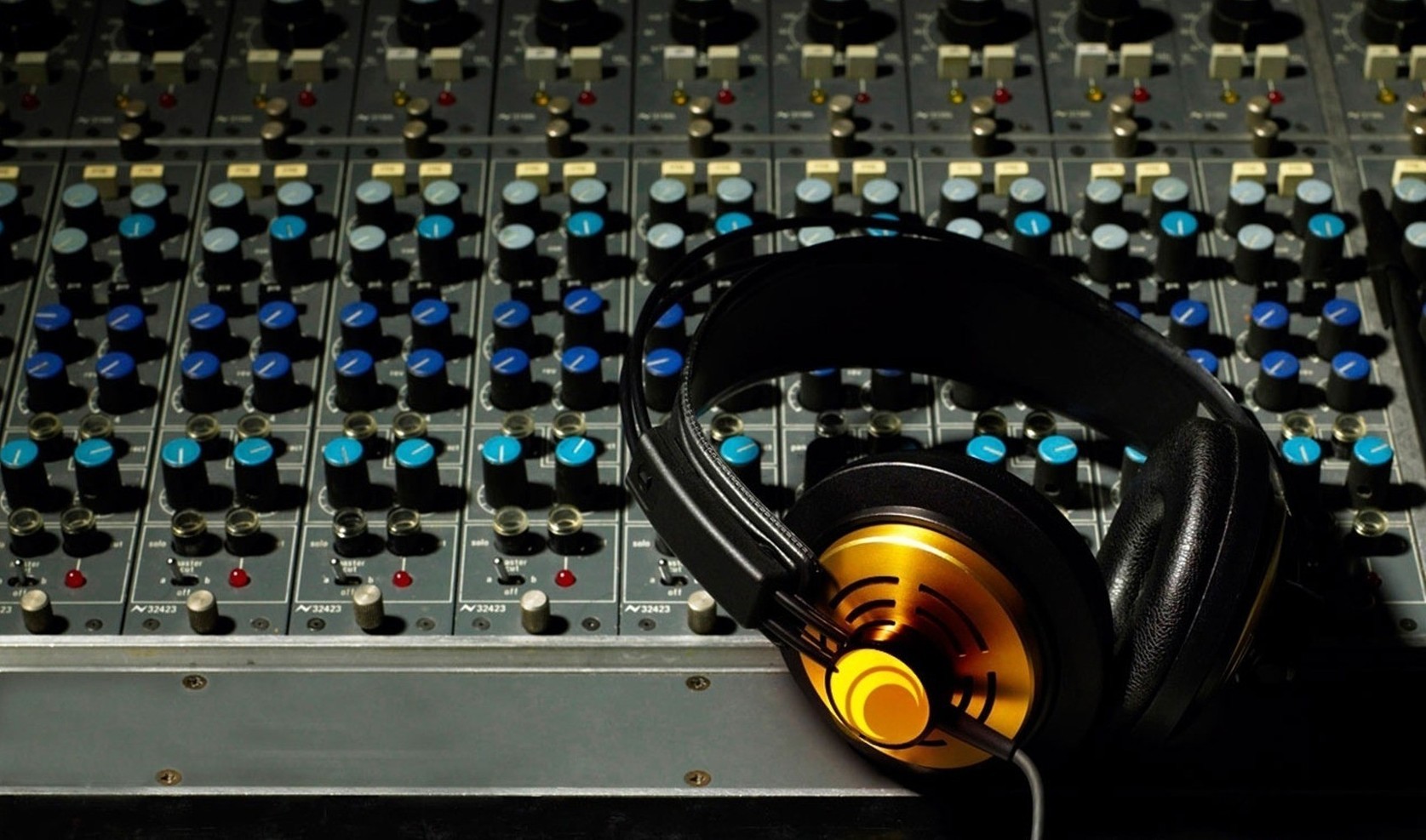

Full-size headphones include the vast majority of systems for recording studios. Almost all reference precision studio headphones, specialized DJ monitors, as well as many representatives of the Hi-End class are full-sized.
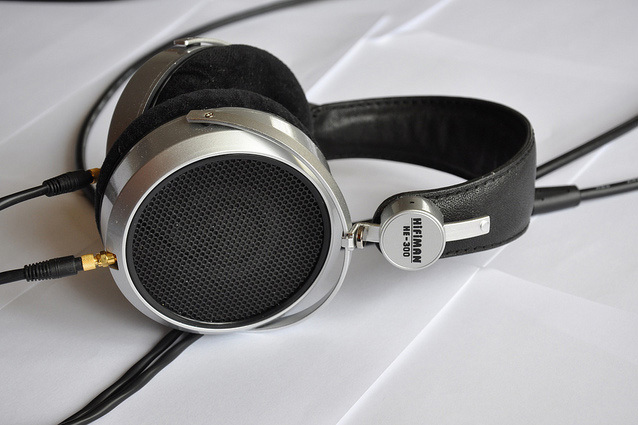


Classic reference headphones are usually of an open type - this is due to the fact that in a closed type, the transmission of low is distorted. For the accurate transmission of frequency response open type like many audiophiles. However, some sound engineers are of the opinion that reference headphones should be of a semi-closed type, as they allow to reproduce low ones without distortion and at the same time have a sufficient degree of sound insulation. Closed type is used as a performer's monitor when recording in the studio, working on a live performance, and also popular with DJs.


Headphones for gamers and numerous systems for PCs also create full-size ones. The latter do not always possess sound quality close in level to their professional counterparts, and the full-size design is used rather as a marketing ploy than a conscious technical need.

There is a strong stereotype that full-size headphones must sound good. A banal frequency response and a quick look at the percentage of SOIs can tell a lot about quality, and in the case of many “pseudo studios” these parameters give impostors. The myth of the obligatory superiority of large "ears" was born when there were few full-size headphones on the market and the vast majority of them were studio ones. But the myth is nothing more than a myth: having ears, let it be heard, having an oscilloscope, see it.
A few words about the frequency response, SOI, resistance, and sensitivity
Just in case:
Frequency response - a graph of the difference of the amplitudes of the output and input signals in the whole range of reproduced frequencies. (Hz)
CED - nonlinear distortion coefficient (%)
Sensitivity - Sound Pressure Intensity (DB)
Power - a characteristic that determines the dynamic range and sound pressure (mW - in the case of headphones)
Everything related to the amplitude component (volume) of the headphone signal depends on the sensitivity. The lower limit of the norm is considered to be 100 dB. Good headphones provide sensitivity of at least 100 dB. Lower sensitivity will not provide enough volume.

Any self-respecting manufacturer notifies the buyer about the level of the SOI headphones. A critical level of harmonic distortion for headphones in the range from 100 to 2 Hz is considered to exceed the limit of 1%, below 100 Hz allow values up to 7-10%. It should be said that the sound with the maximum permissible distortion does not differ in “crystal clarity”. Demanding listeners are sensitive to SOI, therefore, in some professional and Hi-end models, this indicator can be reduced to 0.1% (from 100 Hz.) And 0.9% (below 100 Hz).

Directly affects the sound quality and the appearance of distortion resistance of the headphones. The higher it is, the less current is required to the amplifier to “rock it”, and accordingly - less distortion occurs at the amplification stage. By resistance, it is customary to divide the headphones into high and low impedance. For intra-channel and low-impedance plug-in devices, it is considered to be devices with resistance up to 32 Ohms, high-resistance ones from 32 Ohms. For full - size low - impedance headphones are considered to be with resistance below 100 Ohms, and accordingly above 100 Ohms - high-resistance . Virtually all headsets for professionals, as well as those related to the hi-fi / hi-end class, are high impedance.

It is known that the accuracy and transmission capabilities of frequencies depend on the frequency response. The wider the range and the more uniform the frequency response, the more realistic, more detailed, more accurate the signal transmission. Most people are able to perceive the range from 20 to 20 000 Hz. For many, with age, the high-frequency perception threshold decreases and does not exceed 16,000 Hz. There are people who perceive a wider range. Moreover, many of those who prefer hi-end equipment are also convinced that reproducing frequencies outside the perceptual range affects the sound quality. In either case, really high-quality headphones will have a frequency range of at least between 20 and 20,000 Hz. In professional and hi-end technology, it is usually much wider.
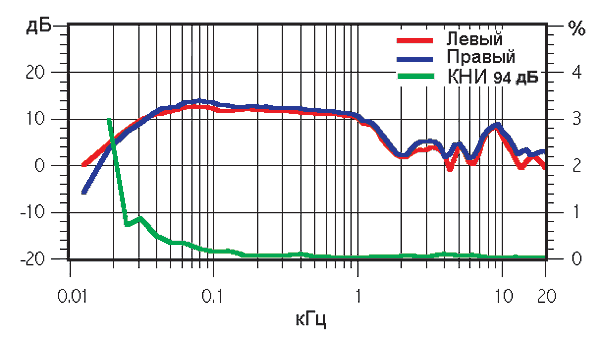
Big peaks and dips in the frequency response graph are the essence of “colored” sound. It is unlikely that headphones with similar characteristics can be considered as professional and even high-quality equipment. They will transmit with significant frequency distortion, unnaturally "paint" it. I cannot help noting that for people who are not too inclined to sound quality, there is a great love for aggressively pronounced low frequencies. For overdemanding audiophiles, the upper threshold of the frequency range is especially valuable.
Type of radiator
Immediately, I note that there is no direct relationship between the sound quality and the type of emitter in the headphones. Perhaps the only exception to this rule is electrostatic drivers. At the same time, the type of emitter indirectly affects both the sound quality and its individual characteristics.
We will look at the 4 most common headphone emitters:
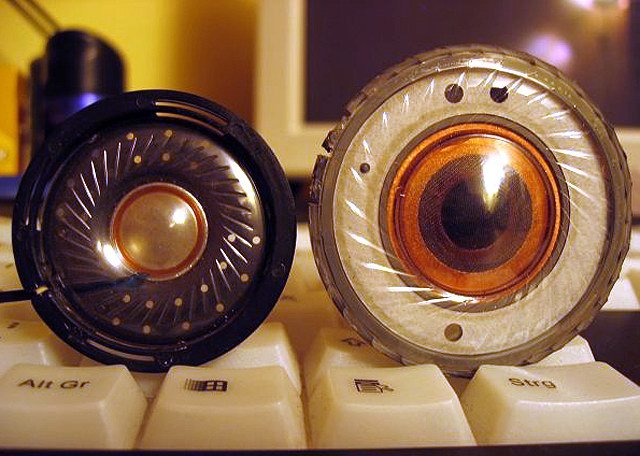
Dynamics - the classics always and everywhere
The most common type of radiator in headphones, as, however, in other acoustic systems, is a classic electrodynamic loudspeaker. The quality of the sound transmitted by such an emitter is influenced by many factors: the material of the diffuser, the design of the coil, etc. Often the speakers have a wider frequency range, which is the most significant advantage over the “armature”.
A noticeable disadvantage of classical electrodynamic drivers is the low reliability compared to the rest (a large number of moving parts, the sensitivity of the coil to high loads) and a high probability of harmonic distortion. In the end, it all depends on the quality of specific speakers.
Today, headphones with speakers remain the most popular in the world and are used in all existing classes. Therefore, the price of headphones equipped with speakers can be any, everything depends on the class, while headphones with other types of emitters (with approximately equal technical parameters) , in comparison with the classical, in most cases they are more expensive.

Reinforcement - from military phones to high-performance "in ear"
Radiators of this type, before using their audio equipment, were widely used in military and medical equipment, after which they found their niche in the consumer segment. Principle of action: the impact of the movable anchor is U-shaped with a coil on the radiating membrane, which reduces the number of moving parts, and accordingly, reduces the likelihood of distortion and increases reliability.
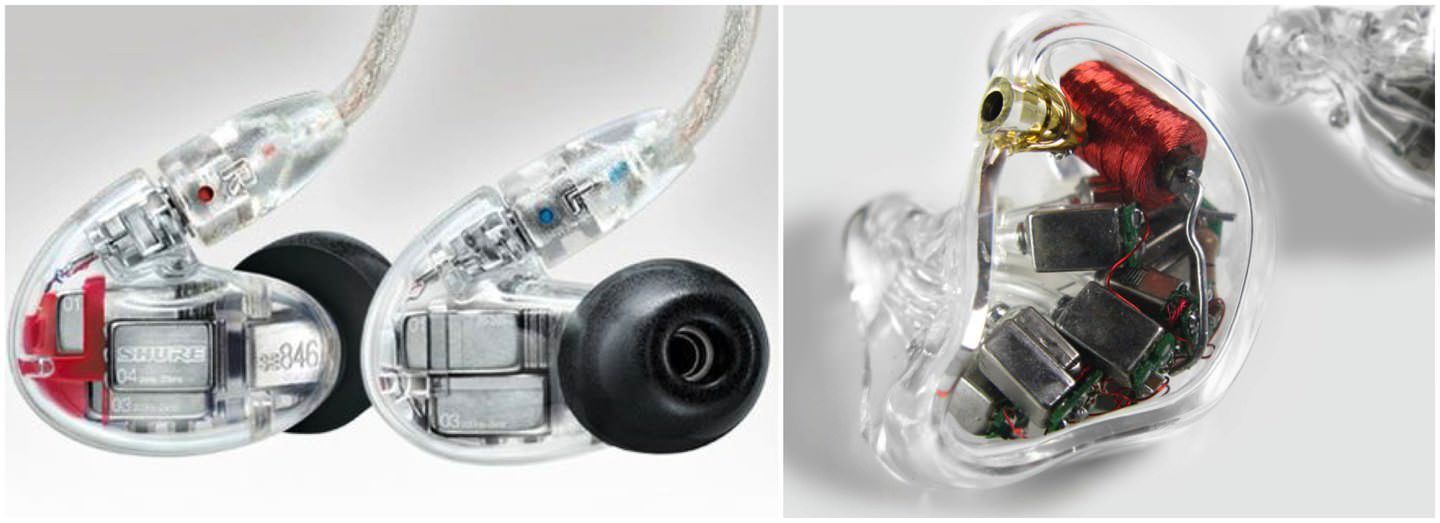

Most often, emitters of this type are used when creating in-ear headphones. This type is often characterized by many emitters in one earpiece (2 or more), which is more difficult to implement with more overall speakers.
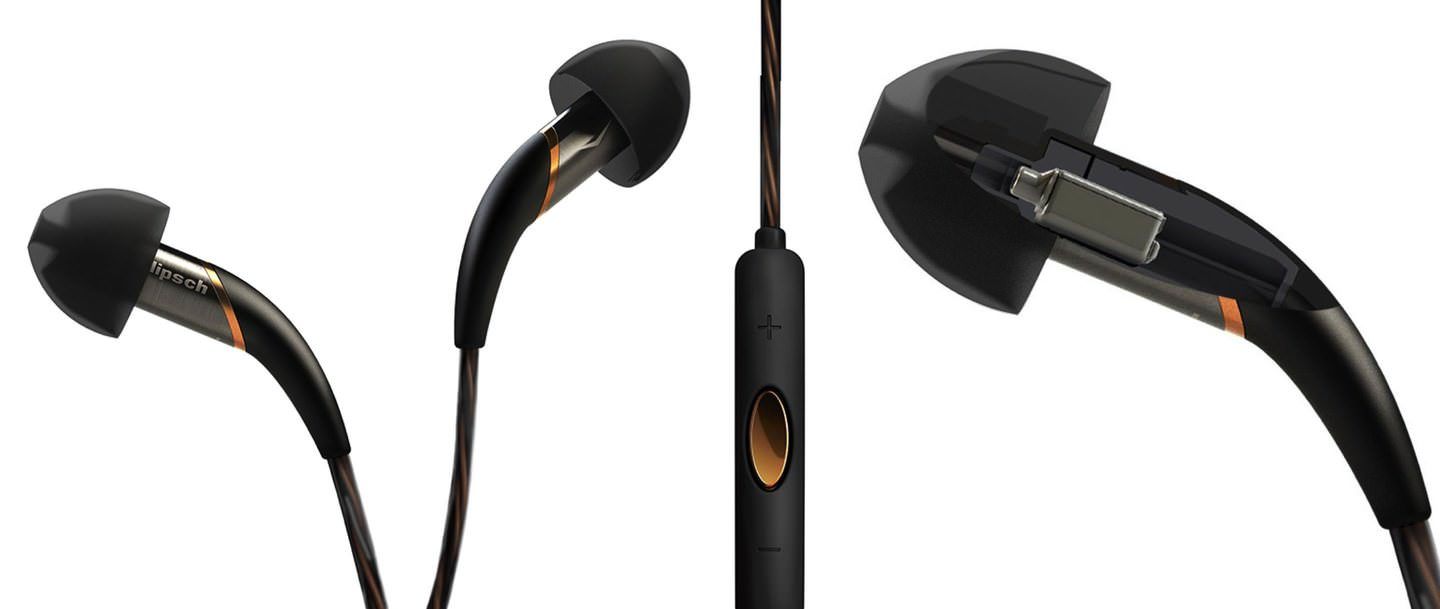

Devices with this radiator are characterized by such features as the severity of high and medium frequencies, high detail of signal transmission, and smoother AHC. Bottoms significantly less accented than the headphones with the electrodynamic principle of operation. The cost of reinforcing headphones are usually higher than those equipped with speakers, other characteristics being equal.
Systems with a combined reinforcement and electrodynamic radiator are also being produced, where the first serves to transmit high and medium, and the second is used for low frequencies.
Isodynamic (planar-magnetic) - well forgotten new
A relatively rare type of emitters for headphones, which, according to some experts, is excellent for reliable and accurate sound transmission. Among the adherents of the isodynamic sound transmission there are quite a few lovers of symphonic classics, jazz and sophisticated chamber music - the most demanding genres for audio equipment.
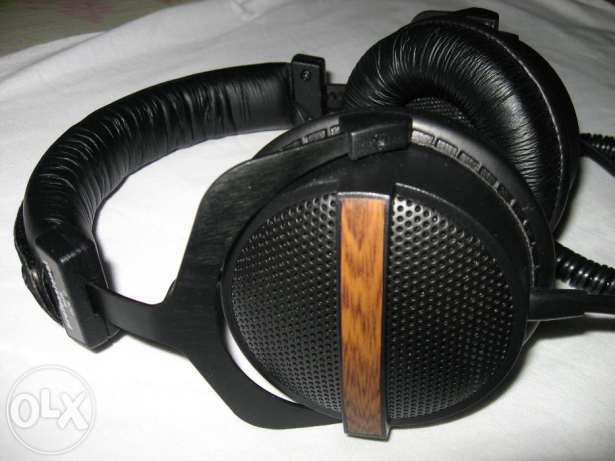

Isodynamic emitters use an ultrathin membrane as an oscillatory element on which metal paths and permanent bar magnets are applied, which allows to transmit sound as accurately as possible without distortion.
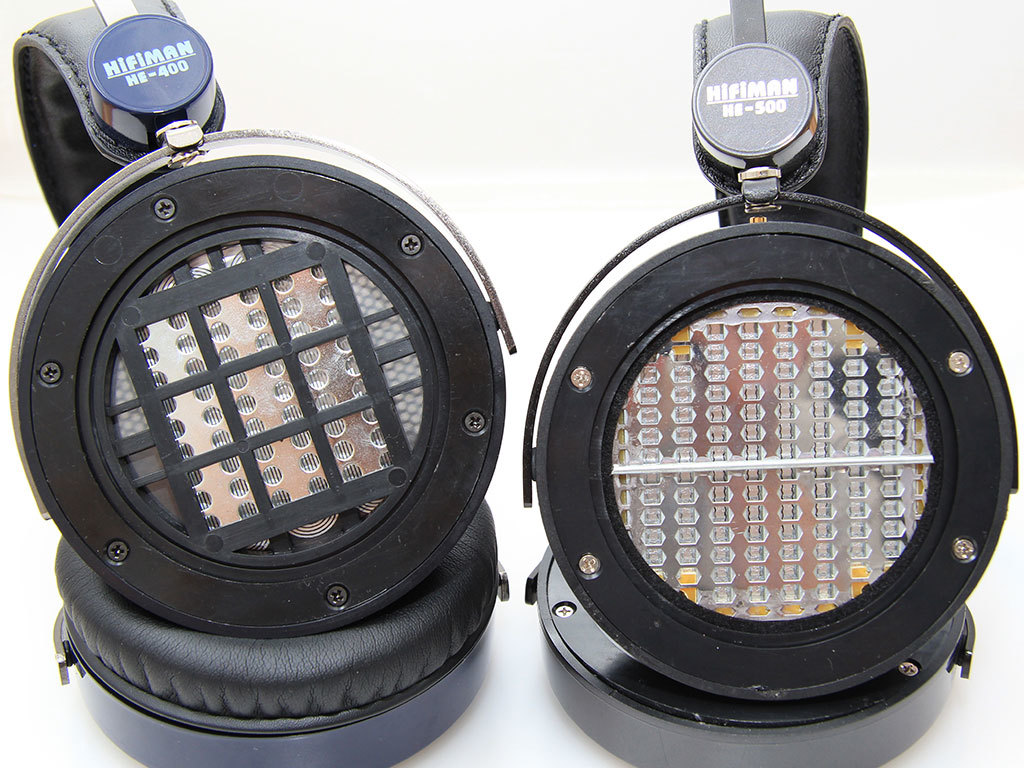

This type of sound is probably not suitable for lovers of supersaturated lows, as the design does not imply low frequency distortions, as is often the case with classical electrodynamic drivers. A serious problem with headphones with this type of emitter is the price. As a rule, the cost of such headphones is prohibitively high for mere mortals, which automatically makes them a subject for non-poor audiophiles and professionals. The lower threshold for the cost of headphones with isodynamic drivers starts from 30-60,000 rubles.
Interestingly, many companies are positioning the isodynamic principle as something new, which, as is the case with the intrachannel design, is far from reality. Back in the 80s of the last century, isodynamic hi-fi headphones were made in Japan and the USSR. Soviet isodynamic headphones TDS - 7 and TDS - 5 possessed worthy characteristics for their time and are now collectible. At the same time, the disadvantages of ergonomics negated all the advantages of TDS-7 and TDS-5. For those who do not have enough money for modern devices of this type, the expected choice is to buy vintage Soviet equipment.
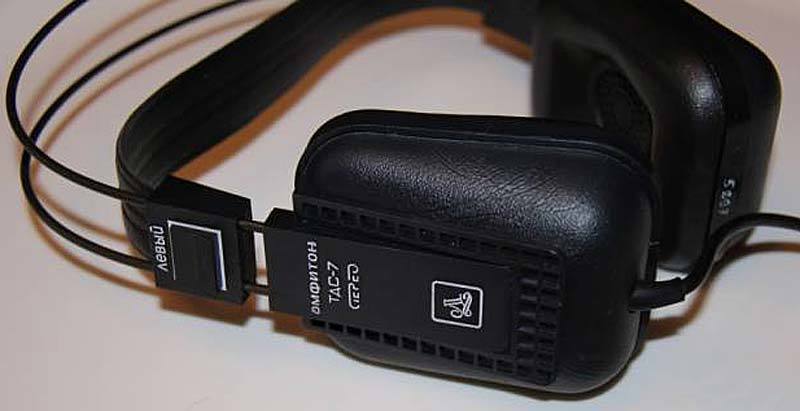

With close to electrostatic emitters, isodynamic headphones do not require pre-amplification, which reduces the cost of acquiring equipment and simplifies operation.
Electrostatic - audiophile delight

Headphones with this type of emitters occupy a special place, since there is no magnet in the design, which virtually eliminates the possibility of significant distortion, and the thinnest electrostatic membrane is capable of transmitting almost imperceptible echoes. Those who are sensitive to the purity and reliability of the sound, recognize this type of radiator as the best.

The most accurate signal transmission of electrostatic headphones made the device the subject of adoration of audiophiles. The principle of operation of the emitters in cases with such headphones requires the use of special preamps, since the voltage required for the buildup can exceed 5000 V. It is completely natural that the price of a device with a preamplifier reaches almost astronomical values, and find a sort of charm in the price range up to 90,000 rubles almost impossible.


Conclusion
The main thing to decide before choosing headphones is how they will be used. Headphones are those devices that do not imply universal application, and each of their type corresponds to its tasks. Of course, a thick wallet will greatly expand the possibilities of choice. At the same time, even if you do not have 15,000 for cool “plugs” or 100,000 for full-sized hi-end “electrostats”, I recommend that you carefully study the characteristics, evaluate the ergonomics for your ears and, of course, listen to everything. Equally your perception will remain. I strongly recommend not buying headphones in the subway, etc. places, as well as with caution to treat "super offers" on platforms such as AliExpress, in most cases, analogs of models of well-known brands from Celestial are very much inferior to "thoroughbred" originals.
Due to the fact that the topic is very extensive and the factors that influence the choice are enough for 10 articles, in this material we decided to give general information about the design and technical features of headphones of various types and purposes. In the future, each of the issues raised in this article will be the reason for a separate publication.

')
I will note that for people who approach the quality of the transmitted sound from the “if only the sound was” position, only a part of this material will be useful. I also emphasize right away that any references to brands and models will be minimized, are for informational purposes only. This article will not answer the question "which headphones are better?". The material was created only in order to facilitate the selection, to tell in detail about the existing technologies and principles.
Type of construction
When purchasing headphones, first of all decide on the type of their design, as the scope of application depends on it. It is well known that the following are currently being produced and widely used:
- Plug-in - they are the "earbuds" - in ear;
- Intra channel - in the people "gags" - in ear;
- Overhead - on ear;
- Full size - ircum-aural (open, closed and semi-closed type.)
Plugin
In 1991, Etymotic Research came to the market as a household gadget. Due to the relatively low cost, today liners are included in the basic configuration of most mobile devices. Their main advantage can be considered a compact size. Among the drawbacks is the low ergonomics - you have to choose the right size for your ears.

In some cases, the disadvantage is a mediocre sound. The latter is not mandatory, but more than 80% of the range does not reach the hi-fi class. Previously, this type was very common, and in the lines of several well-known brands can be distinguished worthy liners. But the market situation is doing its job, and manufacturers are increasingly leaning towards the intra-channel samples when developing flagship models.
Intra channel
" Gags " - one of the most common types of portable headphones today. Principle: the driver is outside, tubes with latex or foam ear cushions are placed in the external auditory canal. Many people mistakenly believe that the intrachannel design appeared later plug-in, but it is not. On the market, “gags” began to appear as concert monitors as early as the 70s, from which they later migrated to less specific segments, but the first mention of such a design dates back to 1895, in which Thomas Edison equipped his kinetophone with the first in-ear headphones.

The main advantages of the design:
• mobility (smaller or equal plug-in in size);
• well suited to lovers of pronounced, dynamic bass (acoustic properties of the structure often distort the frequency response to the bottom);
• Fit well in the ear, which makes them comfortable in sports.

Disadvantages: distortions, often arising in connection with the design features and size, high probability of influence on hearing (intensity of sound pressure + location in the external auditory canal). In most cases, do not have a headband. As before, decently sounding intra-channel systems are used as concert and studio monitors.
Overhead
This type is widely used as a peripheral for the PC, as well as headphones for players. The relatively small size and weight made this type the most popular in offices. Tangible design flaws are:
- lack of sound insulation (external noise is heard in these headphones, the sound of the headphones penetrates to the outside, which can disturb others);
- distortion when changing the correct position.

Many models are equipped with a microphone and a functional unit with a volume control that hints at stationary use and use as a headset. A number of overhead models are created for listening to music, some of them are designed for outdoor use. Some experts believe that the overlay design is a priori less prone to distort the sound than liners and channel samples. Another trend of overhead systems is office, workplace, PC.

Full size
As the name implies, this type cannot boast of compactness. That does not detract from its merits. Large dimensions and often the mass of such devices have a positive effect on the acoustic properties of the structure. This is the case when size matters.

Full-size headphones include the vast majority of systems for recording studios. Almost all reference precision studio headphones, specialized DJ monitors, as well as many representatives of the Hi-End class are full-sized.


Classic reference headphones are usually of an open type - this is due to the fact that in a closed type, the transmission of low is distorted. For the accurate transmission of frequency response open type like many audiophiles. However, some sound engineers are of the opinion that reference headphones should be of a semi-closed type, as they allow to reproduce low ones without distortion and at the same time have a sufficient degree of sound insulation. Closed type is used as a performer's monitor when recording in the studio, working on a live performance, and also popular with DJs.


Headphones for gamers and numerous systems for PCs also create full-size ones. The latter do not always possess sound quality close in level to their professional counterparts, and the full-size design is used rather as a marketing ploy than a conscious technical need.

There is a strong stereotype that full-size headphones must sound good. A banal frequency response and a quick look at the percentage of SOIs can tell a lot about quality, and in the case of many “pseudo studios” these parameters give impostors. The myth of the obligatory superiority of large "ears" was born when there were few full-size headphones on the market and the vast majority of them were studio ones. But the myth is nothing more than a myth: having ears, let it be heard, having an oscilloscope, see it.
A few words about the frequency response, SOI, resistance, and sensitivity
Just in case:
Frequency response - a graph of the difference of the amplitudes of the output and input signals in the whole range of reproduced frequencies. (Hz)
CED - nonlinear distortion coefficient (%)
Sensitivity - Sound Pressure Intensity (DB)
Power - a characteristic that determines the dynamic range and sound pressure (mW - in the case of headphones)
Everything related to the amplitude component (volume) of the headphone signal depends on the sensitivity. The lower limit of the norm is considered to be 100 dB. Good headphones provide sensitivity of at least 100 dB. Lower sensitivity will not provide enough volume.

Any self-respecting manufacturer notifies the buyer about the level of the SOI headphones. A critical level of harmonic distortion for headphones in the range from 100 to 2 Hz is considered to exceed the limit of 1%, below 100 Hz allow values up to 7-10%. It should be said that the sound with the maximum permissible distortion does not differ in “crystal clarity”. Demanding listeners are sensitive to SOI, therefore, in some professional and Hi-end models, this indicator can be reduced to 0.1% (from 100 Hz.) And 0.9% (below 100 Hz).

Directly affects the sound quality and the appearance of distortion resistance of the headphones. The higher it is, the less current is required to the amplifier to “rock it”, and accordingly - less distortion occurs at the amplification stage. By resistance, it is customary to divide the headphones into high and low impedance. For intra-channel and low-impedance plug-in devices, it is considered to be devices with resistance up to 32 Ohms, high-resistance ones from 32 Ohms. For full - size low - impedance headphones are considered to be with resistance below 100 Ohms, and accordingly above 100 Ohms - high-resistance . Virtually all headsets for professionals, as well as those related to the hi-fi / hi-end class, are high impedance.

It is known that the accuracy and transmission capabilities of frequencies depend on the frequency response. The wider the range and the more uniform the frequency response, the more realistic, more detailed, more accurate the signal transmission. Most people are able to perceive the range from 20 to 20 000 Hz. For many, with age, the high-frequency perception threshold decreases and does not exceed 16,000 Hz. There are people who perceive a wider range. Moreover, many of those who prefer hi-end equipment are also convinced that reproducing frequencies outside the perceptual range affects the sound quality. In either case, really high-quality headphones will have a frequency range of at least between 20 and 20,000 Hz. In professional and hi-end technology, it is usually much wider.

Big peaks and dips in the frequency response graph are the essence of “colored” sound. It is unlikely that headphones with similar characteristics can be considered as professional and even high-quality equipment. They will transmit with significant frequency distortion, unnaturally "paint" it. I cannot help noting that for people who are not too inclined to sound quality, there is a great love for aggressively pronounced low frequencies. For overdemanding audiophiles, the upper threshold of the frequency range is especially valuable.
Type of radiator
Immediately, I note that there is no direct relationship between the sound quality and the type of emitter in the headphones. Perhaps the only exception to this rule is electrostatic drivers. At the same time, the type of emitter indirectly affects both the sound quality and its individual characteristics.
We will look at the 4 most common headphone emitters:
- Electrodynamic (speaker)
- Armature (balanced anchor)
- Isodynamic
- Electrostatic
Dynamics - the classics always and everywhere
The most common type of radiator in headphones, as, however, in other acoustic systems, is a classic electrodynamic loudspeaker. The quality of the sound transmitted by such an emitter is influenced by many factors: the material of the diffuser, the design of the coil, etc. Often the speakers have a wider frequency range, which is the most significant advantage over the “armature”.
A noticeable disadvantage of classical electrodynamic drivers is the low reliability compared to the rest (a large number of moving parts, the sensitivity of the coil to high loads) and a high probability of harmonic distortion. In the end, it all depends on the quality of specific speakers.
Today, headphones with speakers remain the most popular in the world and are used in all existing classes. Therefore, the price of headphones equipped with speakers can be any, everything depends on the class, while headphones with other types of emitters (with approximately equal technical parameters) , in comparison with the classical, in most cases they are more expensive.

Reinforcement - from military phones to high-performance "in ear"
Radiators of this type, before using their audio equipment, were widely used in military and medical equipment, after which they found their niche in the consumer segment. Principle of action: the impact of the movable anchor is U-shaped with a coil on the radiating membrane, which reduces the number of moving parts, and accordingly, reduces the likelihood of distortion and increases reliability.

Most often, emitters of this type are used when creating in-ear headphones. This type is often characterized by many emitters in one earpiece (2 or more), which is more difficult to implement with more overall speakers.

Devices with this radiator are characterized by such features as the severity of high and medium frequencies, high detail of signal transmission, and smoother AHC. Bottoms significantly less accented than the headphones with the electrodynamic principle of operation. The cost of reinforcing headphones are usually higher than those equipped with speakers, other characteristics being equal.
Systems with a combined reinforcement and electrodynamic radiator are also being produced, where the first serves to transmit high and medium, and the second is used for low frequencies.
Isodynamic (planar-magnetic) - well forgotten new
A relatively rare type of emitters for headphones, which, according to some experts, is excellent for reliable and accurate sound transmission. Among the adherents of the isodynamic sound transmission there are quite a few lovers of symphonic classics, jazz and sophisticated chamber music - the most demanding genres for audio equipment.

Isodynamic emitters use an ultrathin membrane as an oscillatory element on which metal paths and permanent bar magnets are applied, which allows to transmit sound as accurately as possible without distortion.


This type of sound is probably not suitable for lovers of supersaturated lows, as the design does not imply low frequency distortions, as is often the case with classical electrodynamic drivers. A serious problem with headphones with this type of emitter is the price. As a rule, the cost of such headphones is prohibitively high for mere mortals, which automatically makes them a subject for non-poor audiophiles and professionals. The lower threshold for the cost of headphones with isodynamic drivers starts from 30-60,000 rubles.
Interestingly, many companies are positioning the isodynamic principle as something new, which, as is the case with the intrachannel design, is far from reality. Back in the 80s of the last century, isodynamic hi-fi headphones were made in Japan and the USSR. Soviet isodynamic headphones TDS - 7 and TDS - 5 possessed worthy characteristics for their time and are now collectible. At the same time, the disadvantages of ergonomics negated all the advantages of TDS-7 and TDS-5. For those who do not have enough money for modern devices of this type, the expected choice is to buy vintage Soviet equipment.

With close to electrostatic emitters, isodynamic headphones do not require pre-amplification, which reduces the cost of acquiring equipment and simplifies operation.
Electrostatic - audiophile delight

Headphones with this type of emitters occupy a special place, since there is no magnet in the design, which virtually eliminates the possibility of significant distortion, and the thinnest electrostatic membrane is capable of transmitting almost imperceptible echoes. Those who are sensitive to the purity and reliability of the sound, recognize this type of radiator as the best.

The most accurate signal transmission of electrostatic headphones made the device the subject of adoration of audiophiles. The principle of operation of the emitters in cases with such headphones requires the use of special preamps, since the voltage required for the buildup can exceed 5000 V. It is completely natural that the price of a device with a preamplifier reaches almost astronomical values, and find a sort of charm in the price range up to 90,000 rubles almost impossible.


Conclusion
The main thing to decide before choosing headphones is how they will be used. Headphones are those devices that do not imply universal application, and each of their type corresponds to its tasks. Of course, a thick wallet will greatly expand the possibilities of choice. At the same time, even if you do not have 15,000 for cool “plugs” or 100,000 for full-sized hi-end “electrostats”, I recommend that you carefully study the characteristics, evaluate the ergonomics for your ears and, of course, listen to everything. Equally your perception will remain. I strongly recommend not buying headphones in the subway, etc. places, as well as with caution to treat "super offers" on platforms such as AliExpress, in most cases, analogs of models of well-known brands from Celestial are very much inferior to "thoroughbred" originals.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/398607/
All Articles